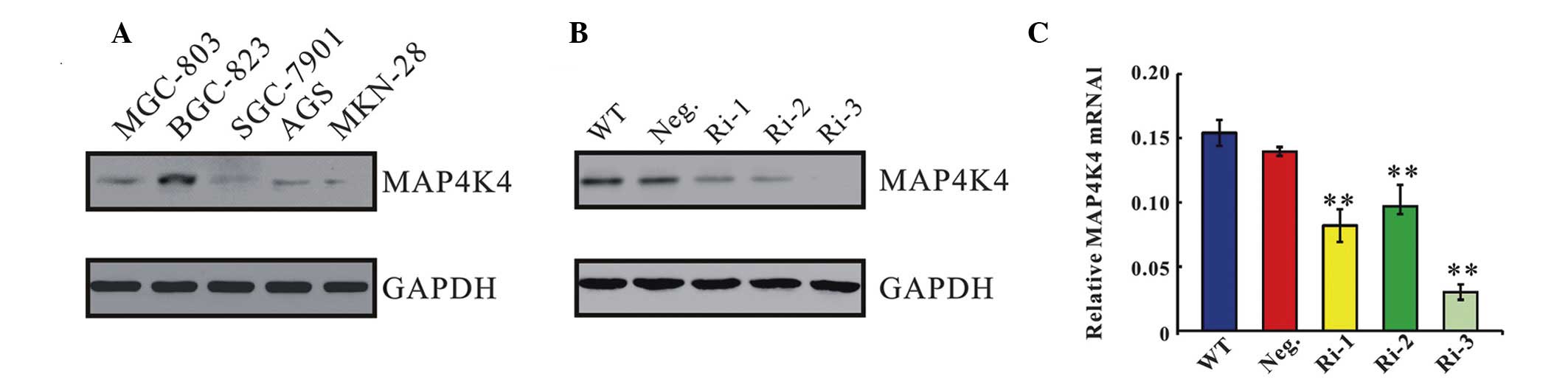
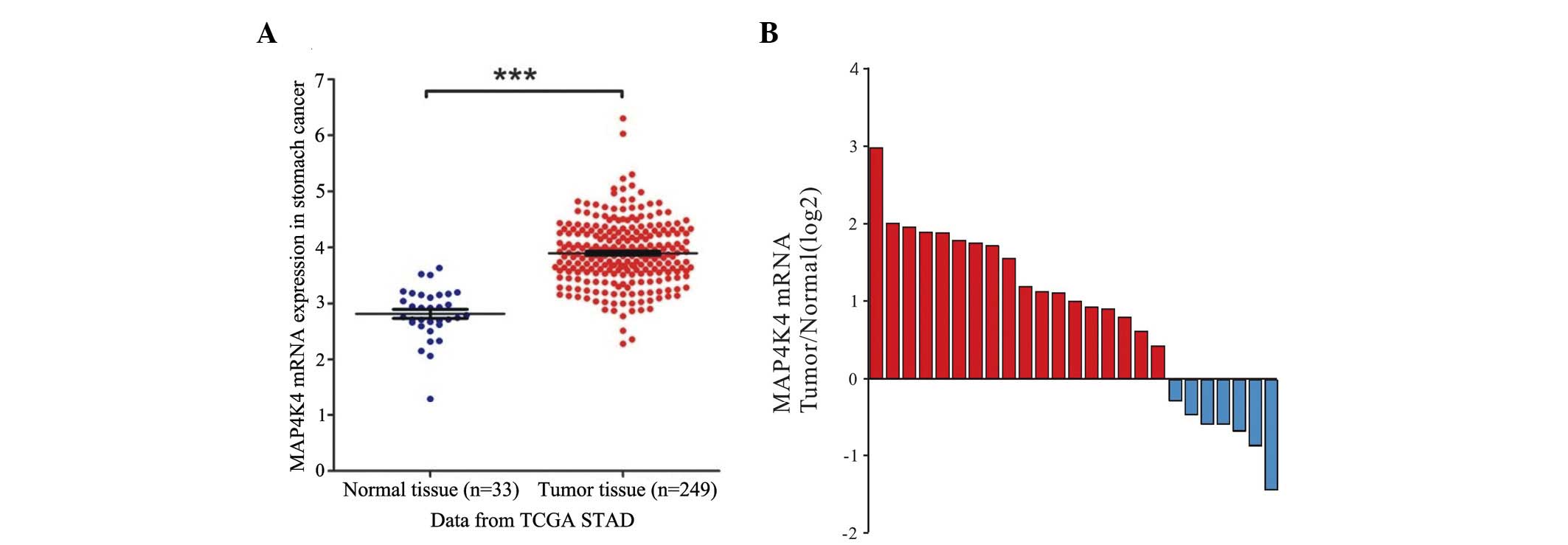
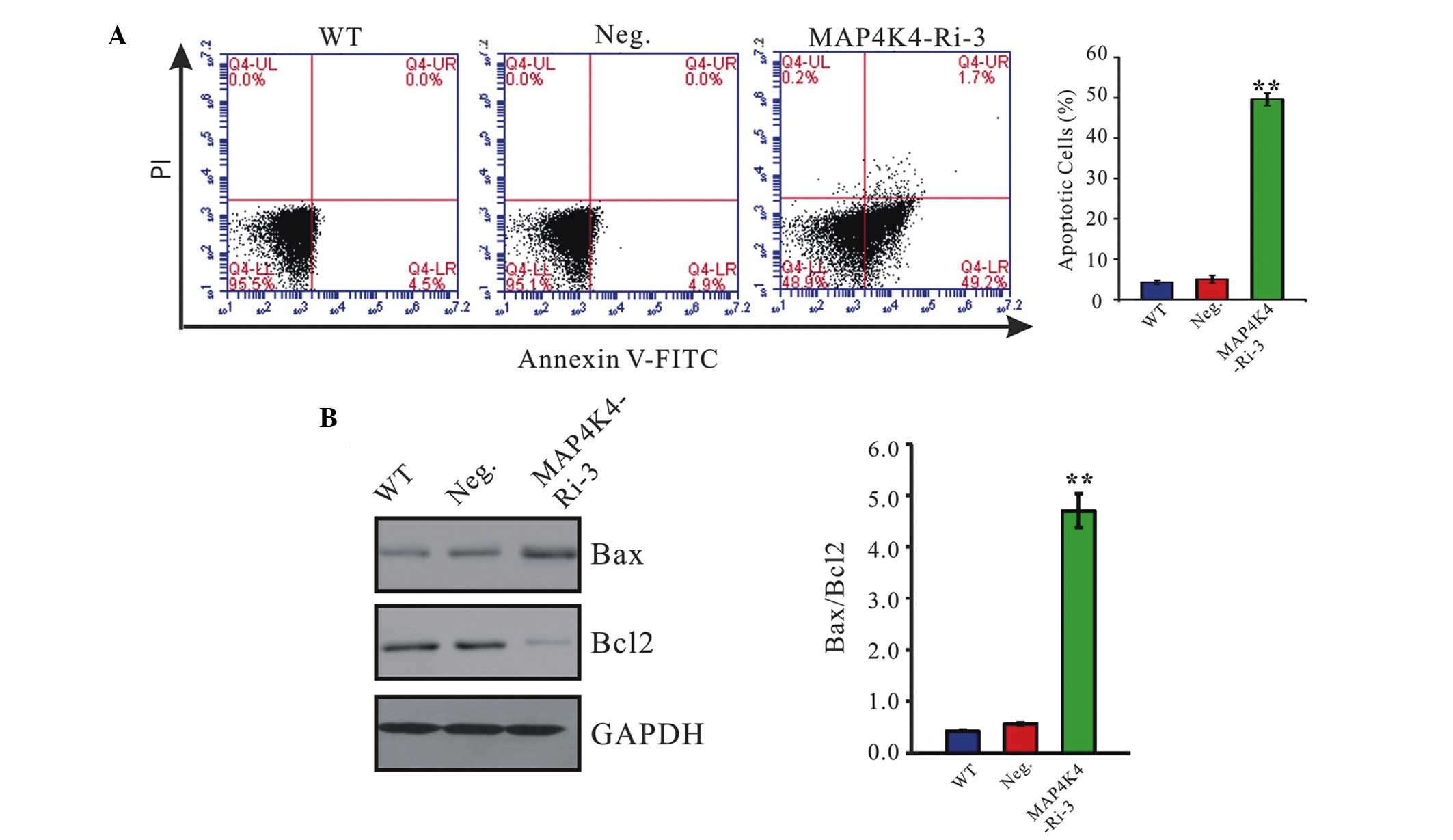
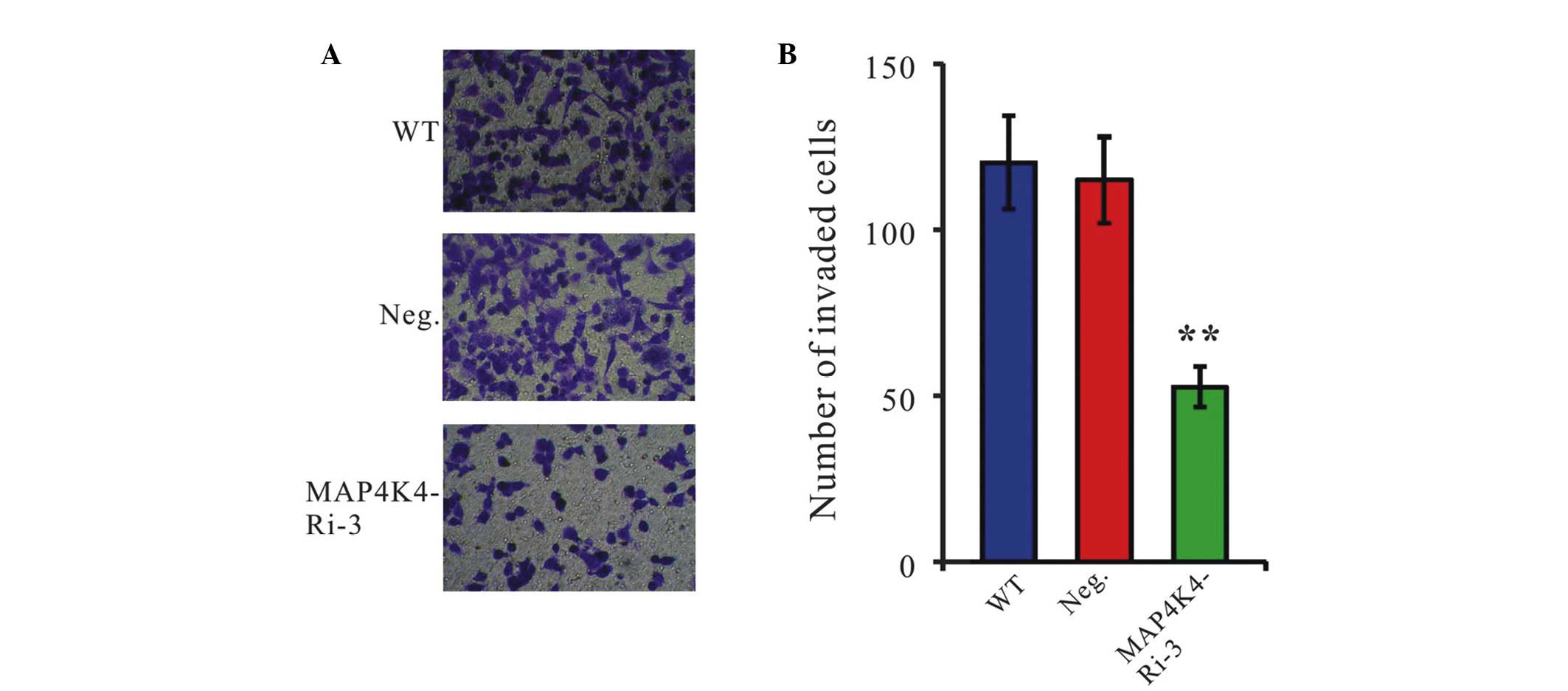
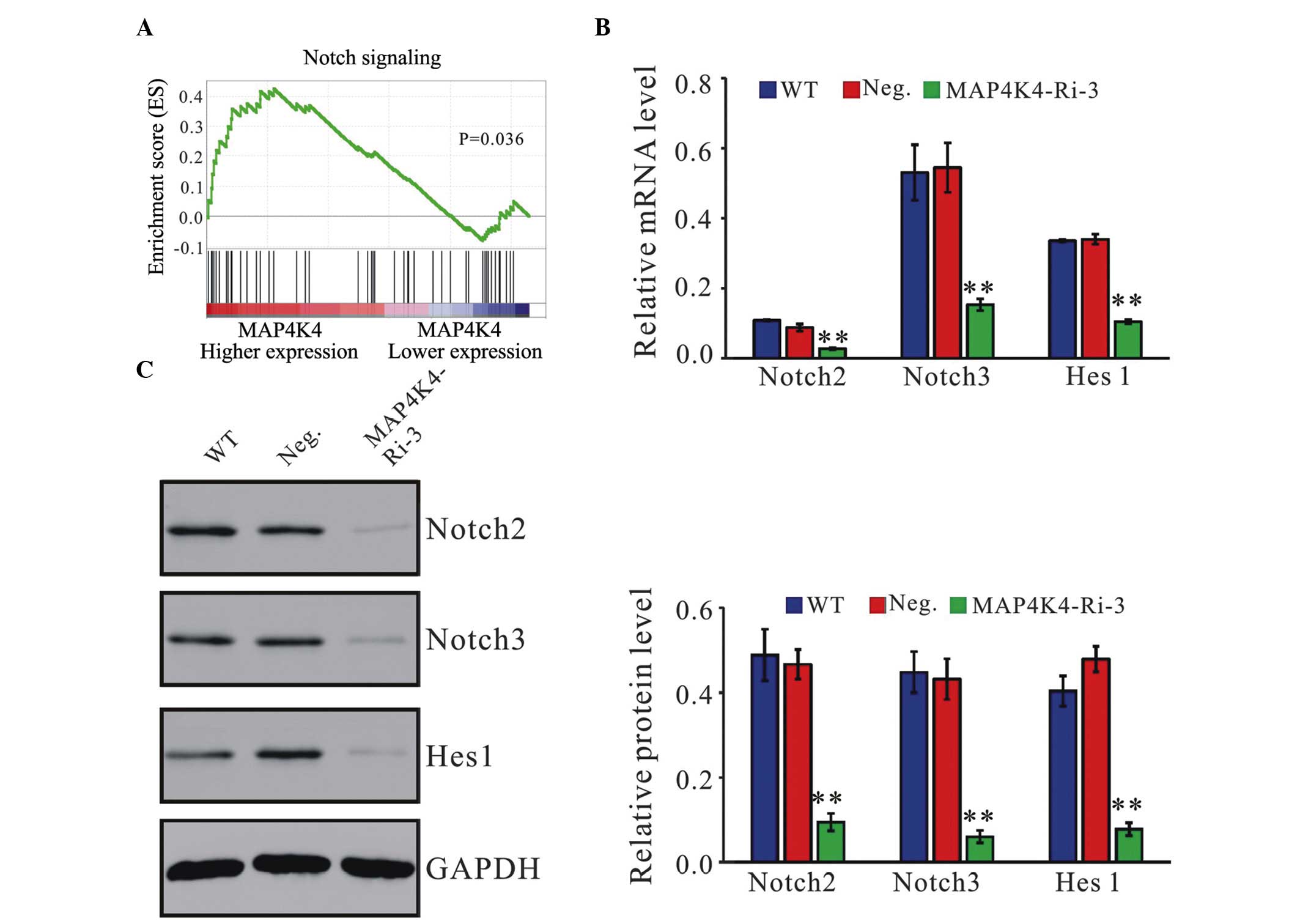
|
1
|
Vogelaar IP, van der Post RS, Bisseling
TM, van Krieken JH, Ligtenberg MJ and Hoogerbrugge N: Familial
gastric cancer: Detection of a hereditary cause helps to understand
