|
1
|
Łowicka E and Bełtowski J: Hydrogen
sulfide (H S) - the third gas of interest for pharmacologists.
Pharmacol Rep. 59:4–24. 2007.
|
|
2
|
Zhao W, Zhang J, Lu Y and Wang R: The
vasorelaxant effect of H(2)S as a novel endogenous gaseous K(ATP)
channel opener. EMBO J. 20:6008–6016. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fiorucci S, Antonelli E, Distrutti E, et
al: Inhibition of hydrogen sulfide generation contributes to
gastric injury caused by anti-inflammatory nonsteroidal drugs.
Gastro-enterology. 129(1): 210–1224. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zhang LM, Jiang CX and Liu DW: Hydrogen
sulfide attenuates neuronal injury induced by vascular dementia via
inhibiting apoptosis in rats. Neurochem Res. 34:1984–1992. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhong G, Chen F, Cheng Y, et al: The role
of hydrogen sulfide generation in the pathogenesis of hypertension
in rats induced by inhibition of nitric oxide synthase. J
Hypertens. 21:1879–1885. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kimura Y, Goto Y and Kimura H: Hydrogen
sulfide increases glutathione production and suppresses oxidative
stress in mitochondria. Antioxid Redox Signal. 12:1–13. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lou LX, Geng B, Du JB and Tang CS:
Hydrogen sulphide-induced hypothermia attenuates stress-related
ulceration in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 35:223–228.
2008.
|
|
8
|
Zhong GZ, Li YB, Liu XL, et al: Hydrogen
sulfide opens the KATP channel on rat atrial and ventricular
myocytes. Cardiology. 115:120–126. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kang K, Zhao M, Jiang H, et al: Role of
hydrogen sulfide in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion-induced injury in
rats. Liver Transpl. 15:1306–1314. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fiorucci S, Antonelli E, Mencarelli A, et
al: The third gas: H S regulates perfusion pressure in both the
isolated and perfused 2 normal rat liver and in cirrhosis.
Hepatology. 42:539–548. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fang L, Li H, Tang C, et al: Hydrogen
sulfide attenuates the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis induced
by bleomycin in rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 87:531–538. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tacke F and Weiskirchen R: Update on
