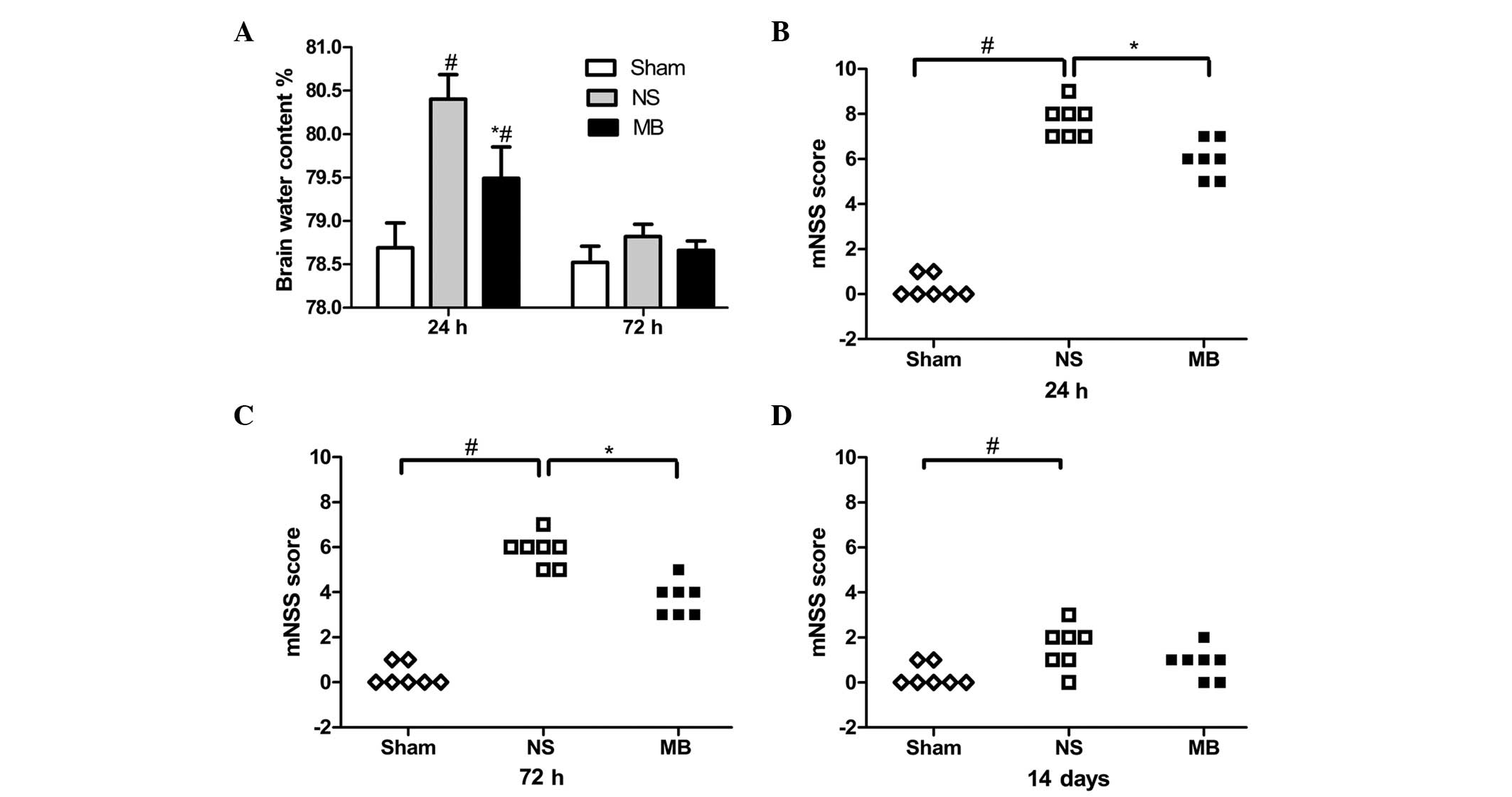
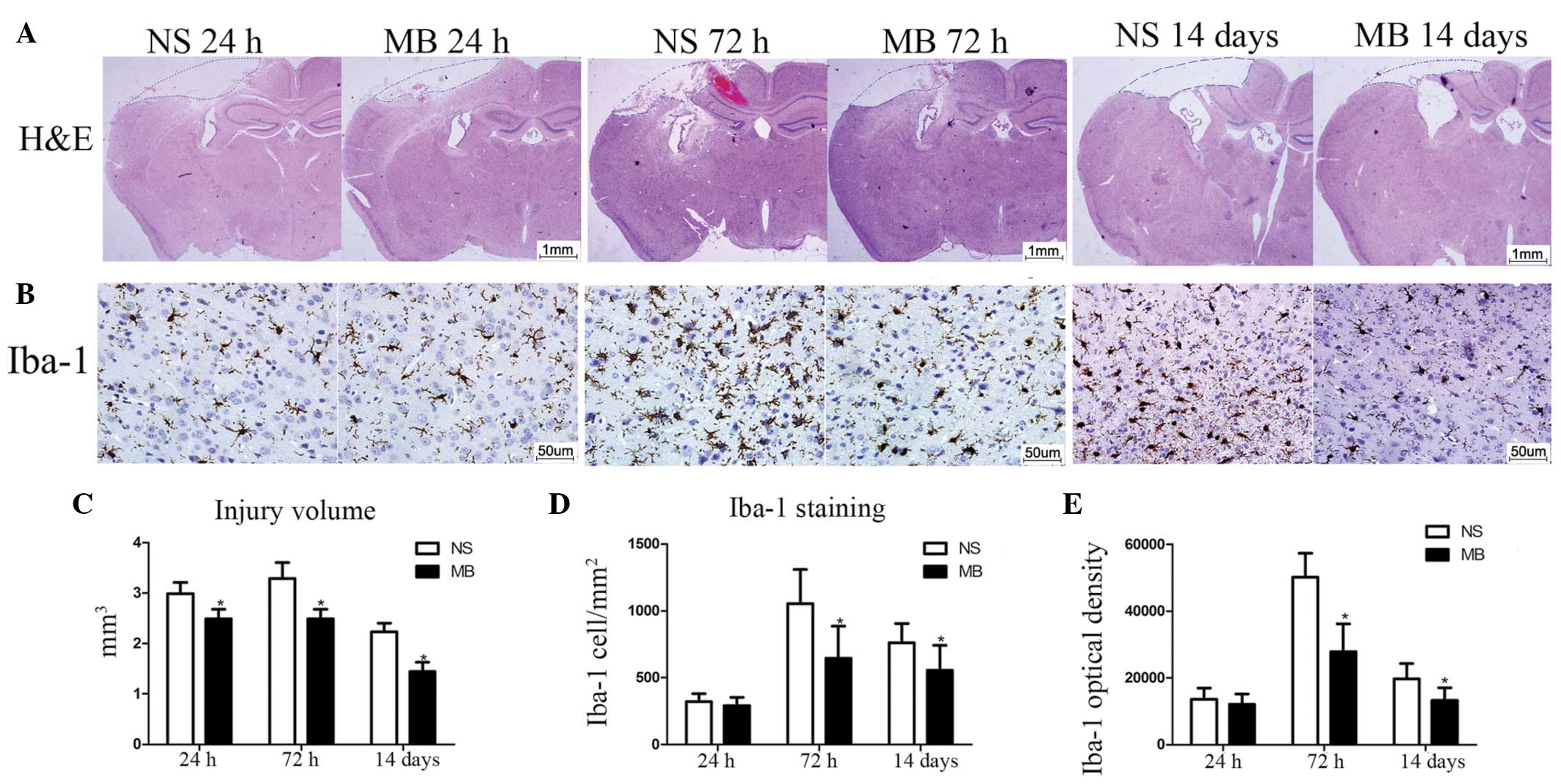
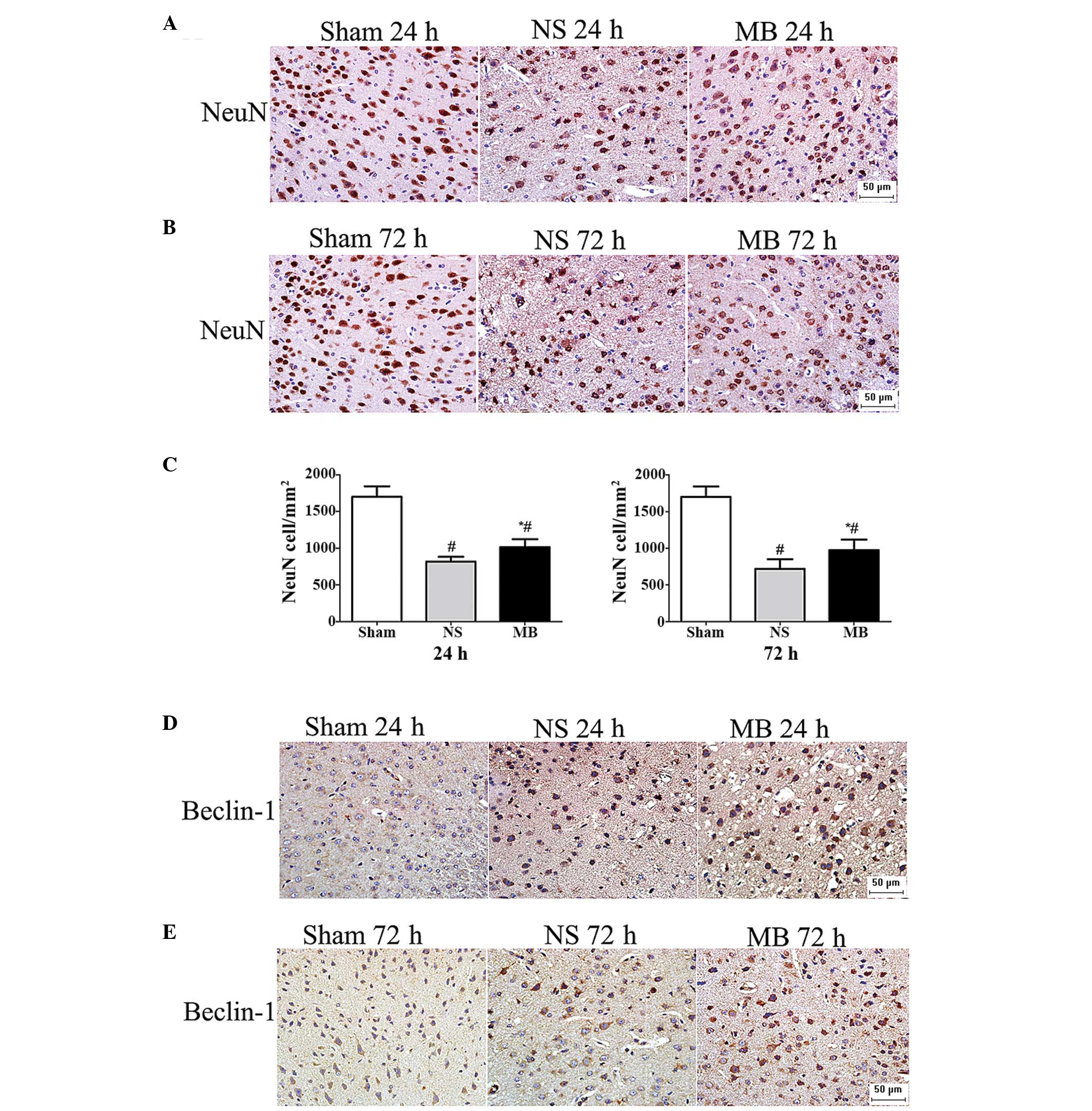
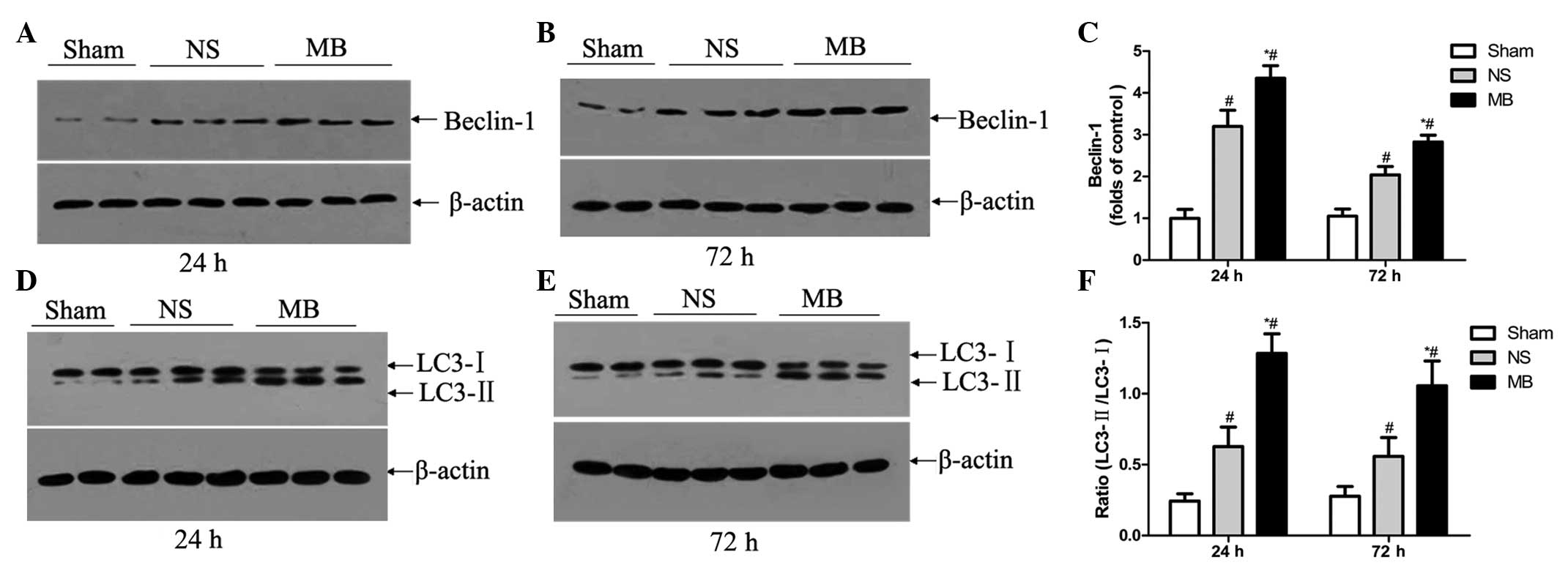
|
1
|
Feigin VL, Theadom A, Barker-Collo S,
Starkey NJ, McPherson K, Kahan M, Dowell A, Brown P, Parag V, Kydd
R, et al BIONIC Study Group: Incidence of traumatic brain injury in
New Zealand: A population-based study. Lancet Neurol. 12:53–64.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Dvela-Levitt M1, Ami HC, Rosen H, Shohami
E and Lichtstein D: Ouabain improves functional recovery following
traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 31:1942–1947. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fenn AM, Skendelas JP, Moussa DN,
Muccigrosso MM, Popovich PG, Lifshitz J, Eiferman DS and Godbout
JP: Methylene blue attenuates traumatic brain injury-associated
neuroinflammation and acute depressive-like behavior in mice. J
Neurotrauma. 32:127–138. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xiong Y, Mahmood A and Chopp M: Animal
models of traumatic brain injury. Nat Rev Neurosci. 14:128–142.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Auchter A, Williams J, Barksdale B,
Monfils MH and Gonzalez-Lima F: Therapeutic benefits of methylene
blue on cognitive impairment during chronic cerebral hypoperfusion.
