|
1
|
Shen L, Shan YS, Hu HM, Price TJ, Sirohi
B, Yeh KH, Yang YH, Sano T, Yang HK, Zhang X, et al: Management of
gastric cancer in Asia: Resource-stratified guidelines. Lancet
Oncol. 14:e535–e547. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sun K and Lai EC: Adult-specific functions
of animal microRNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 14:535–548. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ameres SL and Zamore PD: Diversifying
microRNA sequence and function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 14:475–488.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ling H, Fabbri M and Calin GA: MicroRNAs
and other non-coding RNAs as targets for anticancer drug
development. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 12:847–865. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Song S and Ajani JA: The role of microRNAs
in cancers of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 10:109–118. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Li S, Meng H, Zhou F, Zhai L, Zhang L, Gu
F, Fan Y, Lang R, Fu L, Gu L, et al: MicroRNA-132 is frequently
downregulated in ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) of breast and acts
as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting cell proliferation. Pathol Res
Pract. 209:179–183. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zheng YB, Luo HP, Shi Q, Hao ZN, Ding Y,
Wang QS, Li SB, Xiao GC and Tong SL: MiR-132 inhibits colorectal
cancer invasion and metastasis via directly targeting ZEB2. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:6515–6522. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu X, Yu H, Cai H and Wang Y: The
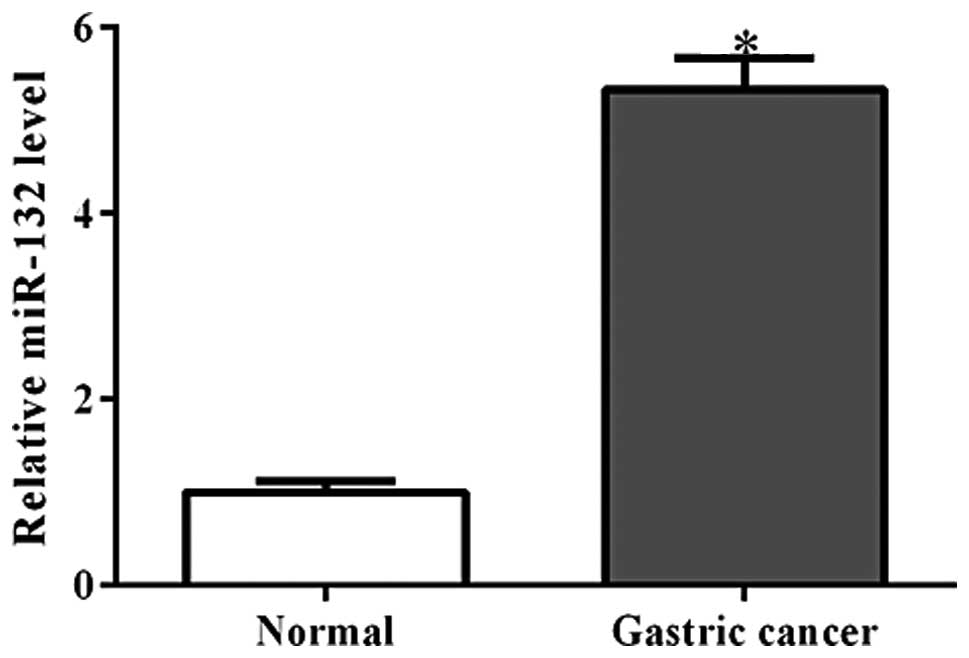
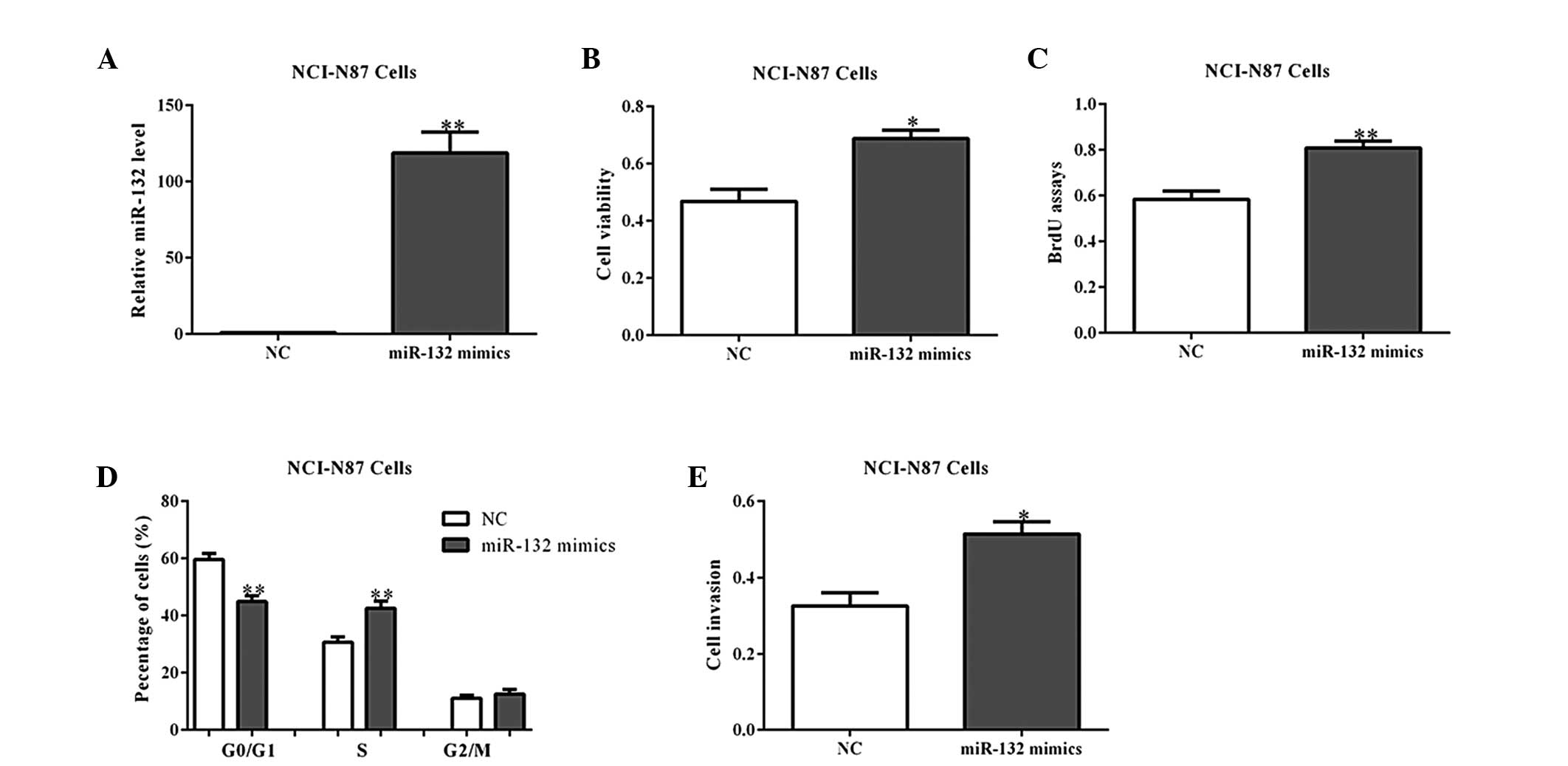
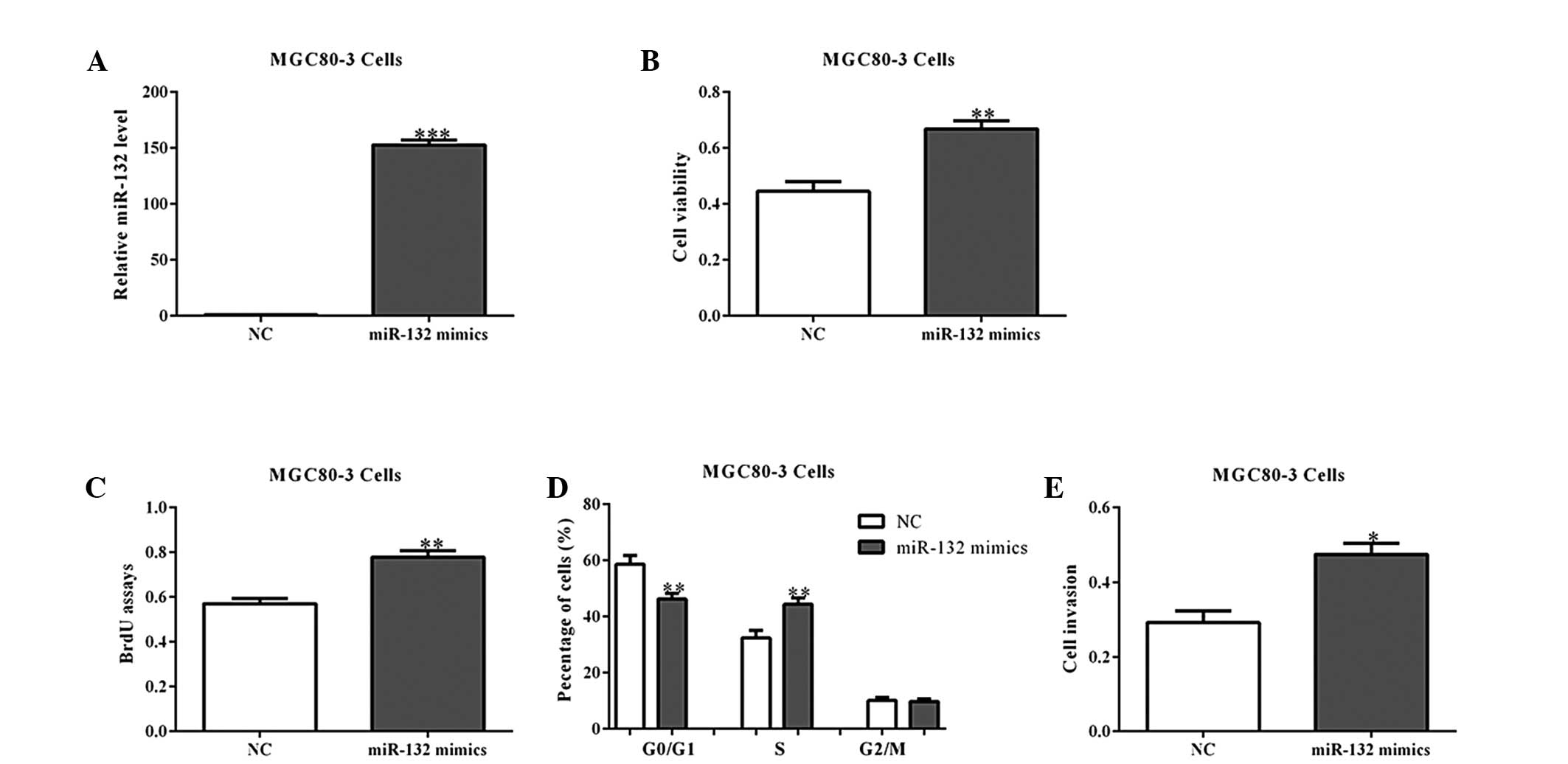
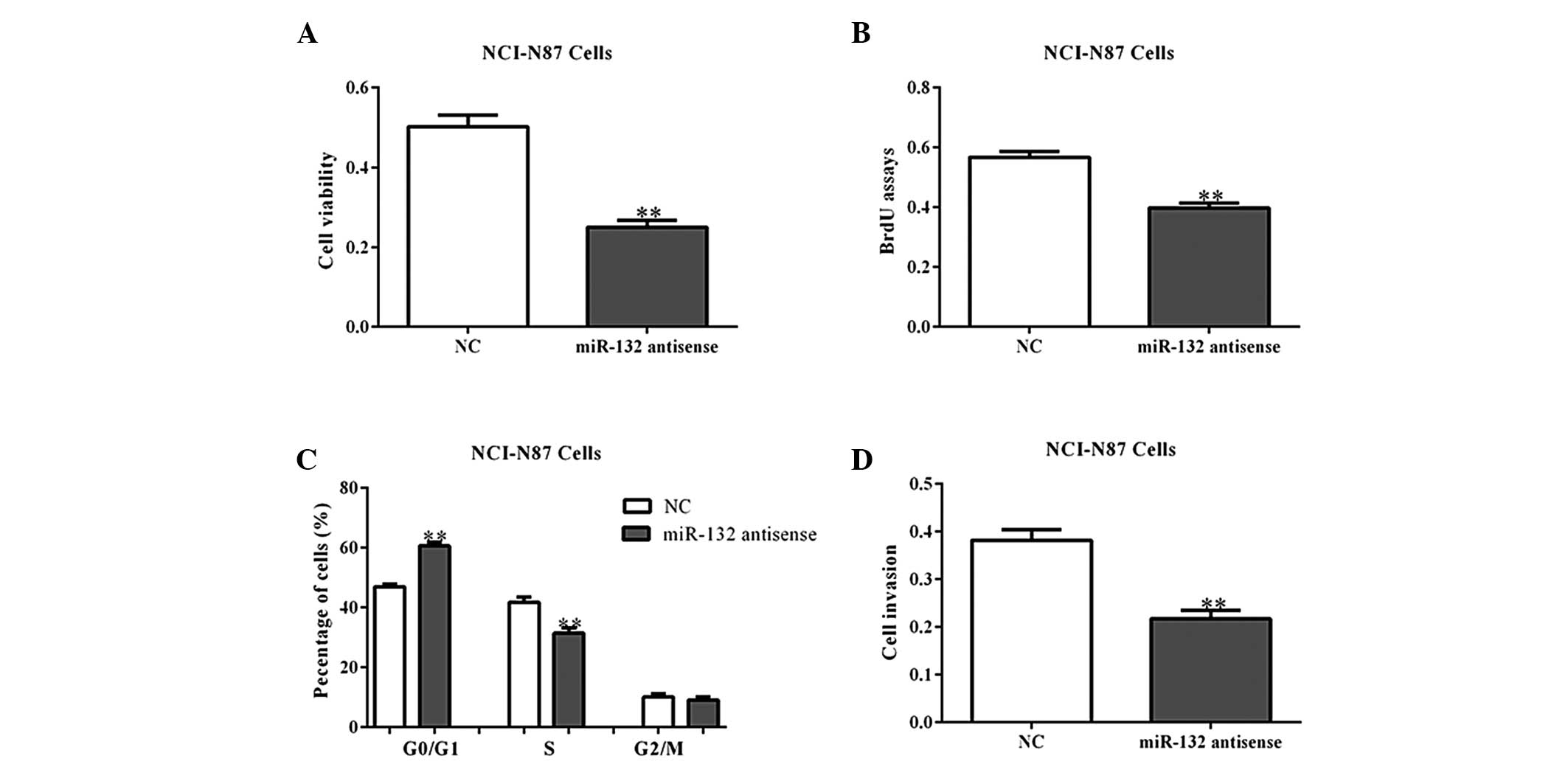
expression and clinical significance of miR-132 in gastric cancer
patients. Diagn Pathol. 9:572014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu R, Li F, Zhu J, Tang R, Qi Q, Zhou X,
Li R, Wang W, Hua D and Chen W: A functional variant at miR-132-3p,
miR-212-3p, and miR-361-5p binding site in CD80 gene alters
susceptibility to gastric cancer in a Chinese Han population. Med
Oncol. 31:602014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang J, Xu G, Shen F and Kang Y: MiR-132
targeting cyclin E1 suppresses cell proliferation in osteosarcoma
cells. Tumour Biol. 35:4859–4865. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tsukamoto Y, Nakada C, Noguchi T, Tanigawa
M, Nguyen LT, Uchida T, Hijiya N, Matsuura K, Fujioka T, Seto M, et
al: MicroRNA-375 is downregulated in gastric carcinomas and
regulates cell survival by targeting PDK1 and 14-3-3zeta. Cancer
