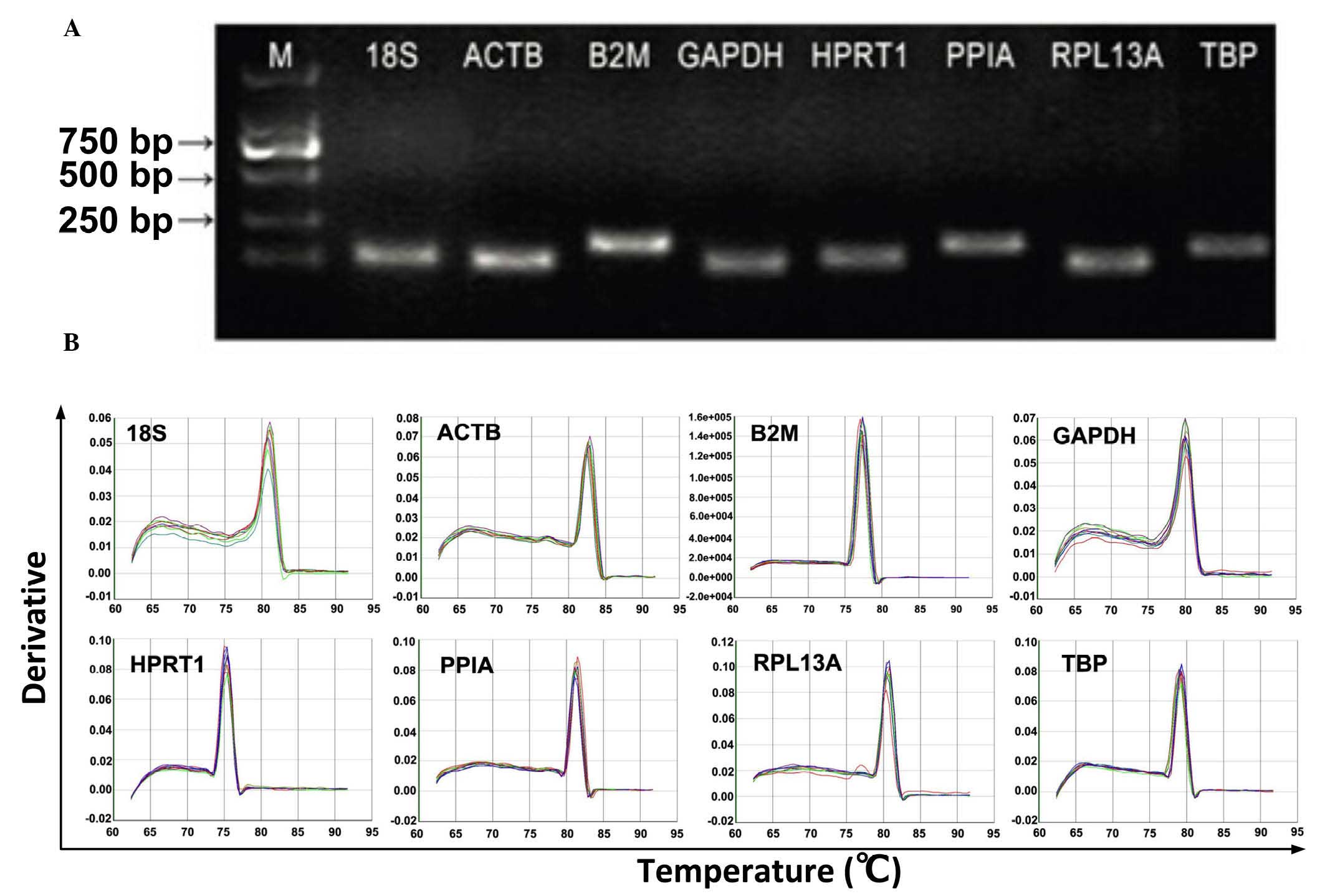
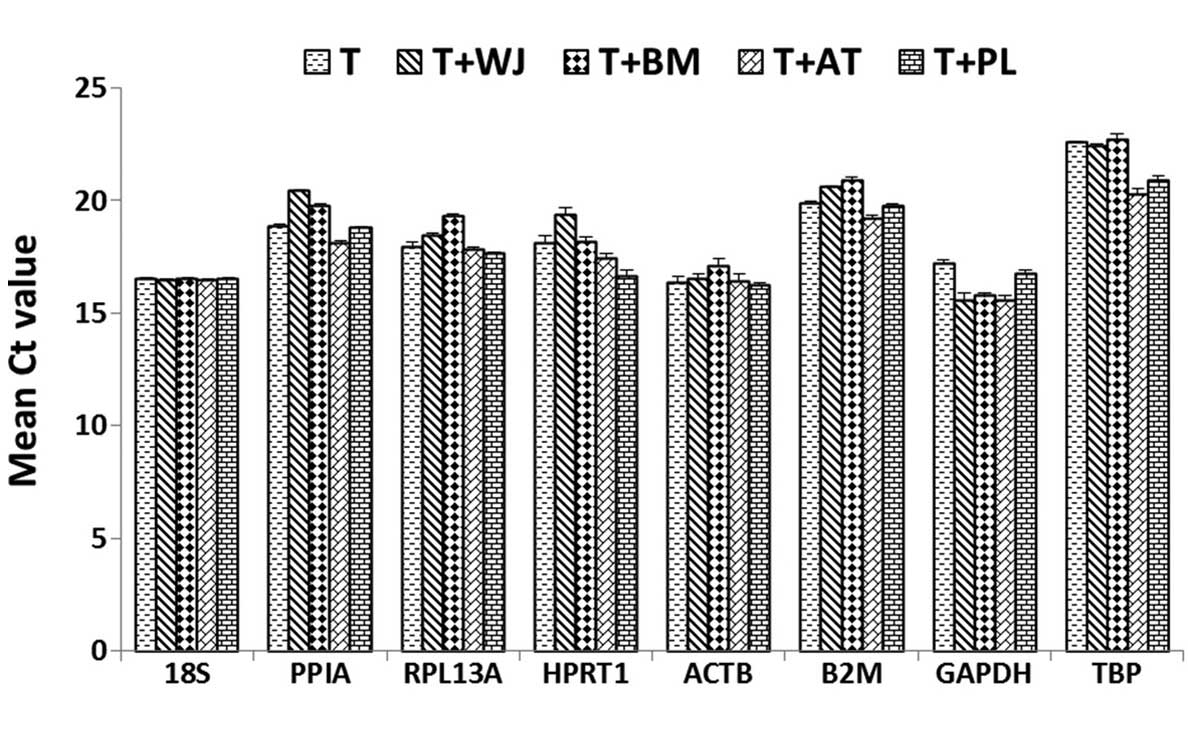
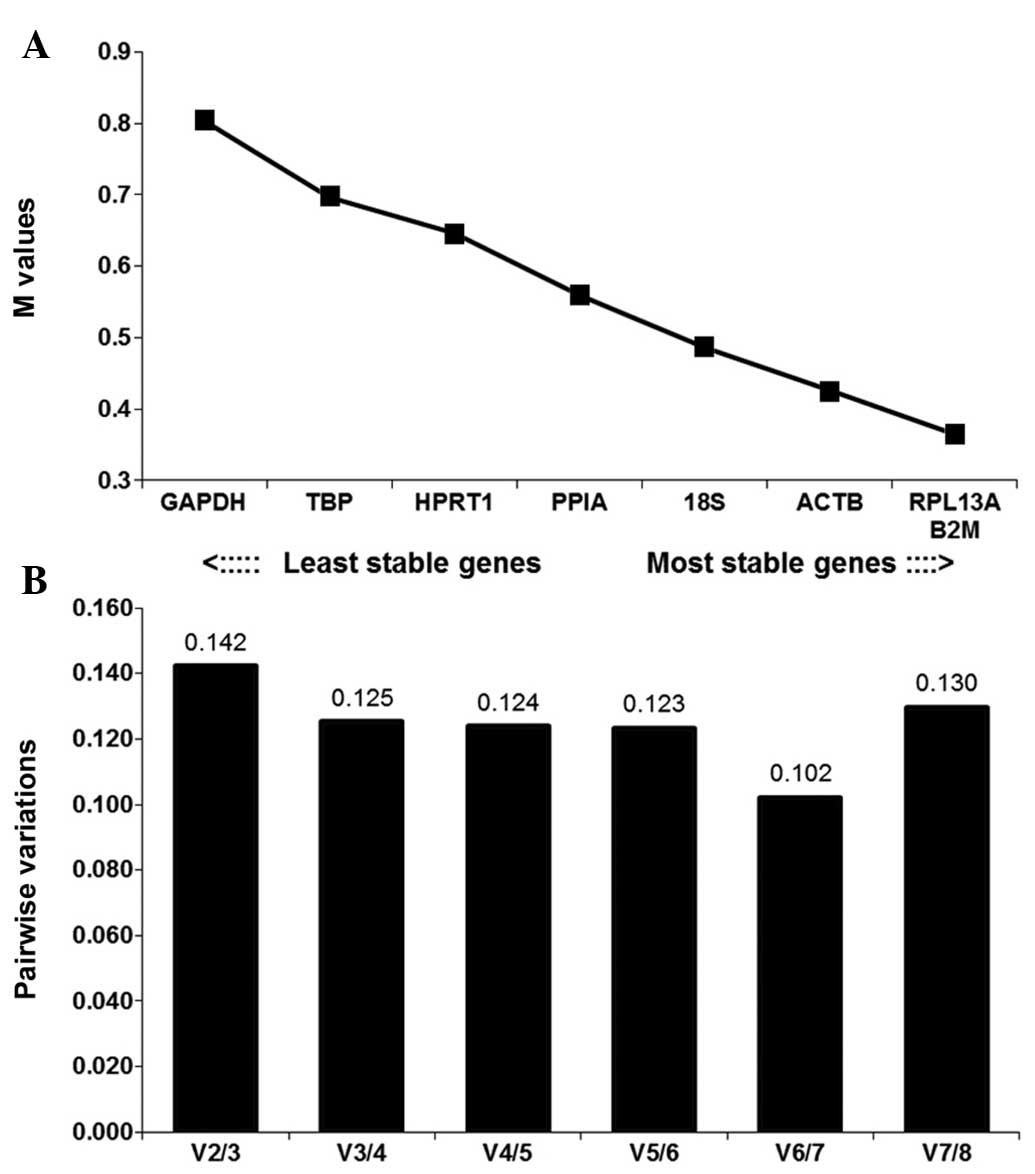
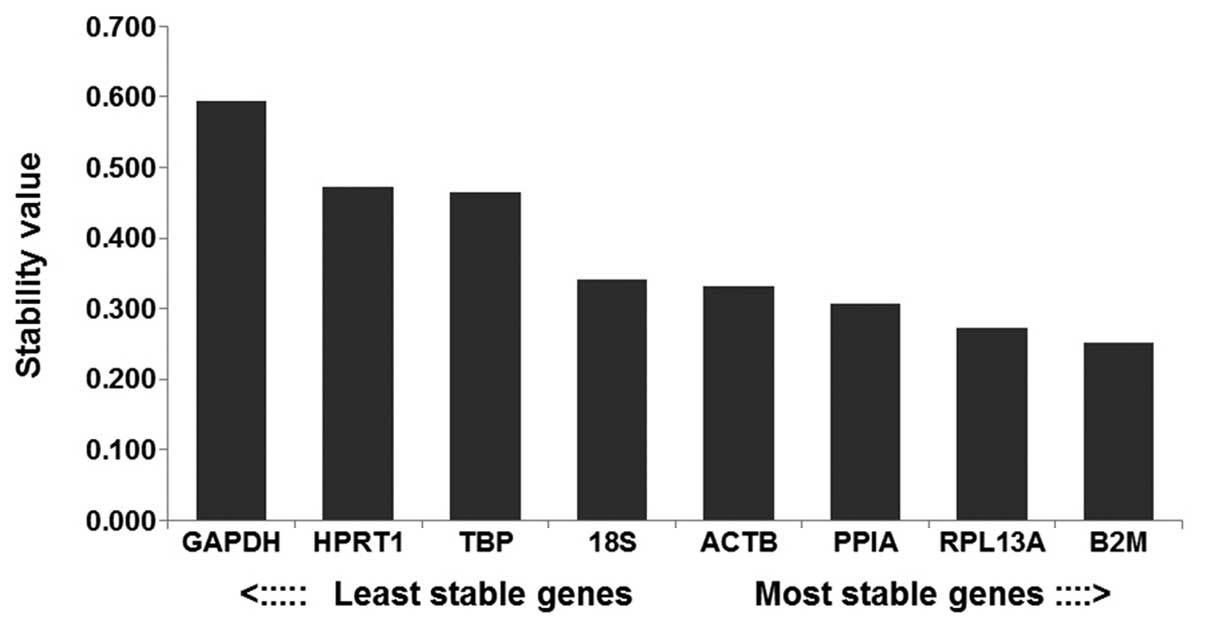
|
1
|
Cikos S and Koppel J: Transformation of
real-time PCR fluorescence data to target gene quantity. Anal
Biochem. 384:1–10. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zhong Q, Zhang Q, Wang Z, Qi J, Chen Y, Li
S, Sun Y, Li C and Lan X: Expression profiling and validation of
potential reference genes during Paralichthys olivaceus
embryogenesis. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 10:310–318. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cordoba EM, Die JV, Gonzalez-Verdejo CI,
Nadal S and Román B: Selection of reference genes in Hedysarum
coronarium under various stresses and stages of development. Anal
Biochem. 409:236–243. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Schmittgen TD and Zakrajsek BA: Effect of
experimental treatment on housekeeping gene expression: Validation
by real-time, quantitative RT-PCR. J Biochem Biophys Methods.
46:69–81. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dheda K, Huggett JF, Bustin SA, Johnson
MA, Rook G and Zumla A: Validation of housekeeping genes for
normalizing RNA expression in real-time PCR. Biotechniques.
