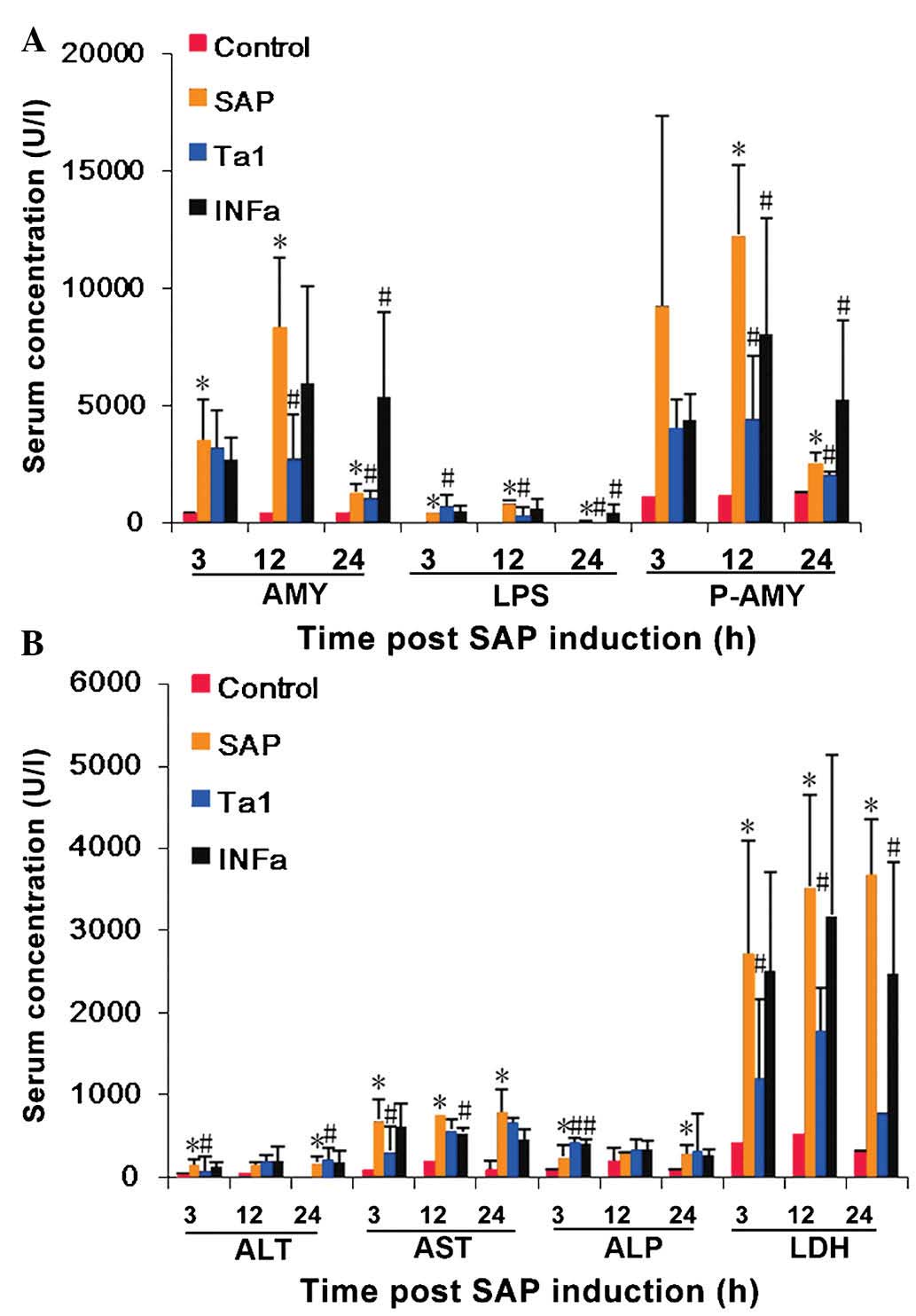
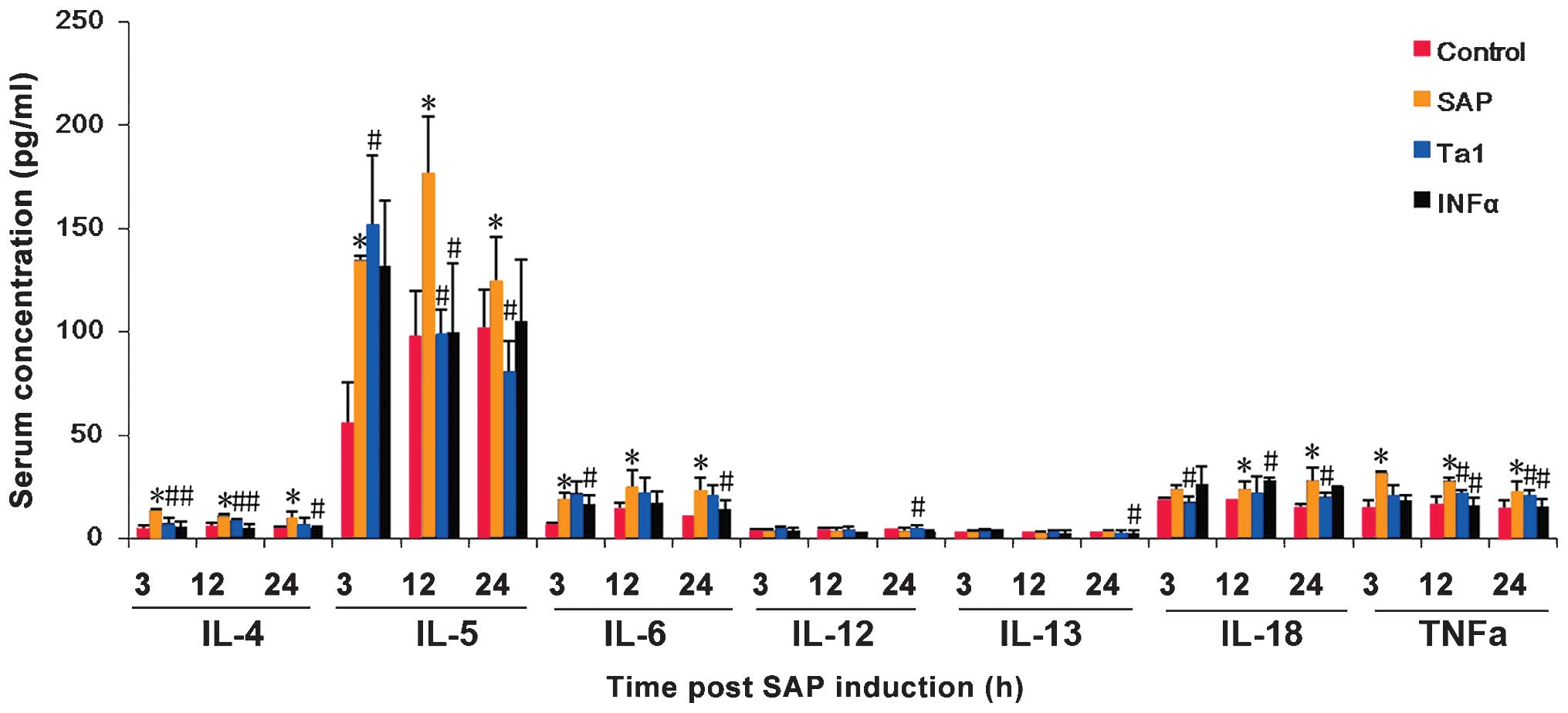
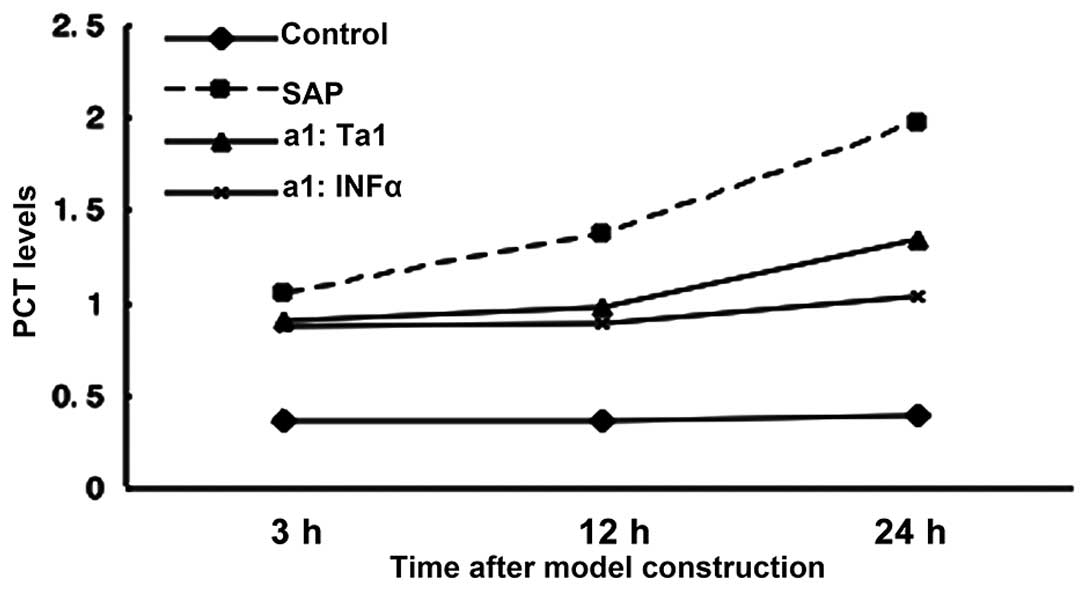
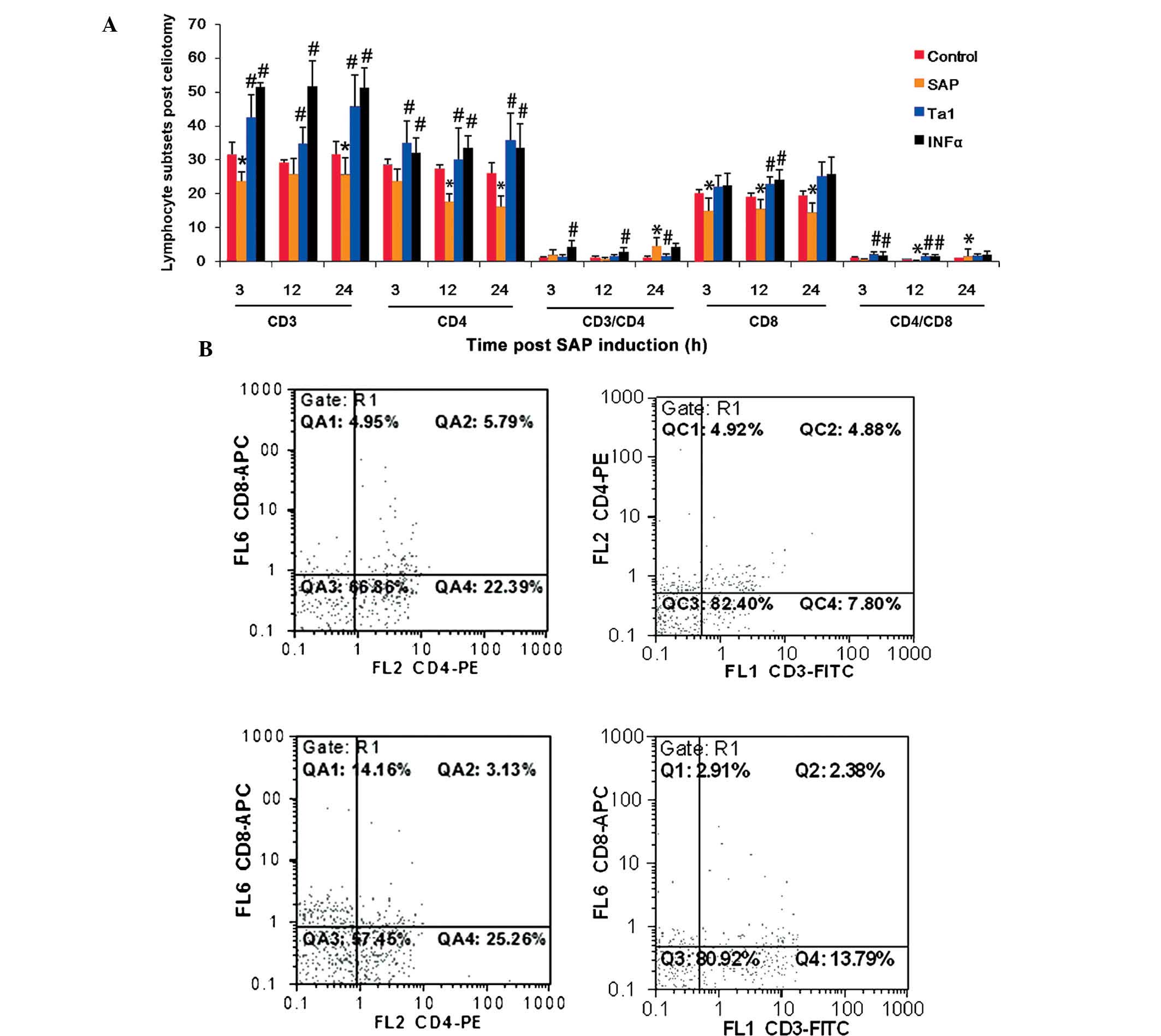
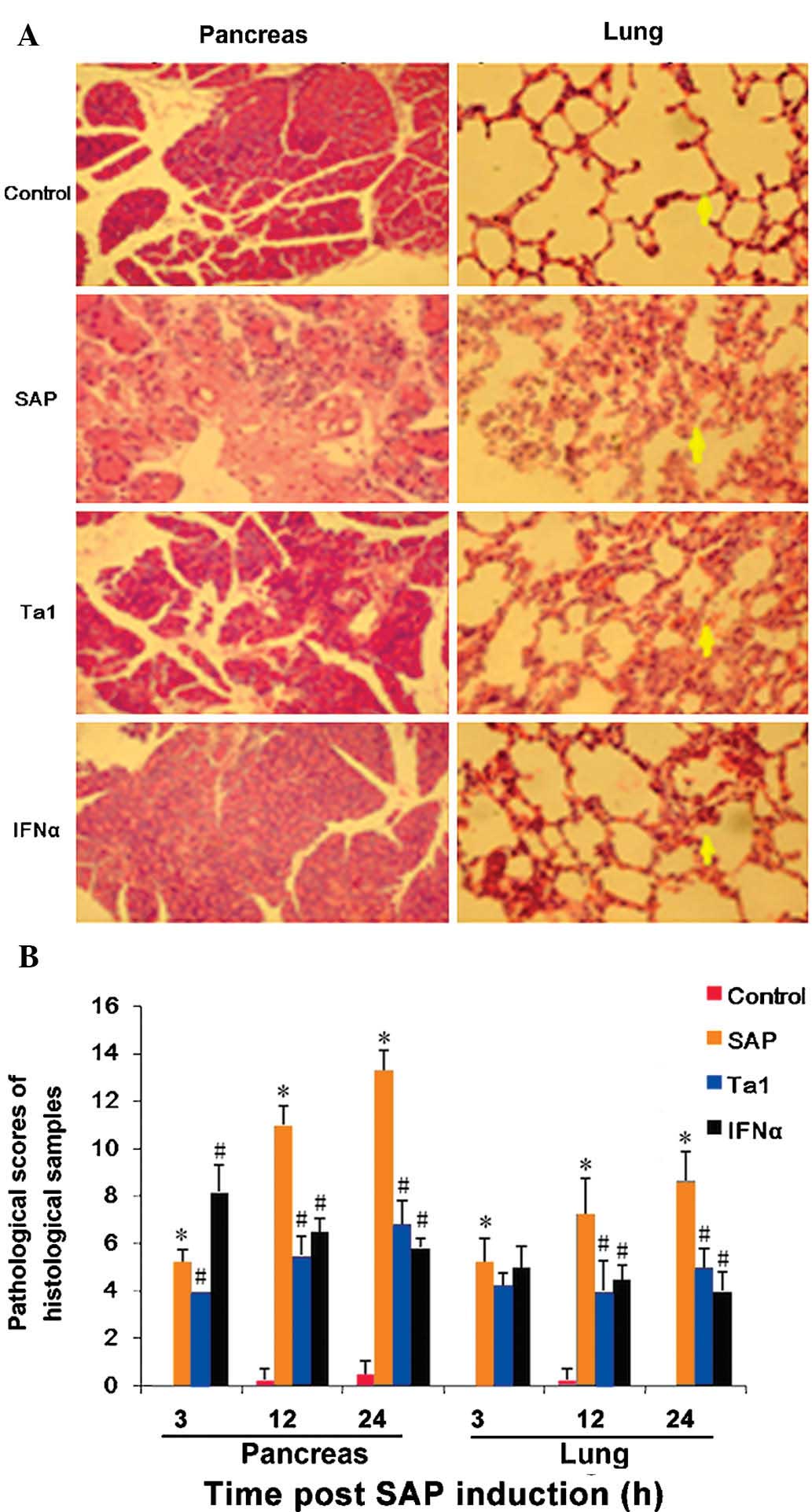
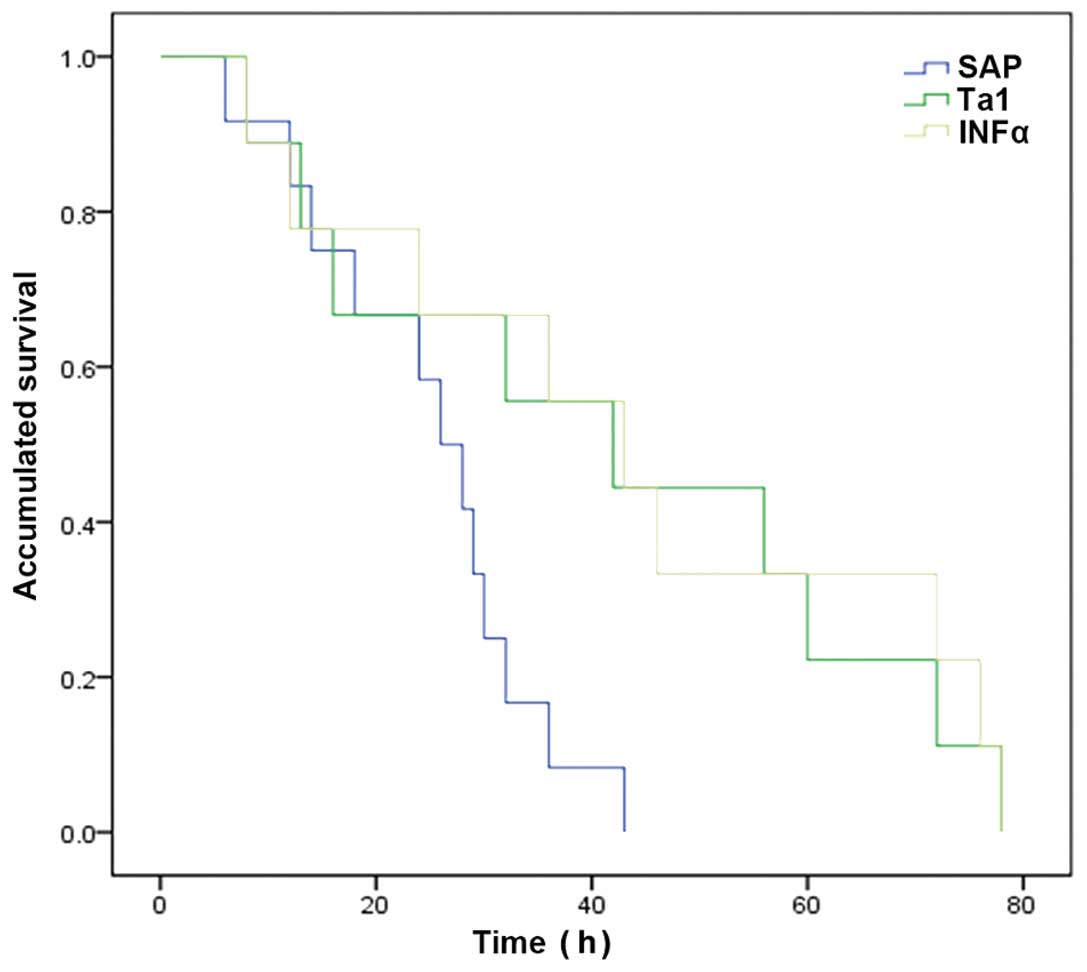
|
1
|
Otsuki M, Takeda K, Matsuno S, Kihara Y,
Koizumi M, Hirota M, Ito T, Kataoka K, Kitagawa M, Inui K and
Takeyama Y: Criteria for the diagnosis and severity stratification
of acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 19:5798–5805. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schepers NJ, Besselink MG, van Santvoort
HC, Bakker OJ and Bruno MJ; Dutch Pancreatitis Study Group: Early
management of acute pancreatitis. Best Pract Res Clin
Gastroenterol. 27:727–743. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Panek J, Karcz D, Pieton R, Zasada J,
Tusinski M, Dolecki M and Winiarski M: Blood serum levels of
proinflammatory cytokines in patients with different degrees of
biliary pancreatitis. Can J Gastroenterol. 20:645–648.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kylanpaa ML, Repo H and Puolakkainen PA:
Inflammation and immunosuppression in severe acute pancreatitis.
World J Gastroenterol. 16:2867–2872. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bone RC: Sir Isaac Newton, sepsis, SIRS
and CARS. Crit Care Med. 24:1125–1128. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Garaci E, Pica F, Sinibaldi-Vallebona P,
Pierimarchi P, Mastino A, Matteucci C and Rasi G: Thymosin alpha
(1) in combination with cytokines and chemotherapy for the
treatment of cancer. Int Immunopharmacol. 3:1145–1150. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Aman MJ, Tretter T, Eisenbeis I, Bug G,
Decker T, Aulitzky WE, Tilg H, Huber C and Peschel C:
Interferon-alpha stimulates production of interleukin-10 in
activated CD4+ T cells and monocytes. Blood. 87:4731–4736.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Romani L, Bistoni F, Montagnoli C, Gaziano
R, Bozza S, Bonifazi P, Zelante T, Moretti S, Rasi G, Garaci E and
Puccetti P: Thymosin alpha1: An endogenous regulator of
inflammation, immunity and tolerance. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1112:326–338. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pestka S, Krause CD and Walter MR:
Interferons, interferon-like cytokines, and their receptors.
