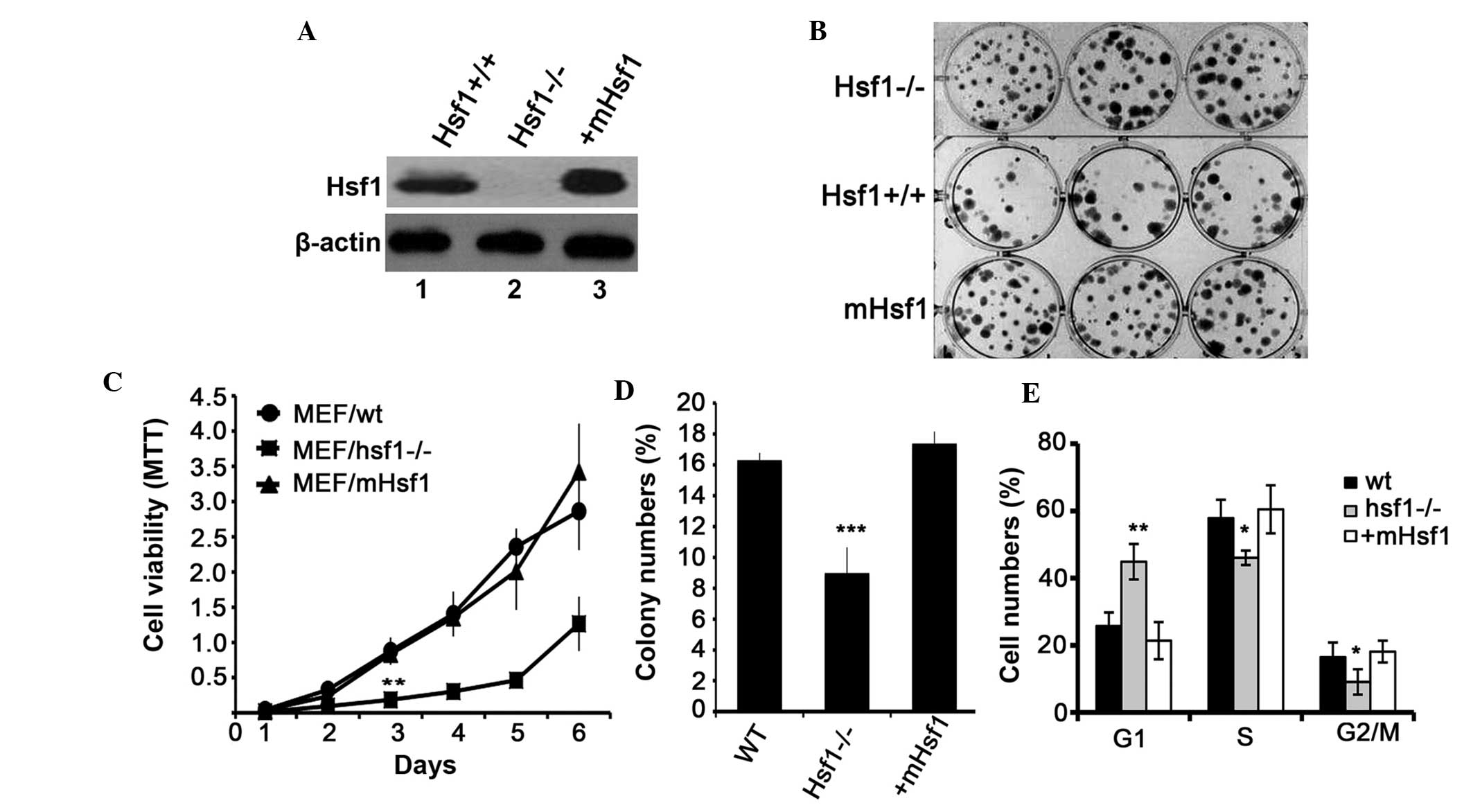
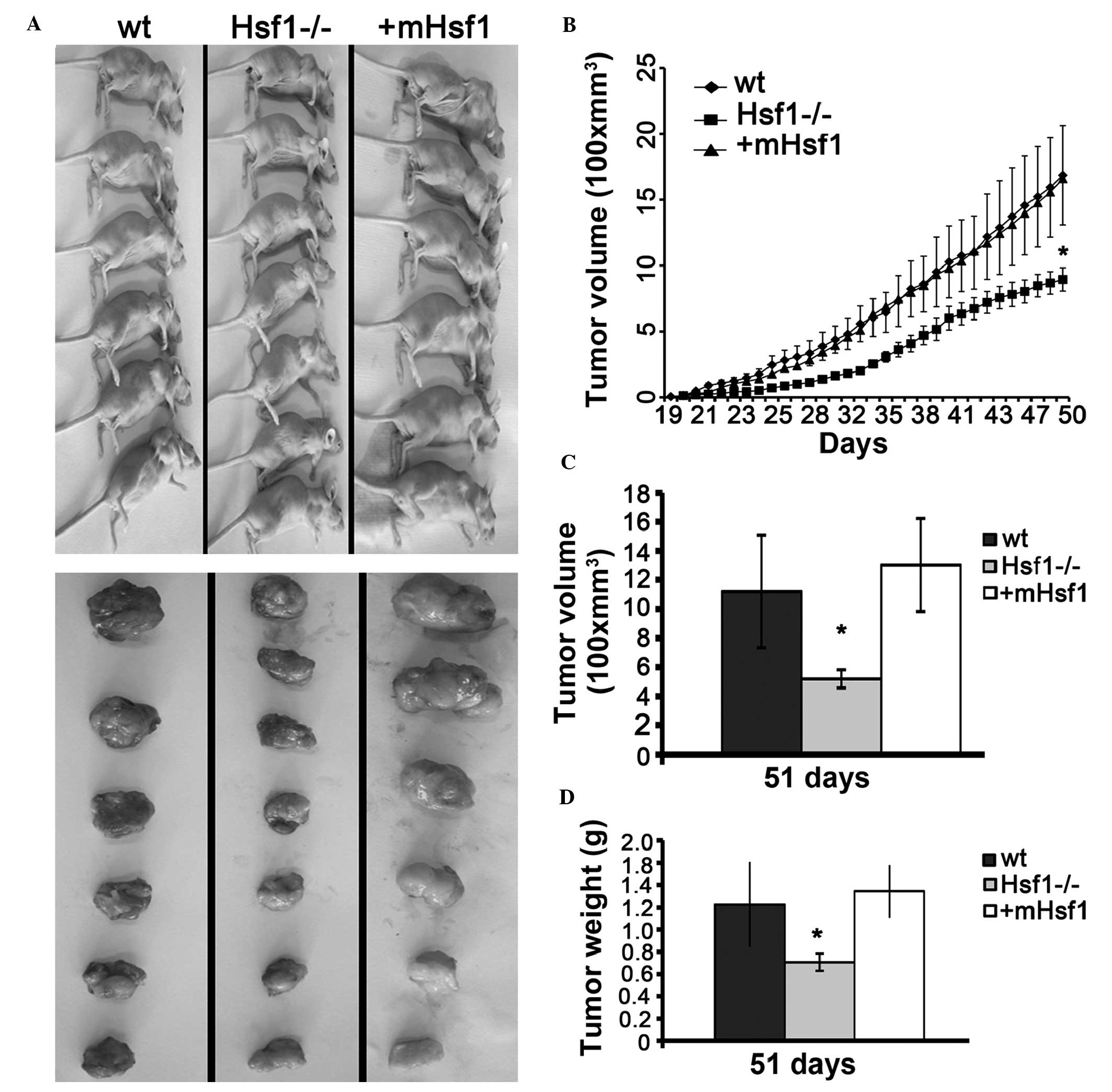
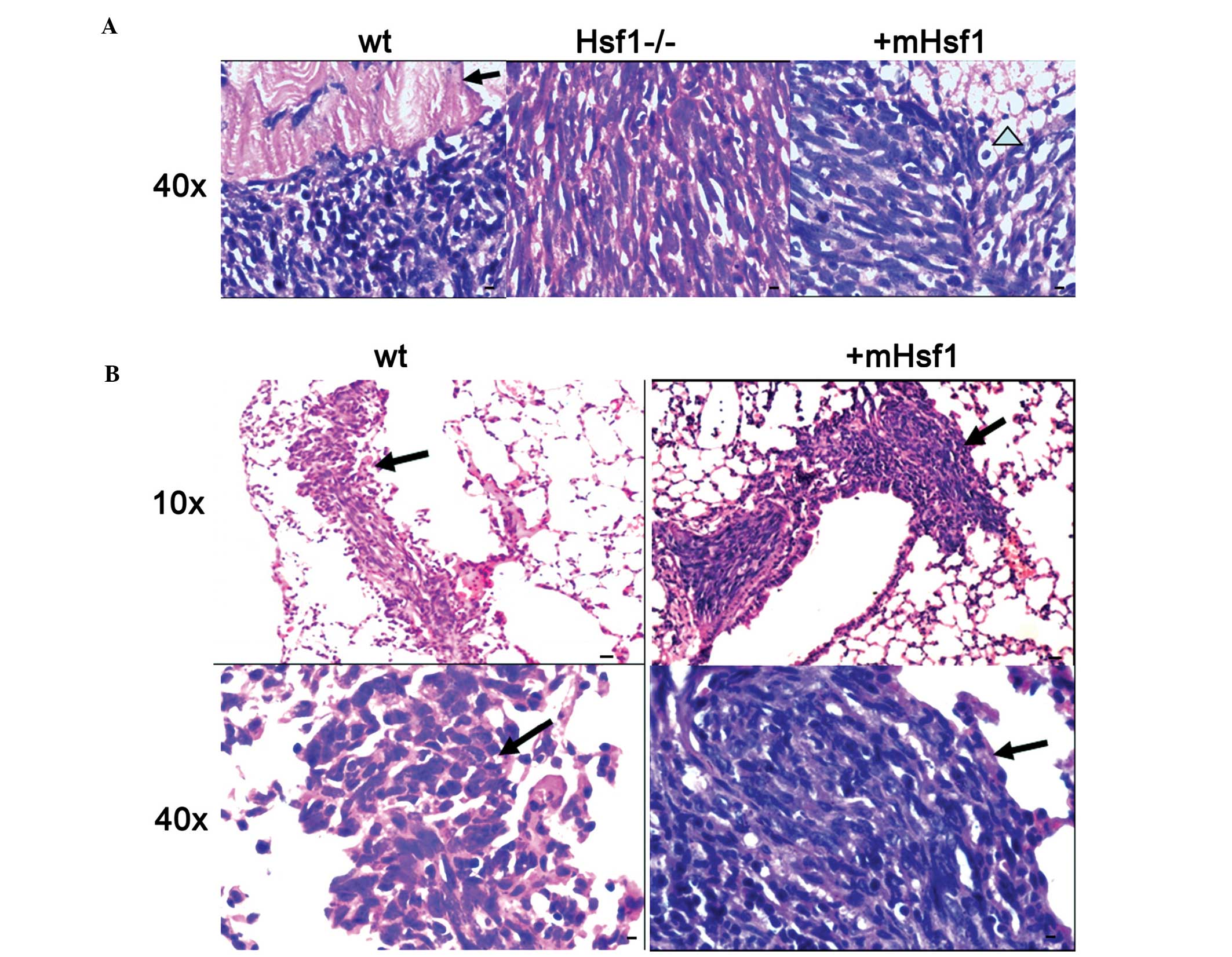
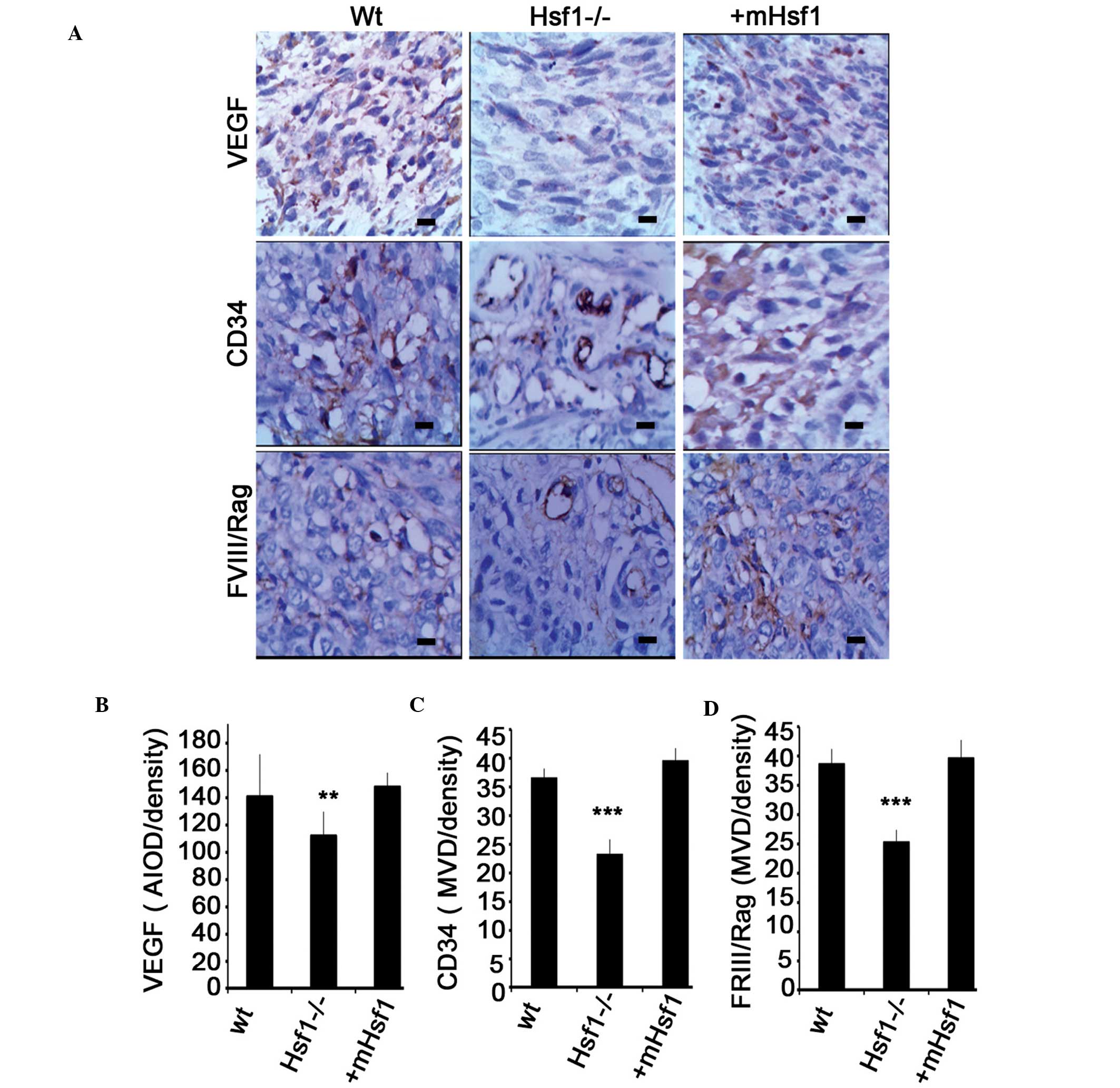
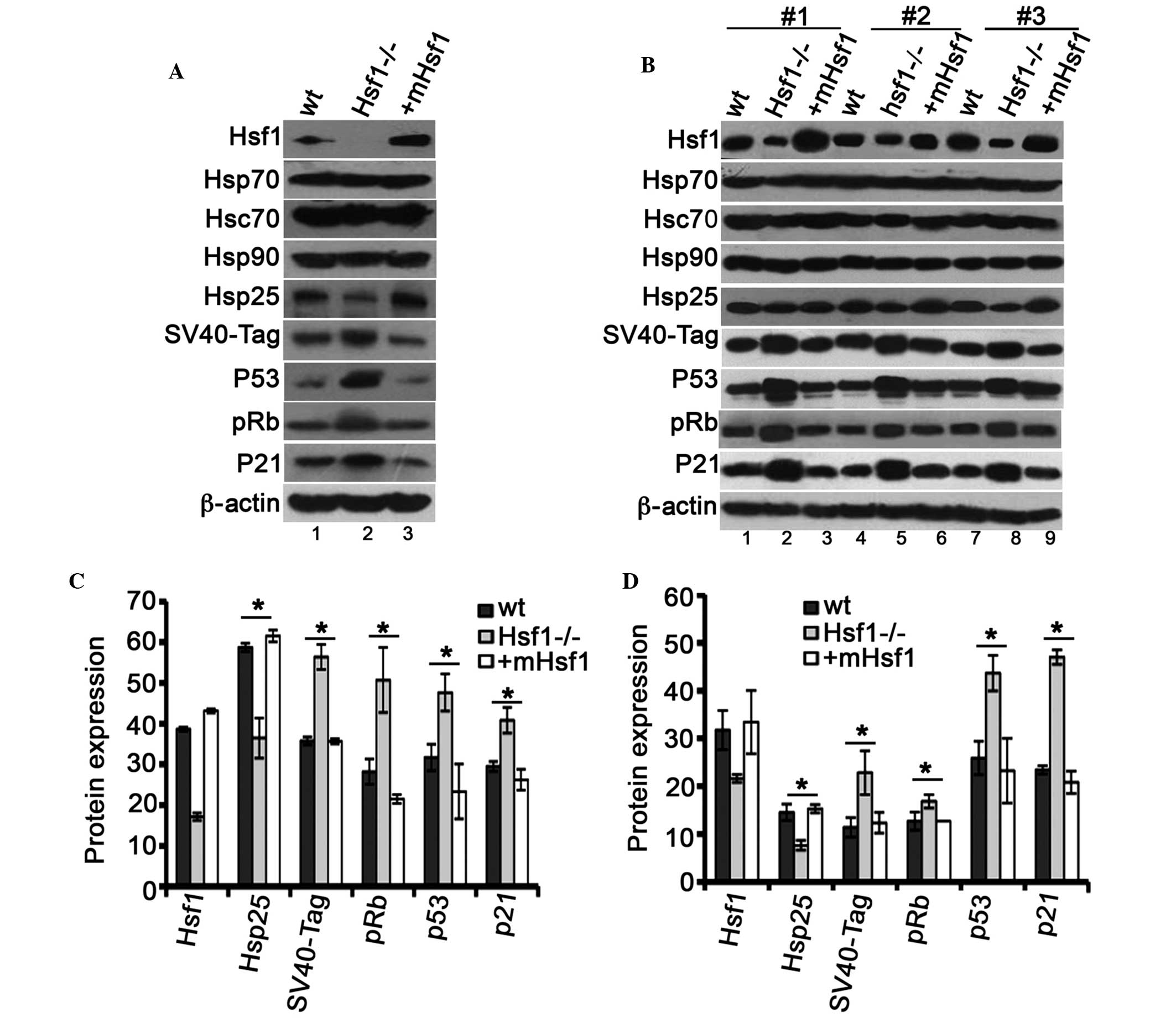
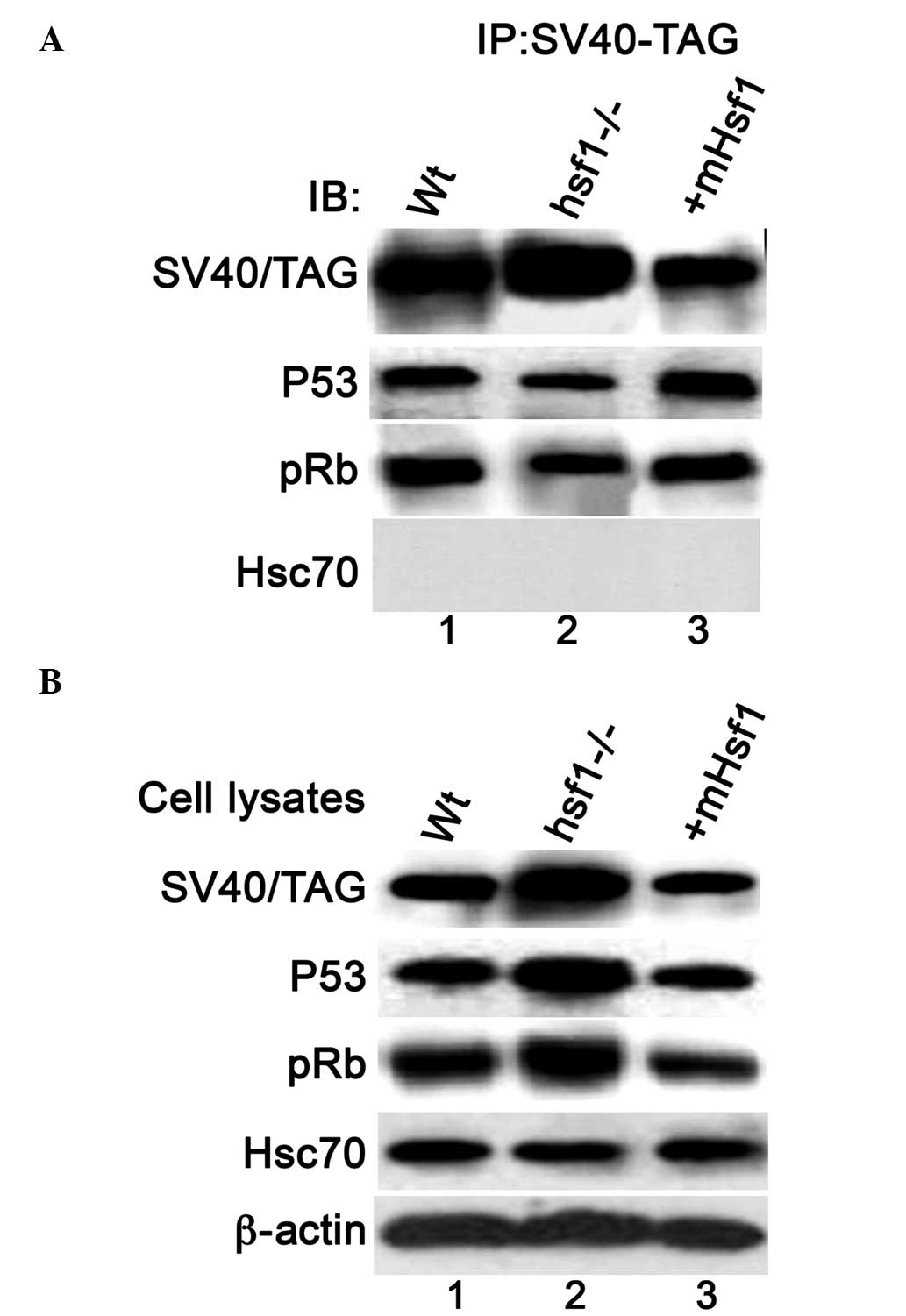
|
1
|
Calderwood SK: Elevated levels of HSF1