its etiology. Hered Cancer Clin Pract. 10:182012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Clegg LX, Ward E, Ries LA, Wu X,
Jamison PM, Wingo PA, Howe HL, Anderson RN and Edwards BK: Annual
report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975–2001, with a
special feature regarding survival. Cancer. 101:3–27. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Turjanski AG, Vaqué JP and Gutkind JS: MAP
kinases and the control of nuclear events. Oncogene. 26:3240–3253.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Collins CS, Hong J, Sapinoso L, Zhou Y,
Liu Z, Micklash K, Schultz PG and Hampton GM: A small interfering
RNA screen for modulators of tumor cell motility identifies MAP4K4
as a promigratory kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:3775–3780.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wright JH, Wang X, Manning G, LaMere BJ,
Le P, Zhu S, Khatry D, Flanagan PM, Buckley SD, Whyte DB, et al:
The STE20 kinase HGK is broadly expressed in human tumor cells and
can modulate cellular transformation, invasion and adhesion. Mol
Cell Biol. 23:2068–2082. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hu Y, Leo C, Yu S, Huang BC, Wang H, Shen
M, Luo Y, Daniel-Issakani S, Payan DG and Xu X: Identification and
functional characterization of a novel human misshapen/Nck
interacting kinase-related kinase, hMINK beta. J Biol Chem.
