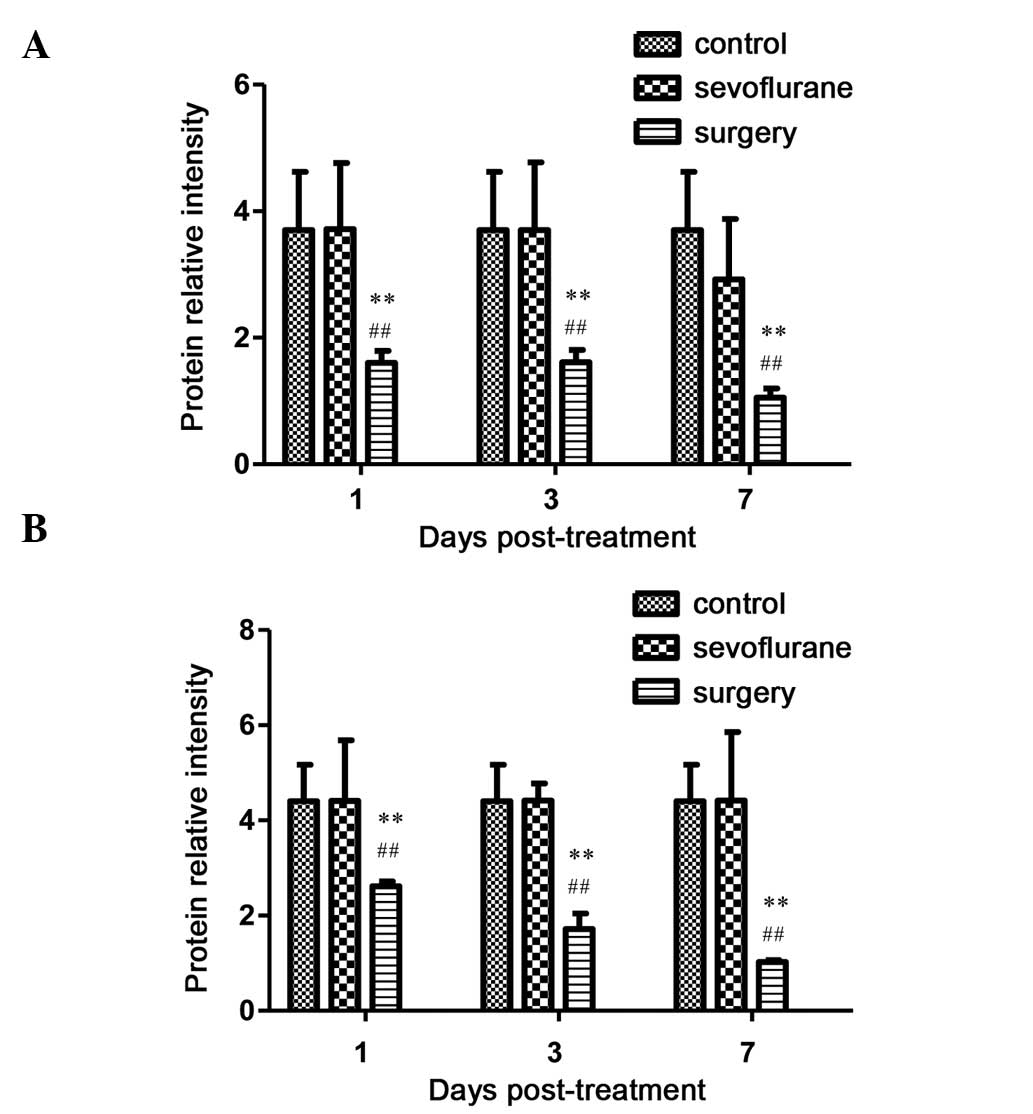
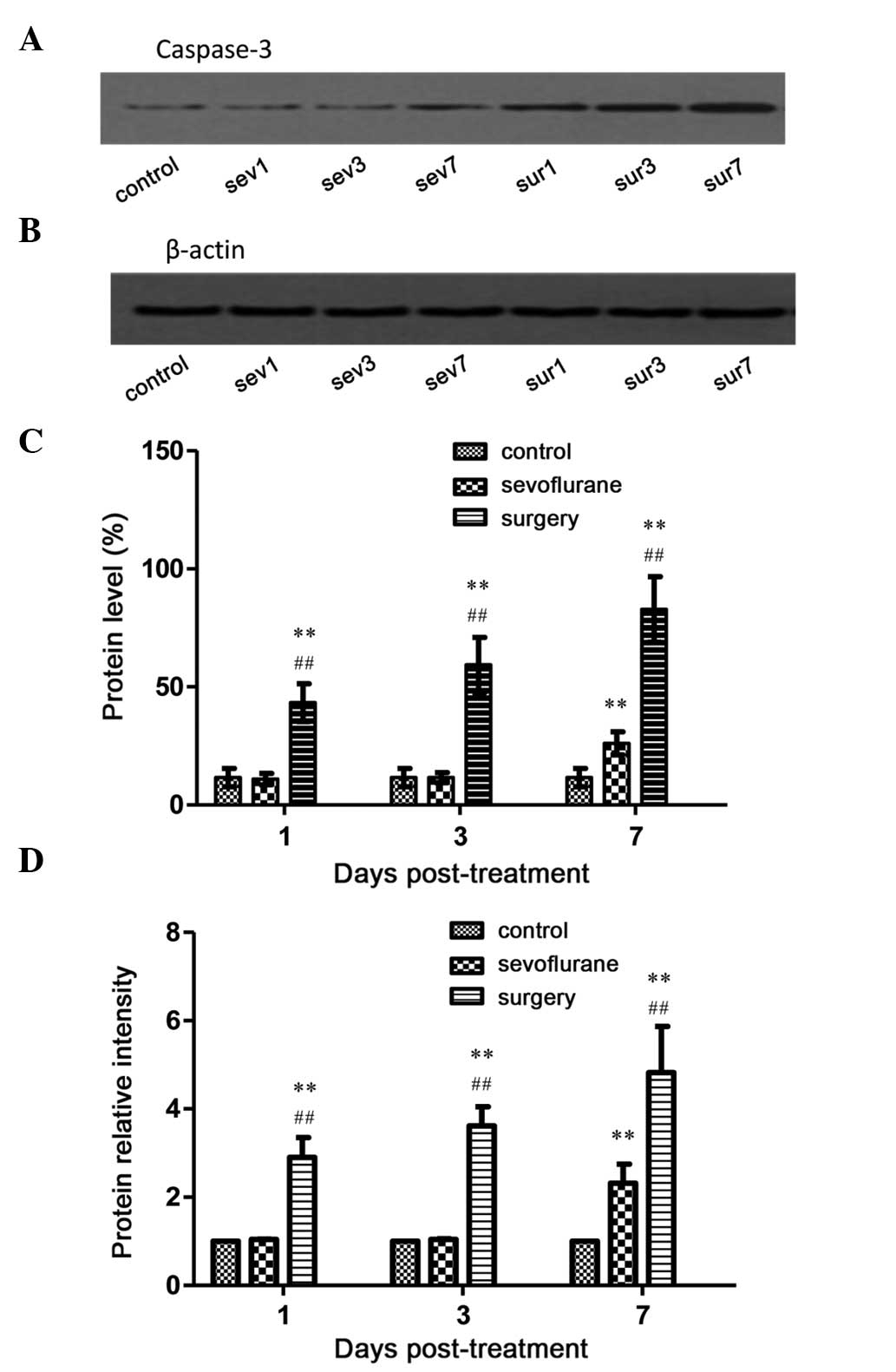
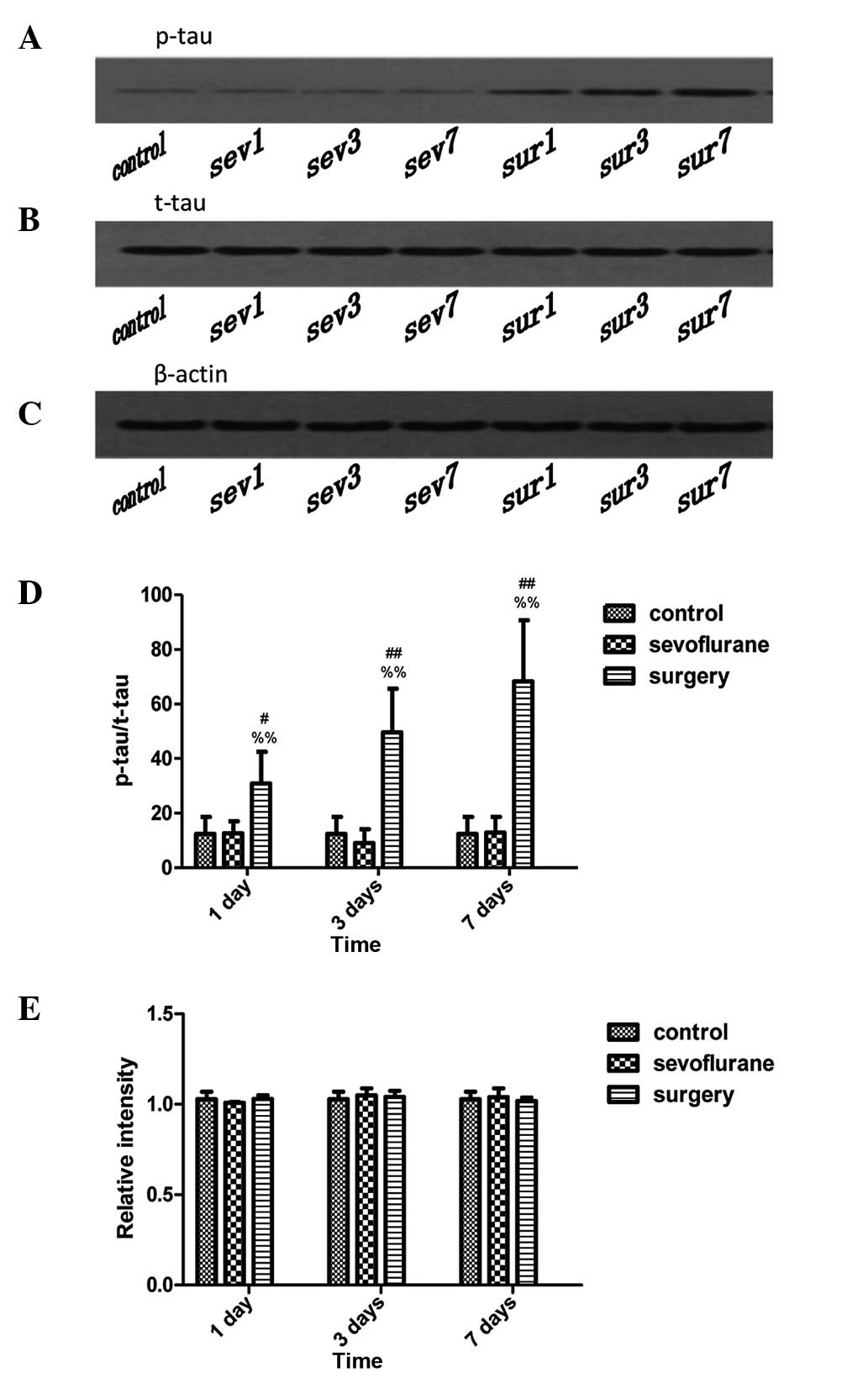
|
1
|
Sarbassov DD, Guertin DA, Ali SM and
Sabatini DM: Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the
rictor-mTOR complex. Science. 307:1098–1101. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schmelzle T and Hall MN: TOR, a central
controller of cell growth. Cell. 103:253–262. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Burnett PE, Barrow RK, Cohen NA, Snyder SH
and Sabatini DM: RAFT1 phosphorylation of the translational
regulators p70 S6 kinase and 4E-BP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:1432–1437. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tang SJ, Reis G, Kang H, Gingras AC,
Sonenberg N and Schuman EM: A rapamycin-sensitive signaling pathway
contributes to long-term synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:467–472. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Abel T and Lattal KM: Molecular mechanisms
of memory acquisition, consolidation and retrieval. Curr Opin
Neurobiol. 11:180–187. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Parsons RG, Gafford GM and Helmstetter FJ:
Translational control via the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway
is critical for the formation and stability of long-term fear
memory in amygdala neurons. J Neurosci. 26:12977–12983. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ehninger D, Han S, Shilyansky C, Zhou Y,
Li W, Kwiatkowski DJ, Ramesh V and Silva AJ: Reversal of learning
deficits in a Tsc2+/− mouse model of tuberous sclerosis. Nat Med.
