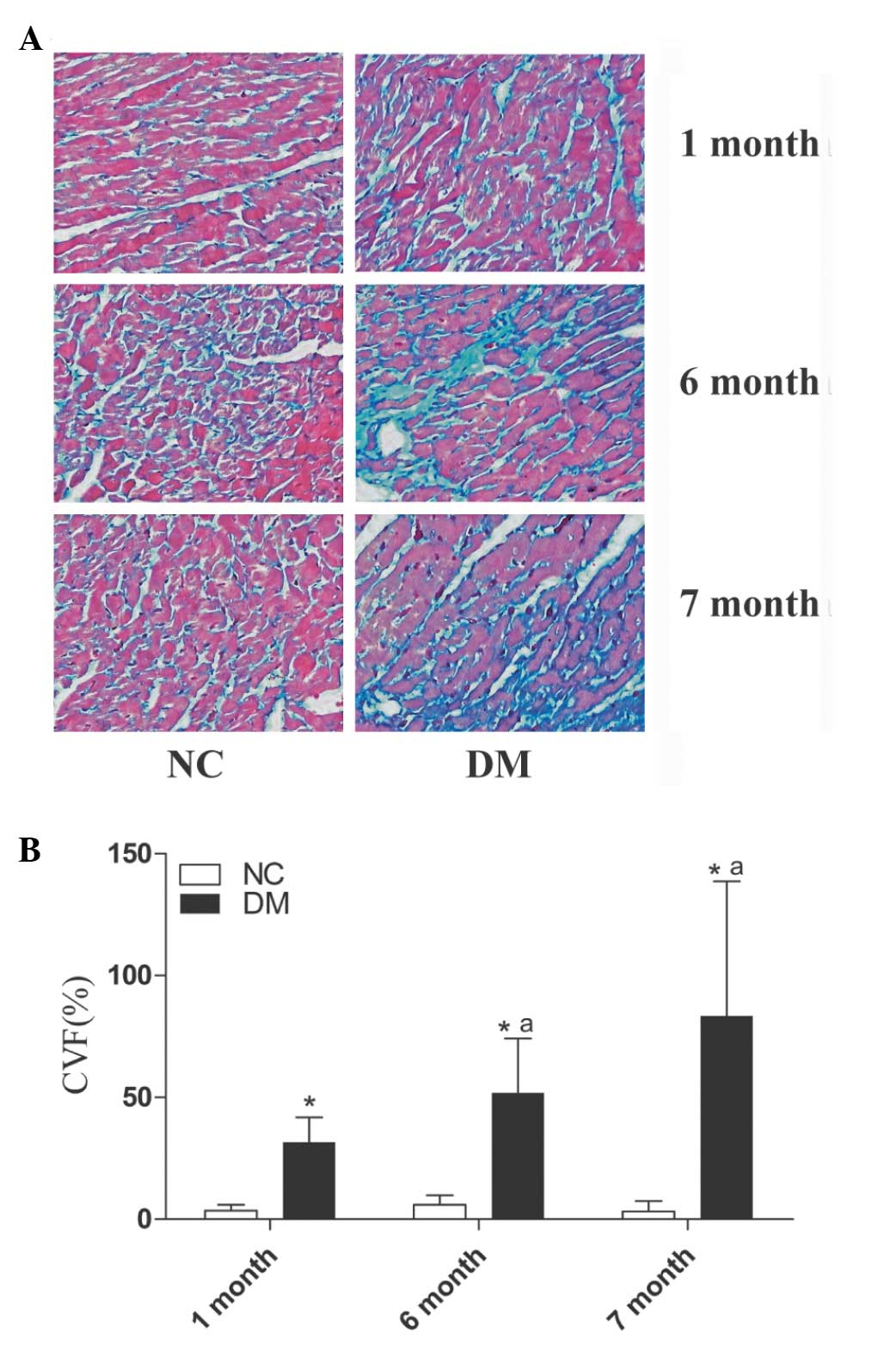
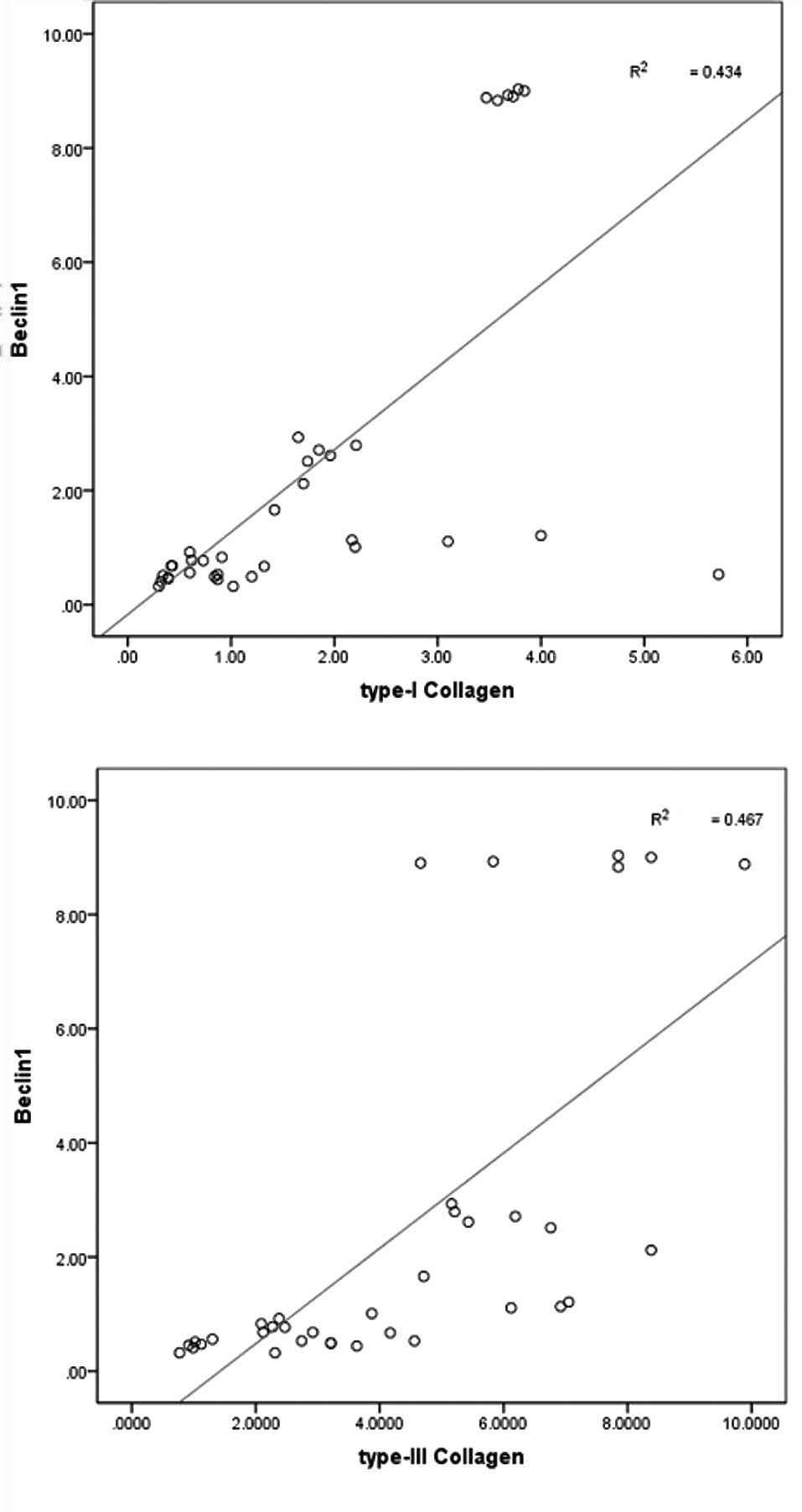
|
1
|
Xu X, Kobayashi S, Chen K, Timm D, Volden
P, Huang Y, Gulick J, Yue Z, Robbins J, Epstein PN and Liang Q:
Diminished autophagy limits cardiac injury in mouse models of type
1 diabetes. J Biol Chem. 288:18077–18092. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xie Z, Lau K, Eby B, Lozano P, He C,
Pennington B, Li H, Rathi S, Dong Y, Tian R, et al: Improvement of
cardiac functions by chronic metformin treatment is associated with
enhanced cardiac autophagy in diabetic OVE26 mice. Diabetes.
60:1770–1778. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rubler S, Dlugash J, Yuceoglu YZ, Kumral
T, Branwood AW and Grishman A: New type of cardiomyopathy
associated with diabetic glomerulosclerosis. Am J Cardiol.
30:595–602. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fischer VW, Barner HB and Larose LS:
Pathomorphologic aspects of muscular tissue in diabetes mellitus.
