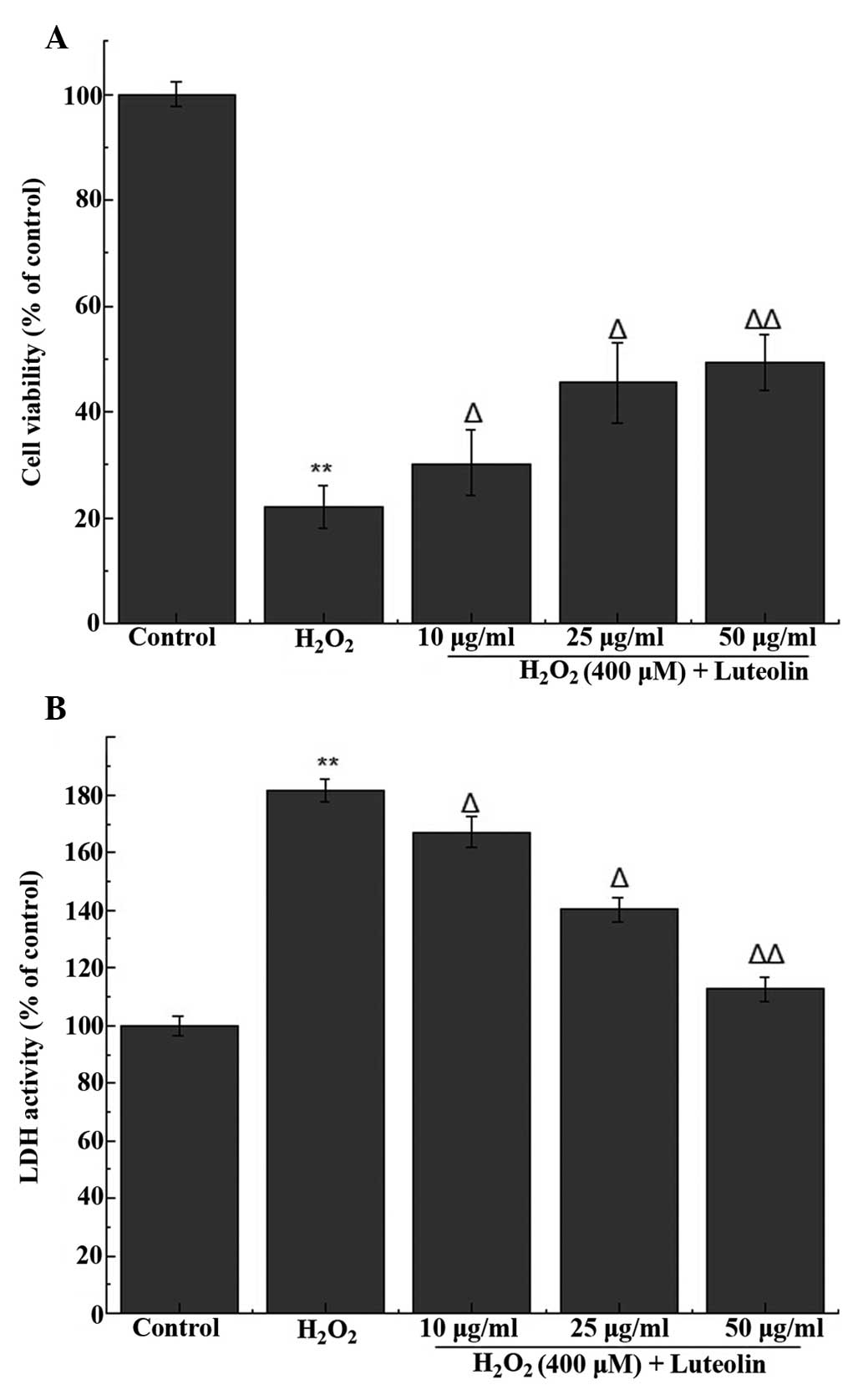
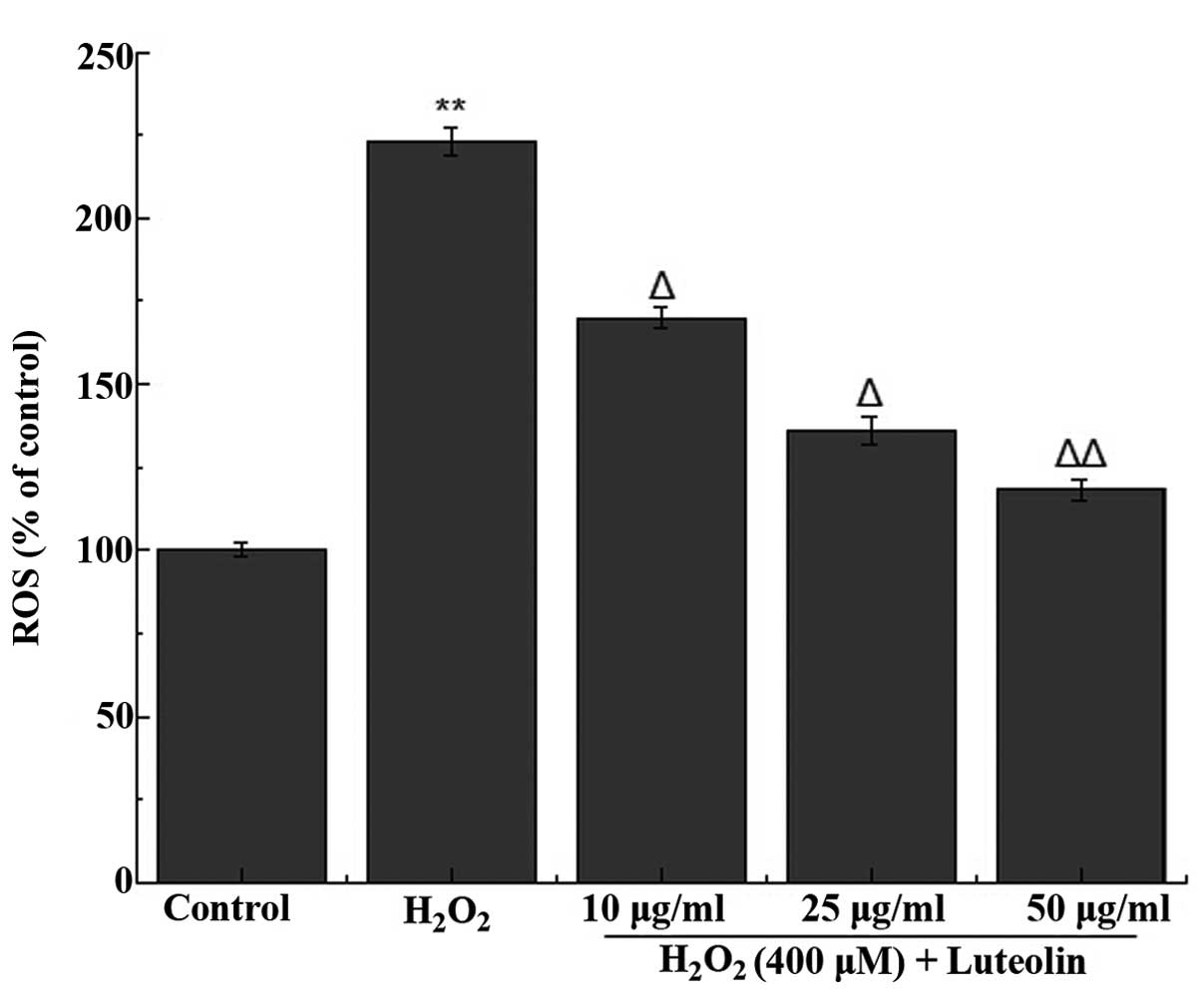
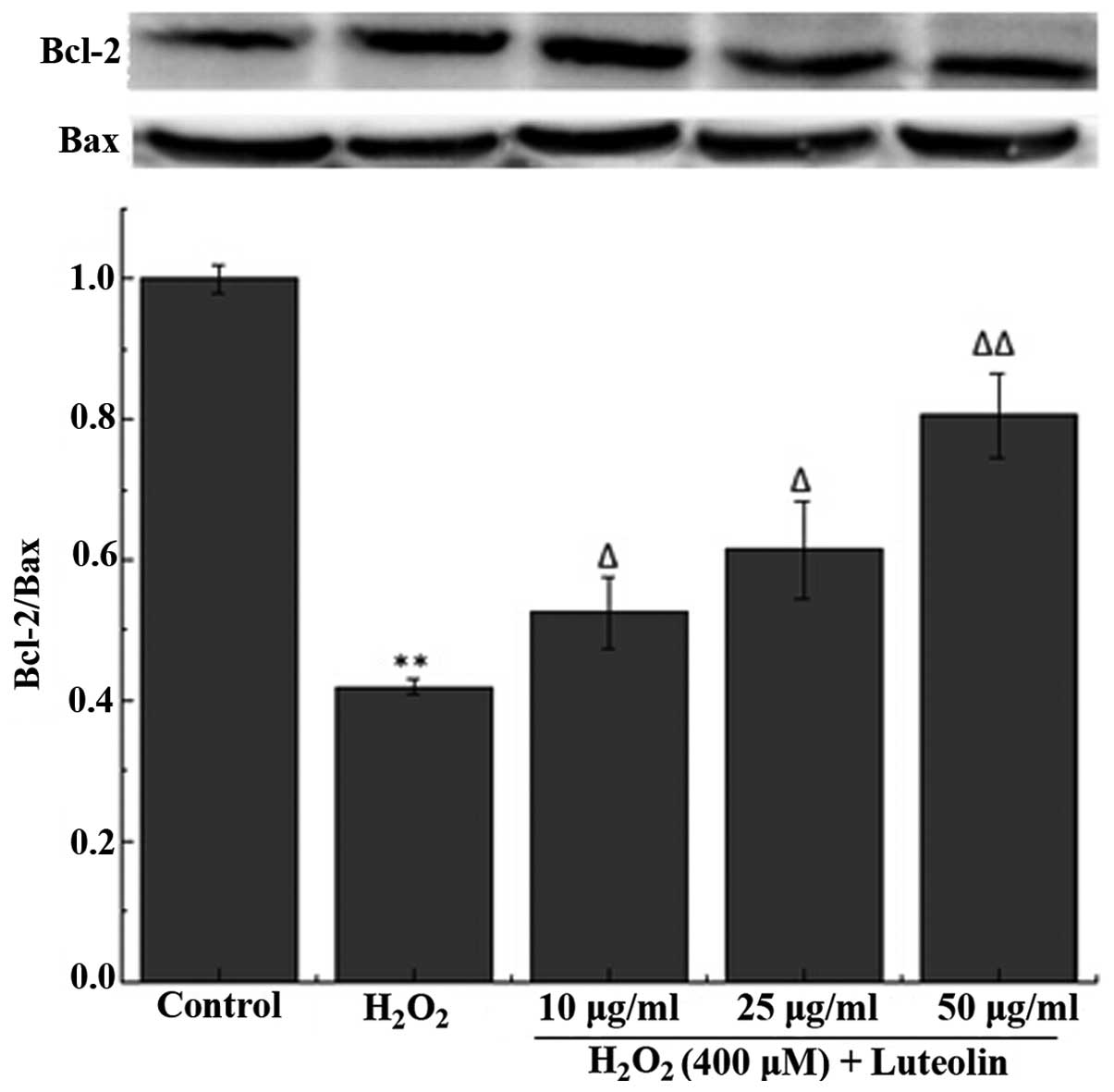
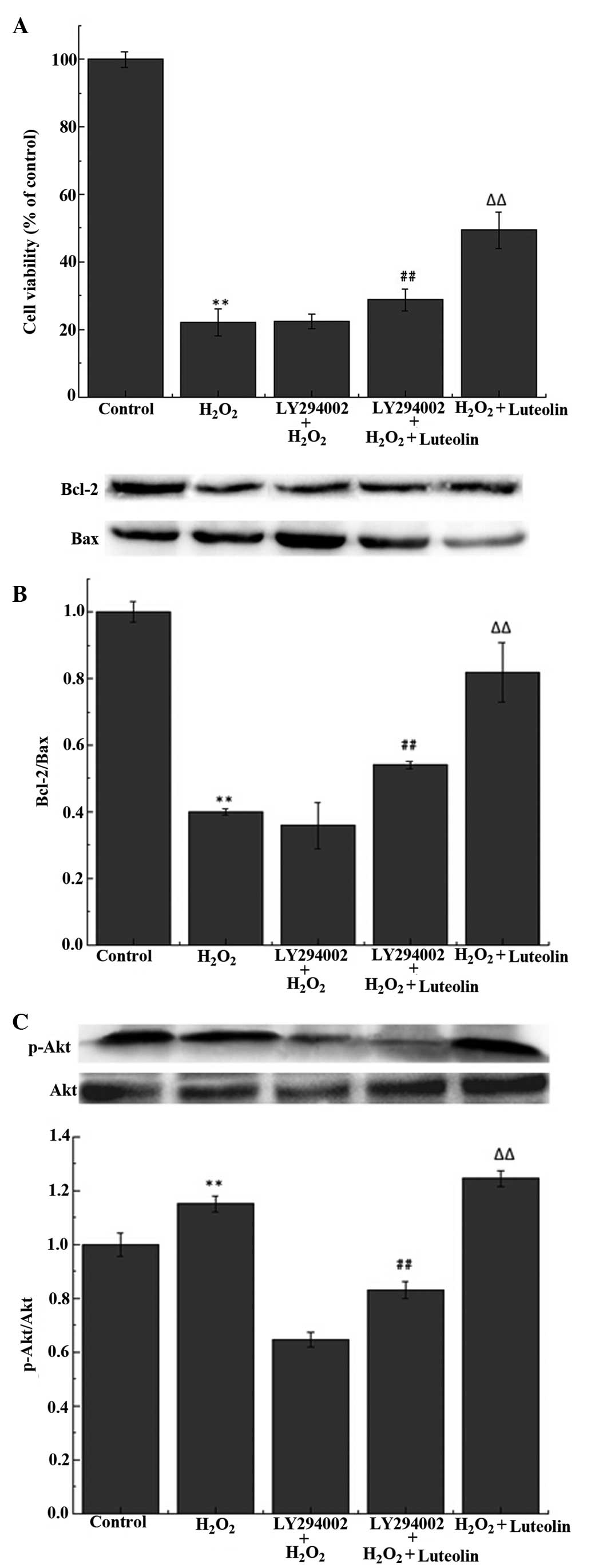
|
1
|
Fahn S and Cohen G: The oxidant stress
hypothesis in Parkinson's disease: Evidence supporting it. Ann
Neurol. 32:804–812. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Smith MA, Perry G, Richey PL, Sayre LM,
Anderson VE, Beal MF and Kowall N: Oxidative damage in Alzheimer's.
