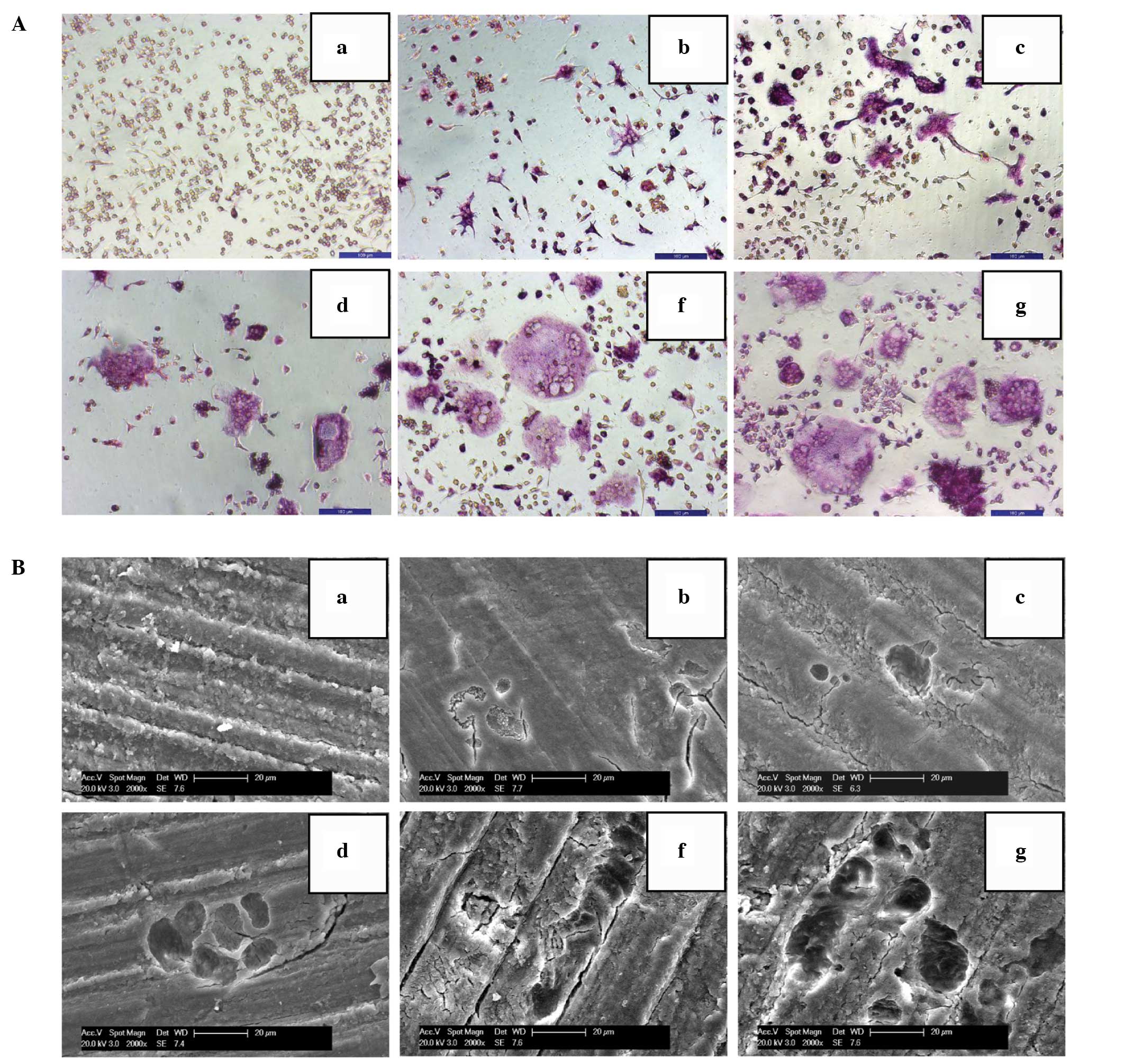
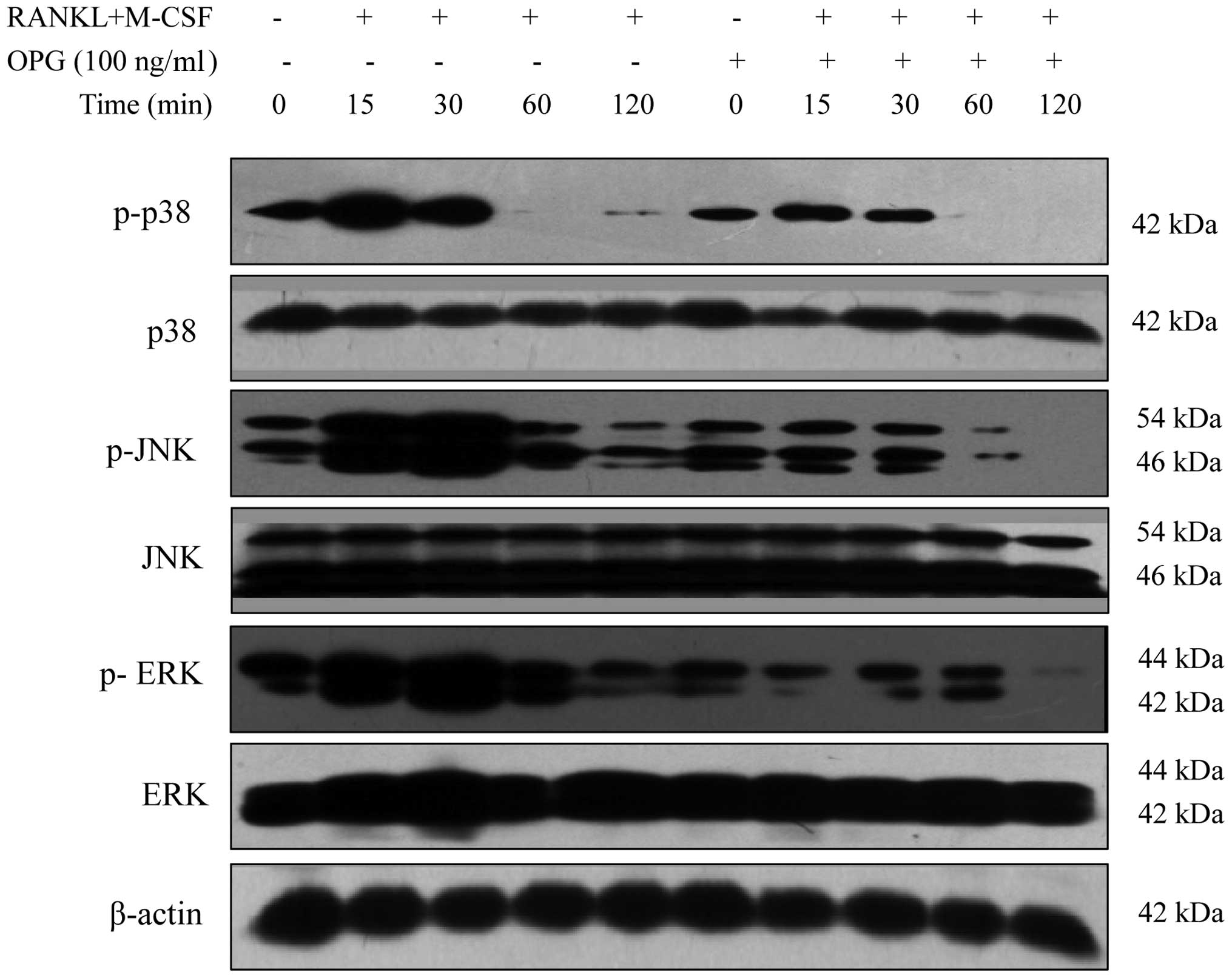
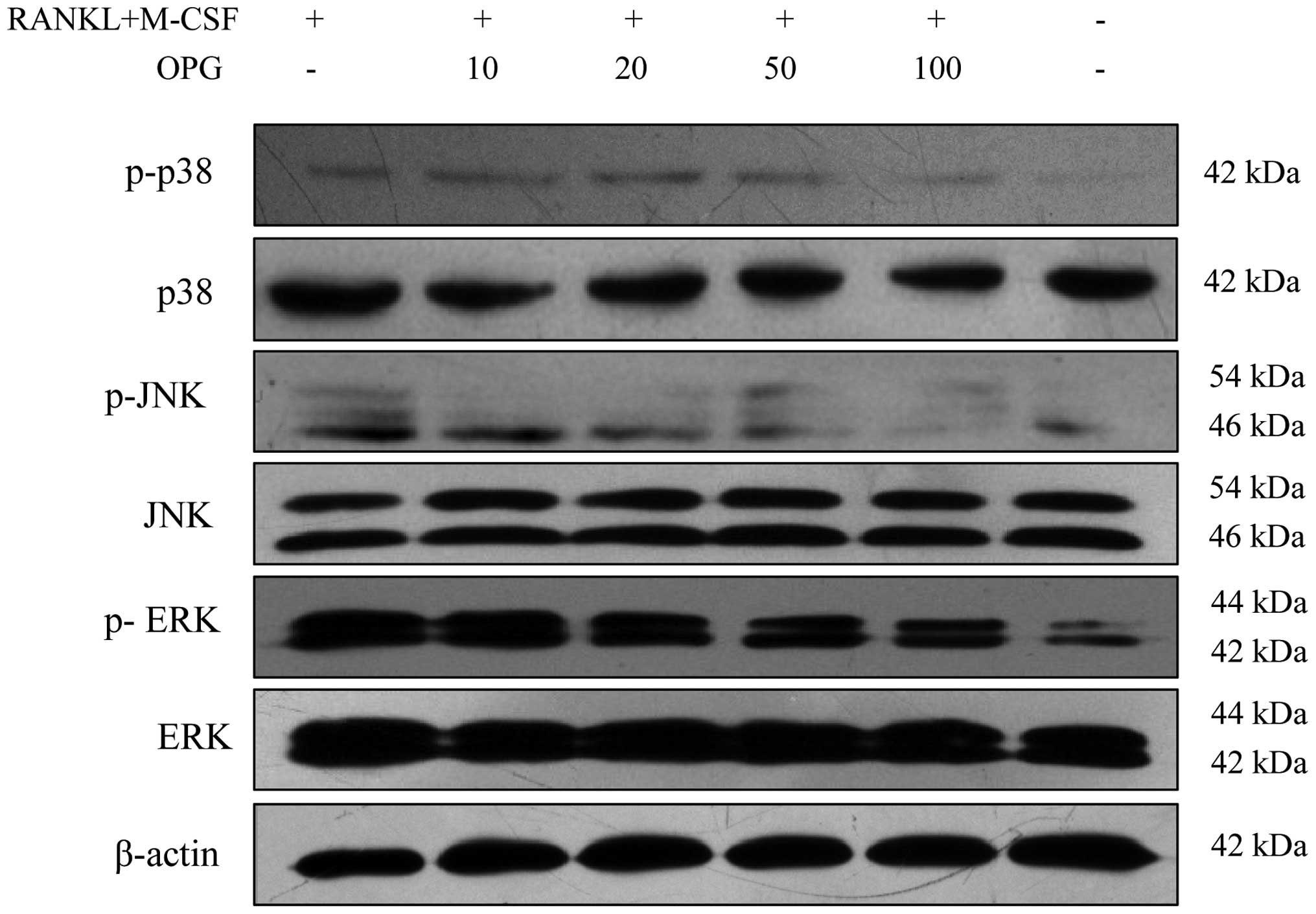
|
1
|
Zhang W and Liu HT: MAPK signal pathways
in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell
Res. 12:9–18. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Seger R and Krebs EG: The MAPK signaling
cascade. FASEB J. 9:726–735. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sompallae R, Stavropoulou V, Houde M and
Masucci MG: The MAPK signaling cascade is a central hub in the
regulation of cell cycle, apoptosis and cytoskeleton remodeling by
tripeptidyl-peptidase II. Gene Regul Syst Bio. 2:253–265.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Robinson MJ and Cobb MH: Mitogen-activated
protein kinase pathways. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 9:180–186. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rossomando AJ, Sanghera JS, Marsden LA,
Weber MJ, Pelech SL and Sturgill TW: Biochemical characterization
of a family of serine/threonine protein kinases regulated by
tyrosine and serine/threonine phosphorylations. J Biol Chem.
266:20270–20275. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brewster JL, de Valoir T, Dwyer ND, Winter
E and Gustin MC: An osmosensing signal transduction pathway in
yeast. Science. 259:1760–1763. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kyriakis JM and Avruch J: pp54
microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase. A novel serine/threonine
protein kinase regulated by phosphorylation and stimulated by
poly-L-lysine. J Biol Chem. 265:17355–17363. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jansen ID, Vermeer JA, Bloemen V, Stap J
and Everts V: Osteoclast fusion and fission. Calcif Tissue Int.
