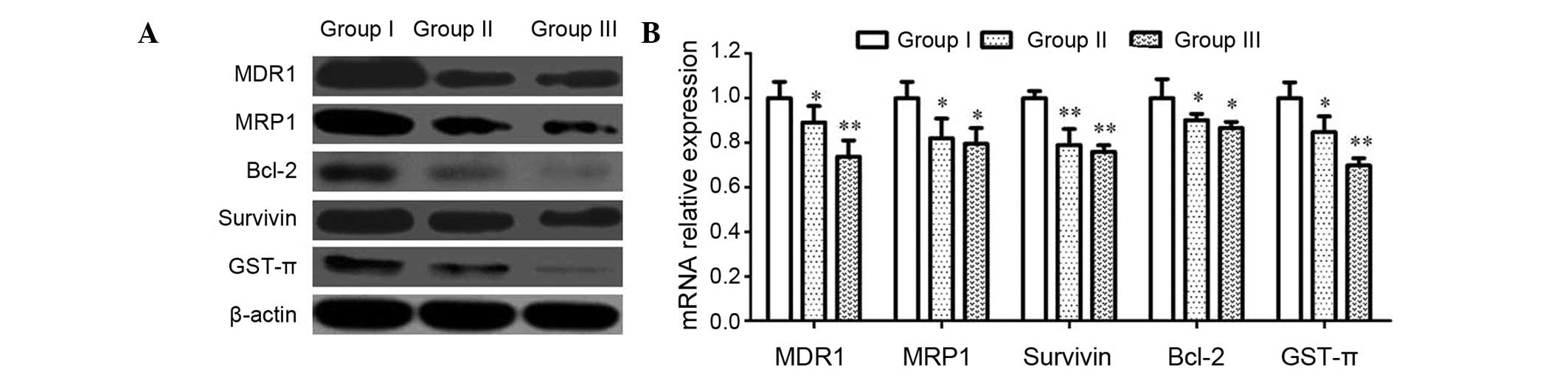
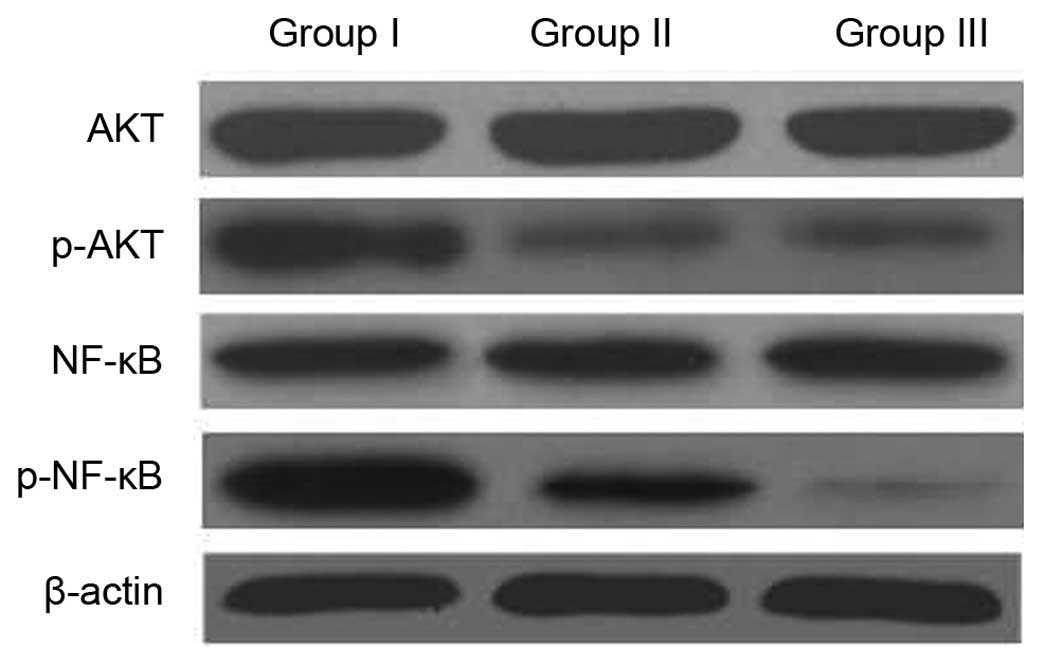
|
1
|
Fan QW and Weiss WA: Targeting the
RTK-PI3K-mTOR axis in malignant glioma: Overcoming resistance. Curr
Top Microbiol Immunol. 347:279–296. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Desjardins A, Rich JN, Quinn JA,
Vredenburgh J, Gururangan S, Sathornsumetee S, Reardon DA, Friedman
AH, Bigner DD and Friedman HS: Chemotherapy and novel therapeutic
approaches in malignant glioma. Front Biosci. 10:2645–2668. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Curiel TJ: Immunotherapy: A useful
strategy to help combat multidrug resistance. Drug Resist Updat.