hepatic stellate cells: Pathogenic role in liver fibrosis and novel
isolation techniques. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 6:67–80.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Stock P, Liefeldt L, Paul M and Ganten M:
Local renin-angiotensin systems in cardiovascular tissues:
Localization and functional role. Cardiology. 86(Suppl 1): 2–8.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yoshiji H, Kuriyama S, Yoshii J, et al:
Angiotensin-II type 1 receptor interaction is a major regulator for
liver fibrosis development in rats. Hepatology. 34:745–750. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bataller R, Sancho-Bru P, Ginès P, et al:
Activated human hepatic stellate cells express the
renin-angiotensin system and synthesize angiotensin II.
Gastroenterology. 125:117–125. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao X, Zhang LK, Zhang CY, et al:
Regulatory effect of hydrogen sulfide on vascular collagen content
in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertens Res. 31:1619–1630.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
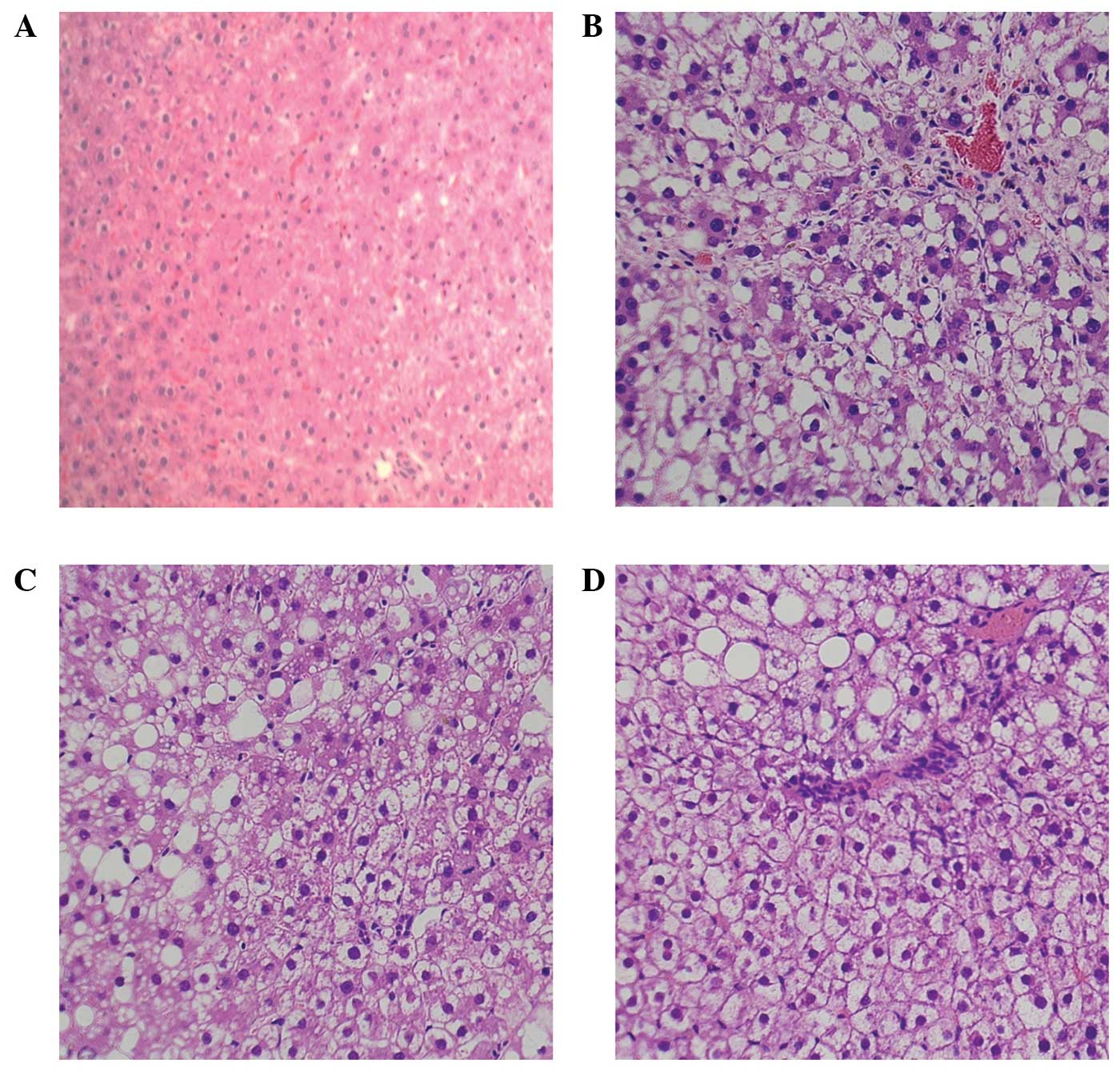
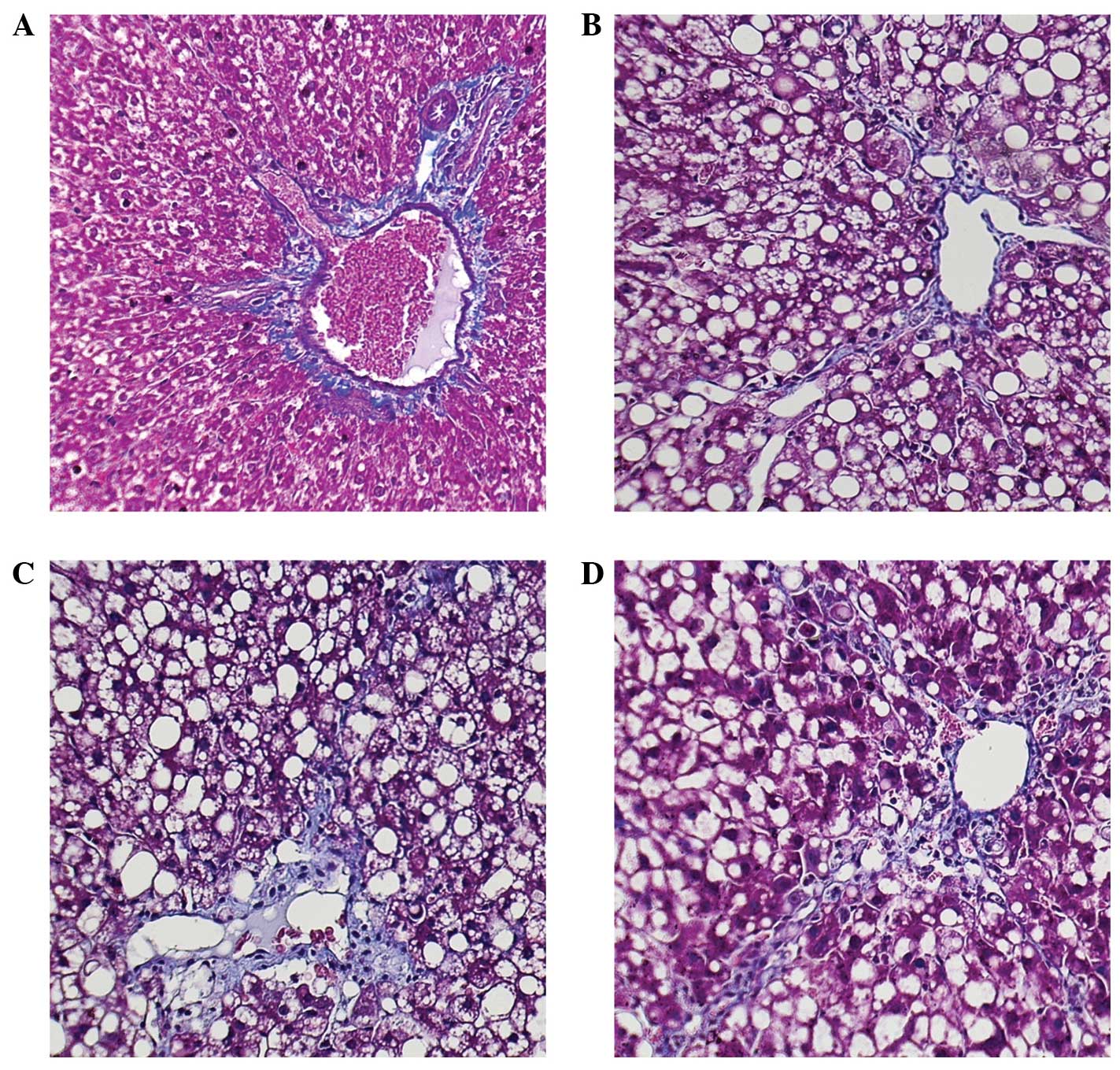
Brunt EM: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis:
Definition and pathology. Semin Liver Dis. 21:3–16. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen P, Sun B, Chen H, et al: Effects of
carbon monoxide releasing molecule-liberated CO on severe acute
pancreatitis in rats. Cytokine. 49:15–23. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Nickenig G, Laufs U, Schnabel P, et al:
Down-regulation of aortic and cardiac AT1 receptor gene expression
in transgenic (mRen-2) 27 rats. Br J Pharmacol. 121:134–140. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yuan L and Kaplowitz N: Glutathione in
liver diseases and hepatotoxicity. Mol Aspects Med. 30:29–41. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Fan HN, Wang HJ, Yang-Dan CR, et al:
Protective effects of hydrogen sulfide on oxidative stress and
fibrosis in hepatic stellate cells. Mol Med Rep. 7:247–53.
2013.
|
|
23
|
Jha S, Calvert JW and Duranski MR:
Hydrogen sulfide attenuates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury:
Role of antioxidant and antiapoptotic signaling. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 295:H801–H806. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sakaida I, Matsumura Y, Kubota M, et al:
