|
1
|
Li DW, Liu ZQ, Chen W, Yao M and Li GR:
Association of glycogen synthase kinase-3β with Parkinson's disease
(review). Mol Med Rep. 9:2043–2050. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Obeso JA, Rodríguez-Oroz MC, Rodríguez M,
Lanciego JL, Artieda J, Gonzalo N and Olanow CW: Pathophysiology of
the basal ganglia in Parkinson's disease. Trends Neurosci.
23(Suppl): S8–S19. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
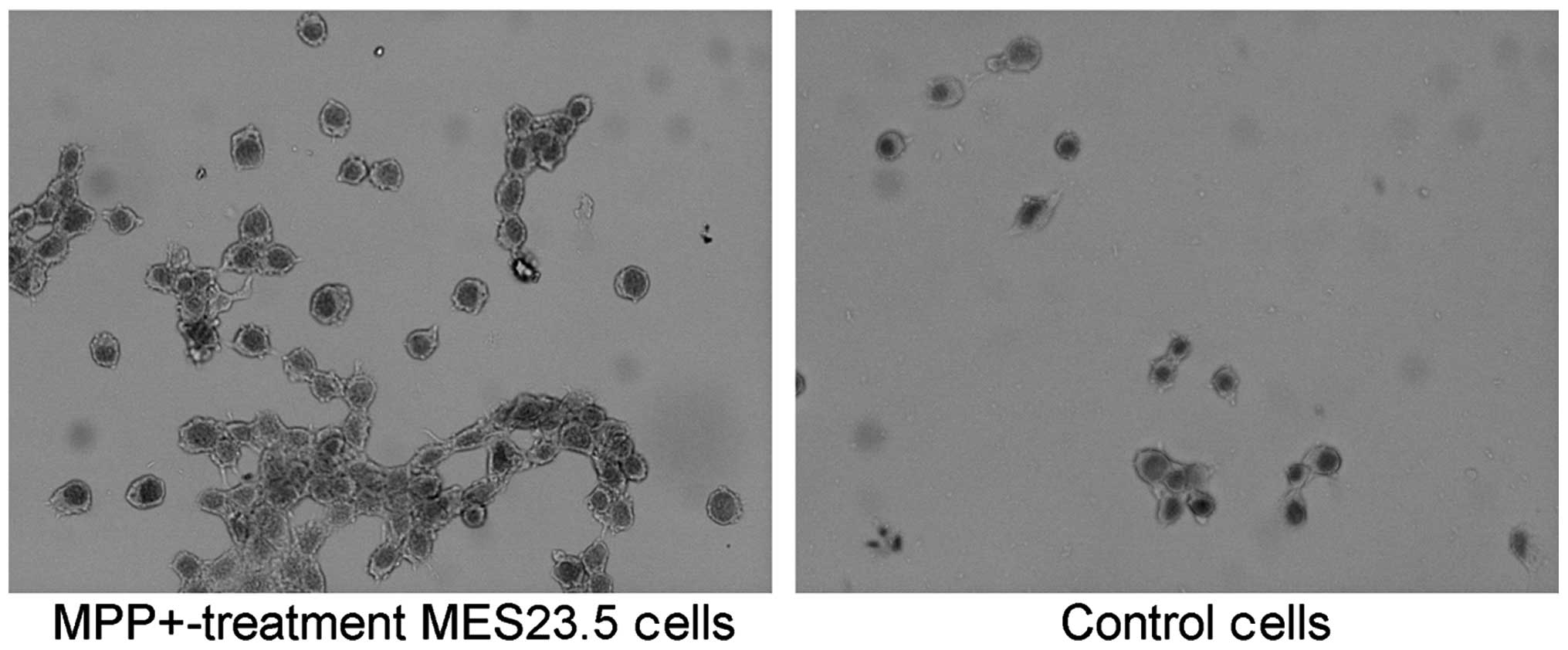
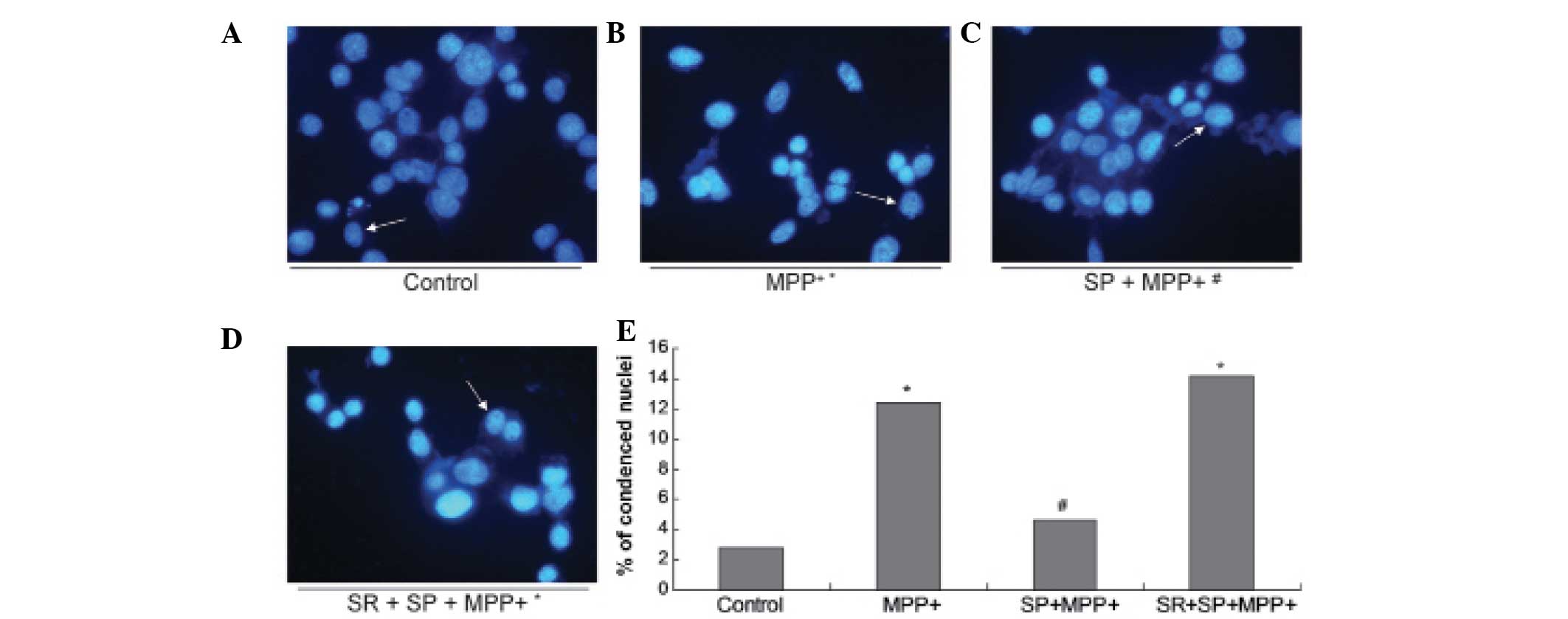
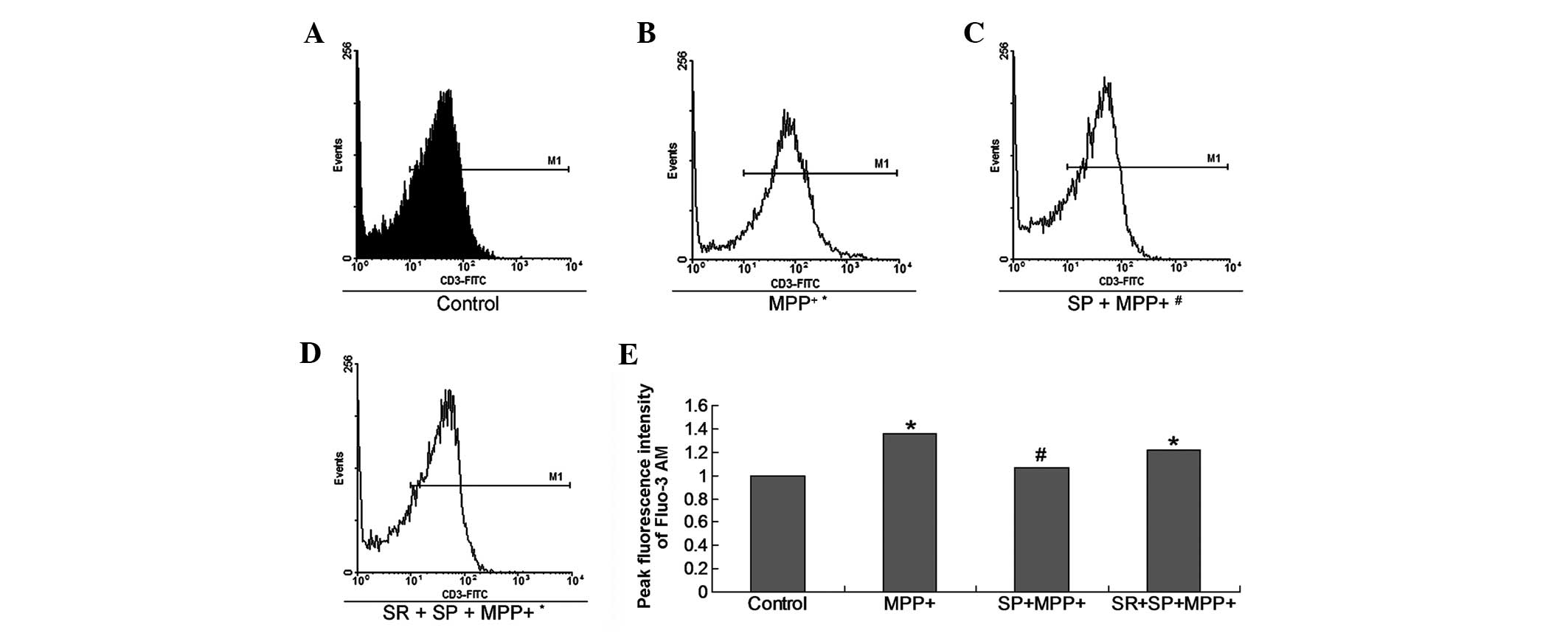
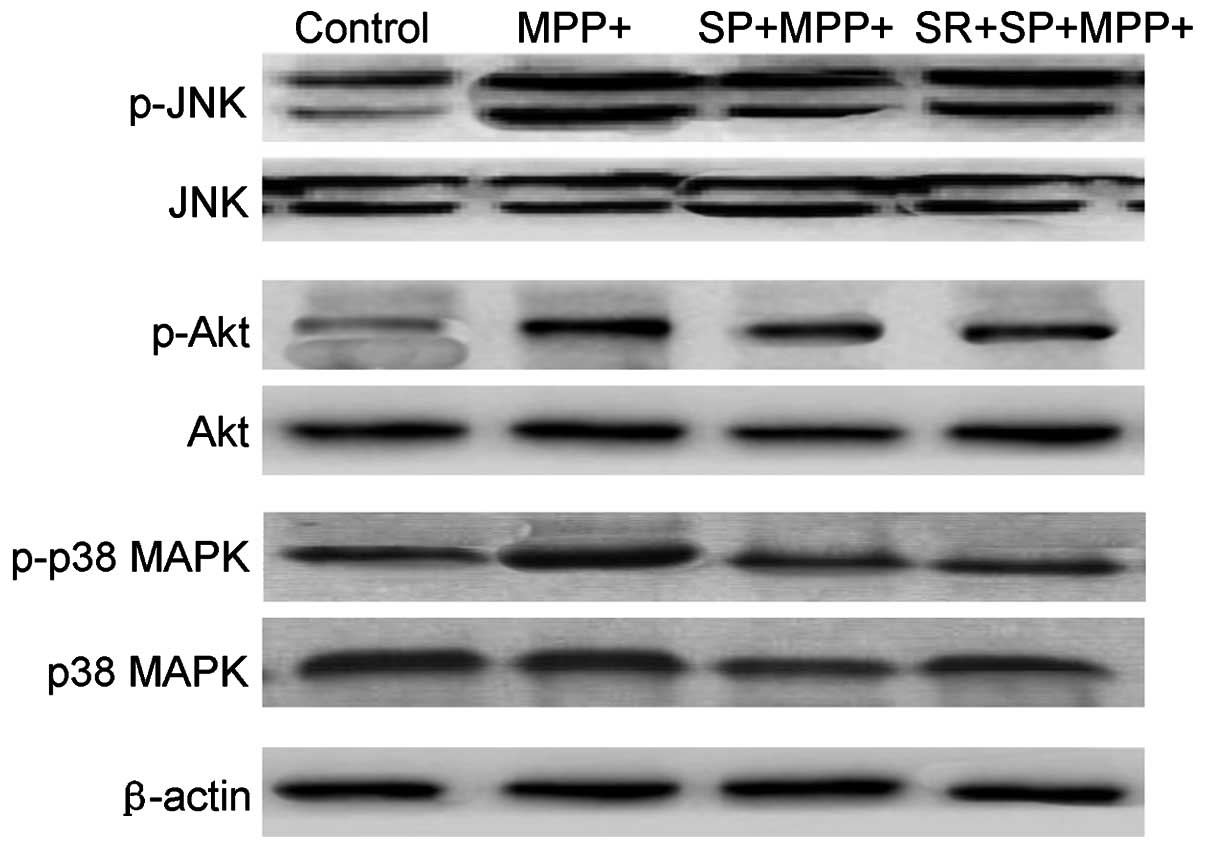
