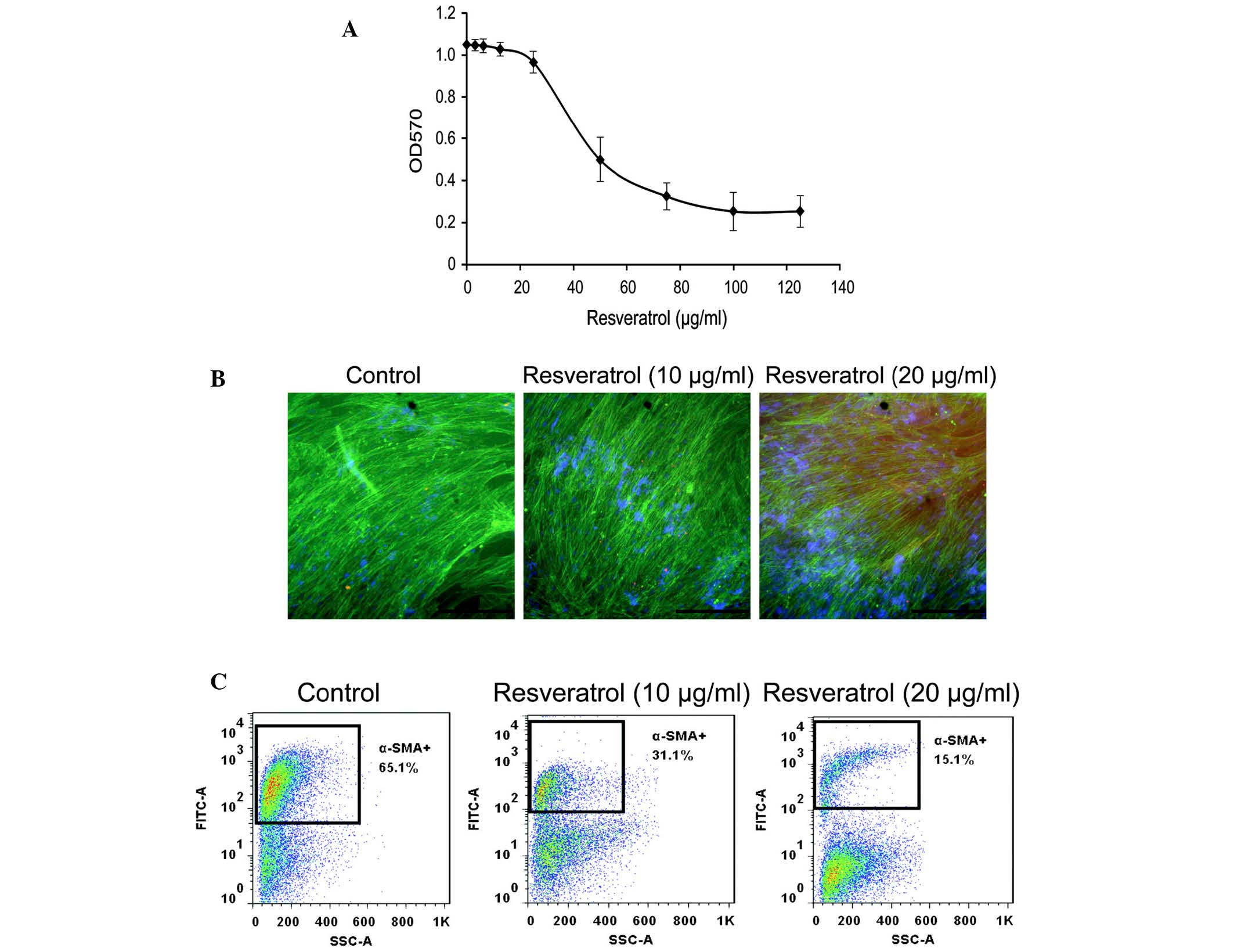
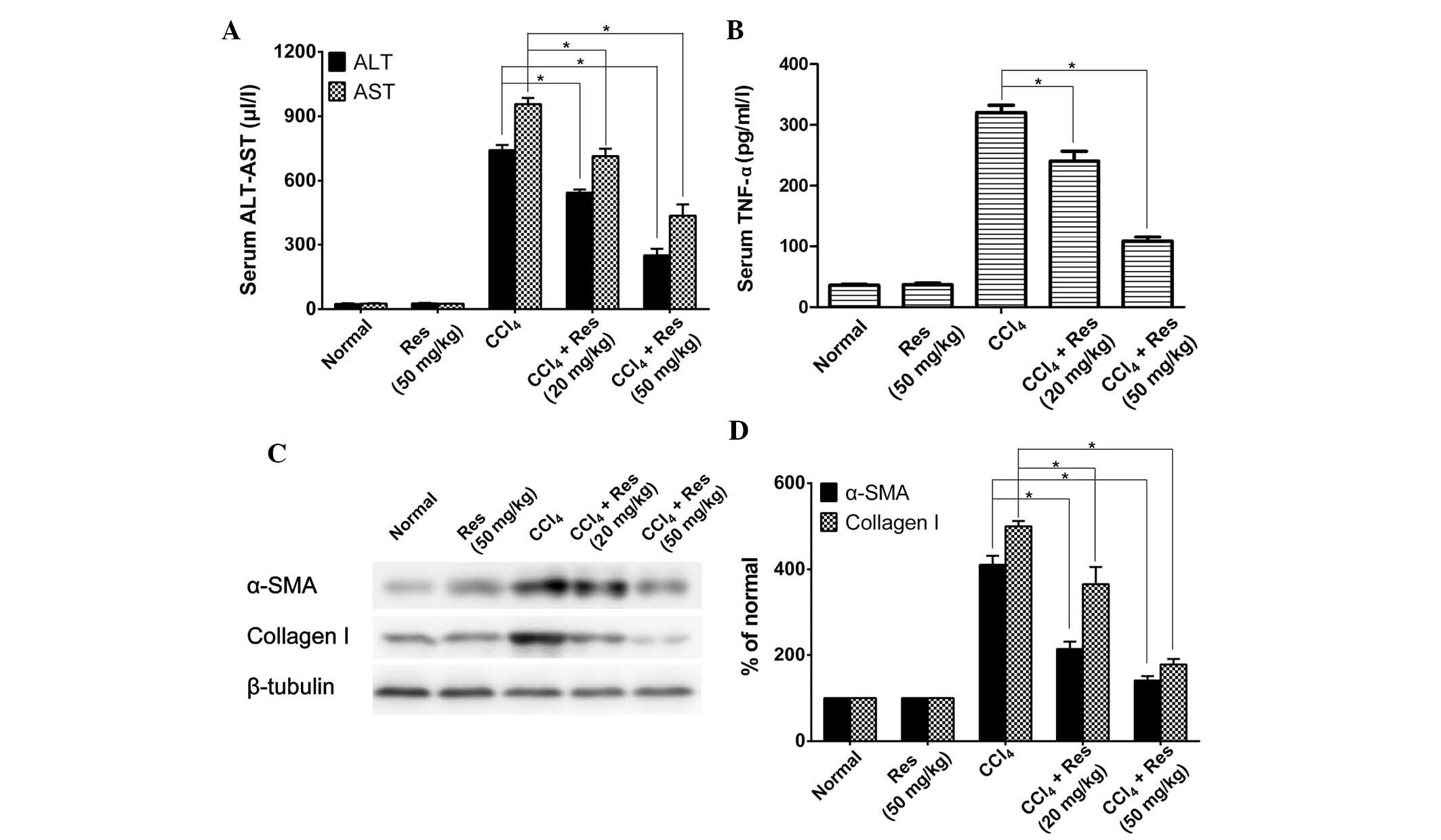
|
1
|
Moreira RK: Hepatic stellate cells and
liver fibrosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 131:1728–1734. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bataller R and Brenner DA: Liver fibrosis.