Nature. 382:120–121. 1996. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Halliwell B: Oxidative stress and
neurodegeneration: Where are we now? J Neurochem. 97:1634–1658.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li MH, Jang JH, Sun B and Surh YJ:
Protective effects of oligomers of grape seed polyphenols against
beta-amyloid-induced oxidative cell death. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1030:317–329. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Fukui K, Takatsu H, Shinkai T, Suzuki S,
Abe K and Urano S: Appearance of amyloid beta-like substances and
delayed-type apoptosis in rat hippocampus CA1 region through aging
and oxidative stress. J Alzheimers Dis. 8:299–309. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kadowaki H, Nishitoh H, Urano F, Sadamitsu
C, Matsuzawa A, Takeda K, Masutani H, Yodoi J, Urano Y, Nagano T
and Ichijo H: Amyloid beta induces neuronal cell death through
ROS-mediated ASK1 activation. Cell Death Differ. 12:19–24. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Heo SR, Han AM and Kwon YK: p62 protects
SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells against H2O2-induced injury through the
PDK1/Akt pathway. Neurosci Lett. 23;450(1): 45–50. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Satoh T, Sakai N, Enokido Y, Uchiyama Y
and Hatanaka H: Free radical-independent protection by nerve growth
factor and Bcl-2 of PC12 cells from hydrogen peroxide-triggered
apoptosis. J Biochem. 120:540–546. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yu BP and Yang R: Critical evaluation of
the free radical theory of aging. A proposal for the oxidative
stress hypothesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 786(1 Near-Earth Ob): 1–11.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Floyd RA: Antioxidants, oxidative stress,
and degenerative neurological disorders. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med.
222:236–245. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sultana R, Newman S, Mohmmad-Abdul H,
Keller JN and Butterfield DA: Protective effect of the xanthate,
D609, on Alzheimer's amyloid betapeptide (1–42)-induced oxidative
stress in primary neuronal cells. Free Radic Res. 38:449–458. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Koh SH, Kwon H, Park KH, Ko JK, Kim JH,
Hwang MS, Yum YN, Kim OH, Kim J, Kim HT, et al: Protective effect
of diallyl disulfide on oxidative stress-injured neuronally
differentiated PC12 cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 133:176–186.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Choi SJ, Kim MJ, Heo HJ, Hong B, Cho HY,
Kim YJ, Kim HK, Lim ST, Jun WJ, Kim EK and Shin DH: Ameliorating
effect of Gardenia jasminoides extract on amyloid beta
peptide-induced neuronal cell deficit. Mol Cells. 24:113–118.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang HY, Liu YH, Wang HQ, Xu JH and Hu
HT: Puerarin protects PC12 cells against beta-amyloid-induced cell
injury. Cell Biol Int. 32:1230–1237. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Soubra L, Sarkis D, Hilan C and Verger P:
Dietary exposure of children and teenagers to benzoates, sulphites,
butylhydroxyanisol (BHA) and butylhydroxytoluen (BHT) in Beirut
(Lebanon). Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 47:68–77. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Pandurangan AK, Dharmalingam P, Ananda
Sadagopan SK and Ganapasam S: Effect of luteolin on the levels of
glycoproteins during azoxymethane-induced colon carcinogenesis in
mice. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:1569–1573. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jung HA, Jin SE, Min BS, Kim BW and Choi
JS: Anti-inflammatory activity of Korean thistle Cirsium maackii
and its major flavonoid, luteolin 5-O-glucoside. Food Chem Toxicol.