|
Oertel WH and Ellgring H: Parkinson's
disease - medical education and psychosocial aspects. Patient Educ
Couns. 26:71–79. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Levy OA, Malagelada C and Greene LA: Cell
death pathways in Parkinson's disease: Proximal triggers, distal
effectors, and final steps. Apoptosis. 14:478–500. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Irrcher I and Park DS: Parkinson's
disease: To live or die by autophagy. Sci Signal. 2:pe212009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hartmann A and Hirsch EC: Parkinson's
disease. The apoptosis hypothesis revisited. Adv Neurol.
86:143–153. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tatton WG, Chalmers-Redman R, Brown D and
Tatton N: Apoptosis in Parkinson's disease: Signals for neuronal
degradation. Ann Neurol. 53(Suppl 3): S61–S72. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chang WA, Lin ES, Tsai MJ, Huang MS and
Kuo PL: Isolinderalactone inhibits proliferation of A549 human non
small cell lung cancer cells by arresting the cell cycle at the
G0/G1 phase and inducing a Fas receptor and soluble Fas
ligand-mediated apoptotic pathway. Mol Med Rep. 9:1653–1659.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Anglade P, Vyas S, Javoy-Agid F, Herrero
MT, Michel PP, Marquez J, Mouatt-Prigent A, Ruberg M, Hirsch EC and
Agid Y: Apoptosis and autophagy in nigral neurons of patients with
Parkinson's disease. Histol Histopathol. 12:25–31. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fornai F, Lenzi P, Gesi M, Soldani P,
Ferrucci M, Lazzeri G, Capobianco L, Battaglia G, De Blasi A,
Nicoletti F, et al: Methamphetamine produces neuronal inclusions in
the nigrostriatal system and in PC12 cells. J Neurochem.
