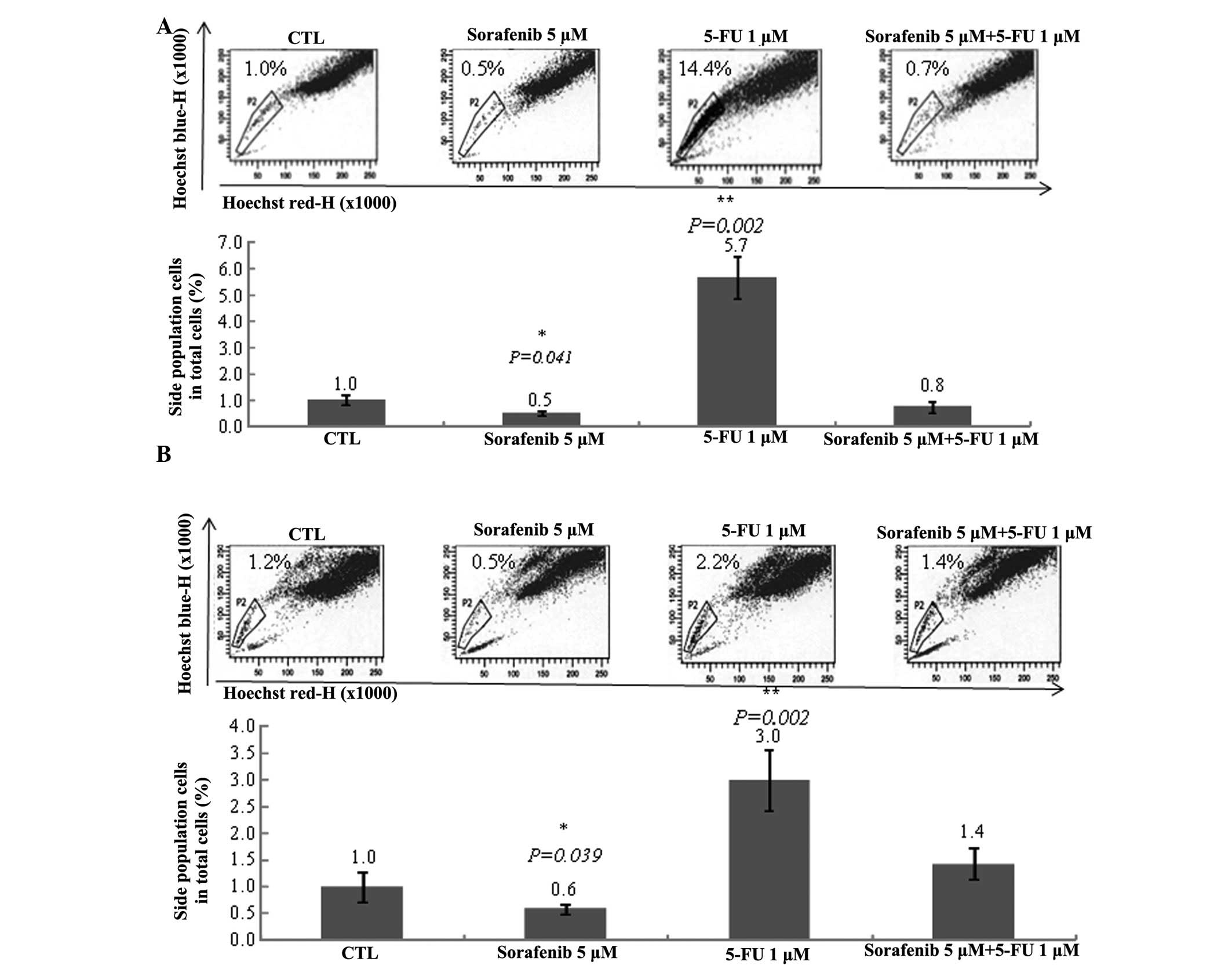
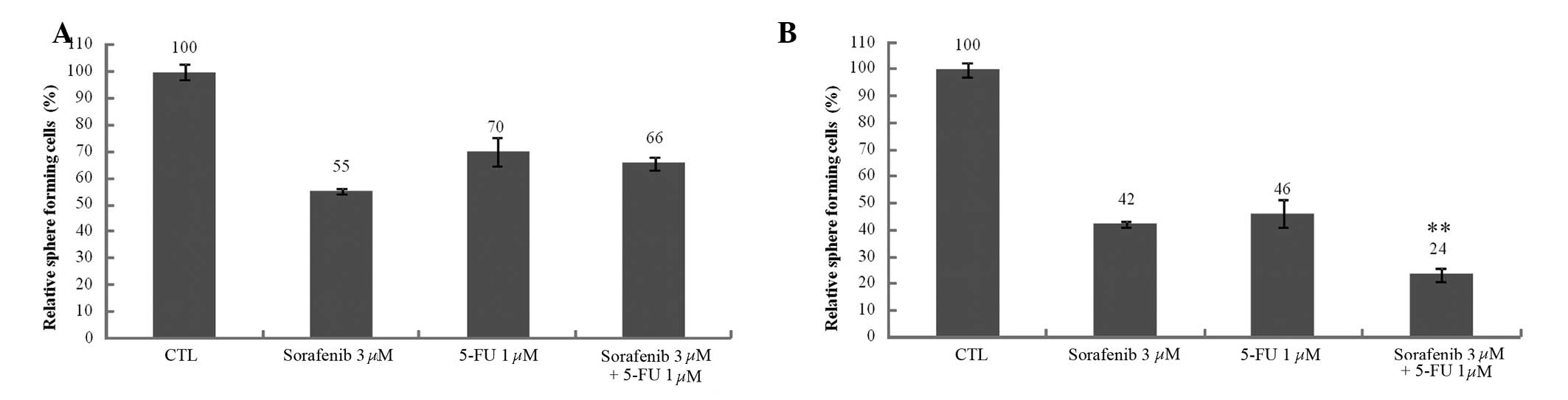
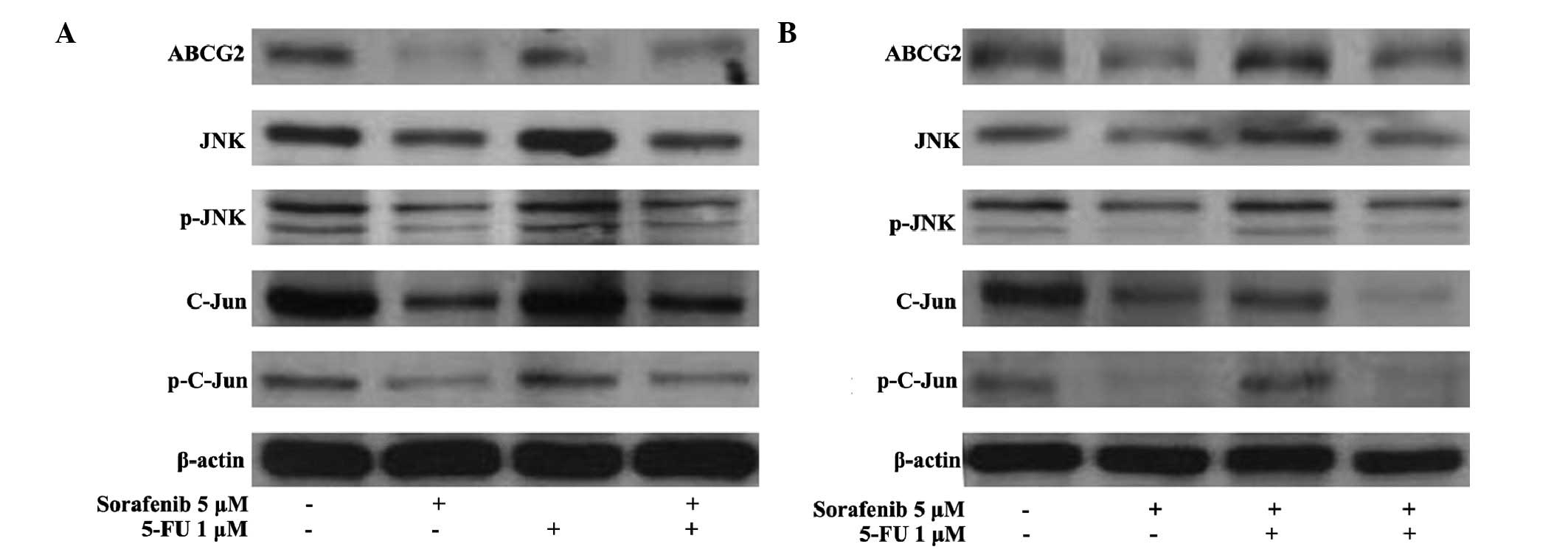
|
1
|
El-Serag HB: Hepatocellular carcinoma. N
Engl J Med. 365:1118–1127. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard
P, Gane E, Blanc JD, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A,
et al: Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. New Engl J
Med. 359:378–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lang L: FDA approves sorafenib for
patients with inoperable liver cancer. Gastroenterology.