Hum Pathol. 15:1127–1136. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhu H, Tannous P, Johnstone JL, Kong Y,
Shelton JM, Richardson JA, Le V, Levine B, Rothermel BA and Hill
JA: Cardiac autophagy is a maladaptive response to hemodynamic
stress. J Clin Invest. 117:1782–1793. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Onodera J and Ohsumi Y: Autophagy is
required for maintenance of amino acid levels and protein synthesis
under nitrogen starvation. J Biol Chem. 280:31582–31586. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dorn GW II: Apoptotic and non-apoptotic
programmed cardiomyocyte death in ventricular remodelling.
Cardiovasc Res. 81:465–473. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Shen S, Kepp O and Kroemer G: The end of
autophagic cell death? Autophagy. 8:1–3. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hernández-Gea V, Ghiassi-Nejad Z,
Rozenfeld R, Gordon R, Fiel MI, Yue Z, Czaja MJ and Friedman SL:
Autophagy releases lipid that promotes fibrogenesis by activated
hepatic stellate cells in mice and in human tissues.
Gastroenterology. 142:938–946. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mellor KM, Bell JR, Young MJ, Ritchie RH
and Delbridge LM: Myocardial autophagy activation and suppressed
survival signaling is associated with insulin resistance in
fructose-fed mice. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 50:1035–1043. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nho RS and Hergert P: IPF fibroblasts are
desensitized to type I collagen matrix-induced cell death by
suppressing low autophagy via aberrant Akt/mTOR kinases. PLoS One.
9:e946162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Srinivasan K, Viswanad B, Asrat L, Kaul CL
and Ramarao P: Combination of high-fat diet-fed and low-dose
streptozotocin-treated rat: A model for type 2 diabetes and
pharmacological screening. Pharmacol Res. 52:313–320. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Islam MS and Choi H: Nongenetic model of
type 2 diabetes: A comparative study. Pharmacology. 79:243–249.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Barth S, Glick D and Macleod KF:
Autophagy: Assays and artifacts. J Pathol. 221:117–124. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bjorkoy G, Lamark T, Brech A, Outzen H,
Perander M, Overvatn A, Stenmark H and Johansen T: p62/SQSTM1 forms
protein aggregates degraded by autophagy and has a protective
effect on huntingtin-induced cell death. J Cell Biol. 171:603–614.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee HS, Daniels BH, Salas E, Bollen AW,
Debnath J and Margeta M: Clinical utility of LC3 and p62
immunohisto-chemistry in diagnosis of drug-induced autophagic
vacuolar myopathies: A case-control study. PLoS One. 7:e362212012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Settembre C, Fraldi A, Jahreiss L,
Spampanato C, Venturi C, Medina D, de Pablo R, Tacchetti C,
Rubinsztein DC and Ballabio A: A block of autophagy in lysosomal
storage disorders. Hum Mol Genet. 17:119–129. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Mizushige K, Yao L, Noma T, Kiyomoto H, Yu
Y, Hosomi N, Ohmori K and Matsuo H: Alteration in left ventricular
diastolic filling and accumulation of myocardial collagen at
insulin-resistant prediabetic stage of a type II diabetic rat
model. Circulation. 101:899–907. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Vadlamudi RV, Rodgers RL and McNeill JH:
The effect of chronic alloxan- and streptozotocin-induced diabetes
on isolated rat heart performance. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
60:902–911. 1982. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kato T, Yamashita T, Sekiguchi A, Sagara
K, Takamura M, Takata S, Kaneko S, Aizawa T and Fu LT: What are
arrhythmogenic substrates in diabetic rat atria? J Cardiovasc
Electrophysiol. 17:890–894. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Boyle AJ, Shih H, Hwang J, Ye J, Lee B,
Zhang Y, Kwon D, Jun K, Zheng D, Sievers R, et al: Cardiomyopathy
of aging in the mammalian heart is characterized by myocardial
hypertrophy, fibrosis and a predisposition towards cardiomyocyte
apoptosis and autophagy. Exp Gerontol. 46:549–559. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Miyata S, Takemura G, Kawase Y, Li Y,
Okada H, Maruyama R, Ushikoshi H, Esaki M, Kanamori H, Li L, et al:
Autophagic cardiomyocyte death in cardiomyopathic hamsters and its
prevention by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Am J Pathol.
168:386–397. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang TZ, Fan B, Chen X, Wang WJ, Jiao YY,
Su GF and Li GY: Suppressing autophagy protects photoreceptor cells
from light-induced injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 450:966–972.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mizushima N and Yoshimori T: How to
interpret LC3 immunoblotting. Autophagy. 3:542–545. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|