Res. 70:2339–2349. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shinozaki A, Sakatani T, Ushiku T, Hino R,
Isogai M, Ishikawa S, Uozaki H, Takada K and Fukayama M:
Downregulation of microRNA-200 in EBV-associated gastric carcinoma.
Cancer Res. 70:4719–4727. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Takei Y, Takigahira M, Mihara K, Tarumi Y
and Yanagihara K: The metastasis-associated microRNA miR-516a-3p is
a novel therapeutic target for inhibiting peritoneal dissemination
of human scirrhous gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 71:1442–1453. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Shin VY and Chu KM: MiRNA as potential
biomarkers and therapeutic targets for gastric cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:10432–10439. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ma J, Hong L, Chen Z, Nie Y and Fan D:
Epigenetic regulation of microRNAs in gastric cancer. Dig Dis Sci.
59:716–723. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Formosa A, Lena AM, Markert EK, Cortelli
S, Miano R, Mauriello A, Croce N, Vandesompele J, Mestdagh P,
Finazzi-Agrò E, et al: DNA methylation silences miR-132 in prostate
cancer. Oncogene. 32:127–134. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
You J, Li Y, Fang N, Liu B, Zu L, Chang R,
Li X and Zhou Q: MiR-132 suppresses the migration and invasion of
lung cancer cells via targeting the EMT regulator ZEB2. PLoS One.
