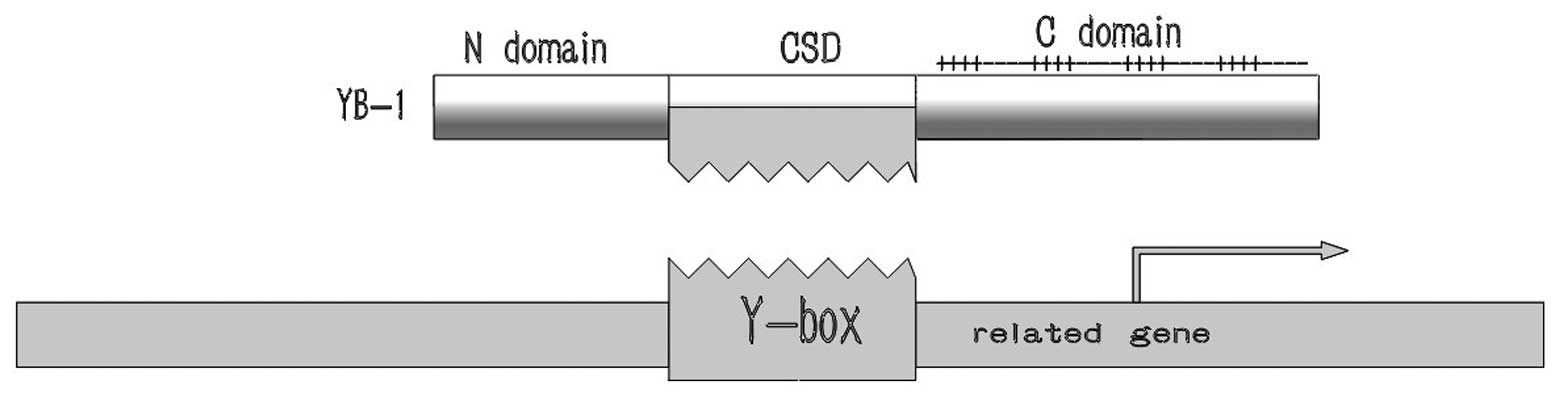
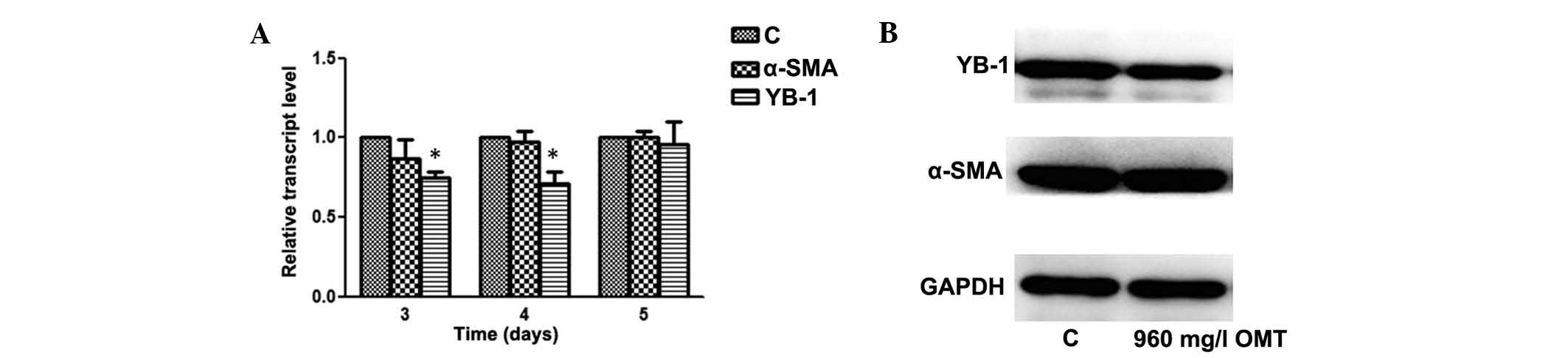
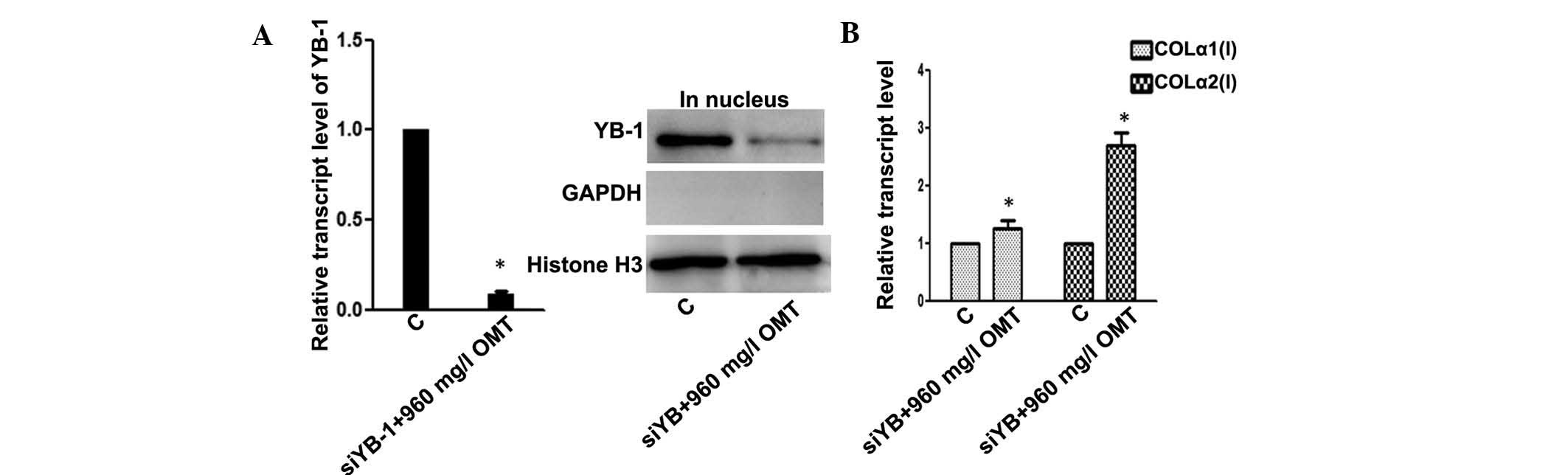
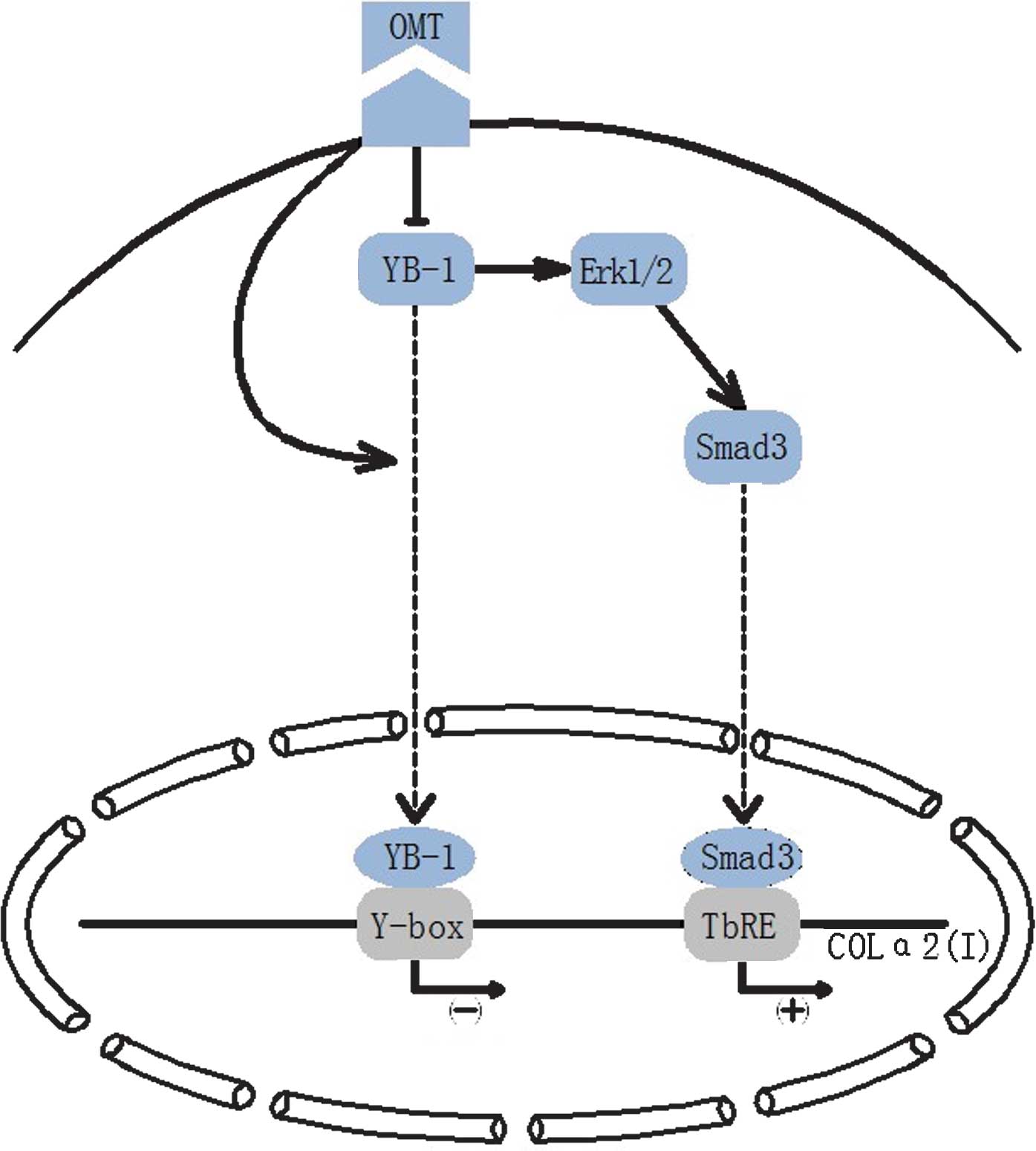
|
1
|
Krohn R, Raffetseder U, Bot I, Zernecke A,
Shagdarsuren E, Liehn EA, van Santbrink PJ, Nelson PJ, Biessen EA,
Mertens PR and Weber C: Y-box binding protein-1 controls CC
chemokine ligand-5 (CCL5) expression in smooth muscle cells and
contributes to neointima formation in atherosclerosis-prone mice.
Circulation. 116:1812–1820. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Stratford AL, Habibi G, Astanehe A, Jiang
H, Hu K, Park E, Shadeo A, Buys TP, Lam W, Pugh T, et al: Epidermal
growth factor receptor (EGFR) is transcriptionally induced by the
