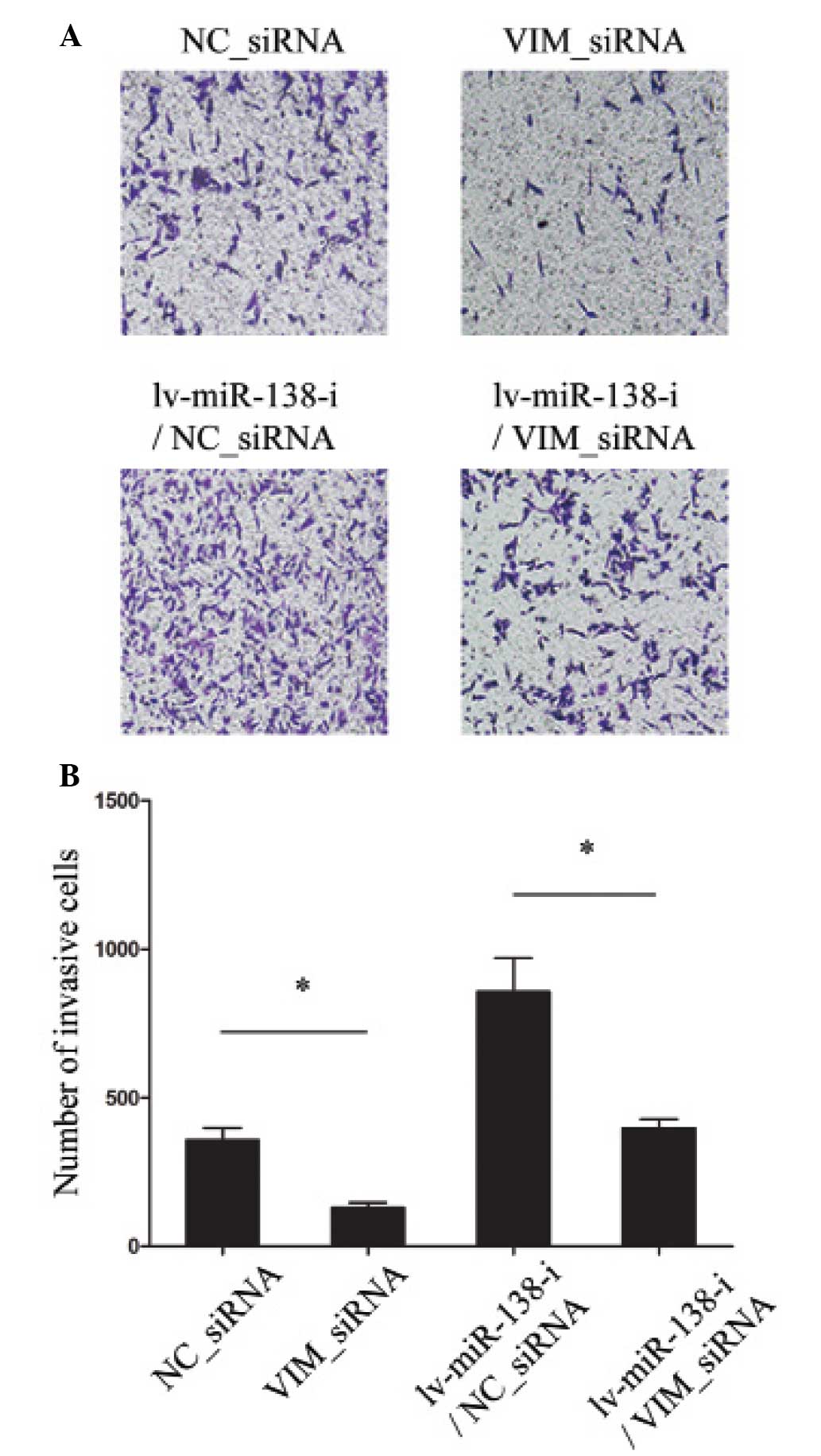
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S, et al: Report of
incidence and mortality in China cancer registries, 2009. Chin J
Cancer Res. 25:10–21. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hirata K, Egawa S, Kimura Y, et al:
Current status of surgery for pancreatic cancer. Dig Surg.
24:137–147. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gillen S, Schuster T, Meyer Zum
Büschenfelde C, Friess H and Kleeff J: Preoperative/neoadjuvant
therapy in pancreatic cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
of response and resection percentages. PLoS Med. 7:e10002672010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pillai RS: MicroRNA function: Multiple
mechanisms for a tiny RNA? RNA. 11:1753–1761. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Feng W and Feng Y: MicroRNAs in neural
cell development and brain diseases. Sci China Life Sci.
54:1103–1112. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Bian S and Sun T: Functions of noncoding
RNAs in neural development and neurological diseases. Mol
Neurobiol. 44:359–373. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Papagiannakopoulos T and Kosik KS:
MicroRNAs: Regulators of oncogenesis and stemness. BMC Med.
6:152008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Blandino G, Fazi F, Donzelli S, et al:
Tumor suppressor microRNAs: A novel non-coding alliance against
cancer. FEBS Lett. 588:2639–2652. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Palanichamy JK and Rao DS: miRNA
dysregulation in cancer: Towards a mechanistic understanding. Front
Genet. 5:542014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang Y, Kim S and Kim IM: Regulation of
metastasis by microRNAs in ovarian cancer. Front Oncol. 4:1432014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Othman N and Nagoor NH: The role of
microRNAs in the regulation of apoptosis in lung cancer and its
application in cancer treatment. Biomed Res Int. 2014:3180302014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Han C, Yu Z, Duan Z and Kan Q: Role of
microRNA-1 in human cancer and its therapeutic potentials. Biomed
Res Int. 2014:4283712014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gao Y, Fan X, Li W, Ping W, Deng Y and Fu
X: miR-138-5p reverses gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung
cancer cells via negatively regulating G protein-coupled receptor
124. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 446:179–186. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang W, Zhao LJ, Tan YX, Ren H and Qi ZT:
MiR-138 induces cell cycle arrest by targeting cyclin D3 in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 33:1113–1120. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao X, Yang L, Hu J and Ruan J: miR-138
might reverse multidrug resistance of leukemia cells. Leuk Res.
34:1078–1082. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Radulovich N, Qian JY and Tsao MS: Human
pancreatic duct epithelial cell model for KRAS transformation.
Methods Enzymol. 439:1–13. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang L, Mizumoto K, Sato N, et al:
Quantitative determination of apoptotic death in cultured human
pancreatic cancer cells by propidium iodide and digitonin. Cancer
Lett. 142:129–137. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Singh S, Sadacharan S, Su S, Belldegrun A,
Persad S and Singh G: Overexpression of vimentin: Role in the
invasive phenotype in an androgen-independent model of prostate
cancer. Cancer Res. 63:2306–2311. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang L, Gu F, Liu CY, Wang RJ, Li J and Xu
JY: High level of FOXC1 expression is associated with poor
prognosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Tumour Biol.
34:853–858. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li ZM, Wen YJ, Yang HB, et al: Enhanced
expression of human vimentin intermediate filaments in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells decreases their proliferative and
invasive abilities in vitro. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 30:408–412.
2008.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gilles C, Polette M, Mestdagt M, et al:
Transactivation of vimentin by beta-catenin in human breast cancer
cells. Cancer Res. 63:2658–2664. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Korsching E, Packeisen J, Liedtke C, et
al: The origin of vimentin expression in invasive breast cancer:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition, myoepithelial histogenesis or
histogenesis from progenitor cells with bilinear differentiation
potential? J Oathol. 206:451–457. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|