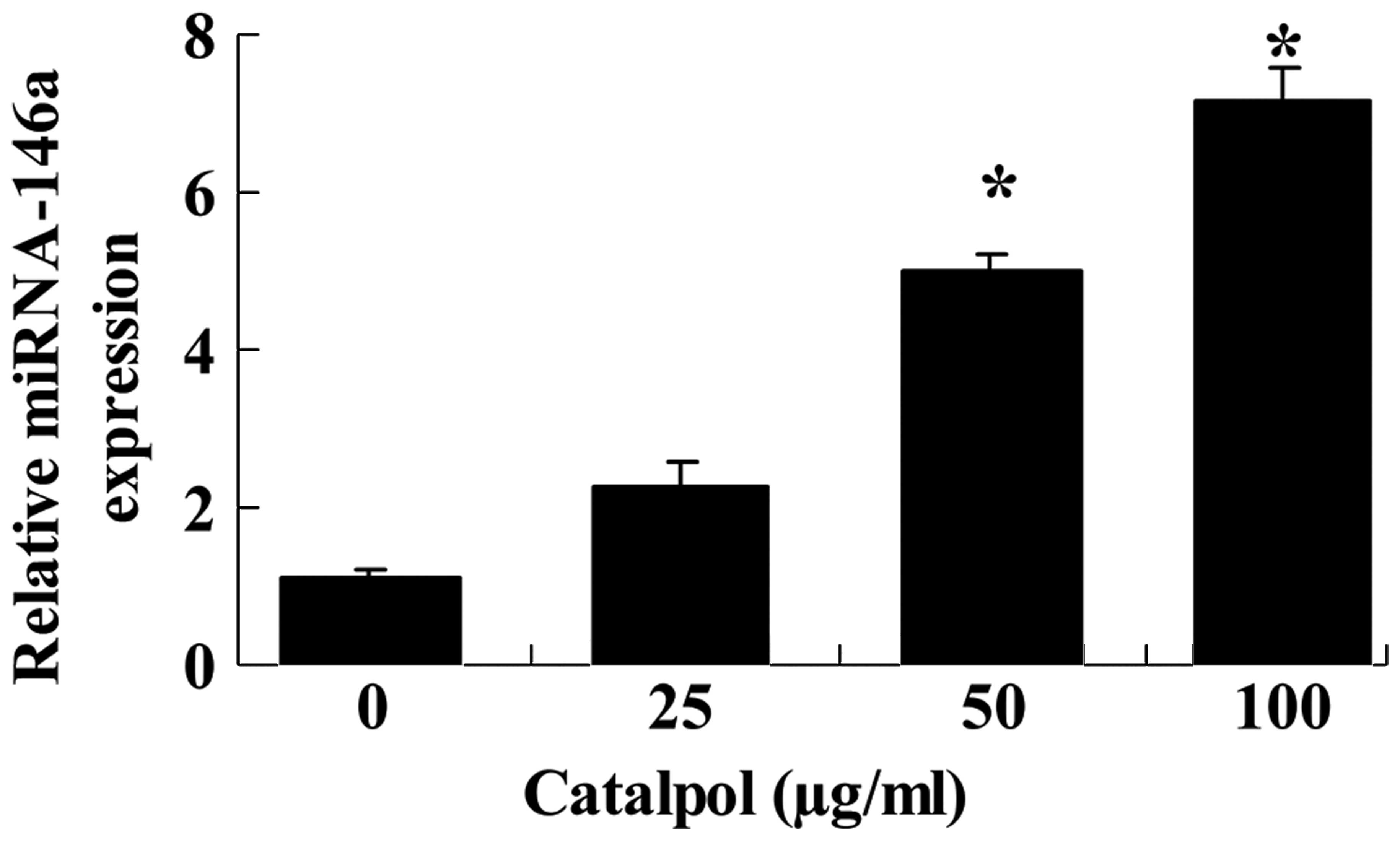
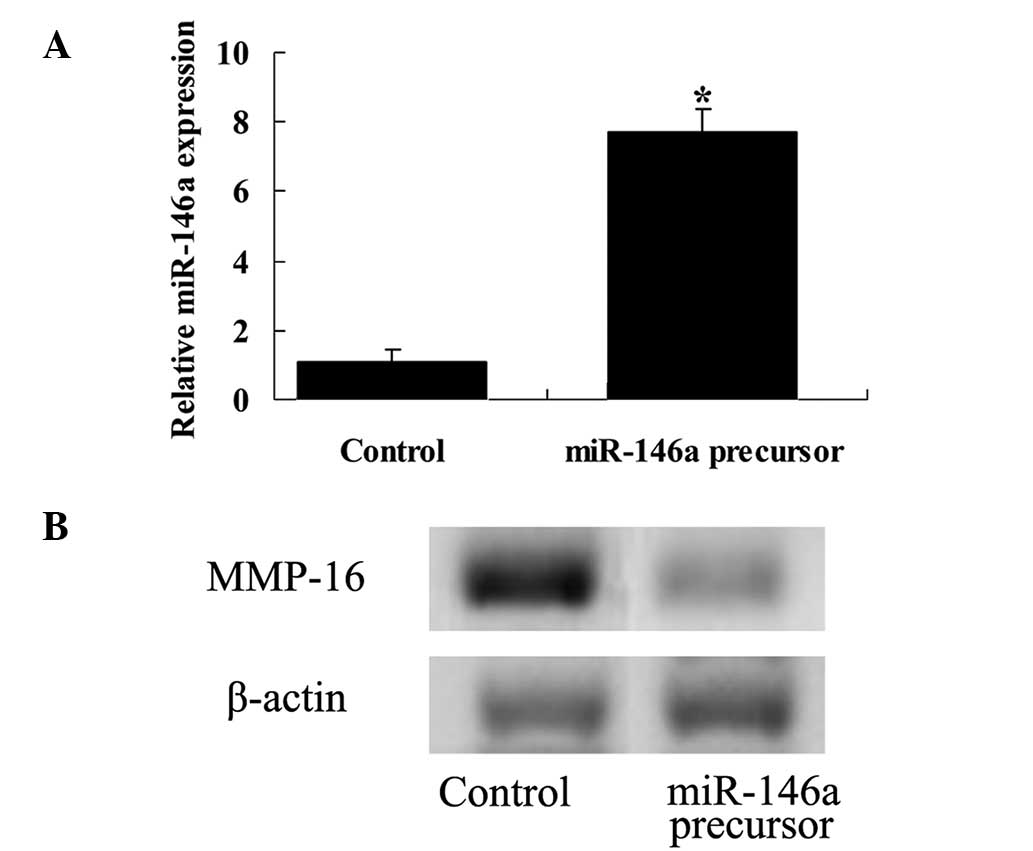
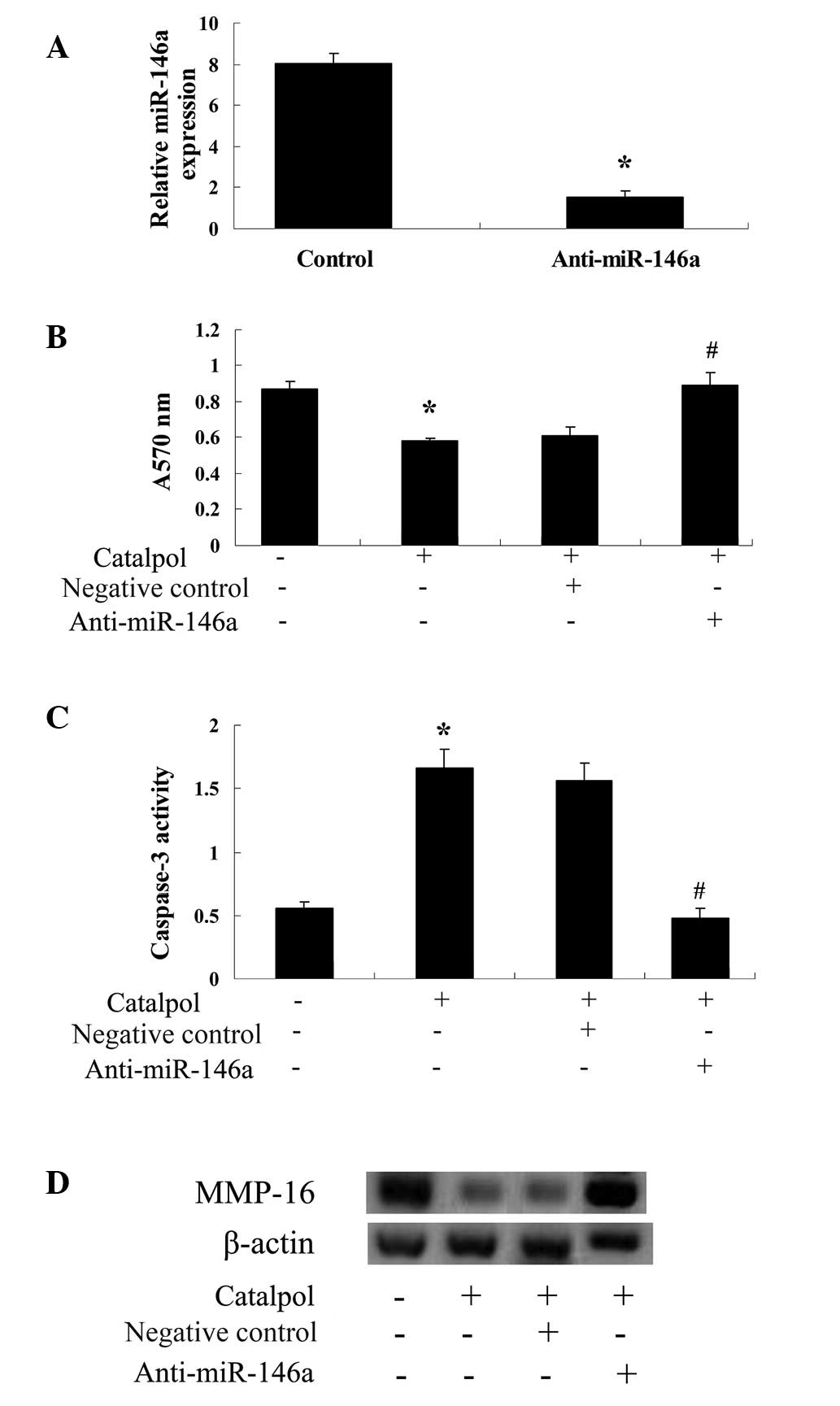
|
1
|
Hu XC, Zhang J, Xu BH, et al: Cisplatin
plus gemcitabine versus paclitaxel plus gemcitabine as first-line
therapy for metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (CBCSG006): A
randomised, open-label, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol.
16:436–446. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fu JF, Chen HL, Yang J, Yi CH and Zheng S:
Feasibility and accuracy of sentinel lymph node biopsy in
clinically node-positive breast cancer after neoadjuvant
chemotherapy: A meta-analysis. PLoS One. 9:e1053162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nie XC, Dong DS, Bai Y and Xia P:
Meta-analysis of black tea consumption and breast cancer risk:
Update 2013. Nutr Cancer. 66:1009–1014. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Noh EM, Chung EY, Youn HJ, Jung SH, Hur H,
Lee YR and Kim JS: Cis-guggulsterone inhibits the IKK/NF-κB
pathway, whereas trans-guggulsterone inhibits MAPK/AP-1 in MCF-7
breast cancer cells: Guggulsterone regulates MMP-9 expression in an
isomer-specific manner. Int J Mol Med. 31:393–399. 2013.
|
|
5
|
Cai KQ, Yang WL, Capo-Chichi CD,
Vanderveer L, Wu H, Godwin AK and Xu XX: Prominent expression of
