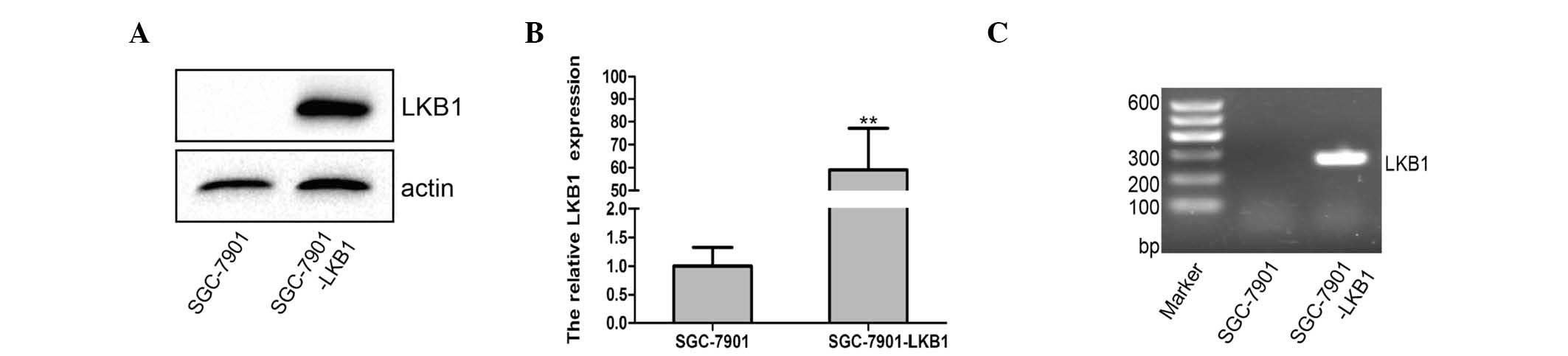
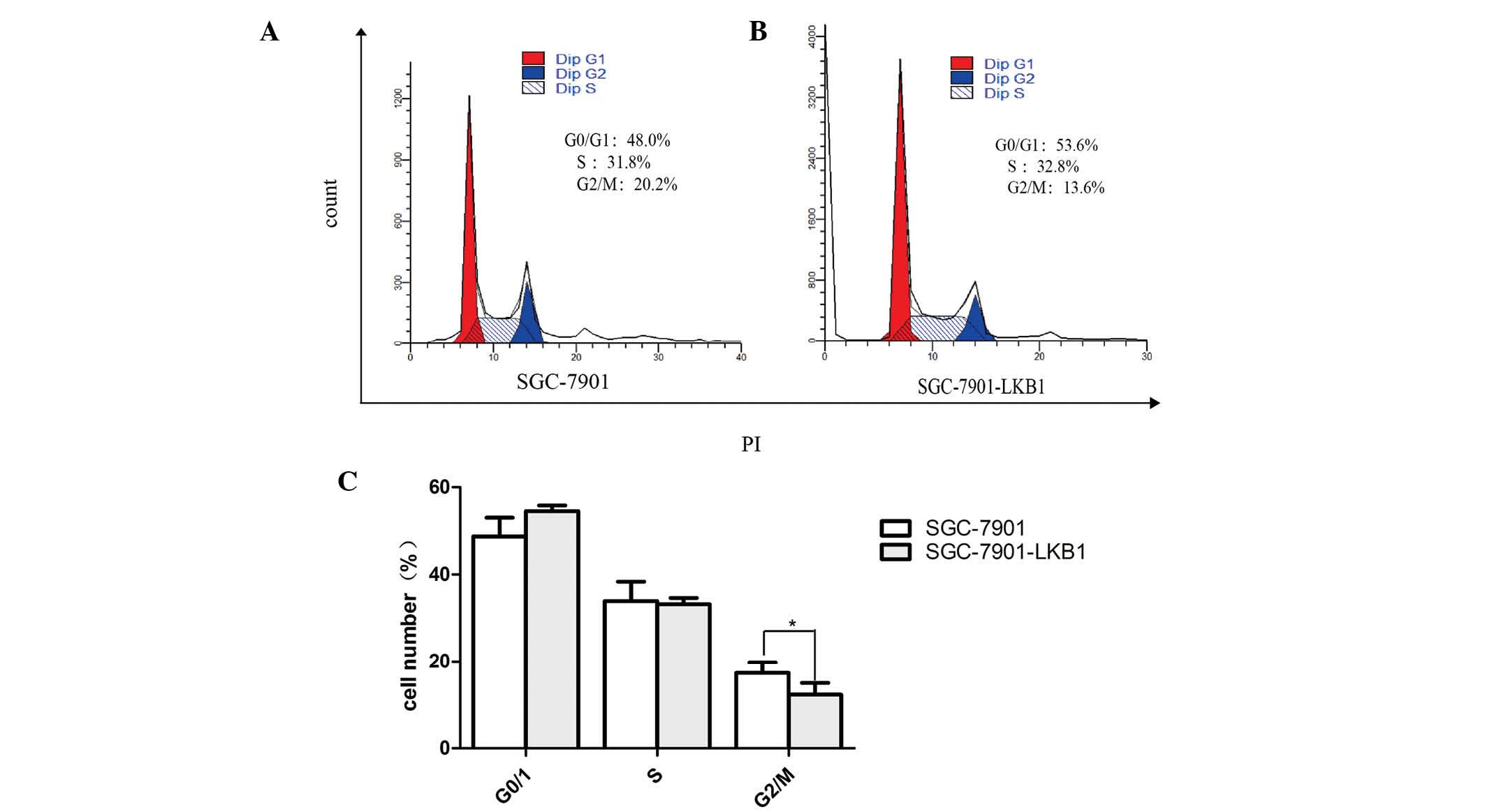
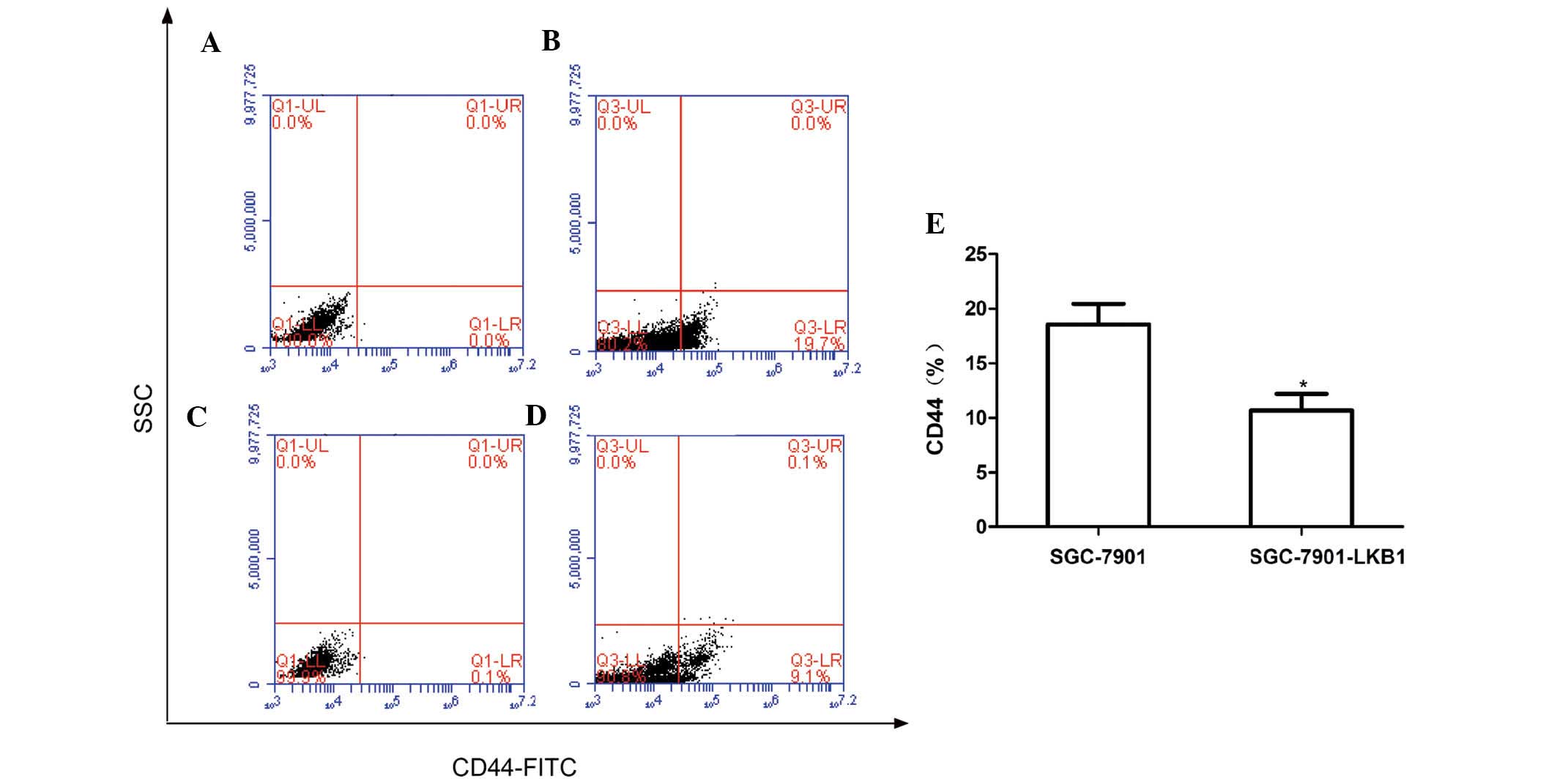
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
He J, Gu D, Wu X, Reynolds K, Duan X, Yao
C, Wang J, Chen CS, Chen J, Wildman RP, et al: Major causes of
death among men and women in china. N Engl J Med. 353:1134. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Fock KM: Review article: The epidemiology
and prevention of gastric cancer. Aliment Pharmacol Ther.
40:250–260. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Øverby A, Zhao CM and Chen D: Plant
phytochemicals: Potential anticancer agents against gastric cancer.
Curr Opin Pharmacol. 19:6–10. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Scartozzi M, Galizia E, Verdecchia L,
Berardi R, Antognoli S, Chiorrini S and Cascinu S: Chemotherapy for
advanced gastric cancer: Across the years for a standard of care.
