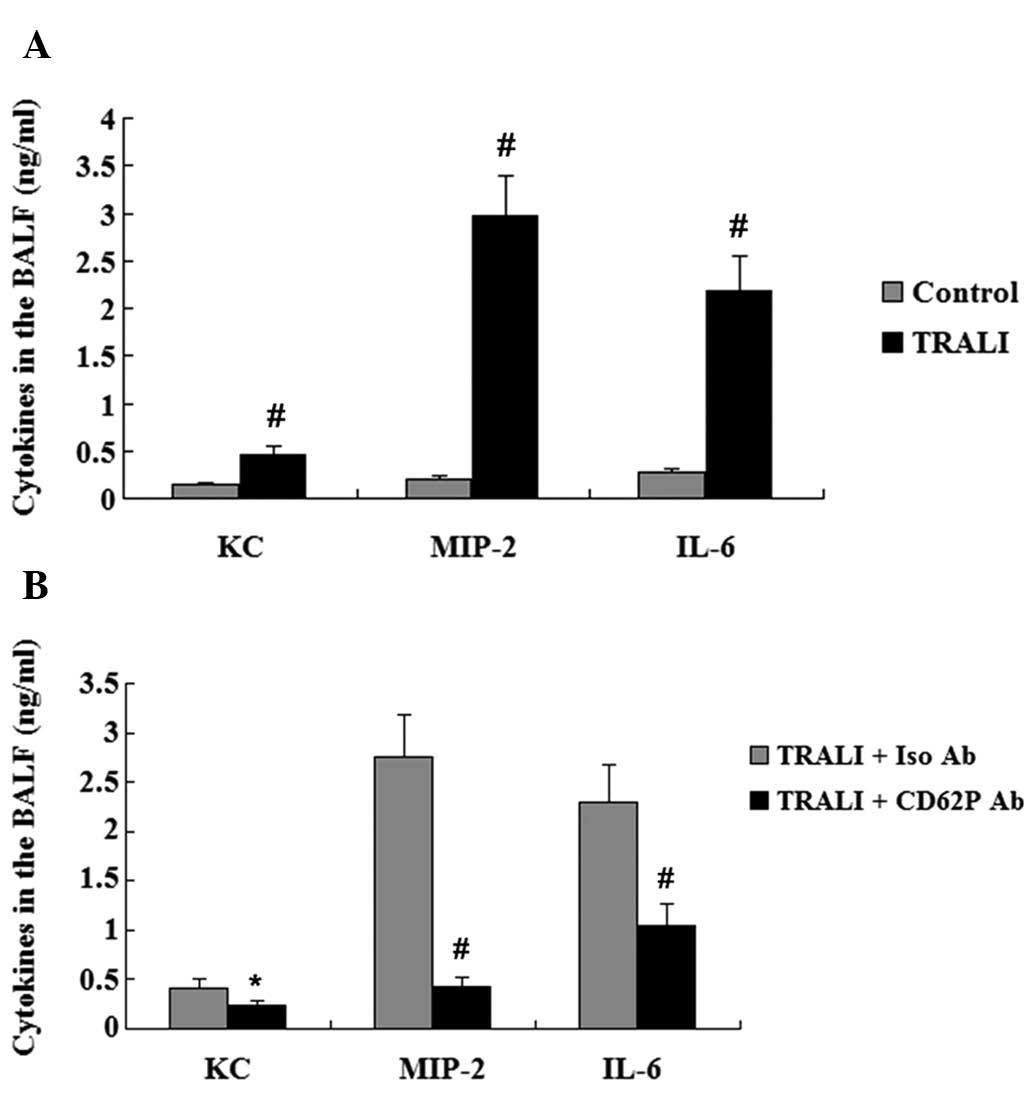
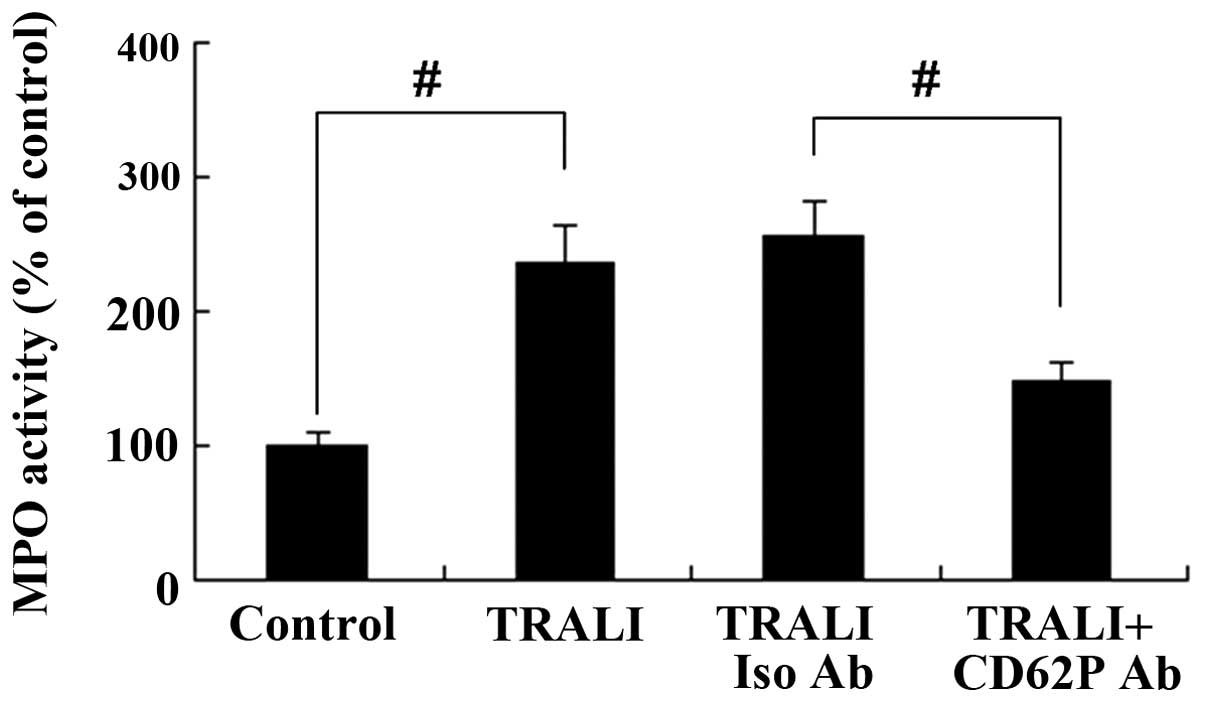
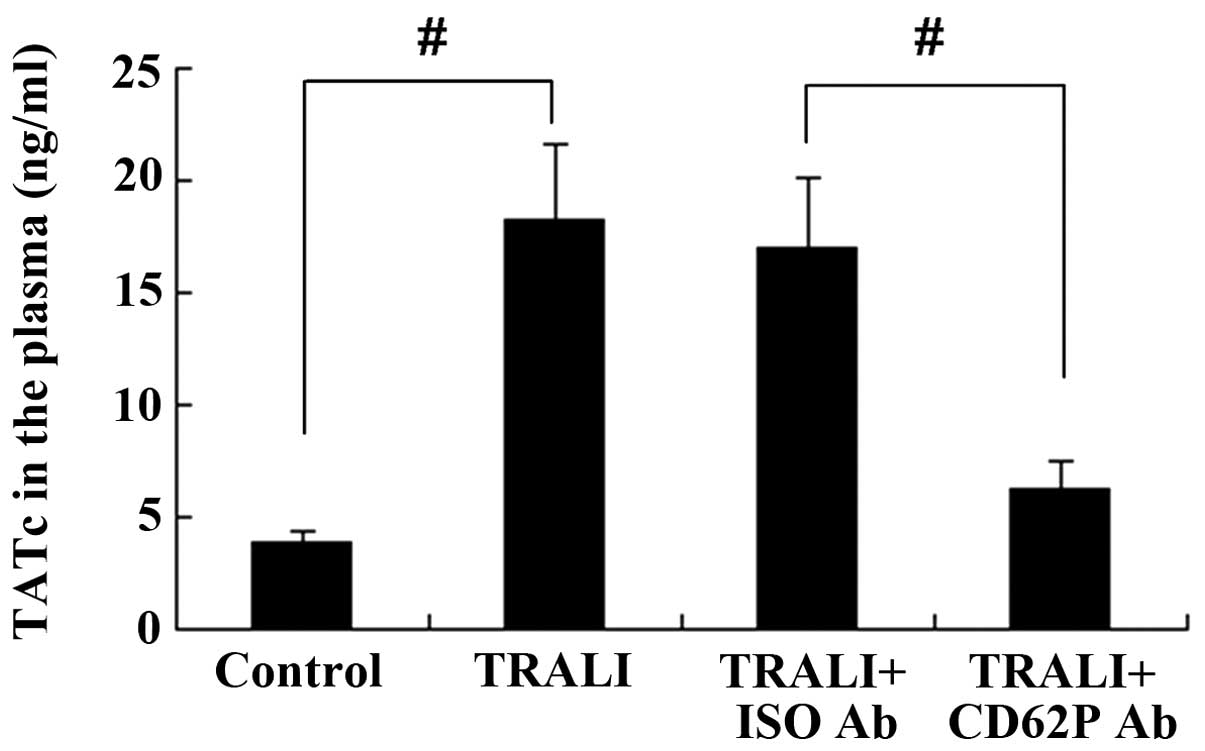
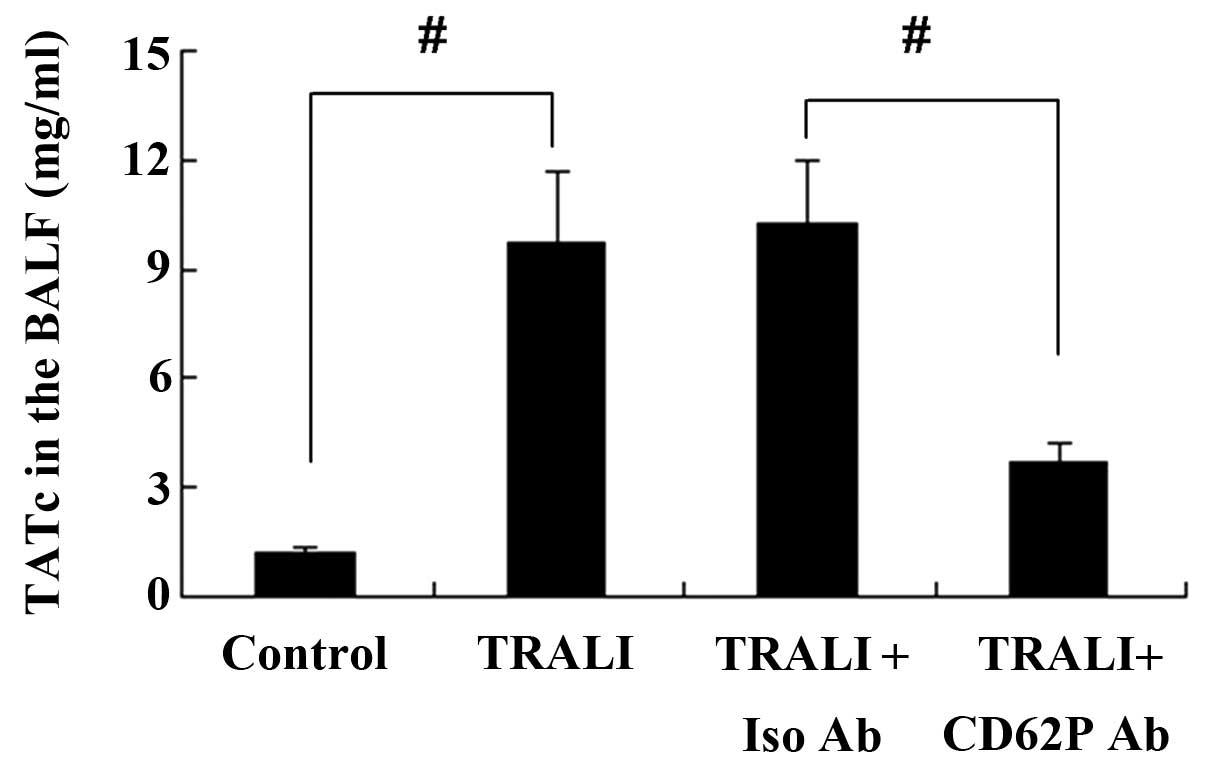
|
1
|
Gajic O and Moore SB: Transfusion-related
acute lung injury. Mayo Clin Proc. 80:766–770. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Toy P, Popovsky MA, Abraham E, Ambruso DR,
Holness LG, Kopko PM, McFarland JG, Nathens AB, Silliman CC and
Stroncek D; National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute Working Group
on TRALI: Transfusion-related acute lung injury: Definition and
review. Crit Care Med. 33:721–726. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Holness L, Knippen MA, Simmons L and
Lachenbruch PA: Fatalities caused by TRALI. Transfus Med Rev.
