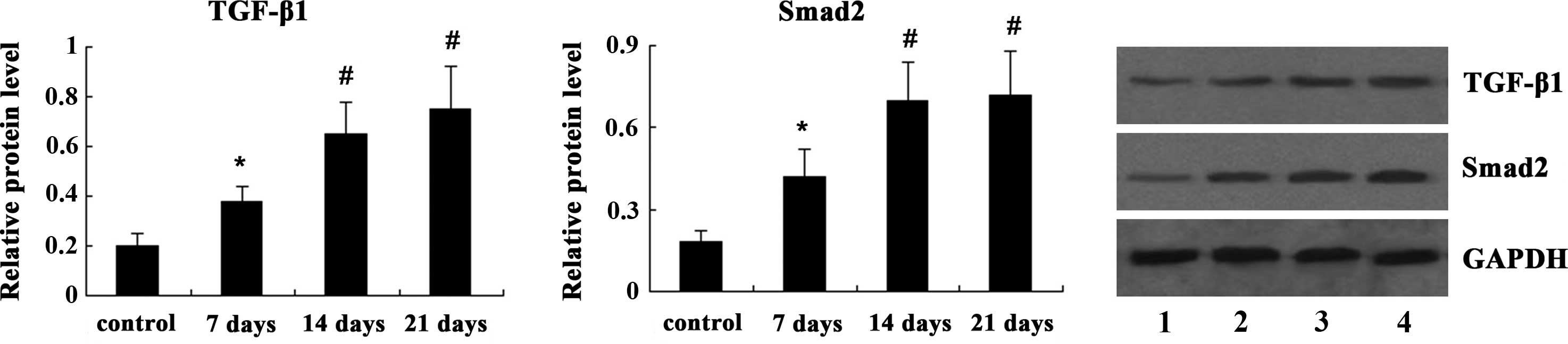
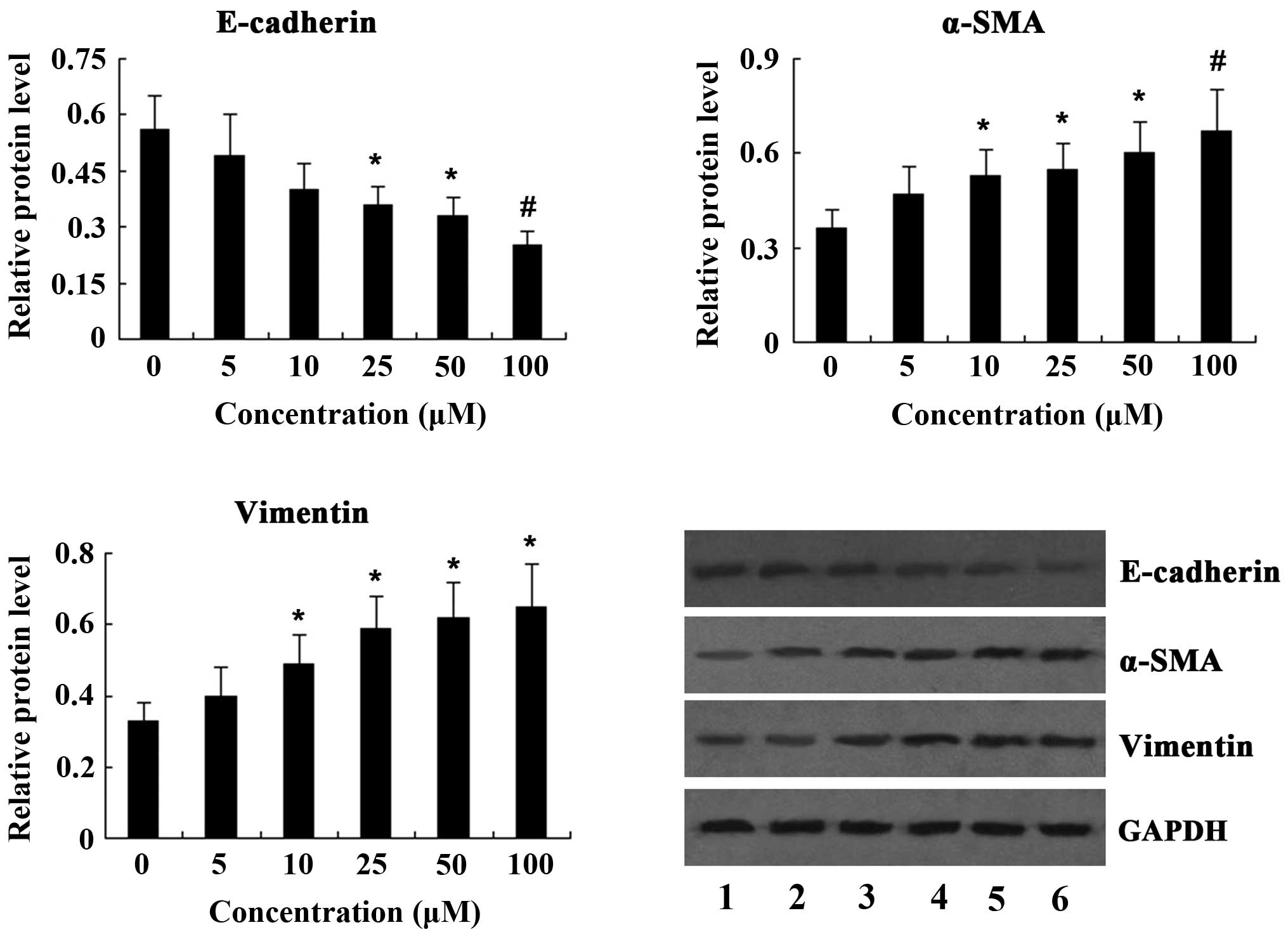
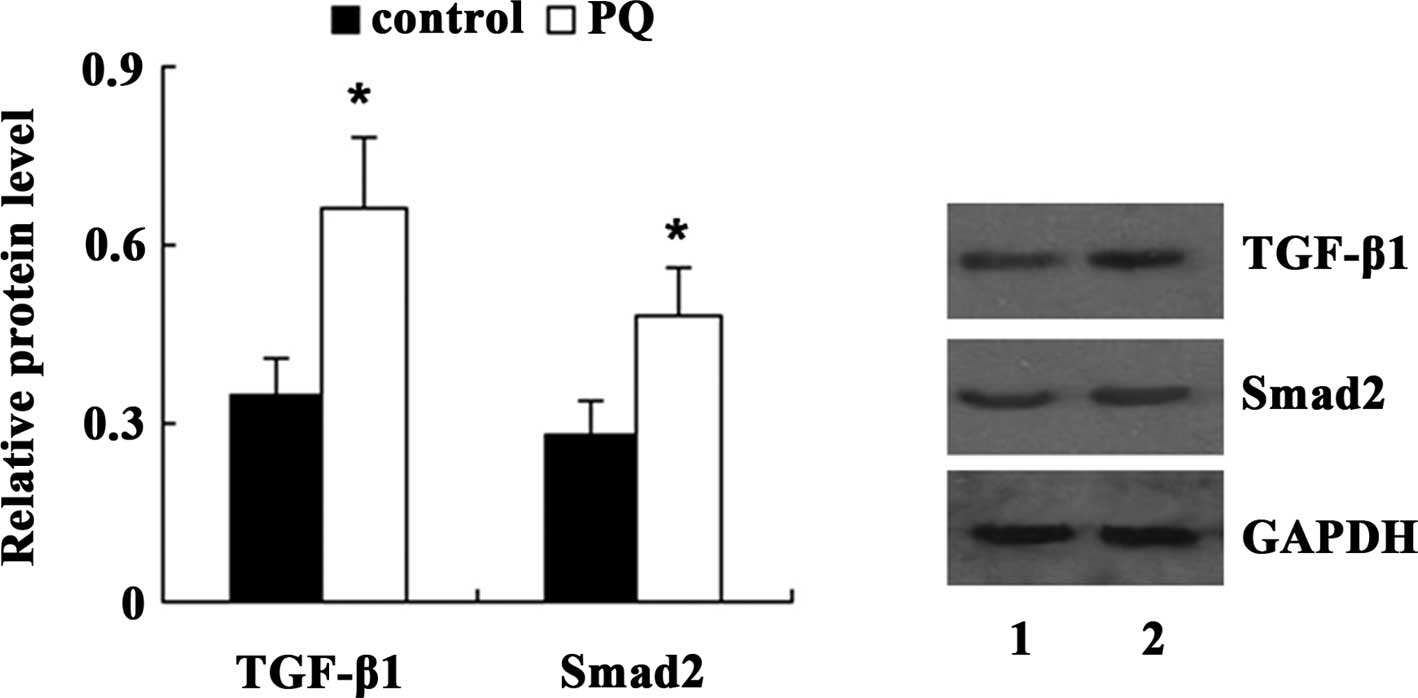
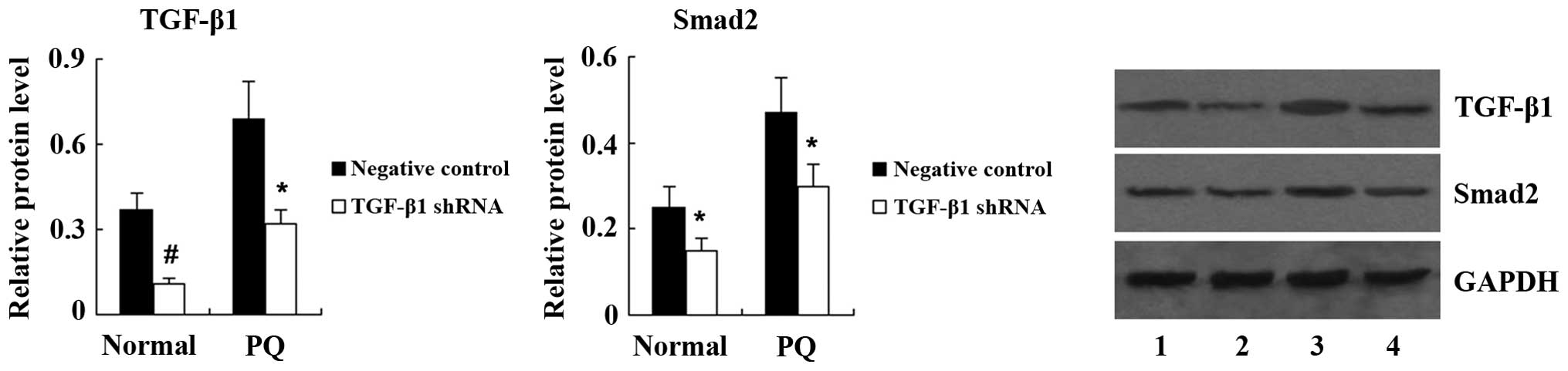
|
1
|
Lee SK, Ameno K, In SW, Yang JY, Kim KU,
Koo KS, Yoo YC, Ameno S and Ijiri I: Levels of paraquat in fatal
intoxications. Int J Legal Med. 112:198–200. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT, Chen KH, Huang WH, Hsu
CW, Hsu HH and Yen TH: Improved survival in severe paraquat
poisoning with repeated pulse therapy of cyclophosphamide and
steroids. Intensive Care Med. 37:1006–1013. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang RL, Tang X, Wu X, Xu R, Yu KL and Xu
K: The relationship between HIF-1a expression and the early lung
fibrosis in rats with acute paraquat poisoning. Chinese Journal of
Industrial Hygiene and Occupational Diseases. 30:273–277. 2012.In
Chinese.
|
|
4
|
Dinis-Oliveira RJ, Duarte JA,
Sánchez-Navarro A, Remião F, Bastos ML and Carvalho F: Paraquat
poisonings: Mechanisms of lung toxicity, clinical features and
treatment. Crit Rev Toxicol. 38:13–71. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Venkatesan N: Pulmonary protective effects
of curcumin against paraquat toxicity. Life Sci. 66:PL21–PL28.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tomita M, Okuyama T, Katsuyama H, Miura Y,
Nishimura Y, Hidaka K, Otsuki T and Ishikawa T: Mouse model of
paraquat-poisoned lungs and its gene expression profile.
