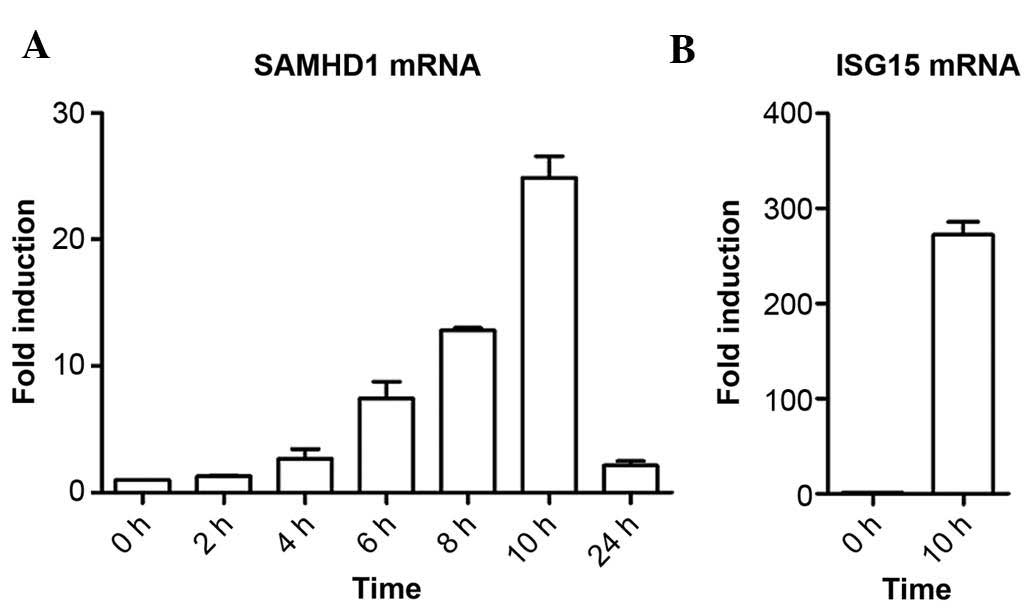
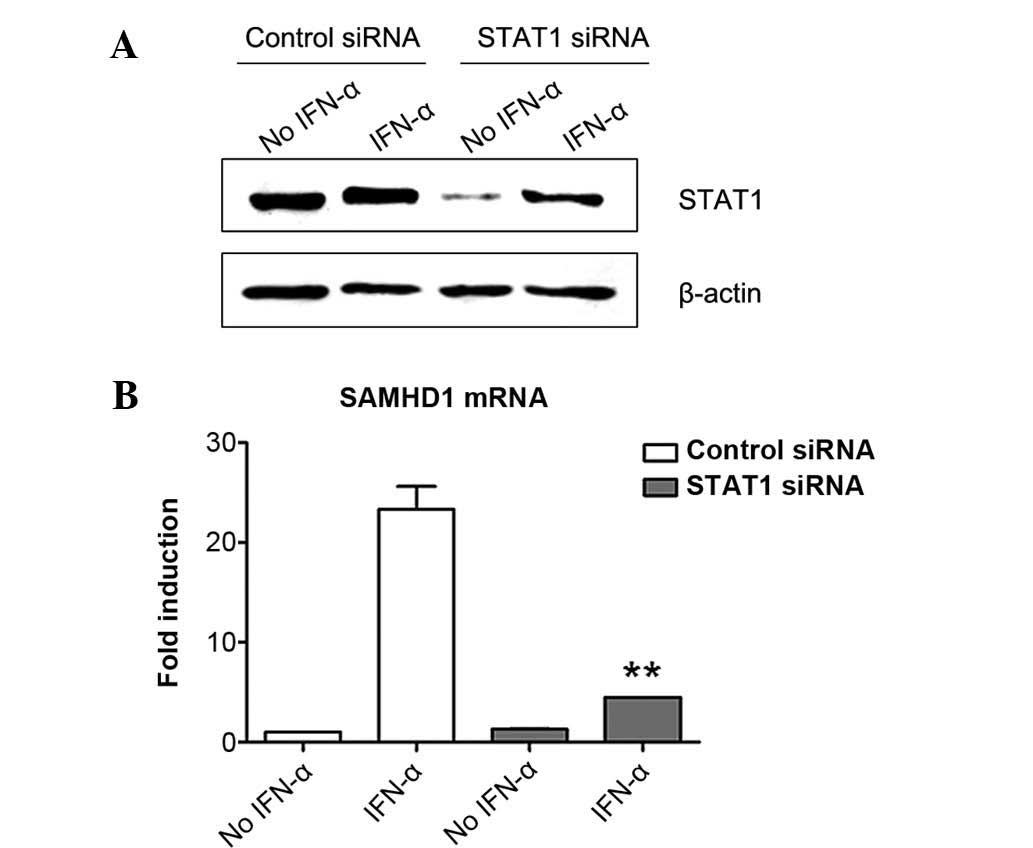
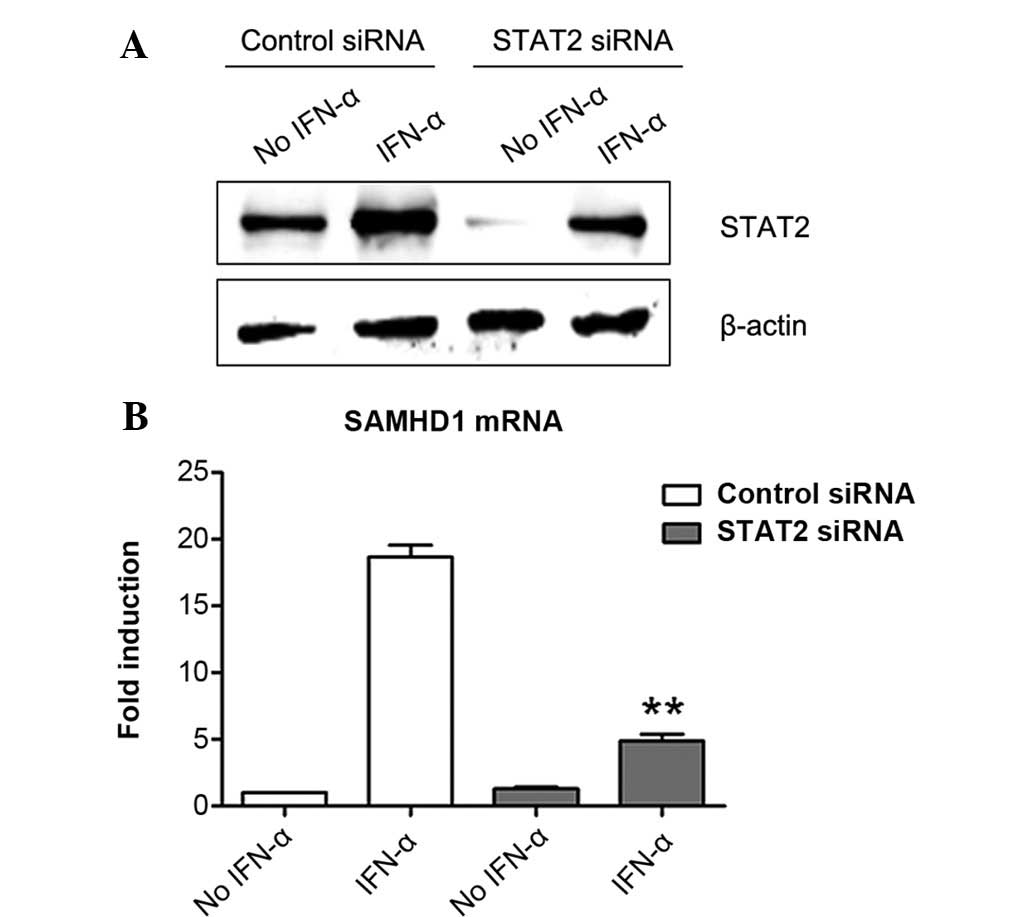
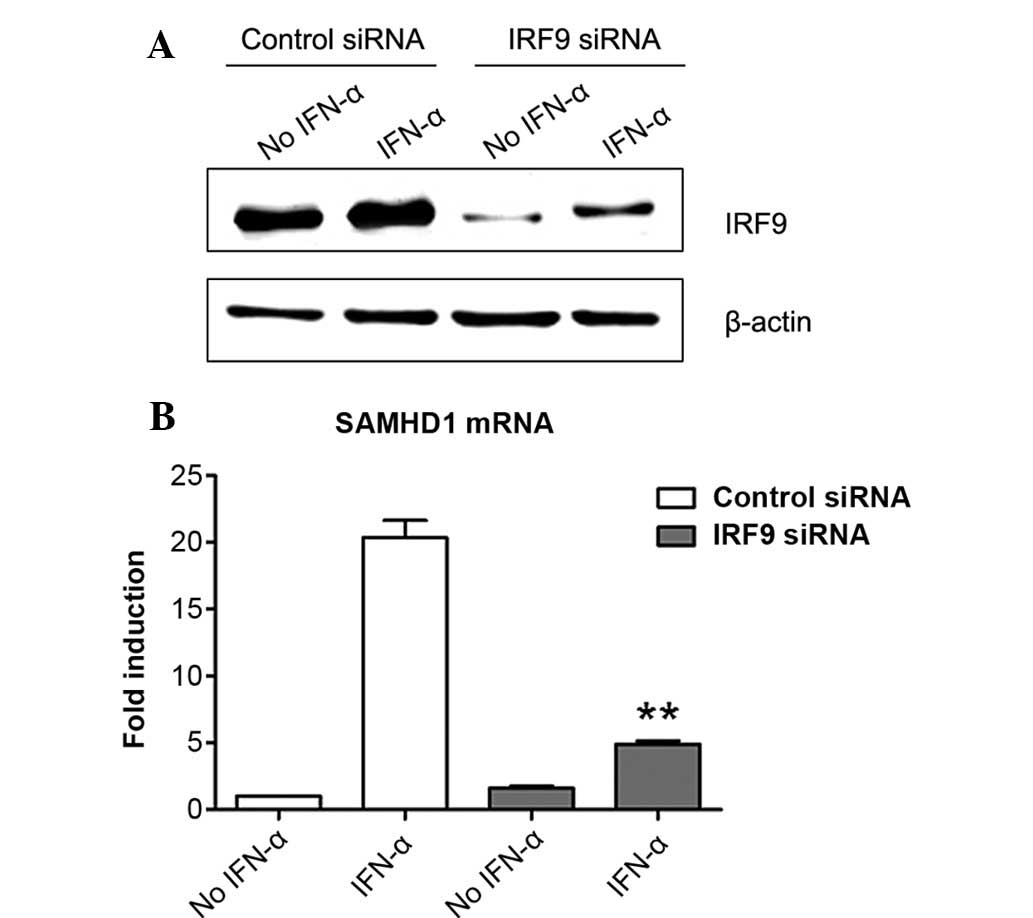
|
1
|
Yan N and Chen ZJ: Intrinsic antiviral
immunity. Nat Immunol. 13:214–222. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kawamura T, Ogawa Y, Aoki R and Shimada S:
Innate and intrinsic antiviral immunity in skin. J Dermatol Sci.
75:159–166. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen Z, Zhang L and Ying S: SAMHD1: A
novel antiviral factor in intrinsic immunity. Future Microbiol.
7:1117–1126. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Laguette N, Sobhian B, Casartelli N,
Ringeard M, Chable-Bessia C, Ségéral E, Yatim A, Emiliani S,
Schwartz O and Benkirane M: SAMHD1 is the dendritic- and
myeloid-cell-specific HIV-1 restriction factor counteracted by Vpx.
Nature. 474:654–657. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hrecka K, Hao C, Gierszewska M, Swanson
