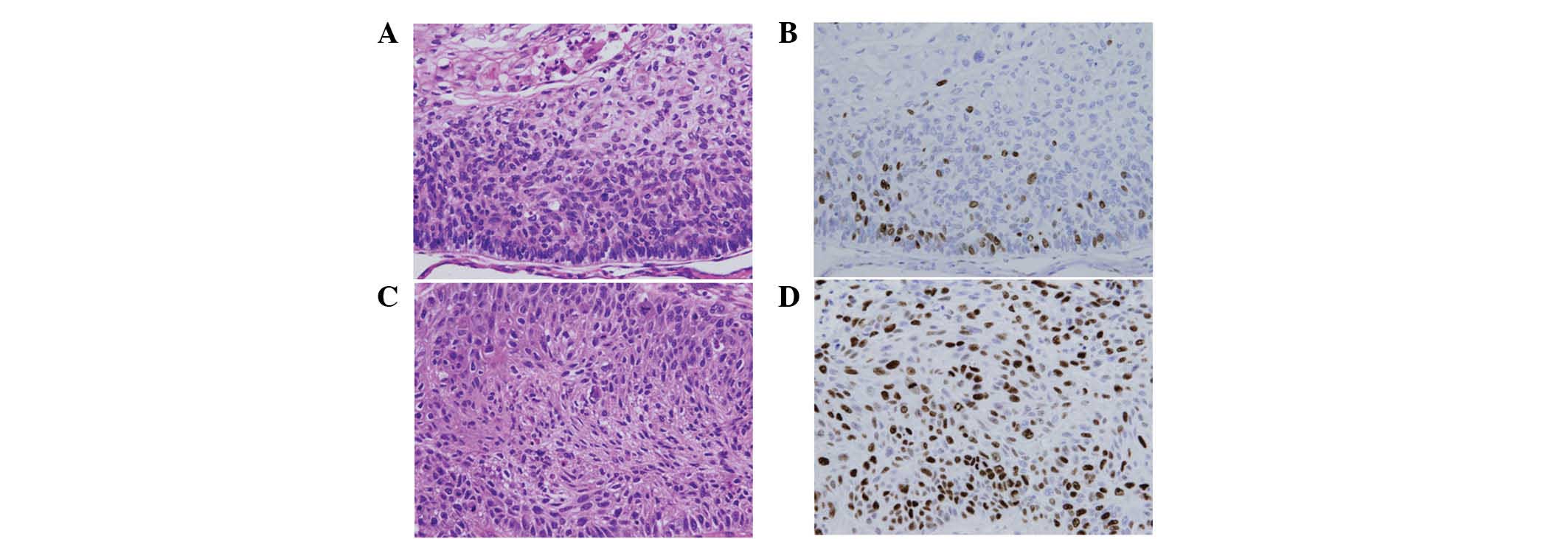
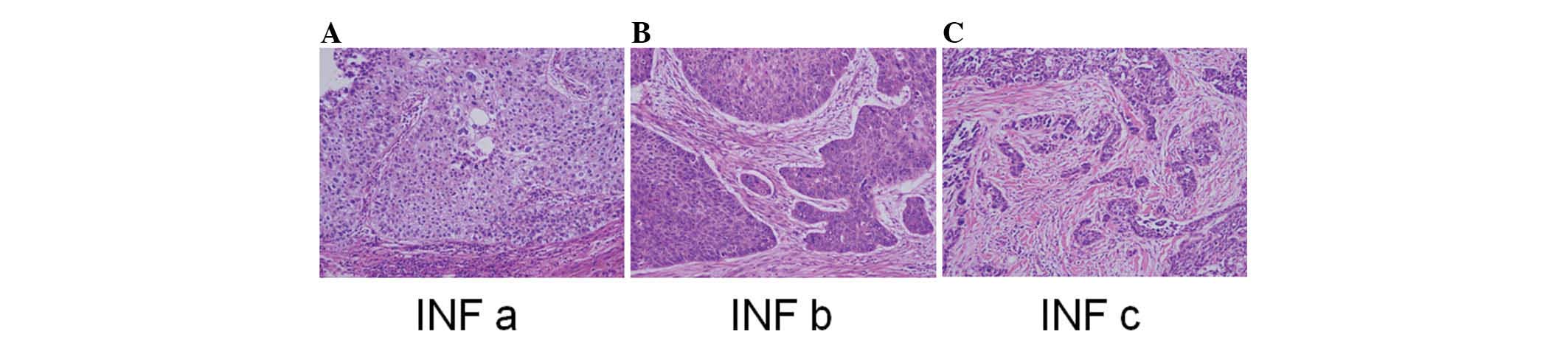
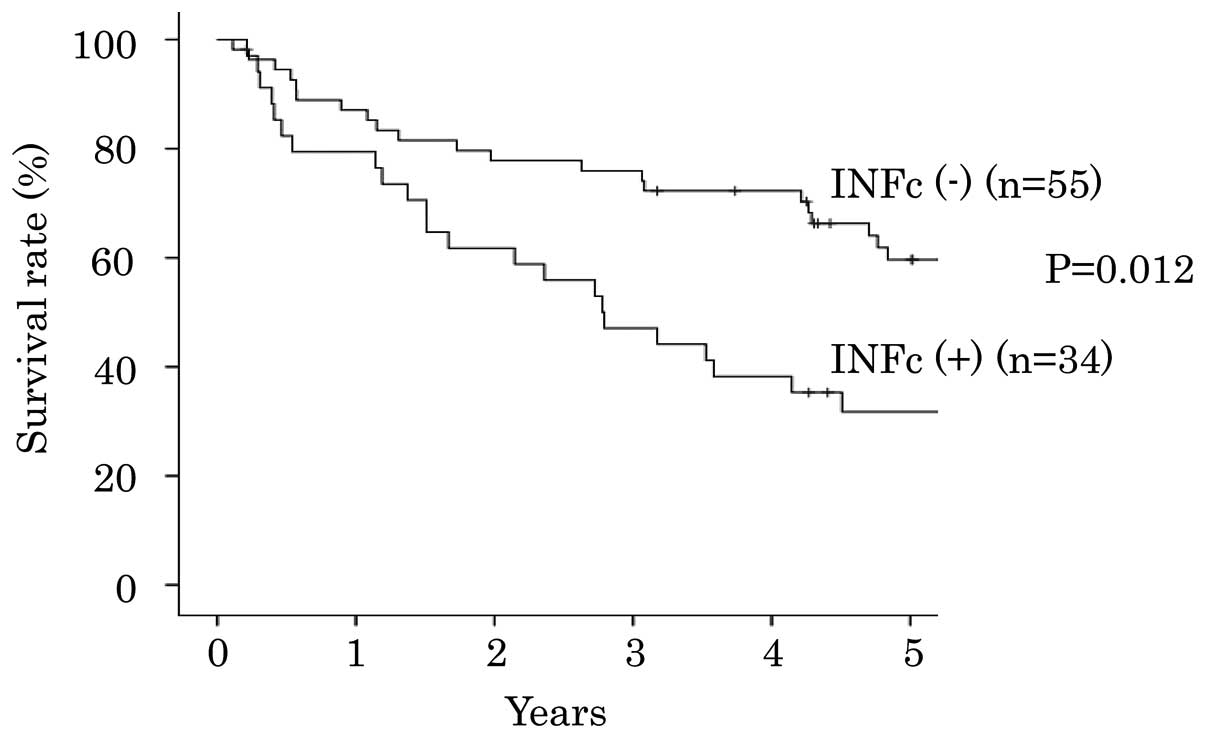
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Beadsmoore CJ and Screaton NJ:
Classification, staging and prognosis of lung cancer. Eur J Radiol.
45:8–17. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Goldstraw P, Crowley J, Chansky K, et al:
The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: proposals for the revision
of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of
the TNM classification of malignant tumours. J Thorac Oncol.
2:706–714. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hong J, Kyung SY, Lee SP, et al:
Pemetrexed versus gefitinib versus erlotinib in previously treated
patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Korean J Intern Med.
25:294–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rossi A, Ricciardi S, Maione P, de Marinis
F and Gridelli C: Pemetrexed in the treatment of advanced
non-squamous lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 66:141–149. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, et al:
Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 355:2542–2550. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Reck M, von Pawel J, Zatloukal P, et al:
Phase III trial of cisplatin plus gemcitabine with either placebo
or bevacizumab as first-line therapy for nonsquamous non-small-cell
lung cancer: AVAil. J Clin Oncol. 27:1227–1234. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rosell R, Perez-Roca L, Sanchez JJ, et al:
Customized treatment in non-small-cell lung cancer based on EGFR
mutations and BRCA1 mRNA expression. PLoS One. 4:e51332009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ciancio N, Galasso MG, Campisi R, Bivona
L, Migliore M and Di Maria GU: Prognostic value of p53 and Ki67
expression in fiberoptic bronchial biopsies of patients with non
small cell lung cancer. Multidiscip Respir Med. 7:292012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kosacka M, Piesiak P, Kowal A, Gołecki M
and Jankowska R: Galectin-3 and cyclin D1 expression in non-small
cell lung cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 30:1012011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sterlacci W, Fiegl M, Hilbe W, et al:
Deregulation of p27 and cyclin D1/D3 control over mitosis is
associated with unfavorable prognosis in non-small cell lung
cancer, as determined in 405 operated patients. J Thorac Oncol.
