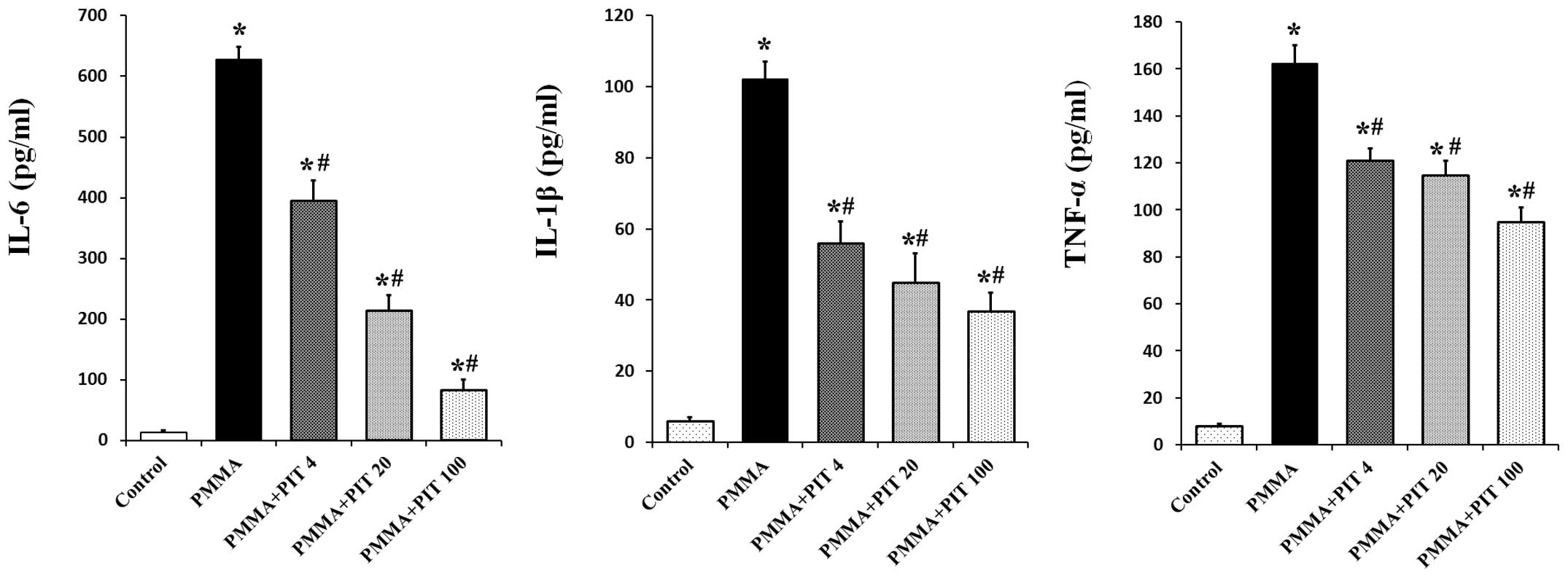
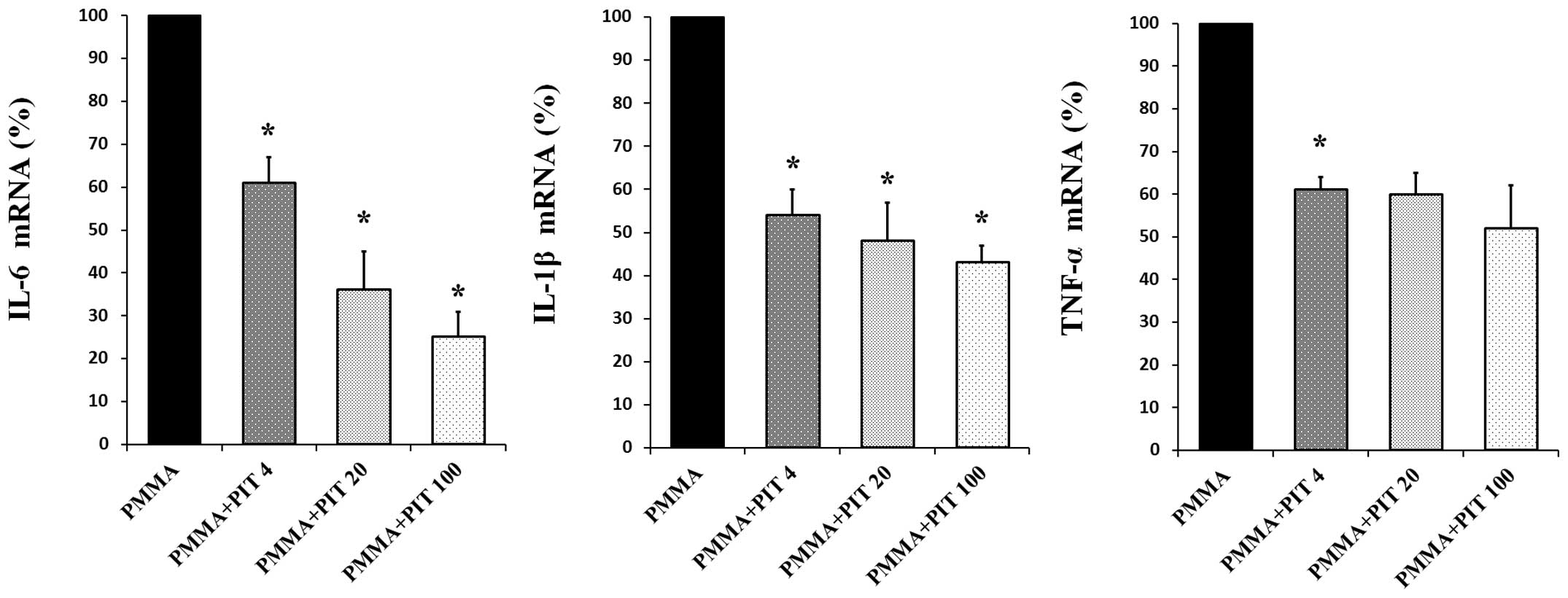
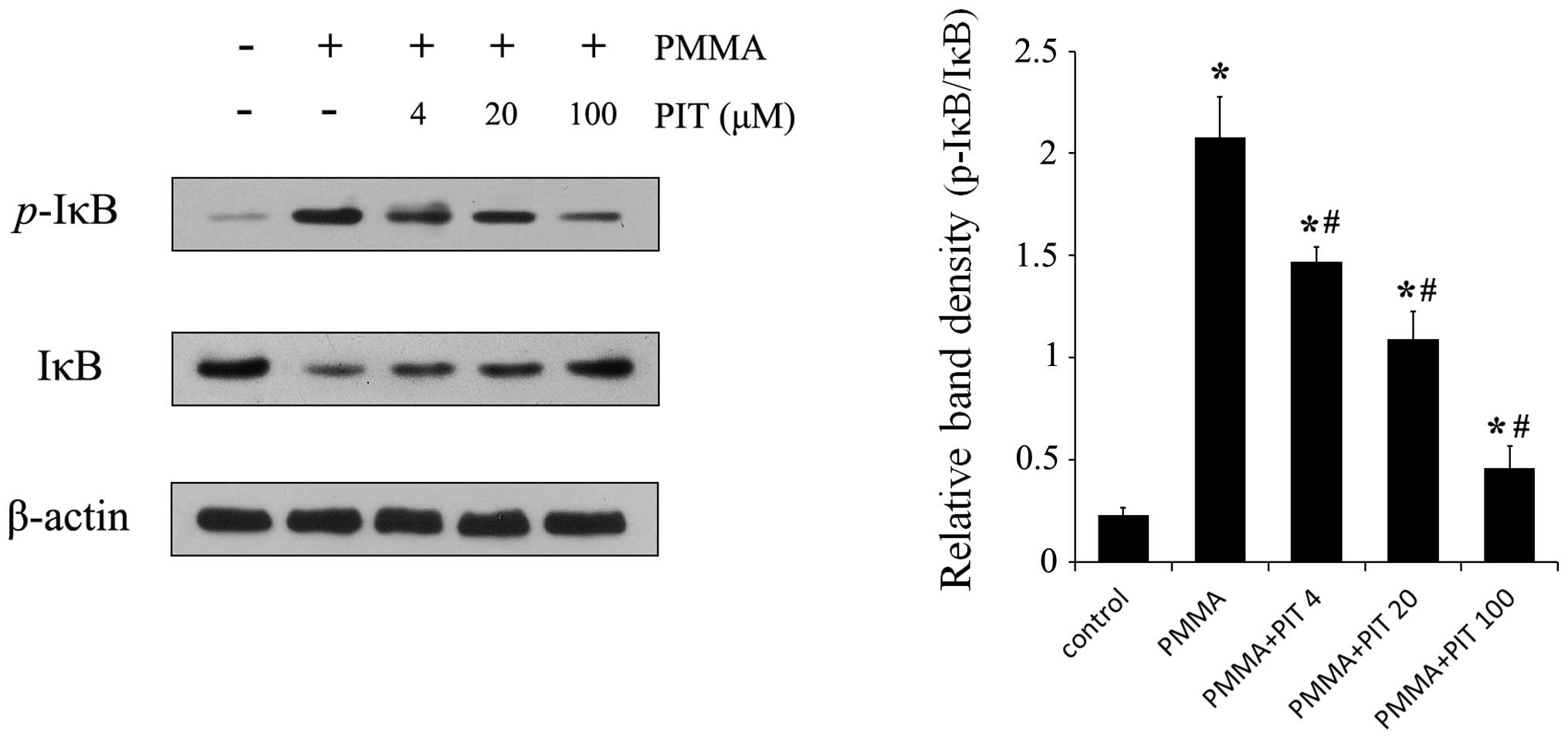
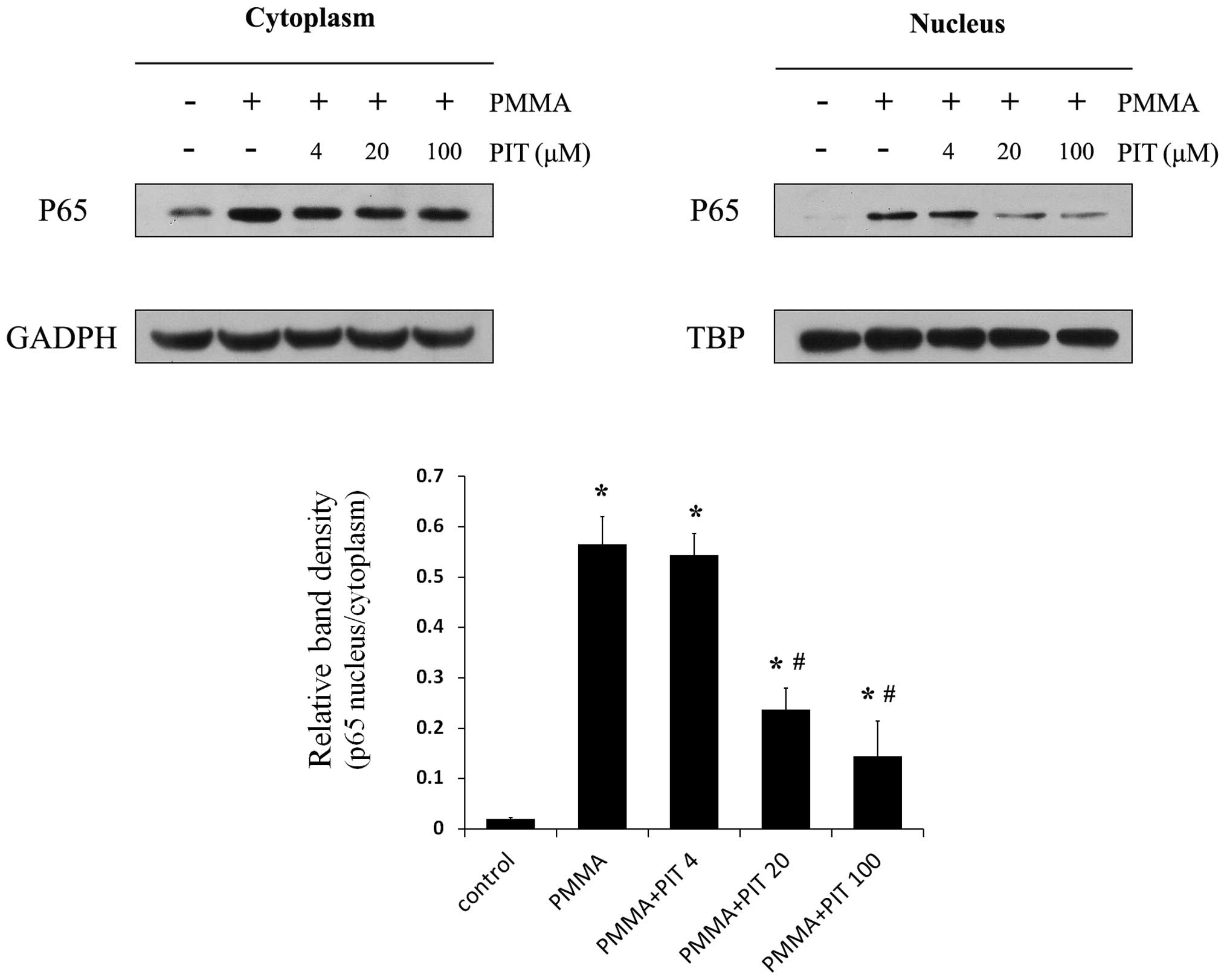
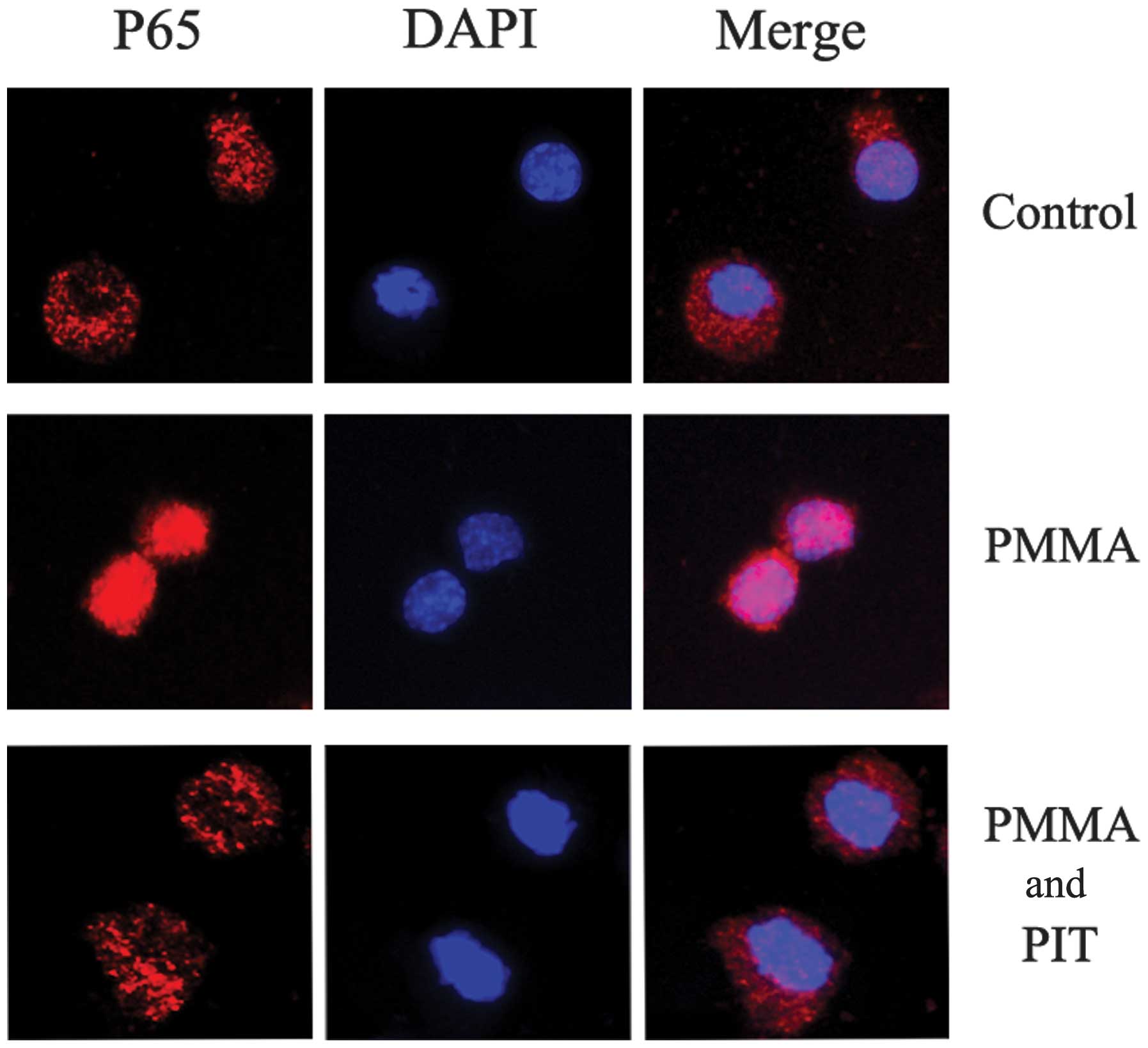
|
1
|
Snow R, Granata J, Ruhil AV, Vogel K,
McShane M and Wasielewski R: Associations between preoperative
physical therapy and post-acute care utilization patterns and cost
in total joint replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 96:e1652014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gallo J, Goodman SB, Konttinen YT and
Raska M: Particle disease: Biologic mechanisms of periprosthetic
osteolysis in total hip arthroplasty. Innate Immun. 19:213–224.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Pearl JI, Ma T, Irani AR, Huang Z,
Robinson WH, Smith RL and Goodman SB: Role of the Toll-like
receptor pathway in the recognition of orthopedic implant