SK, Kesik-Brodacka M, Srivastava S, Florens L, Washburn MP and
Skowronski J: Vpx relieves inhibition of HIV-1 infection of
macrophages mediated by the SAMHD1 protein. Nature. 474:658–661.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Goldstone DC, Ennis-Adeniran V, Hedden JJ,
Groom HC, Rice GI, Christodoulou E, Walker PA, Kelly G, Haire LF,
Yap MW, et al: HIV-1 restriction factor SAMHD1 is a deoxynucleoside
triphosphate triphosphohydrolase. Nature. 480:379–382. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Powell RD, Holland PJ, Hollis T and
Perrino FW: Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome gene and HIV-1 restriction
factor SAMHD1 is a dGTP-regulated deoxynucleotide
triphosphohydrolase. J Biol Chem. 286:43596–43600. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lahouassa H, Daddacha W, Hofmann H, Ayinde
D, Logue EC, Dragin L, Bloch N, Maudet C, Bertrand M, Gramberg T,
et al: SAMHD1 restricts the replication of human immunodeficiency
virus type 1 by depleting the intracellular pool of deoxynucleoside
triphosphates. Nat Immunol. 13:223–228. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ryoo J, Choi J, Oh C, Kim S, Seo M, Kim
SY, Seo D, Kim J, White TE, Brandariz-Nuñez A, et al: The
ribonuclease activity of SAMHD1 is required for HIV-1 restriction.
Nat Med. 20:936–941. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
White TE, Brandariz-Nuñez A, Valle-Casuso
JC, Amie S, Nguyen L, Kim B, Brojatsch J and Diaz-Griffero F:
Contribution of SAM and HD domains to retroviral restriction
mediated by human SAMHD1. Virology. 436:81–90. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Gramberg T, Kahle T, Bloch N, Wittmann S,
Müllers E, Daddacha W, Hofmann H, Kim B, Lindemann D and Landau NR:
Restriction of diverse retroviruses by SAMHD1. Retrovirology.
