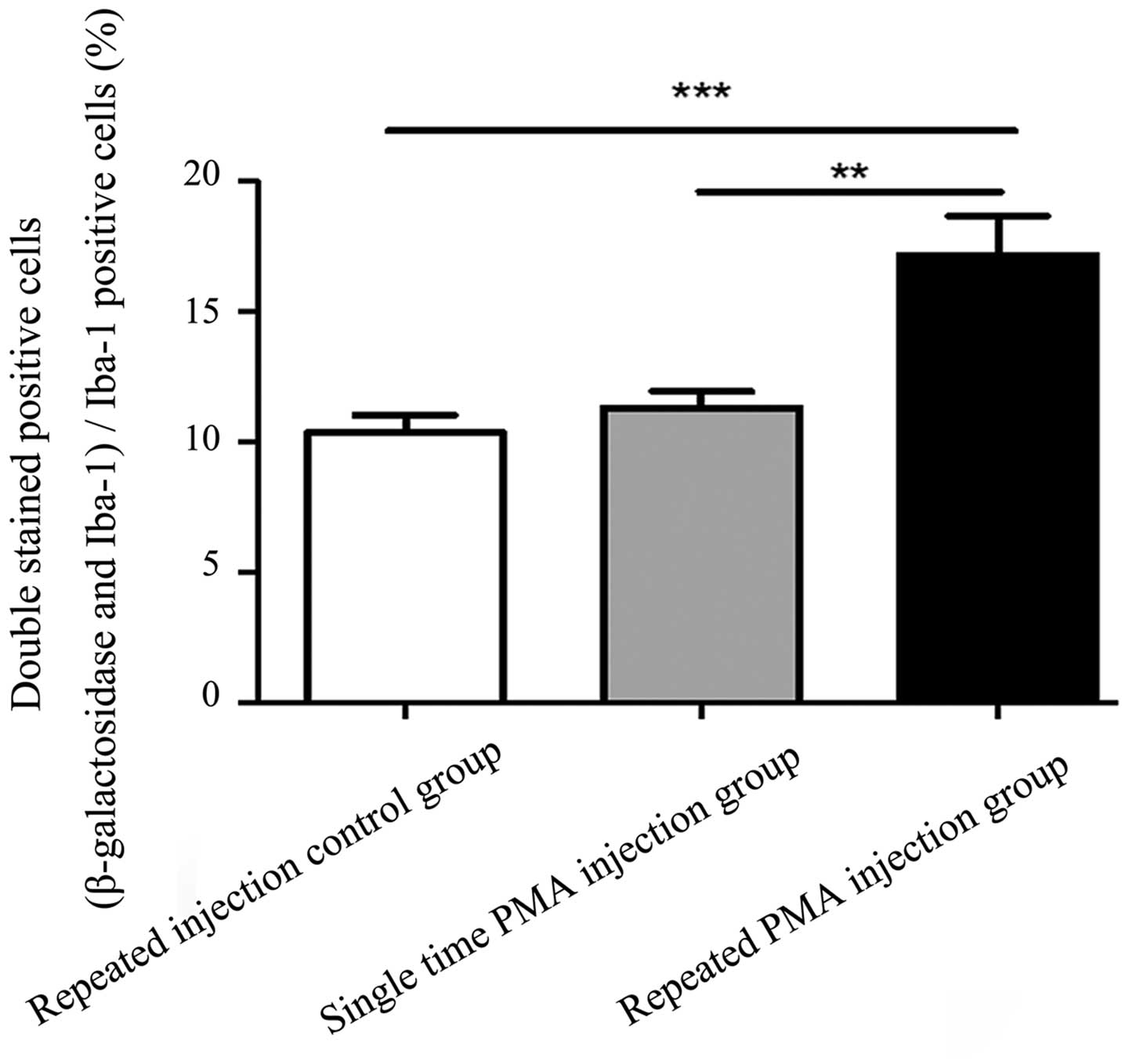
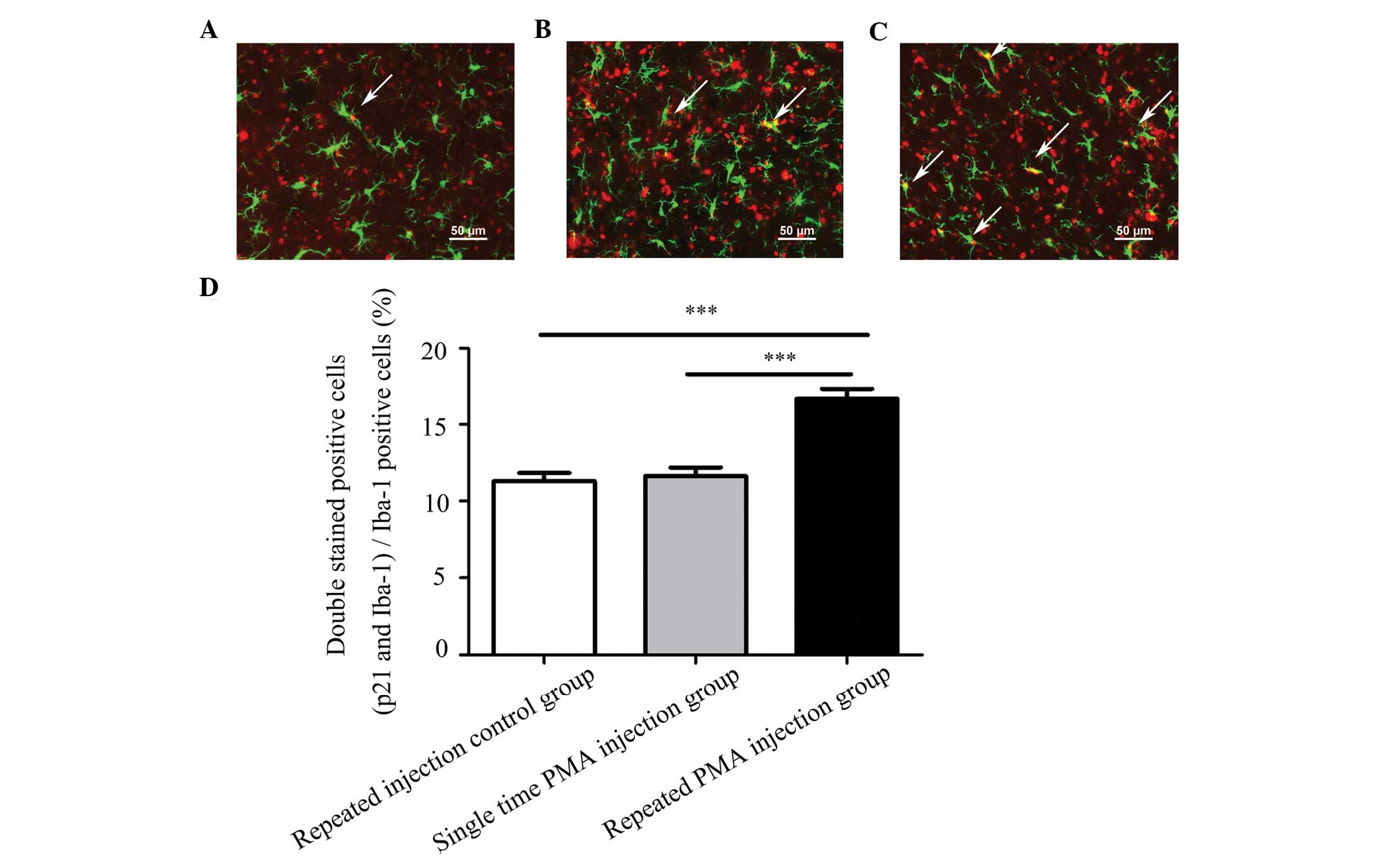
|
1
|
Kielian T: Microglia and chemokines in
infectious diseases of the nervous system: Views and reviews. Front
Biosci. 9:732–750. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kanaan NM, Kordower JH and Collier TJ: Age
and region-specific responses of microglia, but not astrocytes,
suggest a role in selective vulnerability of dopamine neurons after
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine exposure in monkeys.