wear-debris particles. Biomaterials. 32:5535–5542. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Holt G, Murnaghan C, Reilly J and Meek RM:
The biology of aseptic osteolysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
460:240–252. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Masana L: Pitavastatin in cardiometabolic
disease: Therapeutic profile. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 12(Suppl 1):
S22013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Saito Y: Pitavastatin: An overview.
Atheroscler Suppl. 12:271–276. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang J and Kitajima I: Pitavastatin
inactivates NF-kappaB and decreases IL-6 production through Rho
kinase pathway in MCF-7 cells. Oncol Rep. 17:1149–1154.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Takano K, Yamamoto S, Tomita K, Takashina
M, Yokoo H, Matsuda N, Takano Y and Hattori Y: Successful treatment
of acute lung injury with pitavastatin in septic mice: Potential
role of glucocorticoid receptor expression in alveolar macrophages.
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 336:381–390. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Katsuki S, Matoba T, Nakashiro S, Sato K,
Koga J, Nakano K, Nakano Y, Egusa S, Sunagawa K and Egashira K:
Nanoparticle-mediated delivery of pitavastatin inhibits
atherosclerotic plaque destabilization/rupture in mice by
regulating the recruitment of inflammatory monocytes. Circulation.
129:896–906. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wan YD, Sun TW, Kan QC, Guan FX and Zhang
SG: Effect of statin therapy on mortality from infection and
sepsis: A meta-analysis of randomized and observational studies.
Crit Care. 18:R712014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Clohisy JC, Frazier E, Hirayama T and