Y-box binding protein-1 (YB-1) and can be inhibited with Iressa in
basal-like breast cancer, providing a potential target for therapy.
Breast Cancer Res. 9:R612007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Harada M, Kotake Y, Ohhata T, Kitagawa K,
Niida H, Matsuura S, Funai K, Sugimura H, Suda T and Kitagawa M:
YB-1 promotes transcription of cyclin D1 in human non-small-cell
lung cancers. Genes Cells. 19:504–516. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gaudreault I, Guay D and Lebel M: YB-1
promotes strand separation in vitro of duplex DNA containing either
mispaired bases or cisplatin modifications, exhibits
endonucleolytic activities and binds several DNA repair proteins.
Nucleic Acids Res. 32:316–327. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
En-Nia A, Yilmaz E, Klinge U, Lovett DH,
Stefanidis I and Mertens PR: Transcription factor YB-1 mediates DNA
polymerase alpha gene expression. J Biol Chem. 280:7702–7711. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Stein U, Jürchott K, Walther W, Bergmann
S, Schlag PM and Royer HD: Hyperthermia-induced nuclear
translocation of transcription factor YB-1 leads to enhanced
expression of multidrug resistance-related ABC transporters. J Biol
Chem. 276:28562–28569. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sengupta S, Mantha AK, Mitra S and Bhakat
KK: Human AP endonuclease (APE1/Ref-1) and its acetylation regulate
YB-1-p300 recruitment and RNA polymerase II loading in the
drug-induced activation of multidrug resistance gene MDR1.