18:184–188. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Weyrich AS and Zimmerman GA: Platelets:
Signaling cells in the immune continuum. Trends Immunol.
25:489–495. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Semple JW, Italiano JE Jr and Freedman J:
Platelets and the immune continuum. Nat Rev Immunol. 11:264–274.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vieira-de-Abreu A, Campbell RA, Weyrich AS
and Zimmerman GA: Platelets: Versatile effector cells in
hemostasis, inflammation and the immune continuum. Semin
Immunopathol. 34:5–30. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Furie B, Furie BC and Flaumenhaft R: A
journey with platelet P-selectin: The molecular basis of granule
secretion, signalling and cell adhesion. Thromb Haemost.
86:214–221. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
McEver RP: Selectins: Lectins that
initiate cell adhesion under flow. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 14:581–586.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hamburger SA and McEver RP: GMP-140
mediates adhesion of stimulated platelets to neutrophils. Blood.
75:550–554. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Larsen E, Celi A, Gilbert GE, Furie BC,
Erban JK, Bonfanti R, Wagner DD and Furie B: PADGEM protein: A
receptor that mediates the interaction of activated platelets with
neutrophils and monocytes. Cell. 59:305–312. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Geng JG, Bevilacqua MP, Moore KL, McIntyre
TM, Prescott SM, Kim JM, Bliss GA, Zimmerman GA and McEver RP:
Rapid neutrophil adhesion to activated endothelium mediated by
GMP-140. Nature. 343:757–760. 1990. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ma L, Raycroft L, Asa D, Anderson DC and
Geng JG: A sialo-glycoprotein from human leukocytes functions as a
ligand for P-selectin. J Biol Chem. 269:27739–27746.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lorant DE, Patel KD, Mclntyre TM, McEver
RP, Prescott SM and Zimmerman GA: Coexpression of GMP-140 and PAF
by endothelium stimulated by histamine or thrombin: A juxtacrine
system for adhesion and activation of neutrophils. J Cell Biol.