14:843–848. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Masters CL, Cappai R, Barnham KJ and
Villemagne VL: Molecular mechanisms for Alzheimer's disease:
Implications for neuroimaging and therapeutics. J Neurochem.
97:1700–1725. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bohnen N, Warner MA, Kokmen E and Kurland
LT: Early and midlife exposure to anesthesia and age of onset of
Alzheimer's disease. Int J Neurosci. 77:181–185. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dong Y, Zhang G, Zhang B, Moir RD, Xia W,
Marcantonio ER, Culley DJ, Crosby G, Tanzi RE and Xie Z: The common
inhalational anesthetic sevoflurane induces apoptosis and increases
beta-amyloid protein levels. Arch Neurol. 66:620–631. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu Y, Pan N, Ma Y, Zhang S, Guo W, Li H,
Zhou J, Liu G and Gao M: Inhaled sevoflurane may promote
progression of amnestic mild cognitive impairment: A prospective,
randomized parallel-group study. Am J Med Sci. 345:355–360. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Li X, Alafuzoff I, Soininen H, Winblad B
and Pei JJ: Levels of mTOR and its downstream targets 4E-BP1, eEF2,
and eEF2 kinase in relationships with tau in Alzheimer's disease
brain. FEBS J. 272:4211–4220. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Langstrom NS, Anderson JP, Lindroos HG,
Winblad B and Wallace WC: Alzheimer's disease-associated reduction
of polysomal mRNA translation. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 5:259–269.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ding Q, Markesbery WR, Chen Q, Li F and
Keller JN: Ribosome dysfunction is an early event in Alzheimer's
disease. J Neurosci. 25:9171–9175. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Swiech L, Perycz M, Malik A and Jaworski
J: Role of mTOR in physiology and pathology of the nervous system.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1784:116–132. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Meske V, Albert F and Ohm TG: Coupling of
mammalian target of rapamycin with phosphoinositide 3-kinase
signaling pathway regulates protein phosphatase 2A- and glycogen
synthase kinase-3-dependent phosphorylation of Tau. J Biol Chem.
283:100–109. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Khurana V, Lu Y, Steinhilb ML, Oldham S,
Shulman JM and Feany MB: TOR-mediated cell-cycle activation causes
neuro-degeneration in a Drosophila tauopathy model. Curr Biol.
16:230–241. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lafay-Chebassier C, Paccalin M, Page G,
Barc-Pain S, Perault-Pochat MC, Gil R, Pradier L and Hugon J:
mTOR/p70S6k signalling alteration by Abeta exposure as well as in
APP-PS1 transgenic models and in patients with Alzheimer's disease.
J Neurochem. 94:215–225. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tanaka H, Hashizume K, Enosawa S and
Suzuki S: Successful transplantation of a 20% partial liver graft
in rats: A technical innovation. J Surg Res. 110:409–412. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu Y, Gao M, Ma L, Zhang L and Pan N:
Sevoflurane alters the expression of receptors and enzymes involved
in Aβ clearance in rats. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 57:903–910. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhou W, Wang G, Zhao X, Xiong F, Zhou S,
Peng J, Cheng Y, Xu S and Xu X: A multiplex qPCR gene dosage assay
for rapid genotyping and large-scale population screening for
deletional α-thalassemia. J Mol Diagn. 15:642–651. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li M, Yong-Zhe L, Ya-Qun M, Sheng-Suo Z,
Li-Tao Z and Ning-Ling P: Ulinastatin alleviates neuroinflammation
but fails to improve cognitive function in aged rats following
partial hepatectomy. Neurochem Res. 38:1070–1077. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kandel ER: The molecular biology of memory
storage: A dialogue between genes and synapses. Science.
294:1030–1038. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Steward O and Schuman EM: Protein
synthesis at synaptic sites on dendrites. Annu Rev Neurosci.