J Alzheimers Dis. 42(Suppl 4): S525–S535. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kwok ES and Howes D: Use of methylene blue
in sepsis: A systematic review. J Intensive Care Med. 21:359–363.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Maslow AD, Stearns G, Butala P, Schwartz
CS, Gough J and Singh AK: The hemodynamic effects of methylene blue
when administered at the onset of cardiopulmonary bypass. Anesth
Analg. 103:2–8. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Paciullo CA, McMahon Horner D, Hatton KW
and Flynn JD: Methylene blue for the treatment of septic shock.
Pharmacotherapy. 30:702–715. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rojas JC, Bruchey AK and Gonzalez-Lima F:
Neurometabolic mechanisms for memory enhancement and
neuroprotection of methylene blue. Prog Neurobiol. 96:32–45. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Dibaj P, Zschüntzsch J, Steffens H,
Scheffel J, Göricke B, Weishaupt JH, Le Meur K, Kirchhoff F,
Hanisch UK, Schomburg ED, et al: Influence of methylene blue on
microglia-induced inflammation and motor neuron degeneration in the
SOD1(G93A) model for ALS. PLoS One. 7:e439632012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shen Q, Du F, Huang S, Rodriguez P, Watts
LT and Duong TQ: Neuroprotective efficacy of methylene blue in
ischemic stroke: An MRI study. PLoS One. 8:e798332013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Talley Watts L, Long JA, Chemello J, Van
Koughnet S, Fernandez A, Huang S, Shen Q and Duong TQ: Methylene
blue is neuroprotective against mild traumatic brain injury. J
Neurotrauma. 31:1063–1071. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals: Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th
edition. National Academies Press; Washington DC: 2011
|
|
14
|
Hong Y, Yan W, Chen S, Sun CR and Zhang
JM: The role of Nrf2 signaling in the regulation of antioxidants
and detoxifying enzymes after traumatic brain injury in rats and
mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 31:1421–1430. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Callaway NL, Riha PD, Bruchey AK, Munshi Z
and Gonzalez-Lima F: Methylene blue improves brain oxidative
metabolism and memory retention in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav.
77:175–181. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen J, Sanberg PR, Li Y, Wang L, Lu M,
Willing AE, Sanchez-Ramos J and Chopp M: Intravenous administration
of human umbilical cord blood reduces behavioral deficits after
stroke in rats. Stroke. 32:2682–2688. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu J, Wang H, Ding K, Lu X, Li T and Wang
J, Wang C and Wang J: Inhibition of cathepsin S produces
neuroprotective effects after traumatic brain injury in mice.
Mediators Inflamm. 2013:1878732013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang H, Liao Z, Sun X, Shi Q, Huo G, Xie
Y, Tang X, Zhi X and Tang Z: Intravenous administration of Honokiol
provides neuroprotection and improves functional recovery after
traumatic brain injury through cell cycle inhibition.
Neuropharmacology. 86:9–21. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen J, Wang L, Wu C, Hu Q, Gu C, Yan F,
Li J, Yan W and Chen G: Melatonin-enhanced autophagy protects
against neural apoptosis via a mitochondrial pathway in early brain
injury following a subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Pineal Res. 56:12–19.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Congdon EE, Wu JW, Myeku N, Figueroa YH,
Herman M, Marinec PS, Gestwicki JE, Dickey CA, Yu WH and Duff KE:
Methylthioninium chloride (methylene blue) induces autophagy and
attenuates tauopathy in vitro and in vivo. Autophagy. 8:609–622.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Humphreys I, Wood RL, Phillips CJ and
Macey S: The costs of traumatic brain injury: A literature review.
Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 5:281–287. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sivanandam TM and Thakur MK: Traumatic
brain injury: A risk factor for Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci
Biobehav Rev. 36:1376–1381. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Han Z, Du Y, Qi H and Yin W:
Post-traumatic malignant glioma in a pregnant woman: Case report
and review of the literature. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 53:630–634.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kumar A and Loane DJ: Neuroinflammation
after traumatic brain injury: Opportunities for therapeutic
intervention. Brain Behav Immun. 26:1191–1201. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Eroglu B, Kimbler DE, Pang J, Choi J,
Moskophidis D, Yanasak N, Dhandapani KM and Mivechi NF: Therapeutic
inducers of the HSP70/HSP110 protect mice against traumatic brain
injury. J Neurochem. 130:626–641. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lu J, Marmarou A, Choi S, Maas A, Murray G
and Steyerberg EW: Impact and Abic Study Group: Mortality from
traumatic brain injury. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien). 95:281–285.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Xu FF, Sun S, Ho AS, Lee D, Kiang KM,
Zhang XQ, Wang AM, Wu EX, Lui WM, Liu BY and Leung GK: Effects of
progesterone vs. dexamethasone on brain oedema and inflammatory
responses following experimental brain resection. Brain Inj.
28:1594–1601. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Esen F, Erdem T, Aktan D, Kalayci R, Cakar
N, Kaya M and Telci L: Effects of magnesium administration on brain
edema and blood-brain barrier breakdown after experimental
traumatic brain injury in rats. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol.
15:119–125. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Barzó P, Marmarou A, Fatouros P, Hayasaki
K and Corwin F: Contribution of vasogenic and cellular edema to
traumatic brain swelling measured by diffusion-weighted imaging. J
Neurosurg. 87:900–907. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lim SW, Wang CC, Wang YH, Chio CC, Niu KC
and Kuo JR: Microglial activation induced by traumatic brain injury
is suppressed by postinjury treatment with hyperbaric oxygen
therapy. J Surg Res. 184:1076–1084. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Parekkadan B, Berdichevsky Y, Irimia D,
Leeder A, Yarmush G, Toner M, Levine JB and Yarmush ML: Cell-cell
interaction modulates neuroectodermal specification of embryonic
stem cells. Neurosci Lett. 438:190–195. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gentleman SM, Leclercq PD, Moyes L, Graham
DI, Smith C, Griffin WS and Nicoll JA: Long-term intracerebral
inflammatory response after traumatic brain injury. Forensic Sci
Int. 146:97–104. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ramlackhansingh AF, Brooks DJ, Greenwood
RJ, Bose SK, Turkheimer FE, Kinnunen KM, Gentleman S, Heckemann RA,
Gunanayagam K, Gelosa G, et al: Inflammation after trauma:
Microglial activation and traumatic brain injury. Ann Neurol.
70:374–383. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Duan Y, Haugabook SJ, Sahley CL and Muller
KJ: Methylene blue blocks cGMP production and disrupts directed
migration of microglia to nerve lesions in the leech CNS. J
Neurobiol. 57:183–192. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dibaj P, Nadrigny F, Steffens H, Scheller
A, Hirrlinger J, Schomburg ED, Neusch C and Kirchhoff F: NO
mediates microglial response to acute spinal cord injury under ATP
control in vivo. Glia. 58:1133–1144. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gibbs SM and Truman JW: Nitric oxide and
cyclic GMP regulate retinal patterning in the optic lobe of
Drosophila. Neuron. 20:83–93. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Levine B and Klionsky DJ: Development by
self-digestion: Molecular mechanisms and biological functions of
autophagy. Dev Cell. 6:463–477. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Diskin T, Tal-Or P, Erlich S, Mizrachy L,
Alexandrovich A, Shohami E and Pinkas-Kramarski R: Closed head
injury induces upregulation of Beclin 1 at the cortical site of
injury. J Neurotrauma. 22:750–762. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Erlich S, Alexandrovich A, Shohami E and
Pinkas-Kramarski R: Rapamycin is a neuroprotective treatment for
traumatic brain injury. Neurobiol Dis. 26:86–93. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang AM, Morishima Y, Clapp KM, Peng HM,
Pratt WB, Gestwicki JE, Osawa Y and Lieberman AP: Inhibition of
hsp70 by methylene blue affects signaling protein function and
ubiquitination and modulates polyglutamine protein degradation. J
Biol Chem. 285:15714–15723. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|