Glia. 56:1199–1214. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Overmyer M, Helisalmi S, Soininen H,
Laakso M, Riekkinen P Sr and Alafuzoff I: Reactive microglia in
aging and dementia: An immunohistochemical study of postmortem
human brain tissue. Acta Neuropathol. 97:383–392. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Luo XG, Ding JQ and Chen SD: Microglia in
the aging brain: Relevance to neurodegeneration. Mol Neurodegener.
5:122010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sawada M, Sawada H and Nagatsu T: Effects
of aging on neuroprotective and neurotoxic properties of microglia
in neuro-degenerative diseases. Neurodegener Dis. 5:254–256. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Conde JR and Streit WJ: Effect of aging on
the microglial response to peripheral nerve injury. Neurobiol
Aging. 27:1451–1461. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Streit WJ, Sammons NW, Kuhns AJ and Sparks
DL: Dystrophic microglia in the aging human brain. Glia.
45:208–212. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Streit WJ, Miller KR, Lopes KO and Njie E:
Microglial degeneration in the aging brain-bad news for neurons?
Front Biosci. 13:3423–3438. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Olanow CW and Tatton WG: Etiology and
pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Annu Rev Neurosci. 22:123–144.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tha KK, Okuma Y, Miyazaki H, Murayama T,
Uehara T, Hatakeyama R, Hayashi Y and Nomura Y: Changes in
expressions of proinflammatory cytokines IL-1beta, TNF-alpha and
IL-6 in the brain of senescence accelerated mouse (SAM) P8. Brain
Res. 885:25–31. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Campisi J: The biology of replicative
senescence. Eur J Cancer. 33:703–709. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee BY, Han JA, Im JS, Morrone A, Johung
K, Goodwin EC, Kleijer WJ, DiMaio D and Hwang ES:
Senescence-associated beta-galactosidase is lysosomal
beta-galactosidase. Aging Cell. 5:187–195. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Roninson IB: Oncogenic functions of tumour
suppressor p21 (Waf1/Cip1/Sdi1): Association with cell senescence
and tumour-promoting activities of stromal fibroblasts. Cancer
Lett. 179:1–14. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Macip S, Igarashi M, Fang L, Chen A, Pan
ZQ, Lee SW and Aaronson SA: Inhibition of p21-mediated ROS
accumulation can rescue p21-induced senescence. EMBO J.
21:2180–2188. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Campisi J and d'Adda di Fagagna F:
Cellular senescence: When bad things happen to good cells. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 8:729–740. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Blumberg PM: Protein kinase C as the
receptor for the phorbol ester tumor promoters: Sixth Rhoads
memorial award lecture. Cancer Res. 48:1–8. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li YH, Bi HC, Huang L, Jin J, Zhong GP,
Zhou XN and Huang M: Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate inhibits
P-glycoprotein-mediated efflux of digoxin in MDCKII-MDR1 and Caco-2
cell monolayer models. Acta Pharmacologica Sin. 35:283–291. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
O'neill AK, Gallegos LL, Justilien V,
Garcia EL, Leitges M, Fields AP, Hall RA and Newton AC: Protein
kinase Cα promotes cell migration through a PDZ-dependent
interaction with its novel substrate discs large homolog 1 (DLG1).