Expert Opin Pharmacother. 8:797–808. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lordick F, Allum W, Carneiro F, Mitry E,
Tabernero J, Tan P, Van Cutsem E, van de Velde C and Cervantes A:
Unmet needs and challenges in gastric cancer: The way forward.
Cancer Treat Rev. 40:692–700. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kubota E, Williamson CT, Ye R, Elegbede A,
Peterson L, Lees-Miller SP and Bebb DG: Low ATM protein expression
and depletion of p53 correlates with olaparib sensitivity in
gastric cancer cell lines. Cell Cycle. 13:2129–2137. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang S, Schafer-Hales K, Khuri FR, Zhou
W, Vertino PM and Marcus AI: The tumor suppressor LKB1 regulates
lung cancer cell polarity by mediating cdc42 recruitment and
activity. Cancer Res. 68:740–748. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
MacIver NJ, Blagih J, Saucillo DC, Tonelli
L, Griss T, Rathmell JC and Jones RG: The liver kinase B1 is a
central regulator of T cell development, activation and metabolism.
J Immunol. 187:4187–4198. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nakano A and Takashima S: LKB1 and
AMP-activated protein kinase: Regulators of cell polarity. Genes
Cells. 17:737–747. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hezel AF and Bardeesy N: LKB1; linking
cell structure and tumor suppression. Oncogene. 27:6908–6919. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sebbagh M, Olschwang S, Santoni MJ and
Borg JP: The LKB1 complex-AMPK pathway: The tree that hides the
forest. Fam Cancer. 10:415–424. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kyriakis JM: At the crossroads:
AMP-activated kinase and the LKB1 tumor suppressor link cell
proliferation to metabolic regulation. J Biology. 2:262003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Shaw RJ: LKB1 and AMP-activated protein
kinase control of mTOR signalling and growth. Acta Physiol (Oxf).
