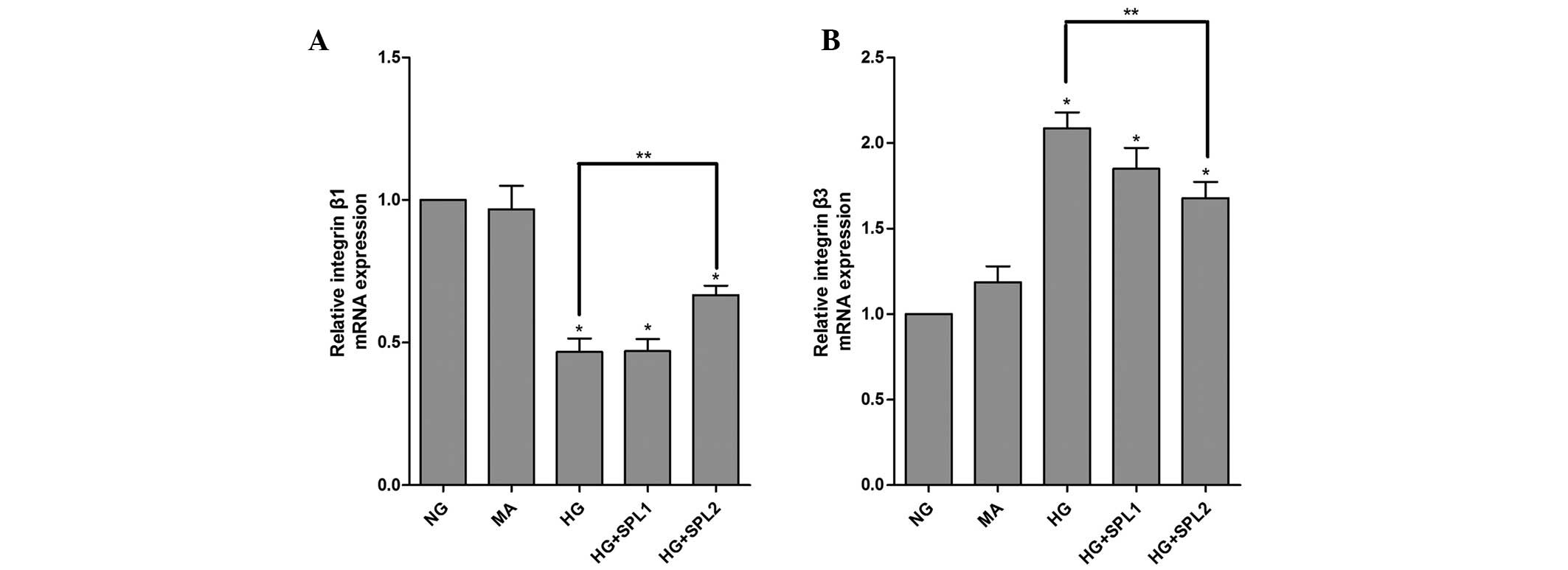
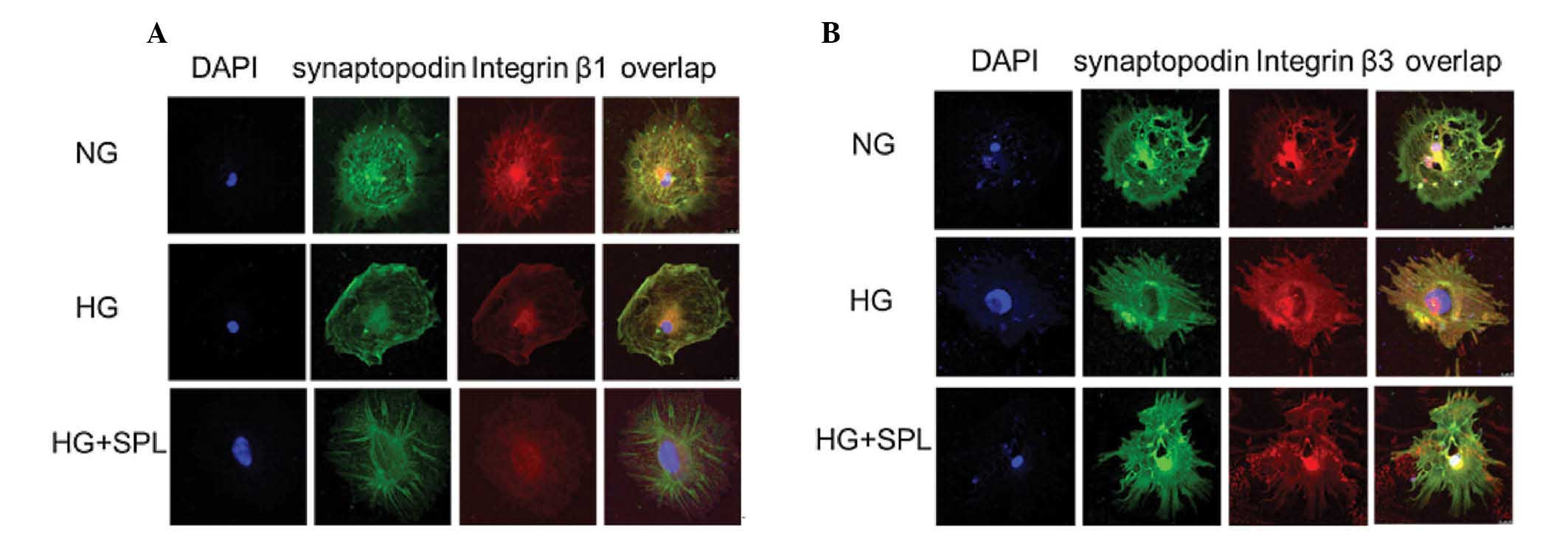
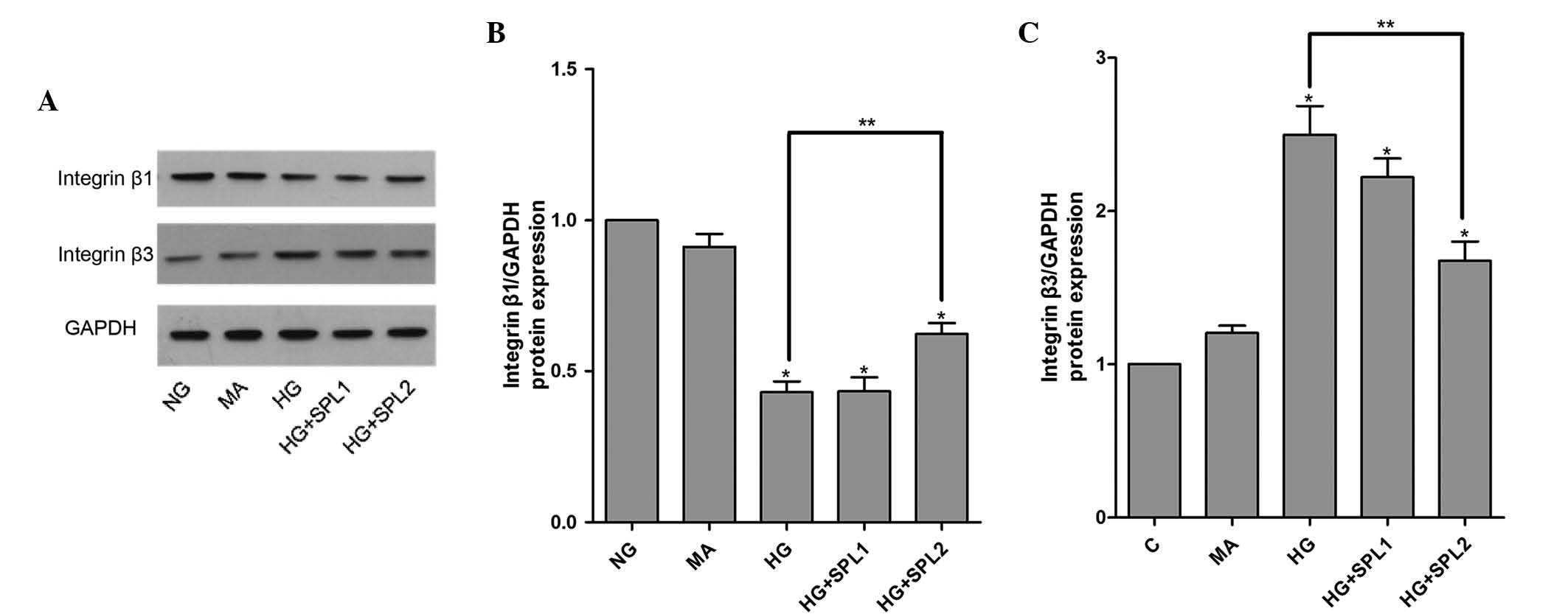
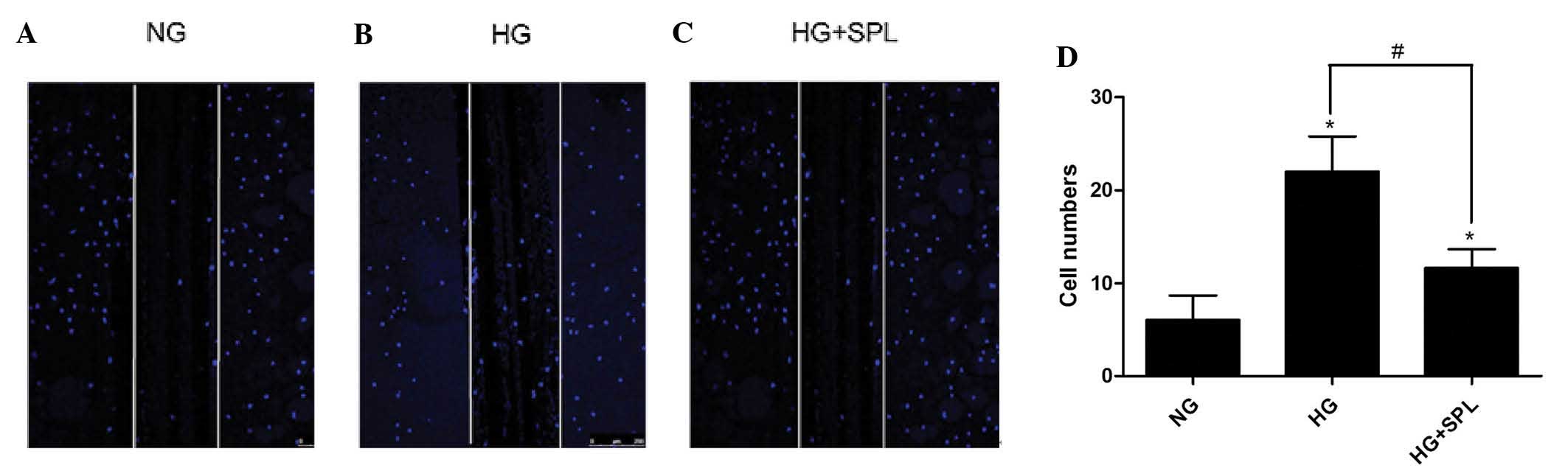
|
1
|
Molitch ME, DeFronzo RA, Franz MJ, Keane
WF, Mogensen CE, Parving HH and Steffes MW; American Diabetes
Association: Nephropathy in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 27(Suppl 1):
S79–S83. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ritz E, Rychlik I, Locatelli F and Halimi
S: End-stage renal failure in type 2 diabetes: A medical
catastrophe of worldwide dimensions. Am J Kidney Dis. 34:795–808.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wolf G, Chen S and Ziyadeh FN: From the
periphery of the glomerular capillary wall toward the center of
disease: Podocyte injury comes of age in diabetic nephropathy.
Diabetes. 54:1626–1634. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li JJ, Kwak SJ, Jung DS, Kim JJ, Yoo TH,
Ryu DR, Han SH, Choi HY, Lee JE, Moon SJ, et al: Podocyte biology
in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int Suppl. S36–S42. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pagtalunan ME, Miller PL, Jumping-Eagle S,
Nelson RG, Myers BD, Rennke HG, Coplon NS, Sun L and Meyer TW:
Podocyte loss and progressive glomerular injury in type II
diabetes. J Clin Invest. 99:342–348. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
White KE, Bilous RW, Marshall SM, El Nahas
M, Remuzzi G, Piras G, De Cosmo S and Viberti G: Podocyte number in
normotensive type 1 diabetic patients with albuminuria. Diabetes.