5:1325–1336. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lei B, Liu S, Qi W, et al: PBK/TOPK
expression in non-small-cell lung cancer: its correlation and
prognostic significance with Ki67 and p53 expression.
Histopathology. 63:696–703. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Motadi LR, Bhoola KD and Dlamini Z:
Expression and function of retinoblastoma binding protein 6 (RBBP6)
in human lung cancer. Immunobiology. 216:1065–1073. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cattoretti G, Becker MH, Key G, et al:
Monoclonal antibodies against recombinant parts of the Ki-67
antigen (MIB 1 and MIB 3) detect proliferating cells in
microwave-processed formalin-fixed paraffin sections. J Pathol.
168:357–363. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gerdes J, Li L, Schlueter C, et al:
Immunobiochemical and molecular biologic characterization of the
cell proliferation-associated nuclear antigen that is defined by
monoclonal antibody Ki-67. Am J Pathol. 138:867–873.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hui AM, Shi YZ, Li X, et al: Proliferative
marker Ki-67 in gallbladder carcinomas: high expression level
predicts early recurrence after surgical resection. Cancer Lett.
176:191–198. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xuan YH, Choi YL, Shin YK, et al: An
immunohistochemical study of the expression of cell-cycle-regulated
proteins p53, cyclin D1, RB, p27, Ki67 and MSH2 in gallbladder
carcinoma and its precursor lesions. Histol Histopathol. 20:59–66.
2005.
|
|
18
|
Haraguchi M, Yamamoto M, Saito A, et al:
Prognostic value of depth and pattern of stomach wall invasion in
patients with an advanced gastric carcinoma. Semin Surg Oncol.
10:125–129. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Japanese Classification of Gastric
Carcinoma - 2nd English Edition. Gastric Cancer. 1:10–24. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Maehara Y, Oshiro T, Adachi Y, Ohno S,
Akazawa K and Sugimachi K: Growth pattern and prognosis of gastric
cancer invading the subserosa. J Surg Oncol. 55:203–208. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Okada K, Kijima H, Imaizumi T, et al:
Wall-invasion pattern correlates with survival of patients with
gallbladder adenocarcinoma. Anticancer Res. 29:685–691.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Song KY, Hur H, Jung CK, et al: Impact of
tumor infiltration pattern into the surrounding tissue on prognosis
of the subserosal gastric cancer (pT2b). Eur J Surg Oncol.
36:563–567. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kong KY, Park JY, Kim DY, et al:
Prognostic significance of stromal microinvasion in the intestinal
type of ovarian mucinous adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol.
18:3462–3468. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Masuda R, Kijima H, Imamura N, et al:
Tumor budding is a significant indicator of a poor prognosis in
lung squamous cell carcinoma patients. Mol Med Rep. 6:937–943.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
C: TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors. 7th edition. Wiley;
Hoboken, New Jersey, NJ, USA: 2010
|
|
26
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Muller-Hermedin HK
and Harris CC: Pathology and Genetics Tumours of the Lung, Pleura,
Thymus and Heart. IARC Press; Lyon, France: 2004
|
|
27
|
Kawano K and Yanagisawa S: Predictive
value of laminin-5 and membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase
expression for cervical lymph node metastasis in T1 and T2 squamous
cell carcinomas of the tongue and floor of the mouth. Head Neck.
28:525–533. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Soomro IN and Whimster WF: Growth fraction
in lung tumours determined by Ki67 immunostaining and comparison
with AgNOR scores. J Pathol. 162:217–222. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Scagliotti GV, Micela M, Gubetta L, et al:
Prognostic significance of Ki67 labelling in resected non small
cell lung cancer. Eur J Cancer. 29A:363–365. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hommura F, Dosaka-Akita H, Mishina T, et
al: Prognostic significance of p27KIP1 protein and ki-67 growth
fraction in non-small cell lung cancers. Clin Cancer Res.
6:4073–4081. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nguyen VN, Mirejovský P, Mirejovský T,
Melinova L and Mandys V: Expression of cyclin D1, Ki-67 and PCNA in
non-small cell lung cancer: prognostic significance and comparison
with p53 and bcl-2. Acta Histochem. 102:323–338. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Maddau C, Confortini M, Bisanzi S, et al:
Prognostic significance of p53 and Ki-67 antigen expression in
surgically treated non-small cell lung cancer: immunocytochemical
detection with imprint cytology. Am J Clin Pathol. 125:425–431.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ishida H, Irie K, Itoh T, Furukawa T and
Tokunaga O: The prognostic significance of p53 and bcl-2 expression
in lung adenocarcinoma and its correlation with Ki-67 growth
fraction. Cancer. 80:1034–1045. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Martin B, Paesmans M, Mascaux C, et al:
Ki-67 expression and patients survival in lung cancer: systematic
review of the literature with meta-analysis. Br J Cancer.
91:2018–2025. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|