196:65–80. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Shaw RJ, Bardeesy N, Manning BD, Lopez L,
Kosmatka M, DePinho RA and Cantley LC: The LKB1 tumor suppressor
negatively regulates mTOR signaling. Cancer Cell. 6:91–99. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li T, Leong MH, Harms B, Kennedy G and
Chen L: MicroRNA-21 as a potential colon and rectal cancer
biomarker. World J Gastroenterol. 19:5615–5621. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Miller RA, Chu Q, Le Lay J, Scherer PE,
Ahima RS, Kaestner KH, Foretz M, Viollet B and Birnbaum MJ:
Adiponectin suppresses gluconeogenic gene expression in mouse
hepatocytes independent of LKB1-AMPK signaling. J Clin Invest.
121:2518–2528. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Luo Z, Zang M and Guo W: AMPK as a
metabolic tumor suppressor: Control of metabolism and cell growth.
Future Oncol. 6:457–470. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hemminki A, Markie D, Tomlinson I,
Avizienyte E, Roth S, Loukola A, Bignell G, Warren W, Aminoff M,
Höglund P, et al: A serine/threonine kinase gene defective in
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Nature. 391:184–187. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhuang ZG, Di GH, Shen ZZ, Ding J and Shao
ZM: Enhanced expression of LKB1 in breast cancer cells attenuates
angiogenesis, invasion and metastatic potential. Mol Cancer Res.
4:843–849. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liang X, Li ZL, Jiang LL, Guo QQ, Liu MJ
and Nan KJ: Suppression of lung cancer cell invasion by LKB1 is due
to the downregulation of tissue factor and vascular endothelial
growth factor, partly dependent on SP1. Int J Oncol. 44:1989–1997.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Park WS, Moon YW, Yang YM, Kim YS, Kim YD,
Fuller BG, Vortmeyer AO, Fogt F, Lubensky IA and Zhuang Z:
Mutations of the STK11 gene in sporadic gastric carcinoma. Int J
Oncol. 13:601–604. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(T) (−Delta Delta C) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Luo LY, Huang W, Tao R, Hu N, Xiao ZX and
Luo Z: ATM and LKB1 dependent activation of AMPK sensitizes cancer
cells to etoposide-induced apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 328:114–119.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Granot Z, Swisa A, Magenheim J,
Stolovich-Rain M, Fujimoto W, Manduchi E, Miki T, Lennerz JK,
Stoeckert CJ Jr, Meyuhas O, et al: LKB1 regulates pancreatic beta
cell size, polarity and function. Cell Metab. 10:296–308. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hopkins AM: A novel mechanism of
regulating breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 162014.
|
|
28
|
Sanchez-Cespedes M, Parrella P, Esteller
M, Nomoto S, Trink B, Engles JM, Westra WH, Herman JG and Sidransky
D: Inactivation of LKB1/STK11 is a common event in adenocarcinomas
of the lung. Cancer Res. 62:3659–3662. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bourguignon LY, Singleton PA, Zhu H and
Diedrich F: Hyaluronan-mediated CD44 interaction with RhoGEF and
Rho kinase promotes Grb2-associated binder-1 phosphorylation and
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling leading to cytokine
(macrophage-colony stimulating factor) production and breast tumor
progression. J Biol Chem. 278:29420–29434. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Babina IS, McSherry EA, Donatello S, Hill
AD and Hopkins AM: A novel mechanism of regulating breast cancer
cell migration via palmitoylation-dependent alterations in the
lipid raft affiliation of CD44. Breast Cancer Res. 16:R192014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bourguignon LY, Zhu H, Shao L and Chen YW:
CD44 interaction with c-Src kinase promotes cortactin-mediated
cytoskeleton function and hyaluronic acid-dependent ovarian tumor
cell migration. J Biol Chem. 276:7327–7336. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wang SJ, Wong G, de Heer AM, Xia WL and
Bourguignon LYW: CD44 variant isoforms in head and neck squamous
cell carcinoma progression. Laryngoscope. 119:1518–1530. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|