9:e918272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tahiri A, Leivonen SK, Luders T, Steinfeld
I, Ragle Aure M, Geisler J, Mäkelä R, Nord S, Riis ML, Yakhini Z,
et al: Deregulation of cancer-related miRNAs is a common event in
both benign and malignant human breast tumors. Carcinogenesis.
35:76–85. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chen HZ, Tsai SY and Leone G: Emerging
roles of E2Fs in cancer: An exit from cell cycle control. Nat Rev
Cancer. 9:785–797. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Deng Y, Huang Z, Xu Y, Jin J, Zhuo W,
Zhang C, Zhang X, Shen M, Yan X, Wang L, et al: MiR-215 modulates
gastric cancer cell proliferation by targeting RB1. Cancer Lett.
342:27–35. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang YF, Zhang AR, Zhang BC, Rao ZG, Gao
JF, Lv MH, Wu YY, Wang SM, Wang RQ and Fang DC: MiR-26a regulates
cell cycle and anoikis of human esophageal adenocarcinoma cells
through Rb1-E2F1 signaling pathway. Mol Biol Rep. 40:1711–1720.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Feng S, Cong S, Zhang X, Bao X, Wang W, Li
H, Wang Z, Wang G, Xu J, Du B, et al: MicroRNA-192 targeting
retinoblastoma 1 inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell
apoptosis in lung cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:6669–6678.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|