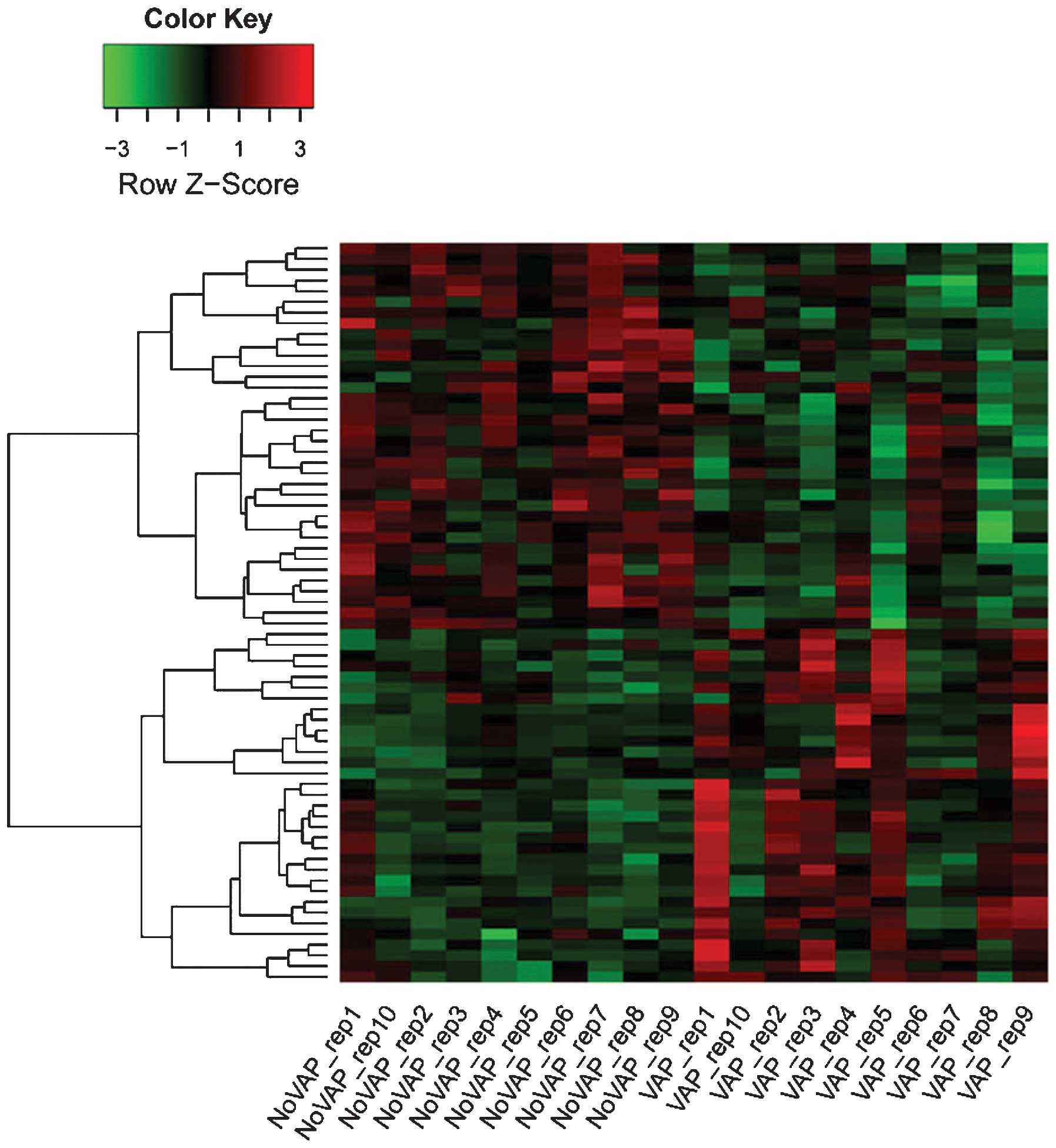
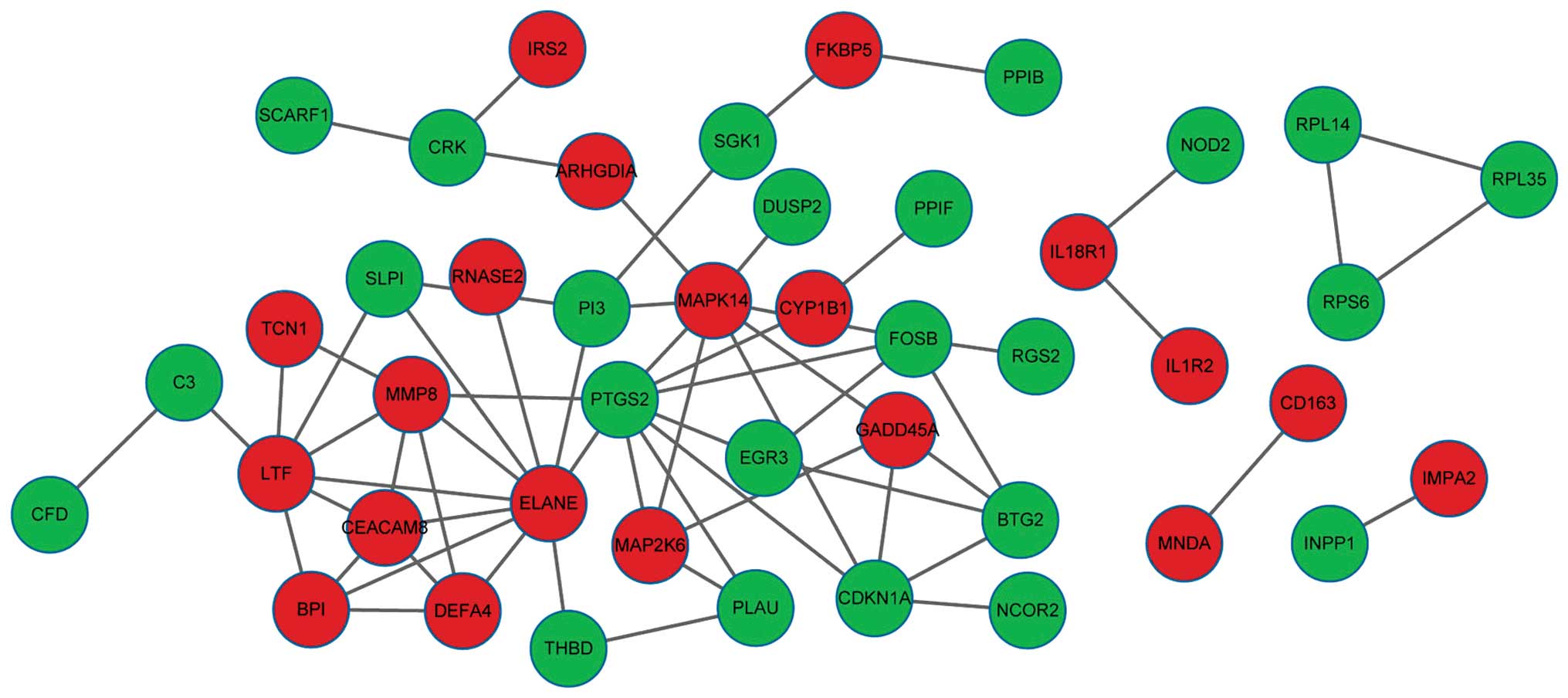
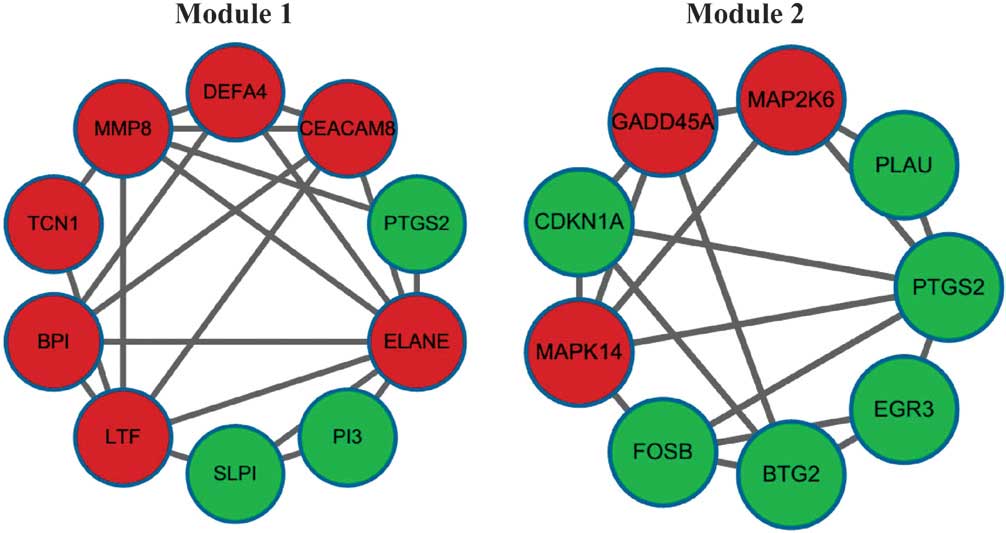
|
1
|
Morehead RS and Pinto SJ:
Ventilator-associated pneumonia. Arch Intern Med. 160:1926–1936.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Koenig SM and Truwit JD:
Ventilator-associated pneumonia: Diagnosis, treatment and
prevention. Clin Microbiol Rev. 19:637–657. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kollef MH, Hamilton CW and Ernst FR:
Economic impact of ventilator-associated pneumonia in a large
matched cohort. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 33:250–256. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Barbier F, Andremont A, Wolff M and
Bouadma L: Hospital-acquired pneumonia and ventilator-associated
pneumonia: Recent advances in epidemiology and management. Curr
Opin Pulm Med. 19:216–228. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
O'Dwyer MJ, Mankan AK, Stordeur P,
O'Connell B, Duggan E, White M, Kelleher DP, McManus R and Ryan T:
The occurrence of severe sepsis and septic shock are related to