indicate a poor prognosis in breast cancer. Future Oncol.
8:399–401. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jin X, Moskophidis D and Mivechi NF: Heat
shock transcription factor 1 is a key determinant of HCC
development by regulating hepatic steatosis and metabolic syndrome.
Cell Metab. 14:91–103. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Santagata S, Hu R, Lin NU, Mendillo ML,
Collins LC, Hankinson SE, Schnitt SJ, Whitesell L, Tamimi RM,
Lindquist S and Ince TA: High levels of nuclear heat-shock factor 1
(HSF1) are associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:18378–18383. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Whitesell L and Lindquist S: Inhibiting
the transcription factor HSF1 as an anticancer strategy. Expert
Opin Ther Targets. 13:469–478. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen Y, Chen J, Loo A, Jaeger S,
Bagdasarian L, Yu J, Chung F, Korn J, Ruddy D, Guo R, et al:
Targeting HSF1 sensitizes cancer cells to HSP90 inhibition.
Oncotarget. 4:816–829. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dai C, Whitesell L, Rogers AB and
Lindquist S: Heat shock factor 1 is a powerful multifaceted
modifier of carcinogenesis. Cell. 130:1005–1018. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xi C, Hu Y, Buckhaults P, Moskophidis D
and Mivechi NF: Heat shock factor Hsf1 cooperates with ErbB2
(Her2/Neu) protein to promote mammary tumorigenesis and metastasis.
