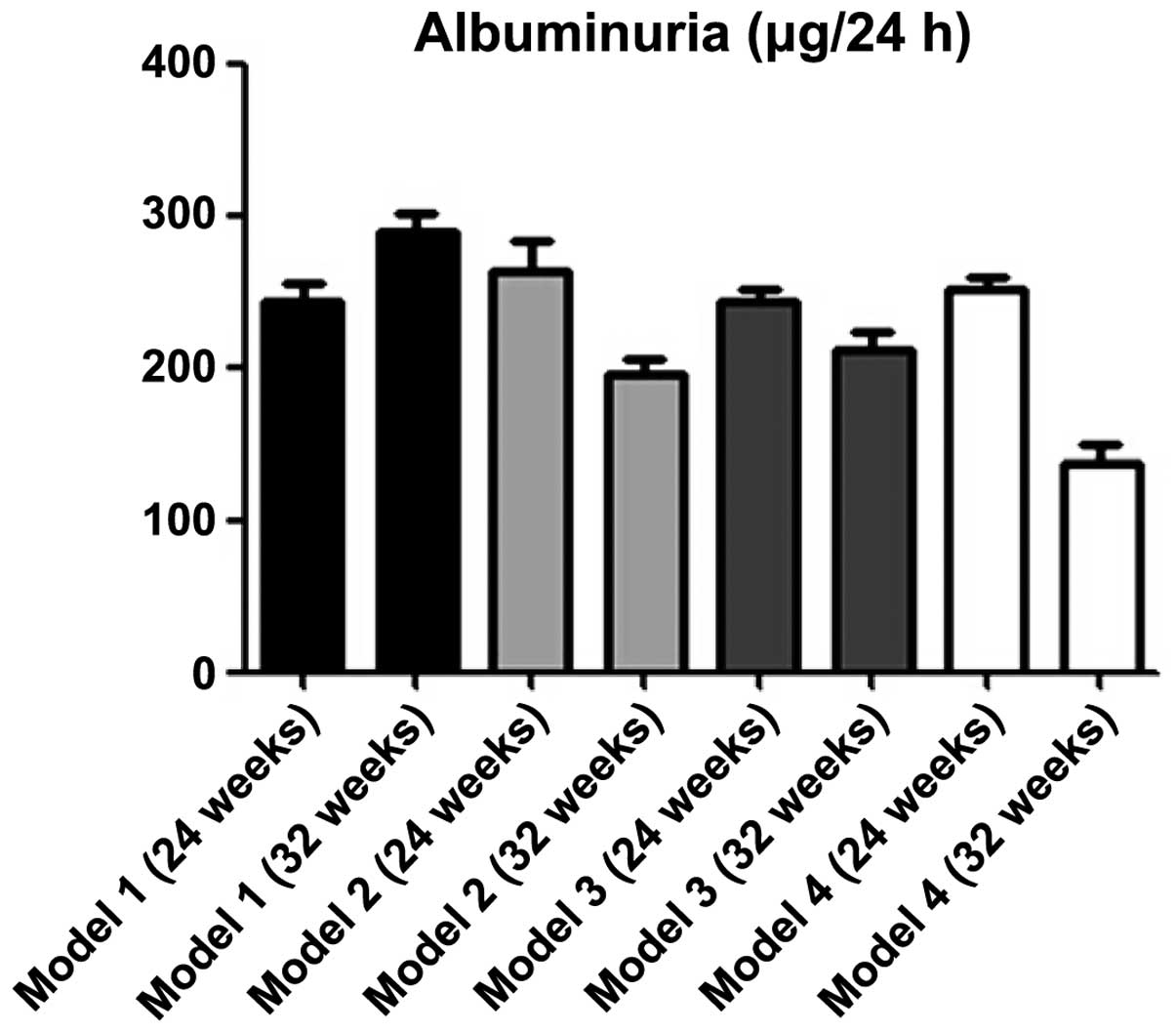
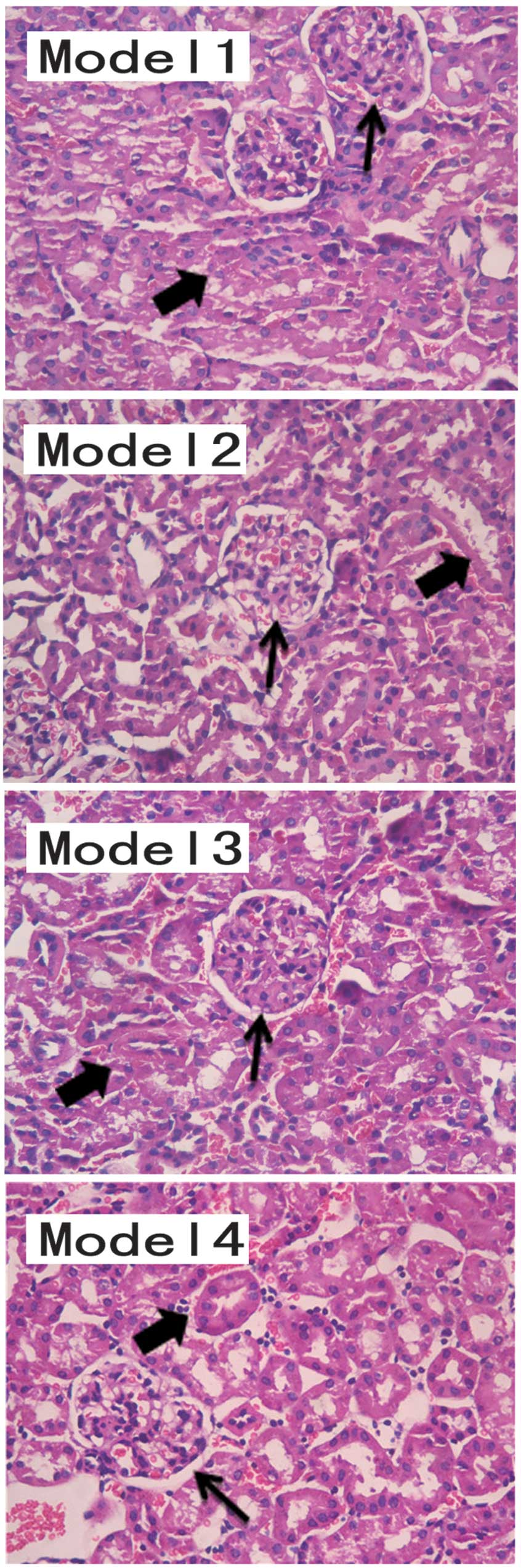
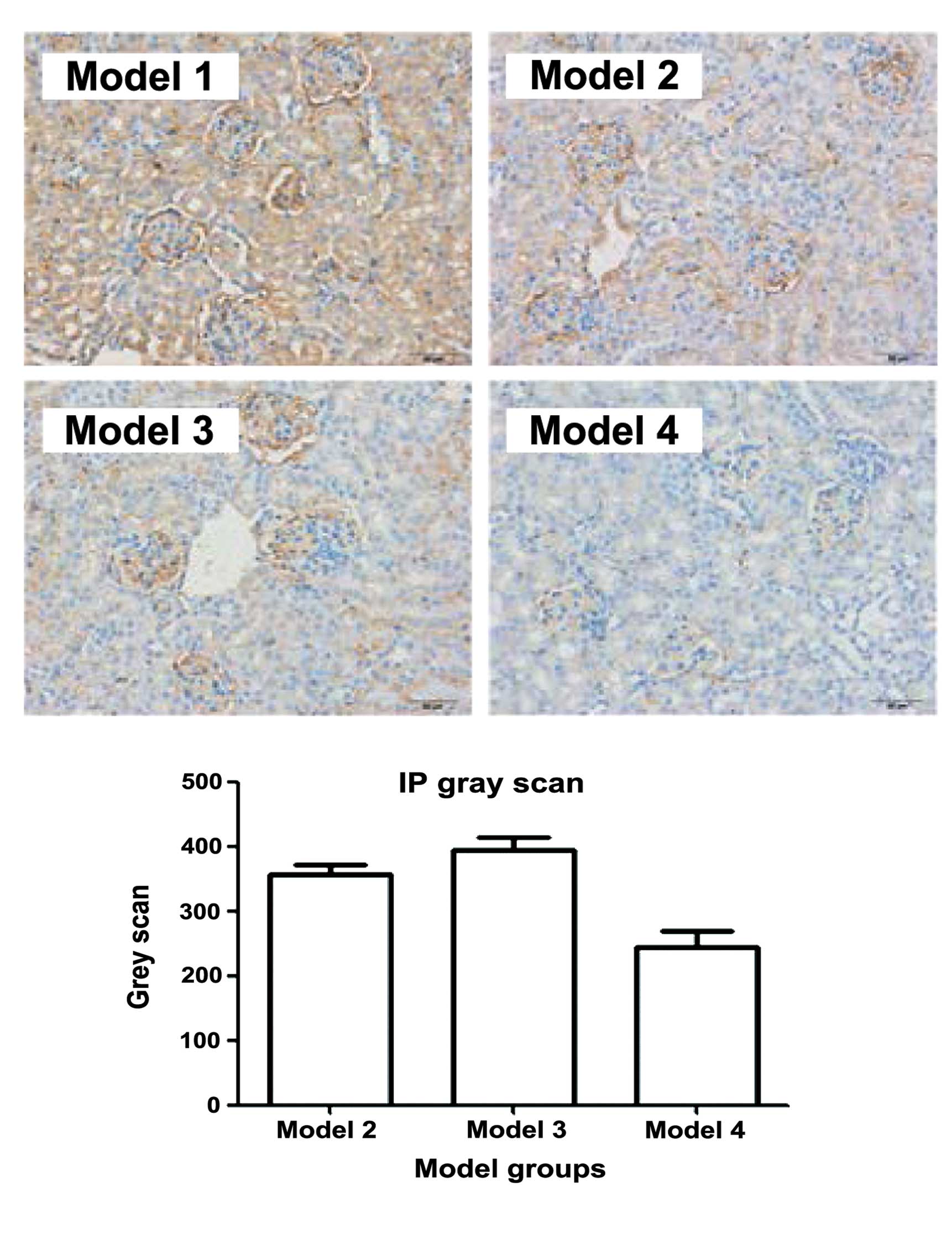
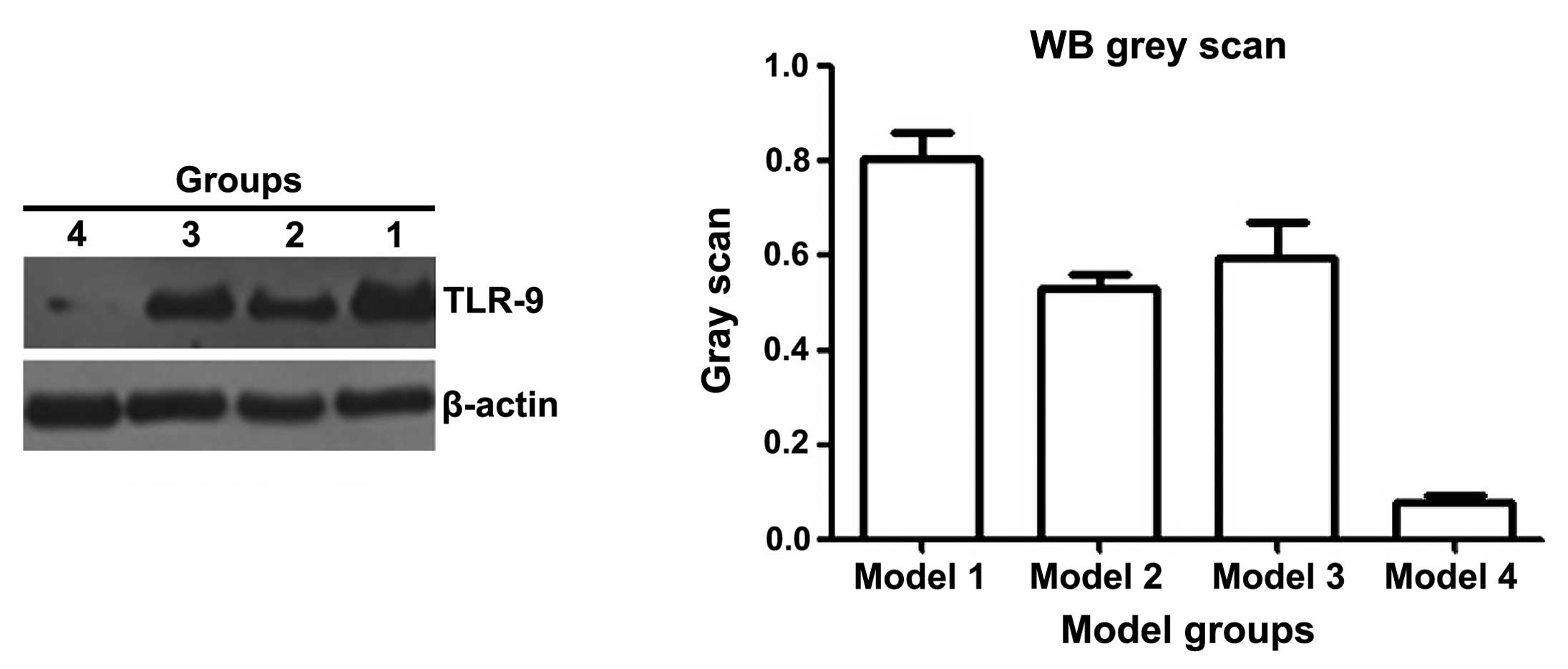
|
1
|
D’Cruz DP, Khamashta MA and Hughes GR:
Systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 369:587–596. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Borchers AT, Leibushor N, Naguwa SM, et
al: Lupus nephritis: A critical review. Autoimmun Rev. 12:174–194.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mak A and Kow NY: The pathology of T cells
in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol Res. 2014:4190292014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mackern-Oberti JP, Llanos C, Vega F, et
al: Role of dendritic cells in the initiation, progress and
modulation of systemic autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev.
14:127–139. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Al Gadban MM, Alwan MM, Smith KJ and
Hammad SM: Accelerated vascular disease in systemic lupus