134:3792008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kane RC, Farrell AT, Saber H, Tang S,
Williams G, Jee JM, Liang C, Booth B, Chidambaram N, Morse D, et
al: Sorafenib for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma.
Clin Cancer Res. 12:7271–7278. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Min L, He B and Hui L: Mitogen-activated
protein kinases in hepatocellular carcinoma development. Semin
Cancer Biol. 21:10–20. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, Wilkie D,
McNabola A, Rong H, Chen C, Zhang X, Vincent P, McHugh M, et al:
BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and
targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases
involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res.
64:7099–7109. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Scartozzi M, Faloppi L, Svegliati Baroni
G, Loretelli C, Piscaglia F, Iavarone M, Toniutto P, Fava G, De
Minicis S, Mandolesi A, et al: VEGF and VEGFR genotyping in the
prediction of clinical outcome for HCC patients receiving
sorafenib: The ALICE-1 study. Int J Cancer. 135:1247–1256. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu L, Cao Y, Chen C, Zhang X, McNabola A,
Wilkie D, Wilhelm S, Lynch M and Carter C: Sorafenib blocks the
RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor
cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5. Cancer
Res. 66:11851–11858. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xue C, Huang Y, Huang PY, Yu QT, Pan JJ,
Liu LZ, Song XQ, Lin SJ, Wu JX, Zhang JW, et al: Phase II study of
sorafenib in combination with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil to treat
recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ann Oncol.
24:1055–1061. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Petrini I, Lencioni M, Ricasoli M,
Iannopollo M, Orlandini C, Oliveri F, Bartolozzi C and Ricci S:
Phase II trial of sorafenib in combination with 5-fluorouracil
infusion in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 69:773–780. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bonnet D and Dick JE: Human acute myeloid
leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a
primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat Med. 3:730–737. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF and
Weissman IL: Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature.
414:105–111. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Seki E, Brenner DA and Karin M: A liver
full of JNK: Signaling in regulation of cell function and disease
pathogenesis, and clinical approaches. Gastroenterology.
143:307–320. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Telbisz Á, Hegedüs C, Váradi A, Sarkadi B
and Özvegy-Laczka C: Regulation of the function of the human ABCG2
multidrug transporter by cholesterol and bile acids: Effects of
mutations in potential substrate and steroid binding sites. Drug
Metab Dispos. 42:575–585. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yoon CH, Kim MJ, Kim RK, Lim EJ, Choi KS,
An S, Hwang SG, Kang SG, Suh Y, Park MJ and Lee SJ: c-Jun
N-terminal kinase has a pivotal role in the maintenance of
self-renewal and tumorigenicity in glioma stem-like cells.
Oncogene. 31:4655–4666. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jia Q, Zhang X, Deng T and Gao J: Positive
correlation of Oct4 and ABCG2 to chemotherapeutic resistance in
CD90(+) CD133(+) liver cancer stem cells.
Cell Reprogram. 15:143–150. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sukowati CH, Rosso N, Pascut D, Anfuso B,
Torre G, Francalanci P, Crocè LS and Tiribelli C: Gene and
functional upregulation of the BCRP/ABCG2 transporter in
hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Gastroenterol. 12:1602012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sancho R, Nateri AS, de Vinuesa AG,
Aguilera C, Nye E, Spencer-Dene B and Behrens A: JNK signalling
modulates intestinal homeostasis and tumourigenesis in mice. EMBO
J. 28:1843–1854. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mucha SR, Rizzani A, Gerbes AL, Camaj P,
Thasler WE, Bruns CJ, Eichhorst ST, Gallmeier E, Kolligs FT, Göke B
and De Toni EN: JNK inhibition sensitises hepatocellular carcinoma
cells but not normal hepatocytes to the TNF-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand. Gut. 58:688–698. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Goodell MA: Multipotential stem cells and
'side population' cells. Cytotherapy. 4:507–508. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Qiu X, Wang Z, Li Y, Miao Y, Ren Y and
Luan Y: Characterization of sphere-forming cells with stem-like
properties from the small cell lung cancer cell line H446. Cancer
Lett. 323:161–170. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ma S: Biology and clinical implications of
CD133(+) liver cancer stem cells. Exp Cell Res.
319:126–132. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lee JH, Shim JW, Choi YJ, Heo K and Yang
K: The combination of sorafenib and radiation preferentially
inhibits breast cancer stem cells by suppressing HIF-1α expression.
Oncol Rep. 29:917–924. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Carra E, Barbieri F, Marubbi D, Pattarozzi
A, Favoni RE, Florio T and Daga A: Sorafenib selectively depletes
human glioblastoma tumor-initiating cells from primary cultures.
Cell Cycle. 12:491–500. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|