distinct patterns of cytokine gene expression. Shock. 26:544–550.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bridge DR, Novotny MJ, Moore ER and Olson
JC: Role of host cell polarity and leading edge properties in
Pseudomonas type III secretion. Microbiology. 156:356–373. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Ferrandi C, Ardissone V, Ferro P, Rückle
T, Zaratin P, Ammannati E, Hauben E, Rommel C and Cirillo R:
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma inhibition plays a crucial role in
early steps of inflammation by blocking neutrophil recruitment. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 322:923–930. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Swanson JM, Wood GC, Xu L, Tang LE,
Meibohm B, Homayouni R, Croce MA and Fabian TC: Developing a gene
expression model for predicting ventilator-associated pneumonia in
trauma patients: A pilot study. PLoS One. 7:152012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ma J and Qin ZS: Different normalization
strategies for microarray gene expression traits affect the
heritability estimation. BMC Proc. 1(Suppl 1): S1542007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Delhomme N, Padioleau I, Furlong EE and
Steinmetz LM: EasyRNASeq: A bioconductor package for processing
RNA-Seq data. Bioinformatics. 28:2532–2533. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Singh B, Ronghe AM, Chatterjee A, Bhat NK
and Bhat HK: MicroRNA-93 regulates NRF2 expression and is
associated with breast carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis.
34:1165–1172. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chand Y and Alam MA: Network biology
approach for identifying key regulatory genes by expression based
study of breast cancer. Bioinformation. 8:1132–1138. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J R Stat Soc B (Statistical Methodology).
57:289–300. 1995.
|
|
14
|
Benjamini Y: Discovering the false
discovery rate. J R Stat Soc B (Statistical Methodology).
72:405–416. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hu YH, Hu YL, Liu DW, Yu JX and Liu DM:
Screening and bioinformatics analysis of differentially expressed
genes in hyperplastic scar. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao.