J Biol Chem. 286:43559–43568. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mason SA, Cozzi SJ, Pierce CJ, Pavey SJ,
Parsons PG and Boyle GM: The induction of senescence-like growth
arrest by protein kinase C-activating diterpene esters in solid
tumor cells. Invest New Drugs. 28:575–586. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Akakura S, Nochajski P, Gao L, Sotomayor
P, Matsui S and Gelman IH: Rb-dependent cellular senescence,
multinucleation and susceptibility to oncogenic transformation
through PKC scaffolding by SSeCKS/AKAP12. Cell Cycle. 9:4656–4665.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Grealish S, Xie L, Kelly M and Dowd E:
Unilateral axonal or terminal injection of 6-hydroxydopamine causes
rapid-onset nigrostriatal degeneration and contralateral motor
impairments in the rat. Brain Res Bull. 77:312–319. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Koziorowski D, Friedman A, Arosio P,
Santambrogio P and Dziewulska D: ELISA reveals a difference in the
structure of substantia nigra ferritin in Parkinson's disease and
incidental lewy body compared to control. Parkinsonism Relat
Disord. 13:214–218. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Itahana K, Zou Y, Itahana Y, Martinez JL,
Beausejour C, Jacobs JJ, Van Lohuizen M, Band V, Campisi J and
Dimri GP: Control of the replicative life span of human fibroblasts
by p16 and the polycomb protein Bmi-1. Mol Cell Biol. 23:389–401.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
West MJ, Slomianka L and Gundersen HJ:
Unbiased stereological estimation of the total number of neurons in
thesubdivisions of the rat hippocampus using the optical
fractionator. Anat Rec. 231:482–497. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pan J, Wang G, Yang HQ, Hong Z, Xiao Q,
Ren RJ, Zhou HY, Bai L and Chen SD: K252a prevents nigral
dopaminergic cell death induced by 6-hydroxydopamine through
inhibition of both mixed-lineage kinase 3/c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase
3 (JNK3) and apoptosis-inducing kinase 1/JNK3 signaling pathways.
Mol Pharmacol. 72:1607–1618. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
German DC and Manaye KF: Midbrain
dopaminergic neurons (nuclei A8, A9 and A10): Three-dimensional
reconstruction in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 331:297–309. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Streit WJ, Braak H, Xue QS and Bechmann I:
Dystrophic (senescent) rather than activated microglial cells are
associated with tau pathology and likely precede neurodegeneration
in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 118:475–485. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Luo XG and Chen SD: The changing phenotype
of microglia from homeostasis to disease. Transl Neurodegener.
1:92012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim YS and Joh TH: Microglia, major player
in the brain inflammation: Their roles in the pathogenesis of
Parkinson's disease. Exp Mol Med. 38:333–347. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Franceschi C, Bonafé M, Valensin S,
Olivieri F, De Luca M, Ottaviani E and De Benedictis G:
Inflamm-aging. An evolutionary perspective on immunosenescence. Ann
N Y Acad Sci. 908:244–254. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Inamizu T, Chang MP and Makinodan T:
Influence of age on the production and regulation of interleukin-1
in mice. Immunology. 55:447–455. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Corsini E, Battaini F, Lucchi L,
Marinovich M, Racchi M, Govoni S and Galli CL: A defective protein
kinase C anchoring system underlying age–zassociated impairment in
TNF-alpha production in rat macrophages. J Immunol. 163:3468–3473.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Plackett TP, Boehmer ED, Faunce DE and
Kovacs EJ: Aging and innate immune cells. J Leukoc Biol.
76:291–299. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dimri GP, Lee X, Basile G, Acosta M, Scott
G, Roskelley C, Medrano EE, Linskens M, Rubelj I and Pereira-Smith
O: A biomarker that identifies senescent human cells in culture and
in aging skin in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:9363–9367. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yu HM, Zhao YM, Luo XG, Feng Y, Ren Y,
Shang H, He ZY, Luo XM, Chen SD and Wang XY: Repeated
lipopolysac-charide stimulation induces cellular senescence in BV2
cells. Neuroimmunomodulation. 19:131–136. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Petiti JP, De Paul AL, Gutiérrez S,
Palmeri CM, Mukdsi JH and Torres AI: Activation of PKC epsilon
induces lactotroph proliferation through ERK1/2 in response to
phorbol ester. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 289:77–84. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Inoue S, Hao Z, Elia AJ, Cescon D, Zhou L,
Silvester J, Snow B, Harris IS, Sasaki M, Li WY, et al:
Mule/Huwe1/Arf-BP1 suppresses Ras-driven tumorigenesis by
preventing c-Myc/Miz1-mediated down-regulation of p21 and p15.