metalloproteinases in early stages of ovarian tumorigenesis. Mol
Carcinog. 46:130–143. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Fan SH, Wang YY, Lu J, et al: CERS2
Suppresses Tumor Cell Invasion and Is Associated with Decreased
V-ATPase and MMP-2/MMP-9 activities in Breast Cancer. J Cell
Biochem. 116:502–513. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Xie M, Hu A, Luo Y, Sun W, Hu X and Tang
S: Interleukin-4 and melatonin ameliorate high glucose and
interleukin-1beta stimulated inflammatory reaction in human retinal
endothelial cells and retinal pigment epithelial cells. Mol Vis.
20:921–928. 2014.
|
|
8
|
Tang C, Chen L, Gu W, et al: Cyclosporin A
enhances the ability of trophoblasts to displace the activated
human umbilical vein endothelial cell monolayers. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 6:2441–2450. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Delassus GS, Cho H, Park J and Eliceiri
GL: New pathway links from cancer-progression determinants to gene
expression of matrix metalloproteinases in breast cancer cells. J
Cell Physiol. 217:739–744. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hegedüs L, Cho H, Xie X and Eliceiri GL:
Additional MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell matrix metalloproteinases
promote invasiveness. J Cell Physiol. 216:480–485. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hede K: Studies define role of microRNA in
cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 97:1114–1115. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Croce CM and Calin GA: miRNAs, cancer, and
stem cell division. Cell. 122:6–7. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gregory RI and Shiekhattar R: MicroRNA
biogenesis and cancer. Cancer Res. 65:3509–3512. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bhaumik D, Scott GK, Schokrpur S, Patil
CK, Campisi J and Benz CC: Expression of microRNA-146 suppresses
NF-kappaB activity with reduction of metastatic potential in breast
cancer cells. Oncogene. 27:5643–5647. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kumar S, Keerthana R, Pazhanimuthu A and
Perumal P: Overexpression of circulating miRNA-21 and miRNA-146a in
plasma samples of breast cancer patients. Indian J Biochem Biophys.
50:210–214. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xiao WQ, Yin GJ, Fan YT, Qiu L, Cang XF,
Yu G, Hu YL, Xing M, Wu Q, Wang XP, et al: Catalpol ameliorates
sodium taurocholate-induced acute pancreatitis in rats via
inhibiting activation of nuclear factor kappa B. Int J Mol Sci.