10:262013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sze A, Belgnaoui SM, Olagnier D, Lin R,
Hiscott J and van Grevenynghe J: Host restriction factor SAMHD1
limits human T cell leukemia virus type 1 infection of monocytes
via STING-mediated apoptosis. Cell Host Microbe. 14:422–434. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hollenbaugh JA, Gee P, Baker J, Daly MB,
Amie SM, Tate J, Kasai N, Kanemura Y, Kim DH, Ward BM, et al: Host
factor SAMHD1 restricts DNA viruses in non-dividing myeloid cells.
PLoS Pathog. 9:e10034812013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim ET, White TE, Brandariz-Núñez A,
Diaz-Griffero F and Weitzman MD: SAMHD1 restricts herpes simplex
virus 1 in macrophages by limiting DNA replication. J Virol.
87:12949–12956. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen Z, Zhu M, Pan X, Zhu Y, Yan H, Jiang
T, Shen Y, Dong X, Zheng N, Lu J, et al: Inhibition of Hepatitis B
virus replication by SAMHD1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
450:1462–1468. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang S, Shan T, Zhou Y, Jiang Y, Tong W,
Liu F, Wen F, Zhang Q and Tong G: Molecular cloning and
characterizations of porcine SAMHD1 and its roles in replication of
highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome
virus. Dev Comp Immunol. 47:234–246. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Harris RS, Hultquist JF and Evans DT: The
restriction factors of human immunodeficiency virus. J Biol Chem.
287:40875–40883. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ivashkiv LB and Donlin LT: Regulation of
type I interferon responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 14:36–49. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Fink K and Grandvaux N: STAT2 and IRF9:
Beyond ISGF3. JAKSTAT. 2:e275212013.
|
|
20
|
Sarkis PT, Ying S, Xu R and Yu XF:
STAT1-independent cell type-specific regulation of antiviral
APOBEC3G by IFN-alpha. J Immunol. 177:4530–4540. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang F, Shang D, Zhang Y and Tian Y:
Interleukin-22 suppresses the growth of A498 renal cell carcinoma
cells via regulation of STAT1 pathway. PLoS One. 6:e203822011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fink K, Martin L, Mukawera E, Chartier S,
De Deken X, Brochiero E, Miot F and Grandvaux N: IFNβ/TNFα
synergism induces a non-canonical STAT2/IRF9-dependent pathway
triggering a novel DUOX2 NADPH oxidase-mediated airway antiviral
response. Cell Res. 23:673–690. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tsuno T, Mejido J, Zhao T, Schmeisser H,
Morrow A and Zoon KC: IRF9 is a key factor for eliciting the
antiproliferative activity of IFN-alpha. J Immunother. 32:803–816.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schmittgen TD1 and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C (T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chen H, Wang LW, Huang YQ and Gong ZJ:
Interferon-alpha induces high expression of APOBEC3G and STAT-1 in
vitro and in vivo. Int J Mol Sci. 11:3501–3512. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Berger A, Sommer AF, Zwarg J, Hamdorf M,
Welzel K, Esly N, Panitz S, Reuter A, Ramos I, Jatiani A, et al:
SAMHD1-deficient CD14+ cells from individuals with
Aicardi-Goutières syndrome are highly susceptible to HIV-1
infection. PLoS Pathog. 7:e10024252011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Goujon C, Schaller T, Galão RP, Amie SM,
Kim B, Olivieri K, Neil SJ and Malim MH: Evidence for IFNα-induced,
SAMHD1-independent inhibitors of early HIV-1 infection.
Retrovirology. 10:232013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
St Gelais C, de Silva S, Amie SM, Coleman
CM, Hoy H, Hollenbaugh JA, Kim B and Wu L: SAMHD1 restricts HIV-1
infection in dendritic cells (DCs) by dNTP depletion, but its
expression in DCs and primary CD4+ T-lymphocytes cannot be
upregulated by interferons. Retrovirology. 9:1052012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang Q, Wang Y, Wei L, Jiang D, Wang JH,
Rao HY, Zhu L, Chen H, Fei R and Cong X: Role of ISGF3 in
modulating the anti-hepatitis B virus activity of interferon-alpha
in vitro. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 23:1747–1761. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lehtonen A, Matikainen S and Julkunen I:
Interferons up-regulate STAT1, STAT2, and IRF family transcription
factor gene expression in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells
and macrophages. J Immunol. 159:794–803. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tenoever BR, Ng SL, Chua MA, McWhirter SM,
García-Sastre A and Maniatis T: Multiple functions of the
IKK-related kinase IKKepsilon in interferon-mediated antiviral
immunity. Science. 315:1274–1278. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|