Oncogene. 30:482–493. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Didier DK, Schiffenbauer J, Woulfe SL,
Zacheis M and Schwartz BD: Characterization of the cDNA encoding a
protein binding to the major histocompatibility complex class II Y
box. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 85:7322–7326. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kuwano M, Oda Y, Izumi H, Yang SJ, Uchiumi
T, Iwamoto Y, Toi M, Fujii T, Yamana H, Kinoshita H, et al: The
role of nuclear Y-box binding protein 1 as a global marker in drug
resistance. Mol Cancer Ther. 3:1485–1492. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jurchott K, Bergmann S, Stein U, Walther
W, Janz M, Manni I, Piaggio G, Fietze E, Dietel M and Royer HD:
YB-1 as a cell cycle-regulated transcription factor facilitating
cyclin A and cyclin B1 gene expression. J Biol Chem.
278:27988–27996. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Eliseeva IA, Kim ER, Guryanov SG,
Ovchinnikov LP and Lyabin DN: Y-box-binding protein 1 (YB-1) and
its functions. Biochemistry (Mosc). 76:1402–1433. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ghiassi-Nejad Z, Hernandez-Gea V, Woodrell
C, Lang UE, Dumic K, Kwong A and Friedman SL: Reduced hepatic
stellate cell expression of Kruppel-like factor 6 tumor suppressor
isoforms amplifies fibrosis during acute and chronic rodent liver
injury. Hepatology. 57:786–796. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sun W, Hou F, Panchenko MP and Smith BD: A
member of the Y-box protein family interacts with an upstream
element in the alpha1(I) collagen gene. Matrix Biol. 20:527–541.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Norman JT, Lindahl GE, Shakib K, En-Nia A,
Yilmaz E and Mertens PR: The Y-box binding protein YB-1 suppresses
collagen alpha 1(I) gene transcription via an evolutionarily
conserved regulatory element in the proximal promoter. J Biol Chem.
276:29880–29890. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Higashi K, Inagaki Y, Suzuki N, Mitsui S,
Mauviel A, Kaneko H and Nakatsuka I: Y-box-binding protein YB-1
mediates transcriptional repression of human alpha 2(I) collagen
gene expression by interferon-gamma. J Biol Chem. 278:5156–5162.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Inagaki Y, Higashiyama R and Higashi K:
Novel anti-fibrotic modalities for liver fibrosis: Molecular
targeting and regenerative medicine in fibrosis therapy. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 27(Suppl 2): S85–S88. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Homer C, Knight DA, Hananeia L, Sheard P,
Risk J, Lasham A, Royds JA and Braithwaite AW: Y-box factor YB1
controls p53 apoptotic function. Oncogene. 24:8314–8325. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Koike K, Uchiumi T, Ohga T, Toh S, Wada M,
Kohno K and Kuwano M: Nuclear translocation of the Y-box binding
protein by ultraviolet irradiation. FEBS Lett. 417:390–394. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Higashi K, Tomigahara Y, Shiraki H, Miyata
K, Mikami T, Kimura T, Moro T, Inagaki Y and Kaneko H: A novel
small compound that promotes nuclear translocation of YB-1
ameliorates experimental hepatic fibrosis in mice. J Biol Chem.
286:4485–4492. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Chen XS, Wang GJ, Cai X, Yu HY and Hu YP:
Inhibition of hepatitis B virus by oxymatrine in vivo. World J
Gastroenterol. 7:49–52. 2001.
|
|
21
|
Pei X, Wang W, Miao N, Xu M, Zhang C, Sun
M, Xu M and Liu Z: The protective effects of the combination of
sodium ferulate and oxymatrine on ethanol-induced liver damage in
mice. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 37:423–430. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang B, Niu W, Xu D, Li Y, Liu M, Wang Y,
Luo Y, Zhao P, Liu Y, Dong M, Sun R, et al: Oxymatrine prevents
hypoxia- and monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats.