88:114–123. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Yakhine-Diop SM, Bravo-San Pedro JM,
Gómez-Sánchez R, Pizarro-Estrella E, Rodríguez-Arribas M, Climent
V, Aiastui A, López de Munain A, Fuentes JM and González-Polo RA:
G2019S LRRK2 mutant fibroblasts from Parkinson's disease patients
show increased sensitivity to neurotoxin
1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium dependent of autophagy. Toxicology.
324:1–9. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Robinson P, Garza A, Moore J, Eckols TK,
Parti S, Balaji V, Vallejo J and Tweardy DJ: Substance P is
required for the pathogenesis of EMCV infection in mice. Int J Clin
Exp Med. 2:76–86. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Barker R: Tachykinins, neurotrophism and
neurodegenerative diseases: A critical review on the possible role
of tachykinins in the aetiology of CNS diseases. Rev Neurosci.
7:187–214. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Thornton E and Vink R: Treatment with a
substance P receptor antagonist is neuroprotective in the
intrastriatal 6-hydroxydopamine model of early Parkinson's disease.
PLoS One. 7:e341382012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nalivaiko E, Michaud JC, Soubrié P, Le Fur
G and Feltz P: Tachykinin neurokinin-1 and neurokinin-3
receptor-mediated responses in guinea-pig substantia nigra: An in
vitro electrophysiological study. Neuroscience. 78:745–757. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Strell C, Sievers A, Bastian P, Lang K,
Niggemann B, Zänker KS and Entschladen F: Divergent effects of
norepinephrine, dopamine and substance P on the activation,
differentiation and effector functions of human cytotoxic T
lymphocytes. BMC Immunol. 10:622009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Crawford GD Jr, Le WD, Smith RG, Xie WJ,
Stefani E and Appel SH: A novel N18TG2 x mesencephalon cell hybrid
expresses properties that suggest a dopaminergic cell line of
substantia nigra origin. J Neurosci. 12:3392–3398. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu L, Xu H, Jiang H, Wang J, Song N and
Xie J: Ghrelin prevents 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion-induced
cytotoxicity through antioxidation and NF-kappaB modulation in
MES23.5 cells. Exp Neurol. 222:25–29. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yao G, Yang L, Hu Y, Liang J, Liang J and
Hou Y: Nonylphenol-induced thymocyte apoptosis involved caspase-3
activation and mitochondrial depolarization. Mol Immunol.
43:915–926. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Feng Z and Zhang JT: Protective effect of
melatonin on b-amyloid induced apoptosis in rat astroglioma c6
cells and its mechanism. Free Radic Biol Med. 2004:1790–1801.
2014.
|
|
21
|
Wei CD, Li Y, Zheng HY, Tong YQ and Dai W:
Palmitate induces H9c2 cell apoptosis by increasing reactive oxygen
species generation and activation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway.
Mol Med Rep. 7:855–861. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao L, Teng B, Wen L, Feng Q, Wang H, Li
N, Wang Y and Liang Z: mTOR inhibitor AZD8055 inhibits
proliferation and induces apoptosis in laryngeal carcinoma. Int J
Clin Exp Med. 7:337–347. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Egnatchik RA, Leamy AK, Jacobson DA,
Shiota M and Young JD: ER calcium release promotes mitochondrial
dysfunction and hepatic cell lipotoxicity in response to palmitate
overload. Mol Metab. 3:544–553. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang XJ and Xu JX: Possible involvement of
Ca2+ signaling in rotenone-induced apoptosis in human
neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Neurosci Lett. 376:127–132. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bhattacharyya S, Ghosh S, Shant J, Ganguly
NK and Majumdar S: Role of the W07-toxin on Vibrio cholerae-induced
diarrhoea. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1670:69–80. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang J, Du XX, Jiang H and Xie JX:
Curcumin attenuates 6-hydroxydopamine-induced cytotoxicity by
anti-oxidation and nuclear factor-kappa B modulation in MES23.5
cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 78:178–183. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Iwasaki Y, Kinoshita M, Ikeda K, Takamiya
K and Shiojima T: Trophic effect of various neuropeptides on the
cultured ventral spinal cord of rat embryo. Neurosci Lett.