34:939–944. 2014.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene
Ontology Consortium Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000.
|
|
17
|
Kanehisa M: The KEGG database. Novartis
Found Symp. 247:91–101; discussion 101–103, 119–128, 244–252. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wingender E: The TRANSFAC project as an
example of framework technology that supports the analysis of
genomic regulation. Brief Bioinform. 9:326–332. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao M, Sun J and Zhao Z: TSGene: A web
resource for tumor suppressor genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 41(Database
Issue): D970–D976. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Chen JS, Hung WS, Chan HH, Tsai SJ and Sun
HS: In silico identification of oncogenic potential of fyn-related
kinase in hepatocellular carcinoma. Bioinformatics. 29:420–427.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering C
and Jensen LJ: STRING v9.1: Protein-protein interaction networks,
with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41(Database Issue): D808–D815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Adamcsek B, Palla G, Farkas IJ, Derényi I
and Vicsek T: CFinder: Locating cliques and overlapping modules in
biological networks. Bioinformatics. 22:1021–1023. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Storey JD and Tibshirani R: Statistical
significance for genomewide studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:9440–9445. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gogos C, Kotsaki A, Pelekanou A,
Giannikopoulos G, Vaki I, Maravitsa P, Adamis S, Alexiou Z,
Andrianopoulos G, Antonopoulou A, et al: Early alterations of the
innate and adaptive immune statuses in sepsis according to the type
of underlying infection. Crit Care. 14:R962010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Surbatovic M, Jevdjic J, Veljovic M,
Popovic N, Djordjevic D and Radakovic S: Immune response in severe
infection: Could life-saving drugs be potentially harmful? Sci
World J. 2013:9618522013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Pelekanou A, Tsangaris I, Kotsaki A,
Karagianni V, Giamarellou H, Armaganidis A and
Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ: Decrease of CD4 -lymphocytes and
apoptosis of CD14-monocytes are characteristic alterations in
sepsis caused by ventilator-associated pneumonia: Results from an
observational study. Crit Care. 13:R1722009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Routsi C,
Plachouras D, Markaki V, Raftogiannis M, Zervakis D, Koussoulas V,
Orfanos S, Kotanidou A and Armaganidis A: Early apoptosis of blood
monocytes in the septic host: Is it a mechanism of protection in
the event of septic shock? Crit Care. 10:R762006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Germeshausen M, Deerberg S, Peter Y,
Reimer C, Kratz CP and Ballmaier M: The spectrum of ELANE mutations
and their implications in severe congenital and cyclic neutropenia.
Hum Mutat. 34:905–914. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shu Z, Li XH, Bai XM, Zhang ZY, Jiang LP,
Tang XM and Zhao XD: Clinical characteristics of severe congenital
neutropenia caused by novel ELANE gene mutations. Pediatr Infect
Dis J. 34:203–207. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Horwitz MS, Corey SJ, Grimes HL and
Tidwell T: ELANE mutations in cyclic and severe congenital
neutropenia: Genetics and pathophysiology. Hematol Oncol Clin North
Am. 27:19–41. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Frioni A, Conte MP, Cutone A, Longhi C,
Musci G, di Patti MC, Natalizi T, Marazzato M, Lepanto MS, Puddu P,
et al: Lactoferrin differently modulates the inflammatory response
in epithelial models mimicking human inflammatory and infectious
diseases. Biometals. 27:843–856. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang SH, Sharrocks AD and Whitmarsh AJ:
MAP kinase signalling cascades and transcriptional regulation.
Gene. 513:1–13. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Slattery ML, Lundgreen A and Wolff RK:
Dietary influence on MAPK-signaling pathways and risk of colon and
rectal cancer. Nutr Cancer. 65:729–738. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cuadrado A and Nebreda AR: Mechanisms and
functions of p38 MAPK signalling. Biochem J. 429:403–417. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yego EC and Dillman JF III: Cytokine
regulation by MAPK activated kinase 2 in keratinocytes exposed to
sulfur mustard. Toxicol In Vitro. 27:2067–2075. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Höcker R, Walker A and Schmitz I:
Inhibition of autophagy through MAPK14-mediated phosphorylation of
ATG5. Autophagy. 9:426–428. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Zhang Y, Liu G, Dull RO, Schwartz DE and
Hu G: Autophagy in pulmonary macrophages mediates lung inflammatory
injury via NLRP3 inflammasome activation during mechanical
ventilation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 307:L173–L185.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|