Immunol Rev. 202:8–32. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sharif S, Broman M, Babcock T, Ong E, Jho
D, Rudnicki M, Helton WS and Espat NJ: A priori dietary omega-3
lipid supplementation results in local pancreatic macrophage and
pulmonary inflammatory response attenuation in a model of
experimental acute edematous pancreatitis (AEP). JPEN J Parenter
Enteral Nutr. 30:271–276. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chooklin S: Pathogenic aspects of
pulmonary complications in acute pancreatitis patients.
Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 8:186–192. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
de Beaux AC, Ross JA, Maingay JP, Fearon
KC and Carter DC: Proinflammatory cytokine release by peripheral
blood mono-nuclear cells from patients with acute pancreatitis. Br
J Surg. 83:1071–1075. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Curley PJ: Endotoxin, cellular immune
dysfunction and acute pancreatitis. Ann R Coll Surg Engl.
78:531–535. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ueda T, Takeyama Y, Yasuda T, Matsumura N,
Sawa H, Nakajima T, Ajiki T, Fujino Y, Suzuki Y and Kuroda Y:
Significant elevation of serum interleukin-18 levels in patients
with acute pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol. 41:158–165. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kaya E, Dervisoglu A and Polat C:
Evaluation of diagnostic findings and scoring systems in outcome
prediction in acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol.
13:3090–3094. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Denham W, Fink G, Yang J, Ulrich P, Tracey
K and Norman J: Small molecule inhibition of tumor necrosis factor
gene processing during acute pancreatitis prevents cytokine cascade
progression and attenuates pancreatitis severity. Am Surg.
63:1045–1049; discussion 1049–1050. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Stimac D, Fisić E, Milić S, Bilić-Zulle L
and Perić R: Prognostic values of IL-6, IL-8 and IL-10 in acute
pancreatitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 40:209–212. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Karne S and Gorelick FS: Etiopathogenesis
of acute pancreatitis. Surg Clin North Am. 79:699–710. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Springer TA: Adhesion receptors of the
immune system. Nature. 346:425–434. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jiang CF, Shiau YC, Ng KW and Tan SW:
Serum interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor alpha and C-reactive
protein in early prediction of severity of acute pancreatitis. J
Chin Med Assoc. 67:442–446. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao X, Andersson R and Wang X, Dib M and
Wang X: Acute pancreatitis-associated lung injury:
Pathophysiological mechanisms and potential future therapies. Scand
J Gastroenterol. 37:1351–1358. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Barbulescu K, Becker C, Schlaak JF,
Schmitt E, Meyer zum Buschenfelde KH and Neurath MF: IL-12 and
IL-18 differentially regulate the transcriptional activity of the
human IFN-gamma promoter in primary CD4+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol.
160:3642–3647. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Matsumoto S, Tsuji-Takayama K, Aizawa Y,
Koide K, Takeuchi M, Ohta T and Kurimoto M: Interleukin-18
activates NF-kappaB in murine T helper type 1 cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 234:454–457. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rau BM, Kemppainen EA, Gumbs AA, Büchler
MW, Wegscheider K, Bassi C, Puolakkainen PA and Beger HG: Early
assessment of pancreatic infections and overall prognosis in severe
acute pancreatitis by procalcitonin (PCT): A prospective
international multicenter study. Ann Surg. 245:745–754. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li J, Yang WJ, Huang LM and Tang CW:
Immunomodulatory therapies for acute pancreatitis. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:16935–16947. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li XM, Chen JZ and Zhang NY: Association
of TCM-bionzheng with Tlymphrocyte subsets and thyroidism in
patients with diabetes mellitus. J Fourth Mil Med Univ. 2:223–234.
2000.In Chinese.
|
|
27
|
Watson J and Mochizuki D: Interleukin 2: A
class of T cell growth factors. Immunol Rev. 51:257–278. 1980.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li J, Yang WJ, Huang LM and Tang CW:
Immunomodulatory therapies for acute pancreatitis. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:16935–16947. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|