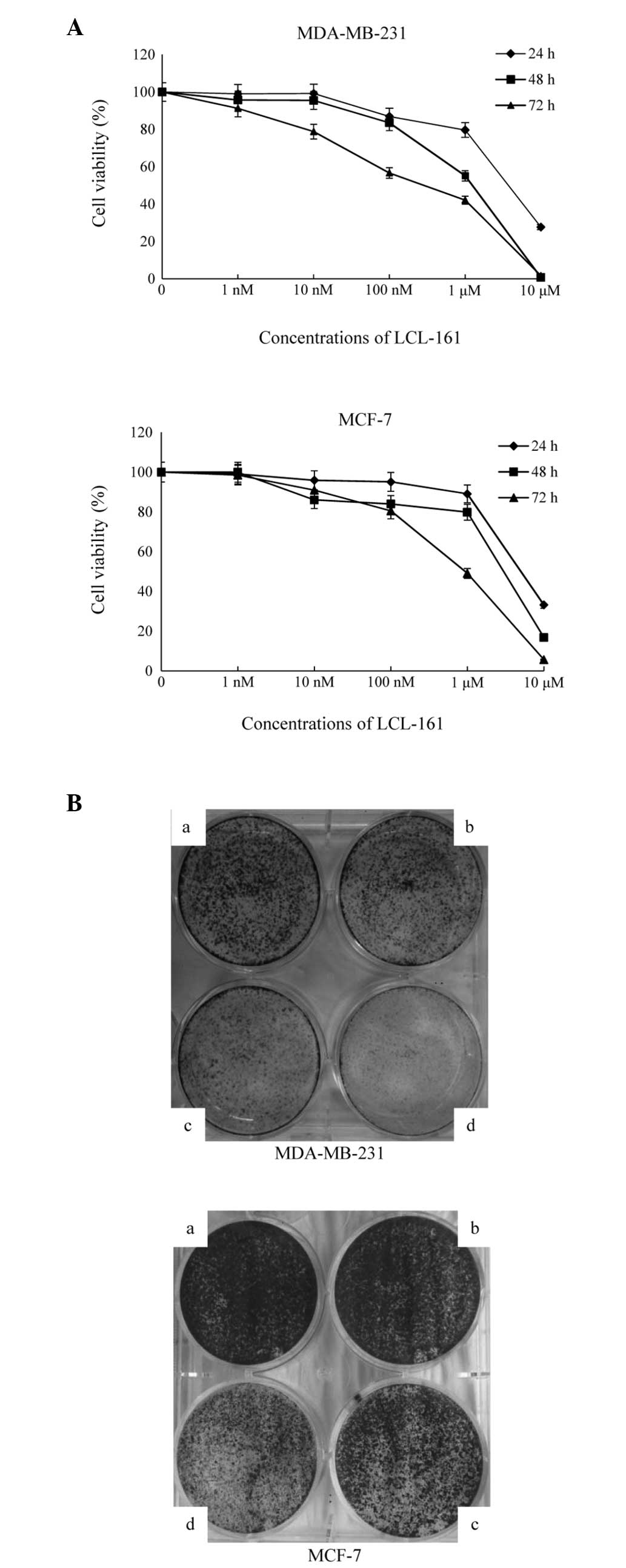
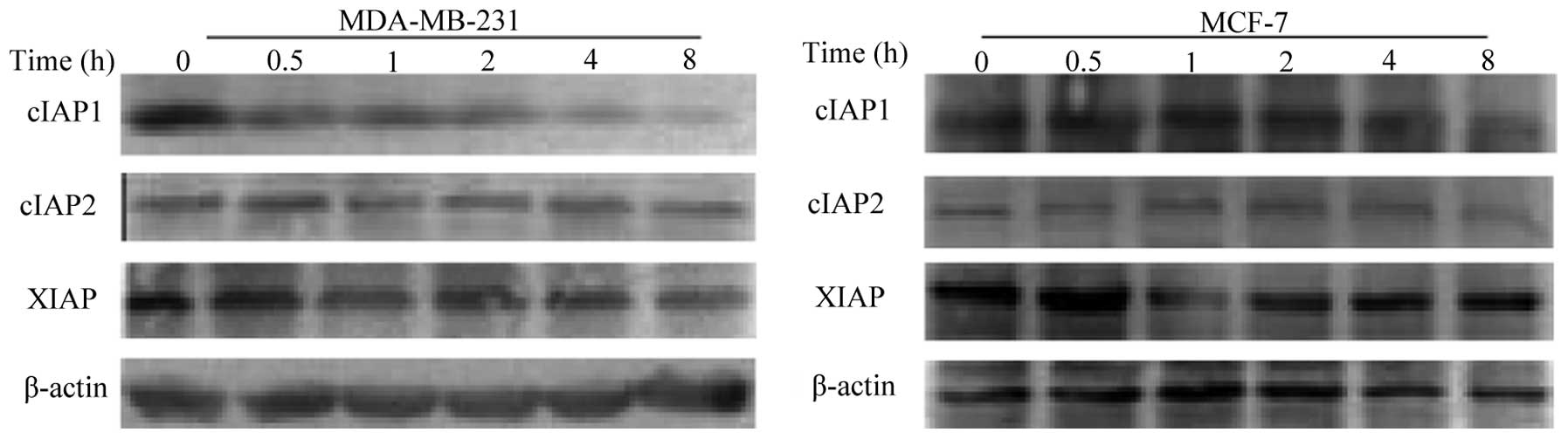
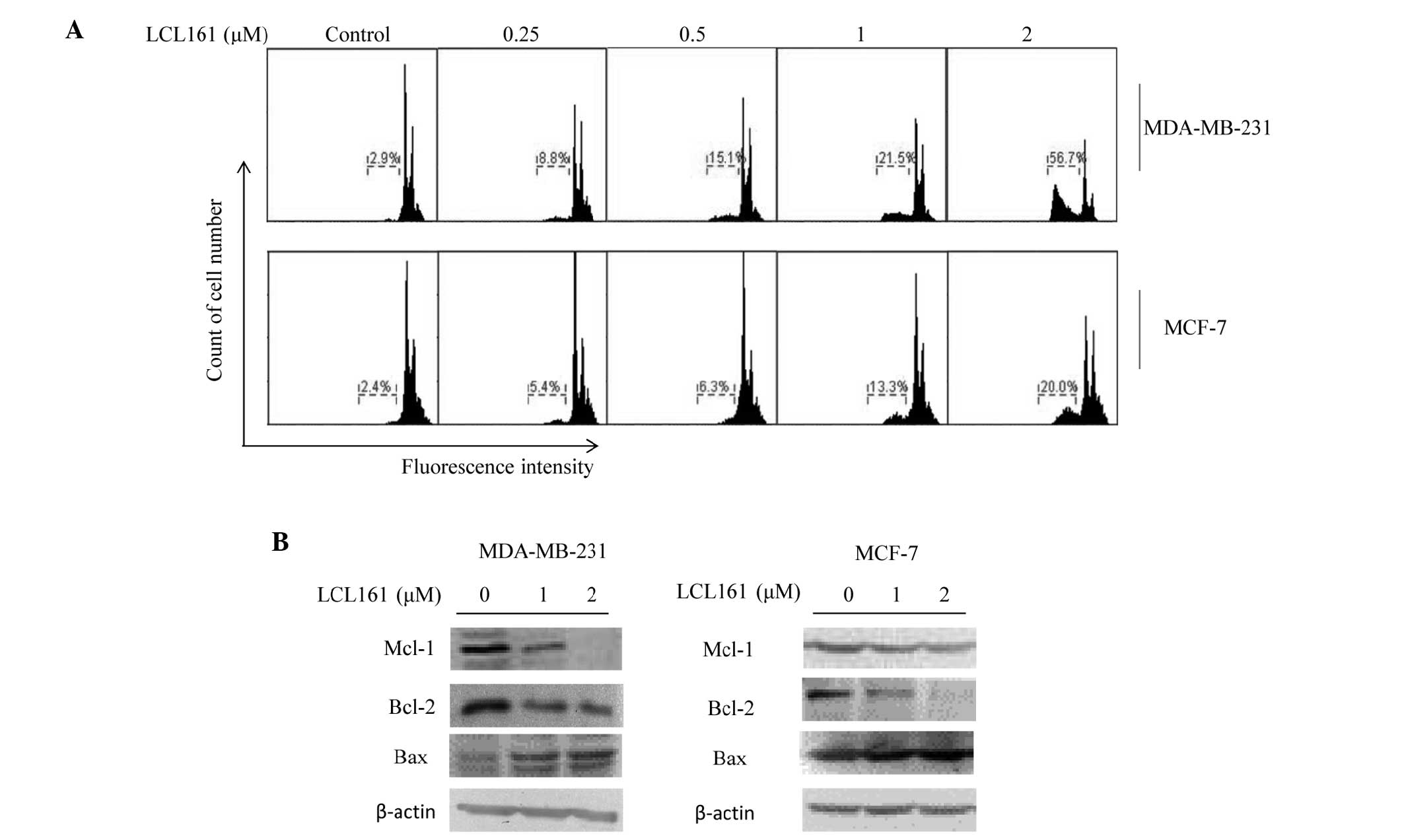
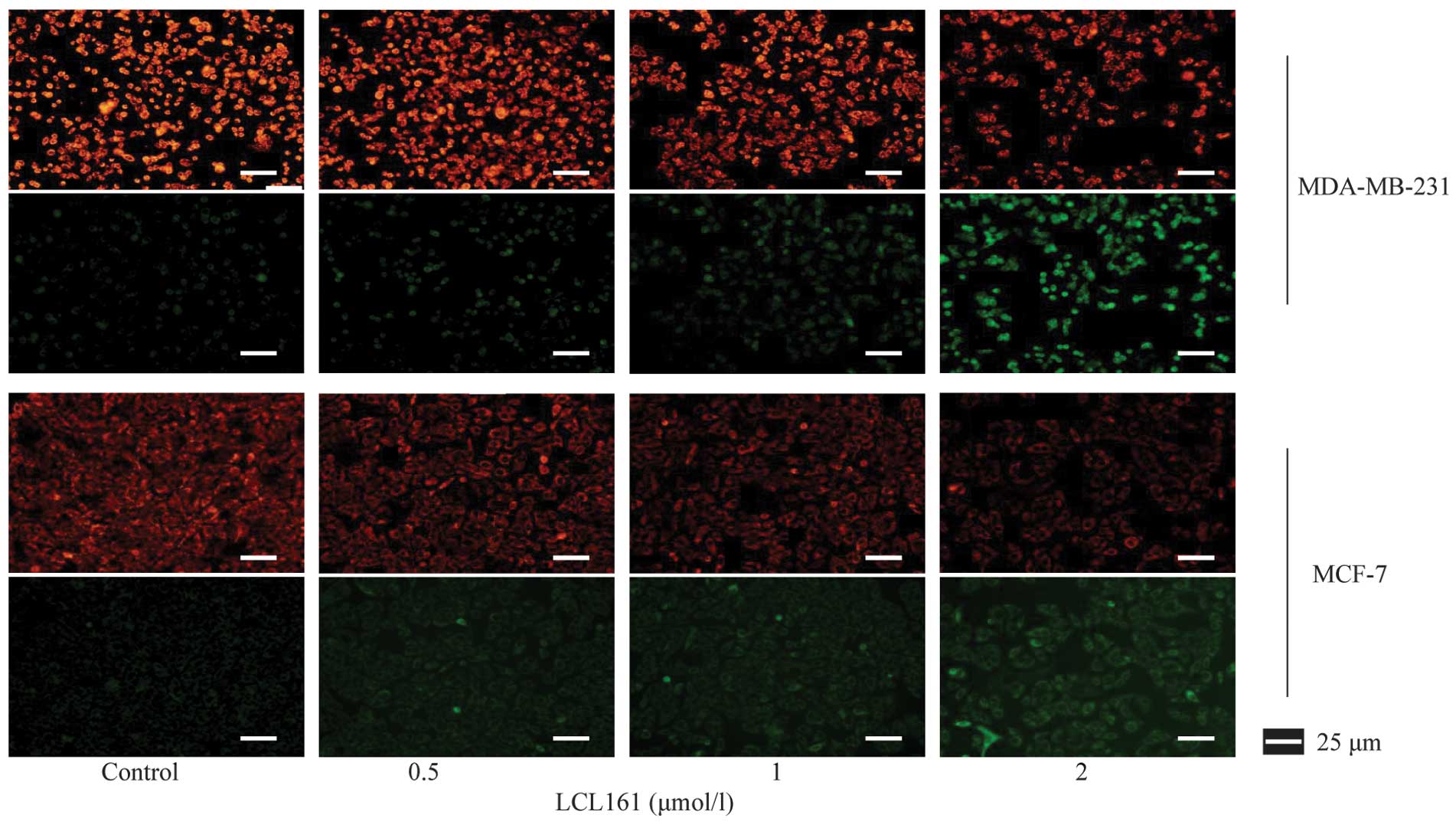
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Ren JS, Masuyer E and Ferlay J:
Global estimates of cancer prevalence for 27 sites in the adult
population in 2008. Int J Cancer. 132:1133–1145. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Fearon ER and Vogelstein B: A genetic
model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 61:759–767. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sherr CJ: Cancer cell cycles. Science.