erythematosus: Role of macrophage. Clin Immunol. 157:133–144. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Laky K, Evans S, Perez-Diez A and Fowlkes
BJ: Notch signaling regulates antigen sensitiviy of naive CD4+ T
cells by tuning co-stimulation. Immunity. 42:80–94. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ohishi K, Varnum-Finney B, Serda RE, et
al: The Notch ligand, Delta-1, inhibits the differentiation of
monocytes into macrophages but permits their differentiation into
dendritic cells. Blood. 98:1402–1407. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cheng P, Zhou J and Gabrilovich D:
Regulation of dendritic cell differentiation and function by Notch
and Wnt pathways. Immunol Rev. 234:105–119. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Backer RA, Helbig C, Gentek R, et al: A
central role for Notch in effector CD8(+) T cell differentiation.
Nat Immunol. 15:1143–1151. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zheng J, Jiang HY, Li J, et al:
Microrna-23b promotes tolerogenic properties of dendritic cells in
vitro through inhibiting notch1/nf-kappab signalling pathways.
Allergy. 67:362–370. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dervovic DD, Liang HC, Cannons JL, et al:
Cellular and molecular requirements for the selection of in
vitro-generated cd8 t cells reveal a role for notch. J Immunol.
191:1704–1715. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Riella LV, Ueno T, Batal I, et al:
Blockade of notch ligand delta1 promotes allograft survival by
inhibiting alloreactive th1 cells and cytotoxic t cell generation.
J Immunol. 187:4629–4638. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Amsen D, Blander JM, Lee GR, et al:
Instruction of distinct cd4 t helper cell fates by different notch
ligands on antigen-presenting cells. Cell. 117:515–526. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dongre A, Surampudi L, Lawlor RG, et al:
Non-canonical Notch signaling drives activation and differentiation
of peripheral CD4(+) T cells. Front Immunol. 5:542014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD and Lake RJ:
Notch signaling: Cell fate control and signal integration in
development. Science. 284:770–776. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Talora C, Campese AF, Bellavia D, et al:
Notch signaling and diseases: An evolutionary journey from a simple
beginning to complex outcomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1782:489–497.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang W, Xu W and Xiong S: Blockade of
notch1 signaling alleviates murine lupus via blunting macrophage
activation and m2b polarization. J Immunol. 184:6465–6478. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Teachey DT, Seif AE, Brown VI, et al:
Targeting notch signaling in autoimmune and lymphoproliferative
disease. Blood. 111:705–714. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Rauen T, Grammatikos AP, Hedrich CM, et
al: Camp-responsive element modulator alpha (cremalpha) contributes
to decreased notch-1 expression in t cells from patients with
active systemic lupus erythematosus (sle). J Biol Chem.