37:112–114. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Radonić A, Thulke S, Mackay IM, Landt O,
Siegert W and Nitsche A: Guideline to reference gene selection for
quantitative real-time PCR. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
313:856–862. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Suzuki T, Higgins PJ and Crawford DR:
Control selection for RNA quantitation. Biotechniques. 29:332–337.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chang E, Shi S, Liu J, Cheng T, Xue L,
Yang X, Yang W, Lan Q and Jiang Z: Selection of reference genes for
quantitative gene expression studies in Platycladus orientalis
(Cupressaceae) Using real-time PCR. PLoS One. 7:e332782012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal
RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S and
Marshak DR: Multilineage potential of adult human mesen-chymal stem
cells. Science. 284:143–147. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tomic S, Djokic J, Vasilijic S, Vucevic D,
Todorovic V, Supic G and Colic M: Immunomodulatory properties of
mesenchymal stem cells derived from dental pulp and dental follicle
are susceptible to activation by toll-like receptor agonists. Stem
Cells Dev. 20:695–708. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ramasamy R, Tong CK, Seow HF, Vidyadaran S
and Dazzi F: The immunosuppressive effects of human bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells target T cell proliferation
but not its effector function. Cell Immunol. 251:131–136. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Che N, Li X, Zhou S, Liu R, Shi D, Lu L
and Sun L: Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells suppress B-cell
proliferation and differentiation. Cell Immunol. 274:46–53. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Spaggiari GM, Capobianco A, Becchetti S,
Mingari MC and Moretta L: Mesenchymal stem cell-natural killer cell
interactions: Evidence that activated NK cells are capable of
killing MSCs, whereas MSCs can inhibit IL-2-induced NK-cell
proliferation. Blood. 107:1484–1490. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F,
Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A and Speleman F: Accurate
normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric
averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol.
3:RESEARCH00342002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Andersen CL, Jensen JL and Ørntoft TF:
Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR
data: A model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes
suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data
sets. Cancer Res. 64:5245–5250. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pfaffl MW, Tichopad A, Prgomet C and
Neuvians TP: Determination of stable housekeeping genes,
differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity:
BestKeeper-Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations.
Biotechnol Lett. 26:509–515. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li X, Bai J, Ji X, Li R, Xuan Y and Wang
Y: Comprehensive characterization of four different populations of
human mesenchymal stem cells as regards their immune properties,
proliferation and differentiation. Int J Mol Med. 34:695–704.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Meirelles Lda S and Nardi NB: Murine
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell: Isolation, in vitro
expansion, and char-acterization. Br J Haematol. 123:702–711. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mane VP, Heuer MA, Hillyer P, Navarro MB
and Rabin RL: Systematic method for determining an ideal
housekeeping gene for real-time PCR analysis. J Biomol Tech.
19:342–347. 2008.
|
|
20
|
Wang T, Liang ZA, Sandford AJ, Xiong XY,
Yang YY, Ji YL and He JQ: Selection of suitable housekeeping genes
for real-time quantitative PCR in CD4 (+) lymphocytes from
asthmatics with or without depression. PloS One. 7:e483672012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Huggett J, Dheda K, Bustin S and Zumla A:
Real-time RT-PCR normalisation; strategies and considerations.
Genes Immun. 6:279–284. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schmittgen TD and Zakrajsek BA: Effect of
experimental treatment on housekeeping gene expression: Validation
by real-time, quantitative RT-PCR. J Biochem Biophys Methods.
46:69–81. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Najar M, Raicevic G, Boufker HI, Fayyad
Kazan H, De Bruyn C, Meuleman N, Bron D, Toungouz M and Lagneaux L:
Mesenchymal stromal cells use PGE2 to modulate activation and
proliferation of lymphocyte subsets: Combined comparison of adipose
tissue, Wharton's Jelly and bone marrow sources. Cell Immunol.
264:171–179. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Colgan J, Asmal M, Neagu M, Yu B,
Schneidkraut J, Lee Y, Sokolskaja E, Andreotti A and Luban J:
Cyclophilin A regulates TCR signal strength in CD4+ T cells via a
proline-directed conformational switch in Itk. Immunity.
21:189–201. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Arora K, Gwinn WM, Bower MA, Watson A,
Okwumabua I, MacDonald HR, Bukrinsky MI and Constant SL:
Extracellular cyclophilins contribute to the regulation of
inflammatory responses. J Immunol. 175:517–522. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Damsker JM, Bukrinsky MI and Constant SL:
Preferential chemotaxis of activated human CD4+ T cells by
extracellular cyclophilin A. J Leukoc Biol. 82:613–618. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|