115:223–234. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Looney MR, Nguyen JX, Hu Y, Van Ziffle JA,
Lowell CA and Matthay MA: Platelet depletion and aspirin treatment
protect mice in a two-event model of transfusion-related acute lung
injury. J Clin Invest. 119:3450–3461. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wachowicz B, Olas B, Zbikowska HM and
Buczyński A: Generation of reactive oxygen species in blond
platelets. Platelets. 13:175–182. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee JH, Kim JT and Cho YG: Effect of
nitric oxide on the cryopreservation of platelets. Korean J Lab
Med. 28:136–143. 2008.In Korean. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hidalgo A, Chang J, Jang JE, Peired AJ,
Chiang EY and Frenette PS: Heterotypic interactions enabled by
polarized neutrophil microdomains mediate thromboinflammatory
injury. Nat Med. 15:384–391. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Looney MR, Su X, Van Ziffle JA, Lowell CA
and Matthay MA: Neutrophils and their Fc gamma receptors are
essential in a mouse model of transfusion-related acute lung
injury. J Clin Invest. 116:1615–1623. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Thomas GM, Carbo C, Curtis BR, Martinod K,
Mazo IB, Schatzberg D, Cifuni SM, Fuchs TA, von Andrian UH,
Hartwig, et al: Extracellular DNA traps are associated with the
pathogenesis of TRALI in humans and mice. Blood. 119:6335–6343.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Khan SY, Kelher MR, Heal JM, Blumberg N,
Boshkov LK, Phipps R, Gettings KF, McLaughlin NJ and Silliman CC:
Soluble CD40 ligand accumulates in stored blood components, primes
neutrophils through CD40, and is a potential cofactor in the
development of transfusion-related acute lung injury. Blood.
108:2455–2462. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sachs UJ, Hattar K, Weissmann N, Bohle RM,
Weiss T, Sibelius U and Bux J: Antibody-induced neutrophil
activation as a trigger for transfusion-related acute lung injury
in an ex vivo rat lung model. Blood. 107:1217–1219. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Silliman CC, Boshkov LK, Mehdizadehkashi
Z, Elzi DJ, Dickey WO, Podlosky L, Clarke G and Ambruso DR:
Transfusion-related acute lung injury: Epidemiology and a
prospective analysis of etiologic factors. Blood. 101:454–462.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Heddle NM, Klama L, Singer J, Richards C,
Fedak P, Walker I and Kelton JG: The role of the plasma from
platelet concentrates in transfusion reactions. N Engl J Med.
331:625–628. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Muylle L, Wouters E, De Bock R and
Peetermans ME: Reactions to platelet transfusion: The effect of the
storage time of the concentrate. Transfus Med. 2:289–293. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sarkodee-Adoo CB, Kendall JM, Sridhara R,
Lee EJ and Schiffer CA: The relationship between the duration of
platelet storage and the development of transfusion reactions.
Transfusion. 38:229–235. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Popovsky MA, Chaplin HC Jr and Moore SB:
Transfusion-related acute lung injury: A neglected, serious
complication of hemotherapy. Transfusion. 32:589–592. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Flesch BK and Neppert J:
Transfusion-related acute lung injury caused by human leucocyte
antigen class II antibody. Br J Haematol. 116:673–676. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kopko PM, Popovsky MA, MacKenzie MR,
Paglieroni TG, Muto KN and Holland PV: HLA class II antibodies in
transfusion-related acute lung injury. Transfusion. 41:1244–1248.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Strait RT, Hicks W, Barasa N, Mahler A,
Khodoun M, Köhl J, Stringer K, Witte D, Van Rooijen N, Susskind BM
and Finkelman FD: MHC class I-specific antibody binding to
nonhematopoietic cells drives complement activation to induce
transfusion-related acute lung injury in mice. J Exp Med.
208:2525–2544. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mackie IJ and Bull HA: Normal haemostasis
and its regulation. Blood Rev. 3:237–250. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vlaar AP, Hofstra JJ, Levi M, Kulik W,
Nieuwland R, Tool AT, Schultz MJ, de Korte D and Juffermans NP:
Supernatant of aged erythrocytes causes lung inflammation and
coagulopathy in a 'two-hit' in vivo syngeneic transfusion model.
Anesthesiology. 113:92–103. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|