15:11957–11972. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang WJ, Niu HS, Lin MH, Cheng JT and Hsu
FL: Antihyperglycemic effect of catalpol in streptozotocin-induced
diabetic rats. J Nat Prod. 73:1170–1172. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lü J, Wang Y, Zhao W, Li N, Li H, Lu J,
Zeng W, Bao S and Bai Y: Effects of catalpol, L-shikonin and
paeonol extracted from radix rehmanniae, radix arnebiae and cortex
moutan on KGF-induced HaCaT cell proliferation. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za
Zhi. 94:1265–1269. 2014.In Chinese.
|
|
20
|
García C, León LG, Pungitore CR, Ríos-Luci
C, Daranas AH, Montero JC, Pandiella A, Tonn CE, Martín VS and
Padrón JM: Enhancement of antiproliferative activity by molecular
simplification of catalpol. Bioorg Med Chem. 18:2515–2523. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen C, Chen Z, Xu F, Zhu C, Fang F, Shu
S, Li M and Ling C: Radio-protective effect of catalpol in cultured
cells and mice. J Radiat Res (Tokyo). 54:76–82. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Pogribny IP, Filkowski JN, Tryndyak VP,
Golubov A, Shpyleva SI and Kovalchuk O: Alterations of microRNAs
and their targets are associated with acquired resistance of MCF-7
breast cancer cells to cisplatin. Int J Cancer. 127:1785–1794.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pungitore CR, León LG, García C, Martín
VS, Tonn CE and Padrón JM: Novel antiproliferative analogs of the
Taq DNA polymerase inhibitor catalpol. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
17:1332–1335. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wang Z, An LJ, Duan YL, Li YC and Jiang B:
Catalpol protects rat pheochromocytoma cells against oxygen and
glucose deprivation-induced injury. Neurol Res. 30:106–112. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Liang JH, Du J, Xu LD, Jiang T, Hao S, Bi
J and Jiang B: Catalpol protects primary cultured cortical neurons
induced by Abeta(1–42) through a mitochondrial-dependent caspase
pathway. Neurochem Int. 55:741–746. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Loo WT, Chen JP, Chow LW and Chou JW:
Effects of Shugansanjie Tang on matrix metalloproteinases 1, 3 and
9 and telomerase reverse transcriptase expression in human breast
cells in vitro. Biomed Pharmacother. 61:601–605. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fagan-Solis KD, Schneider SS, Pentecost
BT, Bentley BA, Otis CN, Gierthy JF and Arcaro KF: The RhoA pathway
mediates MMP-2 and MMP-9-independent invasive behavior in a
triple-negative breast cancer cell line. J Cell Biochem.
114:1385–1394. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Liu YF, Zhao Y, Wen XS and Dong QT:
Advances in research on pharmacodynamics and chemical conversion of
catalpol. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 32:1128–1130. 2007.In Chinese.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Saracoglu I and Harput US: In vitro
cytotoxic activity and structure activity relationships of iridoid
glucosides derived from Veronica species. Phytother Res.
26:148–152. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Adams BD, Kasinski AL and Slack FJ:
Aberrant regulation and function of microRNAs in cancer. Curr Biol.
24:R762–R776. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Maxwell GL, Shoji Y, Darcy K, et al:
MicroRNAs in endometrial cancers from black and white patients. Am
J Obstet Gynecol. 212:e191–e110. 2015.
|
|
32
|
Seven M, Karatas OF, Duz MB and Ozen M:
The role of miRNAs in cancer: from pathogenesis to therapeutic
implications. Future Oncol. 10:1027–1048. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
D'Ippolito E and Iorio MV: MicroRNAs and
triple negative breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 14:22202–22220. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhou Y, Hu Y, Yang M, Jat P, Li K,
Lombardo Y, Xiong D, Coombes RC, Raguz S and Yagüe E: The
miR-106b~25 cluster promotes bypass of doxorubicin-induced
senescence and increase in motility and invasion by targeting the
E-cadherin transcriptional activator EP300. Cell Death Differ.
21:462–474. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
Sandhu R, Rein J, D'Arcy M, Herschkowitz
JI, Hoadley KA and Troester MA: Overexpression of miR-146a in
basal-like breast cancer cells confers enhanced tumorigenic
potential in association with altered p53 status. Carcinogenesis.
35:2567–2575. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang D, Liu D, Gao J, Liu M, Liu S, Jiang
M, Liu Y and Zheng D: TRAIL-induced miR-146a expression suppresses
CXCR4-mediated human breast cancer migration. FEBS J.
280:3340–3353. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|