90:515–522. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Honma M, Ikebuchi Y, Kariya Y and Suzuki
H: Regulatory mechanisms of RANKL presentation to osteoclast
precursors. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 12:115–120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nakashima T: Regulation mechanism of bone
remodeling. Kokubyo Gakkai Zasshi. 80:75–80. 2013.In Japanese.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lemaire V, Tobin FL, Greller LD, Cho CR
and Suva LJ: Modeling the interactions between osteoblast and
osteoclast activities in bone remodeling. J Theor Biol.
229:293–309. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Boyce BF and Xing L: Functions of
RANKL/RANK/OPG in bone modeling and remodeling. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 473:139–146. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wright HL, McCarthy HS, Middleton J and
Marshall MJ: RANK, RANKL and osteoprotegerin in bone biology and
disease. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2:56–64. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pérez-Sayáns M, Somoza-Martín JM,
Barros-Angueira F, Rey JM and García-García A: RANK/RANKL/OPG role
in distraction osteogenesis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral
Radiol Endod. 109:679–686. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fu YX, Gu JH, Zhang YR, Tong XS, Zhao HY,
Yuan Y, Liu XZ, Bian JC and Liu ZP: Osteoprotegerin influences the
bone resorption activity of osteoclasts. Int J Mol Med.
31:1411–1417. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jimi E, Akiyama S, Tsurukai T, Okahashi N,
Kobayashi K, Udagawa N, Nishihara T, Takahashi N and Suda T:
Osteoclast differentiation factor acts as a multifunctional
regulator in murine osteoclast differentiation and function. J
Immunol. 163:434–442. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee SE, Woo KM, Kim SY, Kim HM, Kwack K,
Lee ZH and Kim HH: The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, p38, and
extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways are involved in
osteoclast differentiation. Bone. 30:71–77. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li X, Udagawa N, Itoh K, Suda K, Murase Y,
Nishihara T, Suda T and Takahashi N: p38 MAPK-mediated signals are
required for inducing osteoclast differentiation but not for
osteoclast function. Endocrinology. 143:3105–3113. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Junttila MR, Li SP and Westermarck J:
Phosphatase-mediated crosstalk between MAPK signaling pathways in
the regulation of cell survival. FASEB J. 22:954–965. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Theoleyre S, Wittrant Y, Couillaud S,
Vusio P, Berreur M, Dunstan C, Blanchard F, Rédini F and Heymann D:
Cellular activity and signaling induced by osteoprotegerin in
osteoclasts: Involvement of receptor activator of nuclear factor
kappaB ligand and MAPK. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1644:1–7. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mladenović Ž, Johansson A, Willman B,
Shahabi K, Björn E and Ransjö M: Soluble silica inhibits osteoclast
formation and bone resorption in vitro. Acta Biomater. 10:406–418.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chen X, Zhu G, Jin T, Gu S, Xiao H and Qiu
J: Cadmium induces differentiation of RAW264.7 cells into
osteoclasts in the presence of RANKL. Food Chem Toxicol.
49:2392–2397. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fu YX, Gu JH, Zhang YR, Tong XS, Zhao HY,
Yuan Y, Liu XZ, Bian JC and Liu ZP: Inhibitory effects of
osteoprotegerin on osteoclast formation and function under
serum-free conditions. J Vet Sci. 14:405–412. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Simonet WS, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, Kelley
M, Chang MS, Lüthy R, Nguyen HQ, Wooden S, Bennett L, Boone T, et
al: Osteoprotegerin: A novel secreted protein involved in the
regulation of bone density. Cell. 89:309–319. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Boyle WJ, Simonet WS and Lacey DL:
Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 423:337–342.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hofbauer LC: Osteoprotegerin ligand and
osteoprotegerin: Novel implications for osteoclast biology and bone
metabolism. Eur J Endocrinol. 141:195–210. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wong BR, Besser D, Kim N, Arron JR,
Vologodskaia M, Hanafusa H and Choi Y: TRANCE, a TNF family member,
activates Akt/PKB through a signaling complex involving TRAF6 and
c-Src. Mol Cell. 4:1041–1049. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Shih J, Bauer D, Orloff J, Capizzi T,
Thompson D, Oppenheimer L and Ross PD: Proportion of fracture risk
reduction explained by BMD changes using Freedman analysis depends
on choice of predictors. Osteoporos Int. 13:S38–S39. 2002.