Abu-Amer Y: RANKL is an essential cytokine mediator of
polymethylmethacrylate particle-induced osteoclastogenesis. J
Orthop Res. 21:202–212. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Clohisy JC, Teitelbaum S, Chen S, Erdmann
JM and Abu-Amer Y: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediates
polymethylmethacrylate particle-induced NF-kappaB activation in
osteoclast precursor cells. J Orthop Res. 20:174–181. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Clohisy JC, Yamanaka Y, Faccio R and
Abu-Amer Y: Inhibition of IKK activation, through sequestering
NEMO, blocks PMMA-induced osteoclastogenesis and calvarial
inflammatory osteolysis. J Orthop Res. 24:1358–1365. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Peng Q, Liu H, Shi S and Li M: Lycium
ruthenicum polysaccharide attenuates inflammation through
inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int J Biol Macromol.
67:330–335. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li Q and Verma IM: NF-kappaB regulation in
the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2:725–734. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Grunfeld R, Aydogan U and Juliano P: Ankle
arthritis: Review of diagnosis and operative management. Med Clin
North Am. 98:267–289. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gallo J, Goodman SB, Konttinen YT, Wimmer
MA and Holinka M: Osteolysis around total knee arthroplasty: A
review of pathogenetic mechanisms. Acta Biomater. 9:8046–8058.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu X, Qu X, Wu C, Zhai Z, Tian B, Li H,
Ouyang Z, Xu X, Wang W, Fan Q, et al: The effect of enoxacin on
osteoclastogenesis and reduction of titanium particle-induced
osteolysis via suppression of JNK signaling pathway. Biomaterials.