50:2171–2179. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Manju V and Nalini N: Protective role of
luteolin in 1,2-dimeth-ylhydrazine induced experimental colon
carcinogenesis. Cell Biochem Funct. 25:189–194. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Sun GB, Sun X, Wang M, Ye JX, Si JY, Xu
HB, Meng XB, Qin M, Sun J, Wang HW and Sun XB: Oxidative stress
suppression by luteolin-induced heme oxygenase-1 expression.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 265:229–240. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Casagrande F and Darbon JM: Effects of
structurally related flavonoids on cell cycle progression of human
melanoma cells: Regulation of cyclin-dependent kinases CDK2 and
CDK1. Biochem Pharmacol. 61:1205–1215. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Matsui T, Kobayshi M, Hayashida S and
Matsumoto K: Luteolin, a flavone, does not suppress post prandial
blood glucose absorption through the inhalation of
alpha-glucosidase action. Biosci, Biotechnol and Biochem.
66:689–692. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Ji BS and Gao Y: Protective effect of
trihexyphenidyl on hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage in
PC12 cells. Neurosci Lett. 437:50–54. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee YM, Park SH, Shin DI, Hwang JY, Park
B, Park YJ, Lee TH, Chae HZ, Jin BK, Oh TH and Oh YJ: Oxidative
modification of peroxiredoxin is associated with drug-induced
apoptotic signaling in experimental models of Parkinson disease. J
Biol Chem. 283:9986–9998. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Markesbery WR: Oxidative stress hypothesis
in Alzheimer's disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 23:134–147. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jenner P: Oxidative stress in Parkinson's
disease. Ann Neurol. 53(Suppl 3): S26–S36; discussion S36–S38.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Emerit J, Edeas M and Bricaire F:
Neurodegenerative diseases and oxidative stress. Biomed
Pharmacother. 58:39–46. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gozal E, Sachleben LR Jr, Rane MJ, Vega C
and Gozal D: Mild sustained and intermittent hypoxia induce
apoptosis in PC-12 cells via different mechanisms. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 288:C535–C542. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Hirose M, Takatori M, Kuroda Y, Abe M,
Murata E, Isada T, Ueda K, Shigemi K, Shibazaki M, Shimizu F, et
al: Effect of synthetic cell-penetrating peptides on TrkA activity
in PC12 cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 106:107–113. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang J, Zhang QB, Zhang ZS, Zhang JJ and
Li PC: Synthesized phosphorylated and aminated derivatives of
fucoidan and their potential antioxidant activity in vitro. Int J
Biol Macromol. 44:170–174. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Erten SF, Kocak A, Ozdemir I, Aydemir S,
Colak A and Reeder BS: Protective effect of melatonin on
experimental spinal cord ischemia. Spinal Cord. 41:533–538. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Qian H and Liu D: The time course of
malondialdehyde production following impact injury to rat spinal
cord as measured by microdialysis and high pressure liquid
chromatography. Neurochem Res. 22:1231–1236. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Misao J, Hayakawa Y, Ohno M, Kato S,
Fujiwara T and Fujiwara H: Expression of bcl-2 protein, an
inhibitor of apoptosis, and Bax, an accelerator of apoptosis, in
ventricular myocytes of human hearts with myocardial infarction.
Circulation. 94:1506–1512. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang R, Zhang HY and Tang XC: Huperzine A
attenuates cognitive dysfunction and neuronal degeneration caused
by beta-amyloid protein-(1–40) in rat. Eur J Pharmacol.
421:149–156. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H,
Gotoh Y and Greenberg ME: Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples
survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell.
91:231–241. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Martin D, Salinas M, Fujita N, Tsuruo T
and Cuadrado A: Ceramide and reactive oxygen species generated by
H2O2 induce caspase-3-independent degradation
of Akt/protein kinase B. J Biol Chem. 277:42943–42952. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang X, McCullough KD, Franke TF and
Holbrook NJ: Epidermal growth factor receptor-dependent Akt
activation by oxidative stress enhances cell survival. J Biol Chem.
275:14624–14631. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ma R, Xiong N, Huang C, Tang Q, Hu B,
Xiang J and Li G: Erythropoietin protects PC12 cells from
beta-amyloid(25–35)-induced apoptosis via PI3K/Akt signaling
pathway. Neuropharmacology. 56:1027–1034. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|