|
|
29
|
Miyazaki T, Katagiri H, Kanegae Y,
Takayanagi H, Sawada Y, Yamamoto A, Pando MP, Asano T, Verma IM,
Oda H, et al: Reciprocal role of ERK and NF-kappaB pathways in
survival and activation of osteoclasts. J Cell Biol. 148:333–342.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
David JP, Rincon M, Neff L, Horne WC and
Baron R: Carbonic anhydrase II is an AP-1 target gene in
osteoclasts. J Cell Physiol. 188:89–97. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ye H, Arron JR, Lamothe B, Cirilli M,
Kobayashi T, Shevde NK, Segal D, Dzivenu OK, Vologodskaia M, Yim M,
et al: Distinct molecular mechanism for initiating TRAF6
signalling. Nature. 418:443–447. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Blair HC, Robinson LJ and Zaidi M:
Osteoclast signalling pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
328:728–738. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mizukami J, Takaesu G, Akatsuka H, Sakurai
H, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Matsumoto K and Sakurai N: Receptor activator
of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL) activates TAK1 mitogen-activated
protein kinase kinase kinase through a signaling complex containing
RANK, TAB2, and TRAF6. Mol Cell Biol. 22:992–1000. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Choi HJ, Park YR, Nepal M, Choi BY, Cho
NP, Choi SH, Heo SR, Kim HS, Yang MS and Soh Y: Inhibition of
osteoclastogenic differentiation by Ikarisoside A in RAW 264.7
cells via JNK and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Eur J Pharmacol.
636:28–35. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cano E and Mahadevan LC: Parallel signal
processing among mammalian MAPKs. Trends Biochem Sci. 20:117–122.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Grigoriadis AE, Wang ZQ, Cecchini MG,
Hofstetter W, Felix R, Fleisch HA and Wagner EF: c-Fos: A key
regulator of osteoclast-macrophage lineage determination and bone
remodeling. Science. 266:443–448. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chapurlat RD, Palermo L, Ramsay P and
Cummings SR: Risk of fracture among women who lose bone density
during treatment with alendronate. The Fracture Intervention Trial.
Osteoporos Int. 16:842–848. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Hong SY, Jeon YM, Lee HJ, Kim JG, Baek JA
and Lee JC: Activation of RhoA and FAK induces ERK-mediated
osteopontin expression in mechanical force-subjected periodontal
ligament fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biochem. 335:263–272. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Stanley ER, Berg KL, Einstein DB, Lee PS,
Pixley FJ, Wang Y and Yeung YG: Biology and action of
colony–stimulating factor-1. Mol Reprod Dev. 46:4–10. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tsurukai T, Udagawa N, Matsuzaki K,
Takahashi N and Suda T: Roles of macrophage-colony stimulating
factor and osteoclast differentiation factor in osteoclastogenesis.
J Bone Miner Metab. 18:177–184. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fuller K, Owens JM, Jagger CJ, Wilson A,
Moss R and Chambers TJ: Macrophage colony-stimulating factor
stimulates survival and chemotactic behavior in isolated
osteoclasts. J Exp Med. 178:1733–1744. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Weilbaecher KN, Motyckova G, Huber WE,
Takemoto CM, Hemesath TJ, Xu Y, Hershey CL, Dowland NR, Wells AG
and Fisher DE: Linkage of M-CSF signaling to Mitf, TFE3, and the
osteoclast defect in Mitf(mi/mi) mice. Mol Cell. 8:749–758. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shiotani A, Takami M, Itoh K, Shibasaki Y
and Sasaki T: Regulation of osteoclast differentiation and function
by receptor activator of NFkB ligand and osteoprotegerin. Anat Rec.
268:137–146. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hakeda Y, Kobayashi Y, Yamaguchi K, Yasuda
H, Tsuda E, Higashio K, Miyata T and Kumegawa M: Osteoclastogenesis
inhibitory factor (OCIF) directly inhibits bone-resorbing activity
of isolated mature osteoclasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
251:796–801. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|