279:54387–54397. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zohn IE, Li Y, Skolnik EY, Anderson KV,
Han J and Niswander L: p38 and a p38-interacting protein are
critical for downregulation of E-cadherin during mouse
gastrulation. Cell. 125:957–969. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liang JJ and Wang H, Rashid A, Tan TH,
Hwang RF, Hamilton SR, Abbruzzese JL, Evans DB and Wang H:
Expression of MAP4K4 is associated with worse prognosis in patients
with stage II pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
14:7043–7049. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu AW, Cai J, Zhao XL, Jiang TH, He TF,
Fu HQ, Zhu MH and Zhang SH: ShRNA-targeted MAP4K4 inhibits
hepatocellular carcinoma growth. Clin Cancer Res. 17:710–720. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qiu MH, Qian YM, Zhao XL, Wang SM, Feng
XJ, Chen XF and Zhang SH: Expression and prognostic significance of
MAP4K4 in lung adenocarcinoma. Pathol Res Pract. 208:541–548. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sun M, Xia R, Jin F, Xu T, Liu Z, De W and
Liu X: Downregulated long noncoding RNA MEG3 is associated with
poor prognosis and promotes cell proliferation in gastric cancer.
Tumour Biol. 35:1065–1073. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Adams JM and Cory S: Life-or-death
decisions by the Bcl-2 protein family. Trends Biochem Sci.
26:61–66. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hetz C: BCL-2 protein family. Essential
regulators of cell death. Preface Adv Exp Med Biol. 687:vii–viii.
2010.
|
|
14
|
Reed JC: Regulation of apoptosis by bcl-2
family proteins and its role in cancer and chemoresistance. Curr
Opin Oncol. 7:541–546. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhao G, Wang B, Liu Y, Zhang JG, Deng SC,
Qin Q, Tian K, Li X, Zhu S, Niu Y, et al: miRNA-141, downregulated
in pancreatic cancer, inhibits cell proliferation and invasion by
directly targeting MAP4K4. Mol Cancer Ther. 12:2569–2580. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Evan GI and Vousden KH: Proliferation,
cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature. 411:342–348. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Molinari M: Cell cycle checkpoints and
their inactivation in human cancer. Cell Prolif. 33:261–274. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Koch U and Radtke F: Notch and cancer: A
double-edged sword. Cell Mol Life Sci. 64:2746–2762. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nickoloff BJ, Osborne BA and Miele L:
Notch signaling as a therapeutic target in cancer: A new approach
to the development of cell fate modifying agents. Oncogene.
22:6598–6608. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Westhoff B, Colaluca IN, D'Ario G,
Donzelli M, Tosoni D, Volorio S, Pelosi G, Spaggiari L, Mazzarol G,
Viale G, et al: Alterations of the Notch pathway in lung cancer.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:22293–22298. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stylianou S, Clarke RB and Brennan K:
Aberrant activation of notch signaling in human breast cancer.
Cancer Res. 66:1517–1525. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tseng YC, Tsai YH, Tseng MJ, Hsu KW, Yang
MC, Huang KH, Li AF, Chi CW, Hsieh RH, Ku HH and Yeh TS:
Notch2-induced COX-2 expression enhancing gastric cancer
progression. Mol Carcinog. 51:939–951. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Bauer L, Langer R, Becker K, Hapfelmeier
A, Ott K, Novotny A, Höfler H and Keller G: Expression profiling of
stem cell-related genes in neoadjuvant-treated gastric cancer: A
NOTCH2, GSK3B and β-catenin gene signature predicts survival. PLoS
One. 7:e445662012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kang H, An HJ, Song JY, Kim TH, Heo JH,
Ahn DH and Kim G: Notch3 and Jagged2 contribute to gastric cancer
development and to glandular differentiation associated with MUC2
and MUC5AC expression. Histopathology. 61:576–586. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lu JP, Zhang J, Kim K, Case TC, Matusik
RJ, Chen YH, Wolfe M, Nopparat J and Lu Q: Human homolog of
Drosophila Hairy and enhancer of split 1, Hes1, negatively
regulates δ-catenin (CTNND2) expression in cooperation with E2F1 in
prostate cancer. Mol Cancer. 9:3042010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Leong KG and Gao WQ: The Notch pathway in
prostate development and cancer. Differentiation. 76:699–716. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Villaronga MA, Bevan CL and Belandia B:
Notch signaling: A potential therapeutic target in prostate cancer.
Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:566–580. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|