15:106–113. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ji J, Black KL and Yu JS: Glioma stem cell
research for the development of immunotherapy. Neurosurg Clin N Am.
21:159–166. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Tu W, Cheung PT and Lau YL: Insulin-like
growth factor 1 promotes cord blood T cell maturation and inhibits
its spontaneous and phytohemagglutinin-induced apoptosis through
different mechanisms. J Immunol. 165:1331–1336. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim JS, Chung IS, Lim SH, Park Y, Park MJ,
Kim JY, Kim YG, Hong JT, Kim Y and Han SB: Preclinical and clinical
studies on cytokine-induced killer cells for the treatment of renal
cell carcinoma. Arch Pharm Res. 37:559–566. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rettinger E, Kreyenberg H, Merker M, Kuci
S, Willasch A, Bug G, Ullrich E, Wels WS, Bonig H, Klingebiel T and
Bader P: Immunomagnetic selection or irradiation eliminates
alloreactive cells but also reduces anti-tumor potential of
cytokine-induced killer cells: Implications for unmanipulated
cytokine-induced killer cell infusion. Cytotherapy. 16:835–844.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhou W, Fu XQ, Zhang LL, Zhang J, Huang X,
Lu XH, Shen L, Liu BN, Liu J, Luo HS, et al: The
AKT1/NF-kappaB/Notch1/PTEN axis has an important role in
chemoresistance of gastric cancer cells. Cell Death Dis.
4:e8472013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Y, Li CF, Pan LM and Gao ZL:
7,8-Dihydroxycoumarin inhibits A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cell
proliferation by inducing apoptosis via suppression of Akt/NF-κB
signaling. Exp Ther Med. 5:1770–1774. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Piil K, Juhler M, Jakobsen J and Jarden M:
Controlled rehabilitative and supportive care intervention trials
in patients with high-grade gliomas and their caregivers: A
systematic review. BMJ Support Palliat Care. pii:
bmjspcare-2013-000593. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dirven L, Aaronson NK, Heimans JJ and
Taphoorn MJ: Health-related quality of life in high-grade glioma
patients. Chin J Cancer. 33:40–45. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Melin B and Jenkins R: Genetics in glioma:
Lessons learned from genome-wide association studies. Curr Opin
Neurol. 26:688–692. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li W, Holsinger RM, Kruse CA, Flügel A and
Graeber MB: The potential for genetically altered microglia to
influence glioma treatment. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets.
12:750–762. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang J, Zhu L, Zhang Q, He X, Yin Y, Gu
Y, Guo R, Lu K, Liu L, Liu P and Shu Y: Effects of cytokine-induced
killer cell treatment in colorectal cancer patients: A
retrospective study. Biomed Pharmacother. 68:715–720. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Queiroz RM, Takiya CM, Guimarães LP, Rocha
Gda G, Alviano DS, Blank AF, Alviano CS and Gattass CR:
Apoptosis-inducing effects of melissa officinalis L. essential oil
in glioblastoma multiforme cells. Cancer Invest. 32:226–235. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhu Y, Liu XJ, Yang P, Zhao M, Lv LX,
Zhang GD, Wang Q and Zhang L: Alkylglyceronephosphate synthase
(AGPS) alters lipid signaling pathways and supports chemotherapy
resistance of glioma and hepatic carcinoma cell lines. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 15:3219–3226. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nakai E, Park K, Yawata T, Chihara T,
Kumazawa A, Nakabayashi H and Shimizu K: Enhanced MDR1 expression
and chemoresistance of cancer stem cells derived from glioblastoma.
Cancer Invest. 27:901–908. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Goda K, Bacsó Z and Szabó G: Multidrug
resistance through the spectacle of P-glycoprotein. Curr Cancer
Drug Targets. 9:281–297. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lage H: MDR1/P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) as
target for RNA interference-mediated reversal of multidrug
resistance. Curr Drug Targets. 7:813–821. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu D, Tian W and Shen H: Curcumin prevents
induced drug resistance: A novel function? Chin J Cancer Res.
23:218–223. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang L, Deng Q, Wang J, Bai X, Xiao X, Lv
HR, Zhao MF and Liu PJ: Effect of CIK on multidrug-resistance
reversal and increasing the sensitivity of ADR in K562/ADR cells.
Oncol Lett. 8:1778–1782. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Peklak-Scott C, Smitherman PK, Townsend AJ
and Morrow CS: Role of glutathione S-transferase P1-1 in the
cellular detoxification of cisplatin. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:3247–3255.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Calatozzolo C, Gelati M, Ciusani E,
Sciacca FL, Pollo B, Cajola L, Marras C, Silvani A,
Vitellaro-Zuccarello L, Croci D, et al: Expression of drug
resistance proteins Pgp, MRP1, MRP3, MRP5 and GST-pi in human
glioma. J Neurooncol. 74:113–121. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|