274:1672–1677. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Higgins MJ and Baselga J: Targeted
therapies for breast cancer. J Clin Invest. 121:3797–3803. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sørlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T,
Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey
SS, et al: Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas
distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:10869–10874. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bourdeanu L and Luu T: Targeted therapies
in breast cancer: Implications for advanced oncology practice. J
Adv Pract Oncol. 5:246–260. 2014.
|
|
9
|
Reed JC: Apoptosis-based therapies. Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 1:111–121. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Johnstone RW, Ruefli AA and Lowe SW:
Apoptosis: A link between cancer genetics and chemotherapy. Cell.
108:153–164. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lockshin RA and Williams CM: Programmed
cell Death-I. Cytology of degeneration in the intersegmental
muscles of the pernyi silkmoth. J Insect Physiol. 11:123–133. 1965.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fulda S and Debatin KM: Extrinsic versus
intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene.
25:4798–4811. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bai L, Smith DC and Wang S: Small-molecule
SMAC mimetics as new cancer therapeutics. Pharmacol Ther.
144:82–95. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dubrez L, Berthelet J and Glorian V: IAP
proteins as targets for drug development in oncology. Onco Targets
Ther. 9:1285–1304. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L and Wang X: Smac,
a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent
caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell. 102:33–42.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Salvesen GS and Duckett CS: IAP proteins:
Blocking the road to death's door. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
3:401–410. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li J, McQuade T, Siemer AB, Napetschnig J,
Moriwaki K, Hsiao YS, Damko E, Moquin D, Walz T, McDermott A, et
al: The RIP1/RIP3 necrosome forms a functional amyloid signaling
complex required for programmed necrosis. Cell. 150:339–350. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Holler N, Zaru R, Micheau O, Thome M,
Attinger A, Valitutti S, Bodmer JL, Schneider P, Seed B and Tschopp
J: Fas triggers an alternative, caspase-8-independent cell death
pathway using the kinase RIP as effector molecule. Nat Immunol.
1:489–495. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang DW, Shao J, Lin J, Zhang N, Lu BJ,
Lin SC, Dong MQ and Han J: RIP3, an energy metabolism regulator
that switches TNF-induced cell death from apoptosis to necrosis.
Science. 325:332–336. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun L, Wang H, Wang Z, He S, Chen S, Liao
D, Wang L, Yan J, Liu W, Lei X and Wang X: Mixed lineage kinase
domain-like protein mediates necrosis signaling downstream of RIP3
kinase. Cell. 148:213–227. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Degterev A, Hitomi J, Germscheid M, Ch'en
IL, Korkina O, Teng X, Abbott D, Cuny GD, Yuan C, Wagner G, et al:
Identification of RIP1 kinase as a specific cellular target of
necrostatins. Nat Chem Biol. 4:313–321. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Smith CC, Davidson SM, Lim SY, Simpkin JC,
Hothersall JS and Yellon DM: Necrostatin: A potentially novel
cardioprotective agent? Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 21:227–233. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Linkermann A, Bräsen JH, Himmerkus N, Liu
S, Huber TB, Kunzendorf U and Krautwald S: Rip1
(receptor-interacting protein kinase 1) mediates necroptosis and
contributes to renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Kidney Int.