Free Radic Biol Med. 69:198–207. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang W, Zeng M, Fan Z, Mao Y, Song Y, Jia
Y, Lu L, Chen CW, Peng YS and Zhu HY: Prophylactic and therapeutic
effect of oxymatrine on D-galactosamine-induced rat liver fibrosis.
Chinese Journal of Hepatology. 10:193–196. 2002.In Chinese.
|
|
24
|
Zheng P, Niu FL, Liu WZ, Shi Y and Lu LG:
Anti-inflammatory mechanism of oxymatrine in dextran sulfate
sodium-induced colitis of rats. World J Gastroenterol.
11:4912–4915. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dong XQ, Du Q, Yu WH, Zhang ZY, Zhu Q, Che
ZH, Chen F, Wang H and Chen J: Anti-inflammatory effects of
oxymatrine through inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa B and
mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in
lipopolysac-charide-induced BV2 microglia cells. Iran J Pharm Res.
12:165–174. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang J, Wang M, Zhang Z, Luo Z, Liu F and
Liu J: Celecoxib derivative OSU-03012 inhibits the proliferation
and activation of hepatic stellate cells by inducing cell
senescence. Mol Med Rep. 11:3021–3026. 2015.
|
|
27
|
Chemin I and Zoulim F: Hepatitis B virus
induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 286:52–59. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tacke F, Kanig N, En-Nia A, Kaehne T,
Eberhardt CS, Shpacovitch V, Trautwein C and Mertens PR: Y-box
protein-1/p18 fragment identifies malignancies in patients with
chronic liver disease. BMC Cancer. 11:1852011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yasen M, Kajino K, Kano S, Tobita H,
Yamamoto J, Uchiumi T, Kon S, Maeda M, Obulhasim G, Arii S and Hino
O: The up-regulation of Y-box binding proteins (DNA binding protein
A and Y-box binding protein-1) as prognostic markers of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 11:7354–7361. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chai NL, Fu Q, Shi H, Cai CH, Wan J, Xu SP
and Wu BY: Oxymatrine liposome attenuates hepatic fibrosis via
targeting hepatic stellate cells. World J Gastroenterol.
18:4199–4206. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen X, Sun R, Hu J, Mo Z, Yang Z, Liao D
and Zhong N: Attenuation of bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis by
oxymatrine is associated with regulation of fibroblast
proliferation and collagen production in primary culture. Basic
Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 103:278–286. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Huang XY and Chen CX: Effect of
oxymatrine, the active component from Radix Sophorae flavescentis
(Kushen), on ventricular remodeling in spontaneously hypertensive
rats. Phytomedicine. 20:202–212. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Raman M, Chen W and Cobb MH: Differential
regulation and properties of MAPKs. Oncogene. 26:3100–3112. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yoon S and Seger R: The extracellular
signal-regulated kinase: Multiple substrates regulate diverse
cellular functions. Growth Factors. 24:21–44. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Imada K, Shiota M, Kohashi K, Kuroiwa K,
Song Y, Sugimoto M, Naito S and Oda Y: Mutual regulation between
Raf/MEK/ERK signaling and Y-box-binding protein-1 promotes prostate
cancer progression. Clin Cancer Res. 19:4638–4650. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lee C, Dhillon J, Wang MY, Gao Y, Hu K,
Park E, Astanehe A, Hung MC, Eirew P, Eaves CJ and Dunn SE:
Targeting YB-1 in HER-2 overexpressing breast cancer cells induces
apoptosis via the mTOR/STAT3 pathway and suppresses tumor growth in
mice. Cancer Res. 68:8661–8666. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhao BX, Sun YB, Wang SQ, Duan L, Huo QL,
Ren F and Li GF: Grape seed procyanidin reversal of p-glycoprotein
associated multi-drug resistance via down-regulation of nf-κb and
MAPK/ERK mediated YB-1 activity in A2780/T cells. PLoS One.
8:e710712013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Hayashida T, Decaestecker M and Schnaper
HW: Cross-talk between ERK MAP kinase and Smad signaling pathways
enhances TGF-beta-dependent responses in human mesangial cells.
FASEB J. 17:1576–1578. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|