51:3083–3089. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
D'Agati VD: Podocyte injury in focal
segmental glomerulo-sclerosis: Lessons from animal models (a play
in five acts). Kidney Int. 73:399–406. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wharram BL, Goyal M, Wiggins JE, Sanden
SK, Hussain S, Filipiak WE, Saunders TL, Dysko RC, Kohno K, Hozman
LB and Wiggins RC: Podocyte depletion causes glomerulosclerosis:
Diphtheria toxin-induced podocyte depletion in rats expressing
human diphtheria toxin receptor transgene. J Am Soc Nephrol.
16:2941–2952. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu X, Wang J, Jiang H, Hu Q, Chen J, Zhang
J, Zhu R, Liu W and Li B: Wnt3a activates β1-integrin and regulates
migration and adhesion of vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol Med
Rep. 9:1159–1164. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zaidel-Bar R, Itzkovitz S, Ma'ayan A,
Iyengar R and Geiger B: Functional atlas of the integrin adhesome.
Nat Cell Biol. 9:858–867. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kitsiou PV, Tzinia AK, Stetler-Stevenson
WG, Michael AF, Fan WW, Zhou B and Tsilibary EC: Glucose-induced
changes in integrins and matrix-related functions in cultured human
glomerular epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
284:F671–F679. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fassler R and Meyer M: Consequences of
lack of beta 1 integrin gene expression in mice. Genes Dev.
9:1896–1908. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kanasaki K, Kanda Y, Palmsten K, Tanjore
H, Lee SB, Lebleu VS, Gattone VH Jr and Kalluri R: Integrin
beta1-mediated matrix assembly and signaling are critical for the
normal development and function of the kidney glomerulus. Dev Biol.
313:584–593. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Pozzi A, Jarad G, Moeckel GW, Coffa S,
Zhang X, Gewin L, Eremina V, Hudson BG, Borza B, Harris RC, et al:
Beta1 integrin expression by podocytes is required to maintain
glomerular structural integrity. De Biol. 316:288–301. 2008.
|
|
15
|
Wei C, Möller CC, Altintas MM, Li J,
Schwarz K, Zacchigna S, Xie L, Henger A, Schmid H, Rastaldi MP, et
al: Modification of kidney barrier function by the urokinase
receptor. Nat Med. 14:55–63. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Sachs N and Sonnenberg A: Cell-matrix
adhesion of podocytes in physiology and disease. Nat Rev Nephrol.
9:200–210. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wei C, El Hindi S, Li J, Fornoni A, Goes
N, Sageshima J, Maiguel D, Karumanchi SA, Yap HK, Saleem M, et al:
Circulating urokinase receptor as a cause of focal segmental
glomerulosclerosis. Nat Med. 17:952–960. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cha DR, Kang YS, Han SY, Jee YH, Han KH,
Kim HK, Han JY and Kim YS: Role of aldosterone in diabetic
nephropathy. Nephrology (Carlton). 10(Suppl): S37–S39. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Shibata S, Nagase M, Yoshida S, Kawachi H
and Fujita T: Podocyte as the target for aldosterone: Roles of
oxidative stress and Sgk1. Hypertension. 49:355–364. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schjoedt KJ, Rossing K, Juhl TR, Boomsma
F, Tarnow L, Rossing P and Parving HH: Beneficial impact of
spironolactone on nephrotic range albuminuria in diabetic
nephropathy. Kidney Int. 70:536–542. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Aguilar C and Rodríguez-Delfín L: Effects
of spironolactone administration on the podocytes loss and
progression of experimental diabetic nephropathy. Rev Peru Med Exp
Salud Publica. 29:490–497. 2012.In Spanish. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lin S, Li D, Jia J, Zheng Z, Jia Z and
Shang W: Spironolactone ameliorates podocytic adhesive capacity via
restoring integrin alpha 3 expression in streptozotocin-induced
diabetic rats. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 11:149–157.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mundel P, Reiser J, Zúñiga Mejía Borja A,