J Clin Invest. 115:209–218. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Svegliati-Baroni G, De Minicis S and
Marzioni M: Hepatic fibrogenesis in response to chronic liver
injury: Novel insights on the role of cell-to-cell interaction and
transition. Liver Int. 28:1052–1064. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hernandez-Gea V and Friedman SL:
Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol. 6:425–456. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Schuppan D and Kim YO: Evolving therapies
for liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 123:1887–1901. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Friedman SL: Evolving challenges in
hepatic fibrosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:425–436. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Baur JA and Sinclair DA: Therapeutic
potential of resveratrol: The in vivo evidence. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 5:493–506. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bishayee A, Darvesh AS, Politis T and
McGory R: Resveratrol and liver disease: From bench to bedside and
community. Liver Int. 30:1103–1114. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bishayee A, Politis T and Darvesh AS:
Resveratrol in the chemoprevention and treatment of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer Treat Rev. 36:43–53. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Raj P, Louis XL, Thandapilly SJ, Movahed
A, Zieroth S and Netticadan T: Potential of resveratrol in the
treatment of heart failure. Life Sci. 95:63–71. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Petro TM: Regulatory role of resveratrol
on Th17 in autoimmune disease. Int Immunopharmacol. 11:310–318.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ndiaye M, Philippe C, Mukhtar H and Ahmad
N: The grape antioxidant resveratrol for skin disorders: Promise,
prospects and challenges. Arch Biochem Biophys. 508:164–170. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ciddi V and Dodda D: Therapeutic potential
of resveratrol in diabetic complications: In vitro and in vivo
studies. Pharmacol Rep. 66:799–803. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Athar M, Back JH, Tang X, Kim KH,
Kopelovich L, Bickers DR and Kim AL: Resveratrol: A review of
preclinical studies for human cancer prevention. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 224:274–283. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bujanda L, García-Barcina M, Gutiérrez-de
Juan V, Bidaurrazaga J, de Luco MF, Gutiérrez-Stampa M, Larzabal M,
Hijona E, Sarasqueta C, Echenique-Elizondo M and Arenas JI: Effect
of resveratrol on alcohol-induced mortality and liver lesions in
mice. BMC Gastroenterol. 6:352006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kasdallah-Grissa A, Mornagui B, Aouani E,
Hammami M, El May M, Gharbi N, Kamoun A and El-Fazaâ S:
Resveratrol, a red wine polyphenol, attenuates ethanol-induced
oxidative stress in rat liver. Life Sci. 80:1033–1039. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Heeboll S, Thomsen KL, Pedersen SB,
Vilstrup H, George J and Grønbæk H: Effects of resveratrol in
experimental and clinical non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World
J Hepatol. 6:188–198. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Choi YJ, Suh HR, Yoon Y, Lee KJ, Kim DG,
Kim S and Lee BH: Protective effect of resveratrol derivatives on
high-fat diet induced fatty liver by activating AMP-activated
protein kinase. Arch Pharm Res. 37:1169–1176. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chavez E, Reyes-Gordillo K, Segovia J,
Shibayama M, Tsutsumi V, Vergara P, Moreno MG and Muriel P:
Resveratrol prevents fibrosis, NF-kappaB activation and TGF-beta
increases induced by chronic CCl4 treatment in rats. J Appl
Toxicol. 28:35–43. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hong SW, Jung KH, Zheng HM, Lee HS, Suh
JK, Park IS, Lee DH and Hong SS: The protective effect of
resveratrol on dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver fibrosis in rats.
Arch Pharm Res. 33:601–609. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sener G, Toklu HZ, Sehirli AO,
Velioğlu-Oğünç A, Cetinel S and Gedik N: Protective effects of
resveratrol against acetaminophen-induced toxicity in mice. Hepatol
Res. 35:62–68. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kasdallah-Grissa A, Mornagui B, Aouani E,
Hammami M, Gharbi N, Kamoun A and El-Fazaa S: Protective effect of
resveratrol on ethanol-induced lipid peroxidation in rats. Alcohol
Alcohol. 41:236–239. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Andrade JM, Paraíso AF, de Oliveira MV,
Martins AM, Neto JF, Guimarães AL, de Paula AM, Qureshi M and
Santos SH: Resveratrol attenuates hepatic steatosis in high-fat fed
mice by decreasing lipogenesis and inflammation. Nutrition.
30:915–919. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sun B and Karin M: NF-kappaB signaling,
liver disease and hepatoprotective agents. Oncogene. 27:6228–6244.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Abergel A, Sapin V, Dif N, Chassard C,
Darcha C, Marcand-Sauvant J, Gaillard-Martinie B, Rock E,
Dechelotte P and Sauvant P: Growth arrest and decrease of alpha-SMA
and type I collagen expression by palmitic acid in the rat hepatic
stellate cell line PAV-1. Dig Dis Sci. 51:986–995. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Luedde T and Schwabe RF: NF-κB in the
liver-linking injury, fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat
Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 8:108–118. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang F, Liu S, Du T, Chen H, Li Z and Yan
J: NF-κB inhibition alleviates carbon tetrachloride-induced liver
fibrosis via suppression of activated hepatic stellate cells. Exp
Ther Med. 8:95–99. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Matsuda S, Kobayashi M and Kitagishi Y:
Roles for PI3K/AKT/PTEN pathway in cell signaling of nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease. ISRN Endocrinol. 2013:4724322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Weichhart T and Süemann MD: The
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in innate immune cells: Emerging therapeutic
applications. Ann Rheum Dis. 67(Suppl 3): iii70–iii74. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jackson LN, Larson SD, Silva SR, Rychahou
PG, Chen LA, Qiu S, Rajaraman S and Evers BM: PI3K/Akt activation
is critical for early hepatic regeneration after partial
hepatectomy. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
294:G1401–G1410. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|