287:42525–42532. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Barrat FJ and Coffman RL: Development of
tlr inhibitors for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Immunol
Rev. 223:271–283. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Comery TA, Martone RL, Aschmies S, et al:
Acute gamma-secretase inhibition improves contextual fear
conditioning in the tg2576 mouse model of alzheimer’s disease. J
Neurosci. 25:8898–8902. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Watson ML, Rao JK, Gilkeson GS, et al:
Genetic analysis of mrl-lpr mice: Relationship of the fas apoptosis
gene to disease manifestations and renal disease-modifying loci. J
Exp Med. 176:1645–1656. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Takeda K and Akira S: Toll-like receptors
in innate immunity. Int Immunol. 17:1–14. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Roelofs MF, Wenink MH, Brentano F, et al:
Type i interferons might form the link between toll-like receptor
(tlr) 3/7 and tlr4-mediated synovial inflammation in rheumatoid
arthritis (ra). Ann Rheum Dis. 68:1486–1493. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Marshak-Rothstein A: Toll-like receptors
in systemic autoimmune disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 6:823–835. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lyn-Cook BD, Xie C, Oates J, et al:
Increased expression of toll-like receptors (tlrs) 7 and 9 and
other cytokines in systemic lupus erythematosus (sle) patients:
ethnic differences and potential new targets for therapeutic drugs.
Mol Immunol. 61:38–43. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ghaly NR, Kotb NA, Nagy HM and Ragehel SM:
Toll-like receptor 9 in systemic lupus erythematosus, impact on
glucocorticoid treatment. J Dermatolog Treat. 24:411–417. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Papadimitraki ED, Tzardi M, Bertsias G, et
al: Glomerular expression of toll-like receptor-9 in lupus
nephritis but not in normal kidneys: Implications for the
amplification of the inflammatory response. Lupus. 18:831–835.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Guiducci C, Gong M, Xu Z, et al: Tlr
recognition of self nucleic acids hampers glucocorticoid activity
in lupus. Nature. 465:937–941. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jarrossay D, Napolitani G, Colonna M, et
al: Specialization and complementarity in microbial molecule
recognition by human myeloid and plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Eur
J Immunol. 31:3388–3393. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kadowaki N, Ho S, Antonenko S, et al:
Subsets of human dendritic cell precursors express different
toll-like receptors and respond to different microbial antigens. J
Exp Med. 194:863–869. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dorner M, Brandt S, Tinguely M, et al:
Plasma cell toll-like receptor (tlr) expression differs from that
of b cells and plasma cell tlr triggering enhances immunoglobulin
production. Immunology. 128:573–579. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Horton CG, Pan ZJ and Farris AD: Targeting
toll-like receptors for treatment of SLE. Mediators Inflamm.
2010:4989802010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Harley IT, Kaufman KM, Langefeld CD, et
al: Genetic susceptibility to sle: new insights from fine mapping
and genome-wide association studies. Nat Rev Genet. 10:285–290.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Piotrowski P, Lianeri M, Wudarski M, et
al: Contribution of toll-like receptor 9 gene single-nucleotide
polymorphism to systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Int.
33:1121–1125. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Mu R, Sun XY, Lim LT, et al: Toll-like
receptor 9 is correlated to disease activity in Chinese systemic
lupus erythematosus population. Chin Med J (Engl). 125:2873–2877.
2012.
|
|
37
|
Sodsai P, Hirankarn N, Avihingsanon Y, et
al: Defects in notch1 upregulation upon activation of t cells from
patients with systemic lupus erythematosus are related to lupus
disease activity. Lupus. 17:645–653. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Henderson L, Masson P, Craig JC, et al:
Treatment for lupus nephritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
12:CD0029222012.PubMed/NCBI
|