Toxicology. 231:200–209. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hagiwara S, Iwasaka H, Matsumoto S and
Noguchi T: An antisense oligonucleotide to HSP47 inhibits
paraquat-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Toxicology.
236:199–207. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Willis BC, Liebler JM, Luby-Phelps K,
Nicholson AG, Crandall ED, du Bois RM and Borok Z: Induction of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in alveolar epithelial cells by
transforming growth factor-beta1: Potential role in idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 166:1321–1332. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim KK, Kugler MC, Wolters PJ, Robillard
L, Galvez MG, Brumwell AN, Sheppard D and Chapman HA: Alveolar
epithelial cell mesenchymal transition develops in vivo during
pulmonary fibrosis and is regulated by the extracellular matrix.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:13180–13185. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim KK, Wei Y, Szekeres C, Kugler MC,
Wolters PJ, Hill ML, Frank JA, Brumwell AN, Wheeler SE, Kreidberg
JA and Chapman HA: Epithelial cell alpha3beta1 integrin links
beta-catenin and Smad signaling to promote myofibroblast formation
and pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 119:213–224. 2009.
|
|
11
|
Adler KB, Low RB, Leslie KO, Mitchell J
and Evans JN: Contractile cells in normal and fibrotic lung. Lab
Invest. 60:4773–485. 1989.
|
|
12
|
Mitchell J, Woodcock-Mitchell J, Reynolds
S, Low R, Leslie K, Adler K, Gabbiani G and Skalli O: Alpha-smooth
muscle actin in parenchymal cells of bleomycin-injured rat lung.
Lab Invest. 60:643–650. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kuhn C and McDonald JA: The roles of the
myofibroblast in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Ultrastructural and
immunohisto-chemical features of sites of active extracellular
matrix synthesis. Am J Pathol. 138:1257–1265. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pache JC, Christakos PG, Gannon DE,
Mitchell JJ, Low RB and Leslie KO: Myofibroblasts in diffuse
alveolar damage of the lung. Mod Pathol. 11:1064–1070.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Phan SH: The myofibroblast in pulmonary
fibrosis. Chest. 122(Suppl 6): S286–S289. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Epperly MW, Guo H, Gretton JE and
Greenberger JS: Bone marrow origin of myofibroblasts in irradiation
pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 29:213–224. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Willis BC, duBois RM and Borok Z:
Epithelial origin of myofibroblasts during fibrosis in the lung.
Proc Am Thorac Soc. 3:377–382. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Scotton CJ and Chambers RC: Molecular
targets in pulmonary fibrosis: The myofibroblast in focus. Chest.
132:1311–1321. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kasai H, Allen JT, Mason RM, Kamimura T
and Zhang Z: TGF-beta1 induces human alveolar epithelial to
mesenchymal cell transition (EMT). Respir Res. 6(56)2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesen-chymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Leask A and Abraham DJ: TGF-beta signaling
and the fibrotic response. FASEB J. 18:816–827. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Steen V: Targeted therapy for systemic
sclerosis. Autoimmun Rev. 5:122–124. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bergeron A, Soler P, Kambouchner M,
Loiseau P, Milleron B, Valeyre D, Hance AJ and Tazi A: Cytokine
profiles in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis suggest an important role
for TGF-beta and IL-10. Eur Respir J. 22:69–76. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Thiery JP and Sleeman JP: Complex networks
orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 7:131–142. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chapman HA: Epithelial-mesenchymal
interactions in pulmonary fibrosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 73:413–435.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Xu J, Lamouille S and Derynck R:
TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res.
19:156–172. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Willis BC and Borok Z: TGF-beta-induced
EMT: Mechanisms and implications for fibrotic lung disease. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 293:L525–L534. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|