101:316–320. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bleiblo F, Michael P, Brabant D, Ramana
CV, Tai T, Saleh M, Parrillo JE and Kumar A and Kumar A: JAK
kinases are required for the bacterial RNA and poly I:C induced
tyrosine phosphorylation of PKR. Int J Clin Exp Med. 6:16–25.
2013.
|
|
29
|
Kitamura Y, Shimohama S, Akaike A and
Taniguchi T: The parkinsonian models: Invertebrates to mammals. Jpn
J Pharmacol. 84:237–243. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Siddique YH, Naz F and Jyoti S: Effect of
curcumin on lifespan, activity pattern, oxidative stress, and
apoptosis in the brains of transgenic Drosophila model of
Parkinson's disease. BioMed Res Int. 606928:20142014.
|
|
31
|
Zhang Z, Zhang K, Du X and Li Y:
Neuroprotection of desferrioxamine in lipopolysaccharide-induced
nigrostriatal dopamine neuron degeneration. Mol Med Rep. 5:562–566.
2012.
|
|
32
|
Ekshyyan O and Aw TY: Apoptosis: A key in
neurodegenerative disorders. Curr Neurovasc Res. 1:355–371. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Enari M, Sakahira H, Yokoyama H, Okawa K,
Iwamatsu A and Nagata S: A caspase-activated DNase that degrades
DNA during apoptosis, and its inhibitor ICAD. Nature. 391:43–50.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Beal MF: Excitotoxicity and nitric oxide
in Parkinson's disease pathogenesis. Ann Neurol. 44(Suppl 1):
S110–S114. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ma S, Cai C, Ma Y, Bai Z, Meng X, Yang X,
Zou F and Ge R: Store-operated Ca2+ entry
mediated regulation of polarization in differentiated human
neutrophil-like HL-60 cells under hypoxia. Mol Med Rep. 9:819–824.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kim HY, LaVaute T, Iwai K, Klausner RD and
Rouault TA: Identification of a conserved and functional
iron-responsive element in the 5'-untranslated region of mammalian
mitochondrial aconitase. J Biol Chem. 271:24226–24230. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Scorrano L, Oakes SA, Opferman JT, Cheng
EH, Sorcinelli MD, Pozzan T and Korsmeyer SJ: BAX and BAK
regulation of endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+: A control
point for apoptosis. Science. 300:135–139. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Brecht S, Kirchhof R, Chromik A, Willesen
M, Nicolaus T, Raivich G, Wessig J, Waetzig V, Goetz M, Claussen M,
et al: Specific pathophysiological functions of JNK isoforms in the
brain. Eur J Neurosci. 21:363–377. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dhanasekaran DN and Reddy EP: JNK
signaling in apoptosis. Oncogene. 27:6245–6251. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Eminel S, Roemer L, Waetzig V and Herdegen
T: c-Jun N-terminal kinases trigger both degeneration and neurite
outgrowth in primary hippocampal and cortical neurons. J Neurochem.
104:957–969. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Yeste-Velasco M, Folch J, Casadesús G,
Smith MA, Pallàs M and Camins A: Neuroprotection by c-Jun
NH2-terminal kinase inhibitor SP600125 against potassium
deprivation-induced apoptosis involves the Akt pathway and
inhibition of cell cycle reentry. Neuroscience. 159:1135–1147.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hsu MJ, Hsu CY, Chen BC, Chen MC, Ou G and
Lin CH: Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 in amyloid beta
peptide-induced cerebral endothelial cell apoptosis. J Neurosci.
27:5719–5729. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu XW, Ji EF, He P, Xing RX, Tian BX and
Li XD: Protective effects of the p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 on
NMDA induced injury in primary cerebral cortical neurons. Mol Med
Rep. 10:1942–1948. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|