81:751–761. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Oerlemans MI, Liu J, Arslan F, den Ouden
K, van Middelaar BJ, Doevendans PA and Sluijter JP: Inhibition of
RIP1-dependent necrosis prevents adverse cardiac remodeling after
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion in vivo. Basic Res Cardiol.
107:2702012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lin J, Li H, Yang M, Ren J, Huang Z, Han
F, Huang J, Ma J, Zhang D, Zhang Z, et al: A role of RIP3-mediated
macrophage necrosis in atherosclerosis development. Cell Rep.
3:200–210. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen KF, Lin JP, Shiau CW, Tai WT, Liu CY,
Yu HC, Chen PJ and Cheng AL: Inhibition of Bcl-2 improves effect of
LCL161, a SMAC mimetic, in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem
Pharmacol. 84:268–277. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Varfolomeev E, Blankenship JW, Wayson SM,
Fedorova AV, Kayagaki N, Garg P, Zobel K, Dynek JN, Elliott LO,
Wallweber HJ, et al: IAP antagonists induce autoubiquitination of
c-IAPs, NF-kappaB activation and TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis.
Cell. 131:669–681. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Weisberg E, Ray A, Barrett R, Nelson E,
Christie AL, Porter D, Straub C, Zawel L, Daley JF, Lazo-Kallanian
S, et al: Smac mimetics: Implications for enhancement of targeted
therapies in Leukemia. Leukemia. 24:2100–2109. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Marty M, Cognetti F, Maraninchi D, Snyder
R, Mauriac L, Tubiana-Hulin M, Chan S, Grimes D, Antón A, Lluch A,
et al: Randomized phase II trial of the efficacy and safety of
trastuzumab combined with docetaxel in patients with human
epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive metastatic breast
cancer administered as first-line treatment: The M77001 study
group. J Clin Oncol. 23:4265–4274. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lowe SW and Lin AW: Apoptosis in cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 21:485–495. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang S, Bai L, Lu J, Liu L, Yang CY and
Sun H: Targeting inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (IAP) for new
breast cancer therapeutics. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia.
17:217–228. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hassan M, Watari H, AbuAlmaaty A, Ohba Y
and Sakuragi N: Apoptosis and molecular targeting therapy in
cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2014:1508452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu G, Chai J, Suber TL, Wu JW, Du C, Wang
X and Shi Y: Structural basis of IAP recognition by Smac/DIABLO.
Nature. 408:1008–1012. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Chauhan D, Neri P, Velankar M, Podar K,
Hideshima T, Fulciniti M, Tassone P, Raje N, Mitsiades C, Mitsiades
N, et al: Targeting mitochondrial factor Smac/DIABLO as therapy for
multiple myeloma (MM). Blood. 109:1220–1227. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 protein
family: Arbiters of cell survival. Science. 281:1322–1326. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kvanskul M and Hinds MG: Structural
biology of the Bcl-2 family and its mimicry by viral proteins. Cell
Death Dis. 4:e9092013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kim BM and Chung HW: Desferrioxamine (DFX)
induces apoptosis through the p38-caspase8-Bid-Bax pathway in
PHA-stimulated human lymphocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
228:24–31. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kozopas KM, Yang T, Buchan HL, Zhou P and
Craig RW: MCL1, a gene expressed in programmed myeloid cell
differentiation, has sequence similarity to BCL2. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 90:3516–3520. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sano M, Hayashi E, Murakami H, Kishimoto
H, Fukuzawa R and Nemoto N: Mcl-1, an anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family
member, essentially overlaps with insulin-producing cells in
neonatal nesidioblastosis. Virchows Arch. 452:469–470. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gyrd-Hansen M, Darding M, Miasari M,
Santoro MM, Zender L, Xue W, Tenev T, da Fonseca PC, Zvelebil M,
Bujnicki JM, et al: IAPs contain an evolutionarily conserved
ubiquitin-binding domain that regulates NF-kappaB as well as cell
survival and oncogenesis. Nat Cell Biol. 10:1309–1317. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Vaux DL and Silke J: IAPs, RINGs and
ubiquitylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6:287–297. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Park SM, Yoon JB and Lee TH: Receptor
interacting protein is ubiquitinated by cellular inhibitor of
apoptosis proteins (c-IAP1 and c-IAP2) in vitro. FEBS Lett.
566:151–156. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|