24:299–325. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gong R, Park CS, Abbassi NR and Tang SJ:
Roles of glutamate receptors and the mammalian target of rapamycin
(mTOR) signaling pathway in activity-dependent dendritic protein
synthesis in hippocampal neurons. J Biol Chem. 281:18802–18815.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dash PK, Orsi SA and Moore AN: Spatial
memory formation and memory-enhancing effect of glucose involves
activation of the tuberous sclerosis complex-Mammalian target of
rapamycin pathway. J Neurosci. 26:8048–8056. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lafay-Chebassier C, Pérault-Pochat MC,
Page G, Rioux Bilan A, Damjanac M, Pain S, Houeto JL, Gil R and
Hugon J: The immunosuppressant rapamycin exacerbates neurotoxicity
of Abeta peptide. J Neurosci Res. 84:1323–1334. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
An WL, Cowburn RF, Li L, Braak H,
Alafuzoff I, Iqbal K, Iqbal IG, Winblad B and Pei JJ: Up-regulation
of phosphorylated/activated p70 S6 kinase and its relationship to
neurofibrillary pathology in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol.
163:591–607. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou XW, Tanila H and Pei JJ: Parallel
increase in p70 kinase activation and tau phosphorylation (S262)
with Abeta overproduction. FEBS Lett. 582:159–164. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Planel E, Bretteville A, Liu L, Virag L,
Du AL, Yu WH, Dickson DW, Whittington RA and Duff KE: Acceleration
and persistence of neurofibrillary pathology in a mouse model of
tauopathy following anesthesia. FASEB J. 23:2595–2604. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Maccioni RB, Otth C, Concha II and Muñoz
JP: The protein kinase Cdk5. Structural aspects, roles in
neurogenesis and involvement in Alzheimer's pathology. Eur J
Biochem. 268:1518–1527. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhu X, Lee HG, Raina AK, Perry G and Smith
MA: The role of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in
Alzheimer's disease. Neurosignals. 11:270–281. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Planel E, Sun X and Takashima A: Role of
GSK-3 beta in Alzheimer's disease pathology. Drug Dev Res.
56:491–510. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Litersky JM, Johnson GV, Jakes R, Goedert
M, Lee M and Seubert P: Tau protein is phosphorylated by cyclic
AMP-dependent protein kinase and calcium/calmodulin-dependent
protein kinase II within its microtubule-binding domains at Ser-262
and Ser-356. Biochem J. 316:655–660. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sironi JJ, Yen SH, Gondal JA, Wu Q,
Grundke-Iqbal I and Iqbal K: Ser-262 in human recombinant tau
protein is a markedly more favorable site for phosphorylation by
CaMKII than PKA or PhK. FEBS Lett. 436:471–475. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Planel E, Miyasaka T, Launey T, Chui DH,
Tanemura K, Sato S, Murayama O, Ishiguro K, Tatebayashi Y and
Takashima A: Alterations in glucose metabolism induce hypothermia
leading to tau hyperphosphorylation through differential inhibition
of kinase and phosphatase activities: implications for Alzheimer's
disease. J Neurosci. 24:2401–2411. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xu Z, Dong Y, Wang H, Culley DJ,
Marcantonio ER, Crosby G, Tanzi RE, Zhang Y and Xie Z:
Age-dependent postoperative cognitive impairment and
Alzheimer-related neuropathology in mice. Sci Rep.
4:37662014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Terrando N, Monaco C, Ma D, Foxwell BM,
Feldmann M and Maze M: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha triggers a
cytokine cascade yielding postoperative cognitive decline. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:20518–20522. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lyman M, Lloyd DG, Ji X, Vizcaychipi MP
and Ma D: Neuroinflammation: The role and consequences. Neurosci
Res. 79:1–12. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Marcos B, Aisa B and Ramírez MJ:
Functional interaction between 5-HT(6) receptors and
hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis: Cognitive implications.
Neuropharmacology. 54:708–714. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hu Y, Yang J, Hu Y, Wang Y and Li W:
Amitriptyline rather than lornoxicam ameliorates neuropathic
pain-induced deficits in abilities of spatial learning and memory.
Eur J Anaesthesiol. 27:162–168. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|