J Biol Chem. 287:35646–35657. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lecomte S, Desmots F, Le Masson F, Le Goff
P, Michel D, Christians ES and Le Dréan Y: Roles of heat shock
factor 1 and 2 in response to proteasome inhibition: Consequence on
p53 stability. Oncogene. 29:4216–4224. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mendillo ML, Santagata S, Koeva M, Bell
GW, Hu R, Tamimi RM, Fraenkel E, Ince TA, Whitesell L and Lindquist
S: HSF1 drives a transcriptional program distinct from heat shock
to support highly malignant human cancers. Cell. 150:549–562. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xu R, Zhang X, Zhang W, Fang Y, Zheng S
and Yu XF: Association of human APOBEC3 cytidine deaminases with
the generation of hepatitis virus B x antigen mutants and
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 46:1810–1820. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jin X, Moskophidis D, Hu Y, Phillips A and
Mivechi NF: Heat shock factor 1 deficiency via its downstream
target gene alphaB-crystallin (Hspb5) impairs p53 degradation. J
Cell Biochem. 107:504–515. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Colvin EK, Weir C, Ikin RJ and Hudson AL:
SV40 TAg mouse models of cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 27:61–73.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ludlow JW, Shon J, Pipas JM, Livingston DM
and DeCaprio JA: The retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product
undergoes cell cycle-dependent dephosphorylation and binding to and
release from SV40 large T. Cell. 60:387–396. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pallas DC, Shahrik LK, Martin BL, Jaspers
S, Miller TB, Brautigan DL and Roberts TM: Polyoma small and middle
T antigens and SV40 small t antigen form stable complexes with
protein phosphatase 2A. Cell. 60:167–176. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen W, Possemato R, Campbell KT, Plattner
CA, Pallas DC and Hahn WC: Identification of specific PP2A
complexes involved in human cell transformation. Cancer Cell.
5:127–136. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ahuja D, Sáenz-Robles MT and Pipas JM:
SV40 large T antigen targets multiple cellular pathways to elicit
cellular transformation. Oncogene. 24:7729–7745. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang J and DeFranco DB: Differential roles
of heat shock protein 70 in the in vitro nuclear import of
glucocorticoid receptor and simian virus 40 large tumor antigen.
Mol Cell Biol. 14:5088–5098. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wapnir IL, Wartenberg DE and Greco RS:
Three dimensional staging of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 41:15–19. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kraan MC, Smith MD, Weedon H, Ahern MJ,
Breedveld FC and Tak PP: Measurement of cytokine and adhesion
molecule expression in synovial tissue by digital image analysis.
Ann Rheum Dis. 60:296–298. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hu YZ, Zhang J, Li S, Wang C, Chu L, Zhang
Z, Ma Z, Wang M, Jiang Q, Liu G, et al: The transcription activity
of heat shock factor 4b is regulated by FGF2. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 45:317–325. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sáenz Robles MT and Pipas JM: T antigen
transgenic mouse models. Semin Cancer Biol. 19:229–235. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Omar RA and Lanks KW: Heat shock protein
synthesis and cell survival in clones of normal and simian virus
40-transformed mouse embryo cells. Cancer Res. 44:3976–3982.
1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gabai VL, Meng L, Kim G, Mills TA,
Benjamin IJ and Sherman MY: Heat shock transcription factor Hsf1 is
involved in tumor progression via regulation of hypoxia-inducible
factor 1 and RNA-binding protein HuR. Mol Cell Biol. 32:929–940.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shiota M, Bishop JL, Nip KM, Zardan A,
Takeuchi A, Cordonnier T, Beraldi E, Bazov J, Fazli L, Chi K, et
al: Hsp27 regulates epithelial mesenchymal transition, metastasis,
and circulating tumor cells in prostate cancer. Cancer Res.
73:3109–3119. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pavan S, Musiani D, Torchiaro E, Migliardi
G, Gai M, Di Cunto F, Erriquez J, Olivero M and Di Renzo MF: HSP27
is required for invasion and metastasis triggered by hepatocyte
growth factor. Int J Cancer. 134:1289–1299. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Mese H, Sasaki A, Nakayama S, Yoshioka N,
Yoshihama Y, Kishimoto K and Matsumura T: Prognostic significance
of heat shock protein 27 (HSP27) in patients with oral squamous
cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 9:341–344. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wettstein G, Bellaye PS, Kolb M, Hammann
A, Crestani B, Soler P, Marchal-Somme J, Hazoume A, Gauldie J,
Gunther A, et al: Inhibition of HSP27 blocks fibrosis development
and EMT features by promoting Snail degradation. FASEB J.
27:1549–1560. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
de Thonel A, Vandekerckhove J, Lanneau D,
Selvakumar S, Courtois G, Hazoume A, Brunet M, Maurel S, Hammann A,
Ribeil JA, et al: HSP27 controls GATA-1 protein level during
erythroid cell differentiation. Blood. 116:85–96. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|