The prolyl 4-hydroxylase inhibitor HOE 077 prevents activation of
Ito cells, reducing procollagen gene expression in rat liver
fibrosis induced by choline-deficient L-amino acid-defined diet.
Hepatology. 23:755–63. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jonsson JR, Clouston AD, Ando Y, et al:
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition attenuates the progression
of rat hepatic fibrosis. Gastroenterology. 121:148–155. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tuncer I, Ozbek H, Ugras S and Bayram I:
Anti-fibrogenic effects of captopril and candesartan cilexetil on
the hepatic fibrosis development in rat. The effect of AT1-R
blocker on the hepatic fibrosis. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 55:159–166.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Töx U, Scheller I, Kociok N, et al:
Expression of angiotensin II receptor type 1 is reduced in advanced
rat liver fibrosis. Dig Dis Sci. 52:1995–2005. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tan G, Pan S, Li J, et al: Hydrogen
sulfide attenuates carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity,
liver cirrhosis and portal hypertension in rats. Plos One.
6:e259432011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Distrutti E, Mencarelli A, Santucci L, et
al: The methionine connection: Homocysteine and hydrogen sulfide
exert opposite effects on hepatic microcirculation in rats.
Hepatology. 47:659–667. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bataller R, Gabele E, Parsons CJ, et al:
Systemic infusion of angiotensin II exacerbates liver fibrosis in
bile duct-ligated rats. Hepatology. 41:1046–1055. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Grotendorst GR: Connective tissue growth
factor: A mediator of TGF-beta action on fibroblasts. Cytokine
Growth Factor Rev. 8:171–179. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Paradis V, Dargere D, Bonvoust F, et al:
Effects and regulation of connective tissue growth factor on
hepatic stellate cells. Lab Invest. 82:767–774. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tamaki Y, Nakade Y, Yamauchi T, et al:
Angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonist prevents hepatic
carcinoma in rats with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J
Gastroenterol. 48:491–503. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|