Pavenstadt H, Davidson GR, Kriz W and Zeller R: Rearrangements of
the cytoskeleton and cell contacts induce process formation during
differentiation of conditionally immortalized mouse podocyte cell
lines. Exp Cell Res. 236:248–258. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang B, Xie S, Shi W and Yang Y:
Amiloride off-target effect inhibits podocyte urokinase receptor
expression and reduces proteinuria. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
27:1746–1755. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Weil EJ, Lemley KV, Yee B, Lovato T,
Richardson M, Myers BD and Nelson RG: Podocyte detachment in type 2
diabetic nephropathy. Am J Nephrol. 33(Suppl 1): 21–24. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kitsiou PV, Tzinia AK, Stetler-Stevenson
WG, Michael AF, Fan WW, Zhou B and Tsilibary EC: Glucose-induced
changes in integrins and matrix-related functions in cultured human
glomerular epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
284:F671–F679. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang L, Li R, Shi W, Liang X, Liu S, Ye
Z, Yu C, Chen Y, Zhang B, Wang W, et al: NFAT2 inhibitor
ameliorates diabetic nephropathy and podocyte injury in db/db mice.
Br J Pharmacol. 170:426–439. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Borza CM, Pozzi A, Borza DB, Pedchenko V,
Hellmark T, Hudson BG and Zent R: Integrin alpha3beta1, a novel
receptor for alpha3(IV) noncollagenous domain and a trans-dominant
inhibitor forintegrin alphavbeta3. J Biol Chem. 281:20932–20939.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nagase M and Fujita T: Aldosterone and
glomerular podocyte injury. Clin Exp Nephrol. 12:233–242. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Siragy HM and Xue C: Local renal
aldosterone production induces inflammation and matrix formation in
kidneys of diabetic rats. Exp Physiol. 93:817–824. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee SH, Yoo TH, Nam BY, Kim DK, Li JJ,
Jung DS, Kwak SJ, Ryu DR, Han SH, Lee JE, et al: Activation of
local aldosterone system within podocytes is involved in apoptosis
under diabetic conditions. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
297:F1381–F1390. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Han SY, Kim CH, Kim HS, Jee YH, Song HK,
Lee MH, Han KH, Kim HK, Kang YS, Han JY, et al: Spironolactone
prevents diabetic nephropathy through an anti-inflammatory
mechanism in type 2 diabetic rats. J Am Soc Nephrol. 17:1362–1372.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Toyonaga J, Tsuruya K, Ikeda H, Noguchi H,
Yotsueda H, Fujisaki K, Hirakawa M, Taniguchi M, Masutani K and
Iida M: Spironolactone inhibits hyperglycemia-induced podocyte
injury by attenuating ROS production. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
26:2475–2484. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Taira M, Toba H, Murakami M, Iga I,
Serizawa R, Murata S, Kobara M and Nakata T: Spironolactone
exhibits direct renoprotective effects and inhibits renal
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in diabetic rats. Eur J
Pharmacol. 589:264–271. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Han KH, Kang YS, Han SY, Jee YH, Lee MH,
Han JY, Kim HK, Kim YS and Cha DR: Spironolactone ameliorates renal
injury and connective tissue growth factor expression in type II
diabetic rats. Kidney Int. 70:111–120. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nielsen SE, Persson F, Frandsen E, Sugaya
T, Hess G, Zdunek D, Shjoedt KJ, Parving HH and Rossing P:
Spironolactone diminishes urinary albumin excretion in patients
with type 1 diabetes and microalbuminuria: A randomized
placebo-controlled crossover study. Diabet Med. 29:e184–e190. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rossing K, Schjoedt KJ, Smidt UM, Boomsma
F and Parving HH: Beneficial effects of adding spironolactone to
recommended anti-hypertensive treatment in diabetic nephropathy: A
randomized, double-masked, cross-over study. Diabetes Care.
28:2106–2112. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|