Genes Dev. 27:1101–1114. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mowla S, Pinnock R, Leaner VD, Goding CR
and Prince S: PMA-induced up-regulation of TBX3 is mediated by AP-1
and contributes to breast cancer cell migration. Biochem J.
433:145–153. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Serrano M, Lin AW, Mccurrach ME, Beach D
and Lowe SW: Oncogenic ras provokes premature cell senescence
associated with accumulation of p53 and p16INK4a. Cell. 88:593–602.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
John R, Chand V, Chakraborty S, Jaiswal N
and Nag A: DNA damage induced activation of Cygb stabilizes p53 and
mediates G1 arrest. DNA Repair (Amst). 2014:107–112. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Sarkisian CJ, Keister BA, Stairs DB, Boxer
RB, Moody SE and Chodosh LA: Dose-dependent oncogene-induced
senescence in vivo and its evasion during mammary tumorigenesis.
Nat Cell Biol. 9:493–505. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Courtois-Cox S, Genther Williams SM,
Reczek EE, Johnson BW, McGillicuddy LT, Johannessen CM, Hollstein
PE, MacCollin M and Cichowski K: A negative feedback signaling
network underlies oncogene-induced senescence. Cancer Cell.
10:459–472. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chinta SJ, Lieu CA, Demaria M, Laberge RM,
Campisi J and Andersen JK: Environmental stress, ageing and glial
cell senescence: A novel mechanistic link to Parkinson's disease? J
Intern Med. 273:429–436. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kumar A, Chen SH, Kadiiska MB, Hong JS,
Zielonka J, Kalyanaraman B and Mason RP: Inducible nitric oxide
synthase is key to peroxynitrite-mediated, LPS-induced protein
radical formation in murine microglial BV2 cells. Free Radical Bio
Med. 73:51–59. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Collado M and Serrano M: Senescence in
tumours: Evidence from mice and humans. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:51–57.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Parrinello S, Samper E, Krtolica A,
Goldstein J, Melov S and Campisi J: Oxygen sensitivity severely
limits the replicative lifespan of murine fibroblasts. Nat Cell
Biol. 5:741–747. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chen JH, Ozanne SE and Hales CN: Methods
of cellular senescence induction using oxidative stress. Methods
Mol Biol. 371:179–189. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bitto A, Sell C, Crowe E, Lorenzini A,
Malaguti M, Hrelia S and Torres C: Stress-induced senescence in
human and rodent astrocytes. Exp Cell Res. 316:2961–2968. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Inoue Y, Matsuda T, Sugiyama KI, Izawa S
and Kimura A: Genetic analysis of glutathione peroxidase in
oxidative stress response of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem.
274:27002–27009. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kaneto H, Kajimoto Y, Fujitani Y, Matsuoka
T, Sakamoto K, Matsuhisa M, Yamasaki Y and Hori M: Oxidative stress
induces p21 expression in pancreatic islet cells: Possible
implication in beta-cell dysfunction. Diabetologia. 42:1093–1097.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Croce CM: Oncogenes and cancer. N Engl J
Med. 358:502–511. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Streit WJ and Xue QS: Human CNS immune
senescence and neurodegeneration. Curr Opin Immunol. 29:93–96.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lehmann AR and Carr AM: The
ataxia-telangiectasia gene: A link between checkpoint controls,
neurodegeneration and cancer. Trends Genet. 11:375–377. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Vanacore N, Spila-Alegiani S, Raschetti R
and Meco G: Mortality cancer risk in parkinsonian patients: A
population-based study. Neurology. 52:395–398. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ong EL, Goldacre R and Goldacre M:
Differential risks of cancer types in people with Parkinson's
disease: A national record-linkage study. Eur J Cancer.
50:2456–2462. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|