35:5721–5730. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sabokbar A, Fujikawa Y, Murray DW and
Athanasou NA: Bisphosphonates in bone cement inhibit PMMA particle
induced bone resorption. Ann Rheum Dis. 57:614–618. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lohmann CH, Dean DD, Küster G, Casasola D,
Buchhorn GH, Fink U, Schwartz Z and Boyan BD: Ceramic and PMMA
particles differentially affect osteoblast phenotype. Biomaterials.
23:1855–1863. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ramachandran R, Goodman SB and Smith RL:
The effects of titanium and polymethylmethacrylate particles on
osteoblast phenotypic stability. J Biomed Mater Res A. 77:512–517.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zambonin G, Colucci S, Cantatore F and
Grano M: Response of human osteoblasts to polymethylmetacrylate in
vitro. Calcif Tissue Int. 62:362–365. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu FX, Wu CL, Zhu ZA, Li MQ, Mao YQ, Liu
M, Wang XQ, Yu DG and Tang TT: Calcineurin/NFAT pathway mediates
wear particle-induced TNF-α release and osteoclastogenesis from
mice bone marrow macrophages in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
34:1457–1466. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Crotti TN, Smith MD, Findlay DM, Zreiqat
H, Ahern MJ, Weedon H, Hatzinikolous G, Capone M, Holding C and
Haynes D: Factors regulating osteoclast formation in human tissues
adjacent to peri-implant bone loss: Expression of receptor
activator NFkappaB, RANK ligand and osteoprotegerin. Biomaterials.
25:565–573. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Jiang Y, Jia T, Gong W, Wooley PH and Yang
SY: Effects of Ti, PMMA, UHMWPE and Co-Cr wear particles on
differentiation and functions of bone marrow stromal cells. J
Biomed Mater Res A. 101:2817–2825. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fuller K, Murphy C, Kirstein B, Fox SW and
Chambers TJ: TNFalpha potently activates osteoclasts, through a
direct action independent of and strongly synergistic with RANKL.
Endocrinology. 143:1108–1118. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guo H, Zhang J, Hao S and Jin Q:
Adenovirus-mediated small interfering RNA targeting tumor necrosis
factor-α inhibits titanium particle-induced osteoclastogenesis and
bone resorption. Int J Mol Med. 32:296–306. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Quinn JM, Horwood NJ, Elliott J, Gillespie
MT and Martin TJ: Fibroblastic stromal cells express receptor
activator of NF-kappaB ligand and support osteoclast
differentiation. J Bone Miner Res. 15:1459–1466. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
García-López S, Villanueva R and Meikle
MC: Alterations in the synthesis of IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6 and their
downstream targets RANKL and OPG by mouse calvarial osteoblasts in
vitro: Inhibition of bone resorption by cyclic mechanical strain.
Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 4:1602013.
|
|
30
|
Simsa-Maziel S, Zaretsky J, Reich A, Koren
Y, Shahar R and Monsonego-Ornan E: IL-1RI participates in normal
growth plate development and bone modeling. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 305:E15–E21. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Uekawa K, Hasegawa Y, Ma M, Nakagawa T,
Katayama T, Sueta D, Toyama K, Kataoka K, Koibuchi N, Kawano T, et
al: Rosuvastatin ameliorates early brain injury after subarachnoid
hemorrhage via suppression of superoxide formation and nuclear
factor-kappaB activation in rats. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis.
23:1429–1439. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Moon GJ, Kim SJ, Cho YH, Ryoo S and Bang
OY: Antioxidant effects of statins in patients with atherosclerotic
cerebrovascular disease. J Clin Neurol. 10:140–147. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
McGuire TR, Kalil AC, Dobesh PP, Klepser
DG and Olsen KM: Anti-inflammatory effects of rosuvastatin in
healthy subjects: A prospective longitudinal study. Curr Pharm Des.
20:1156–1160. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yamanaka Y, Karuppaiah K and Abu-Amer Y:
Polyubiquitination events mediate polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA)
particle activation of NF-kappaB pathway. J Biol Chem.
286:23735–23741. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hayden MS and Ghosh S: NF-κB in
immunobiology. Cell Res. 21:223–244. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|