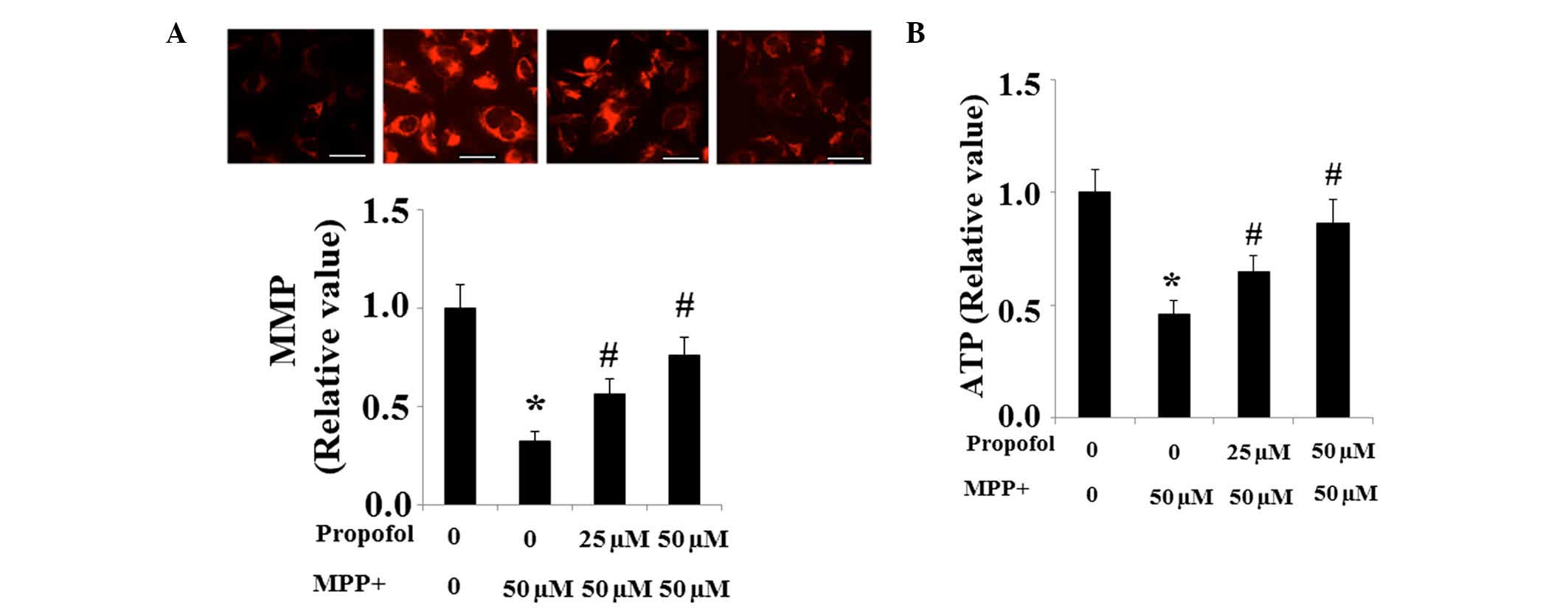
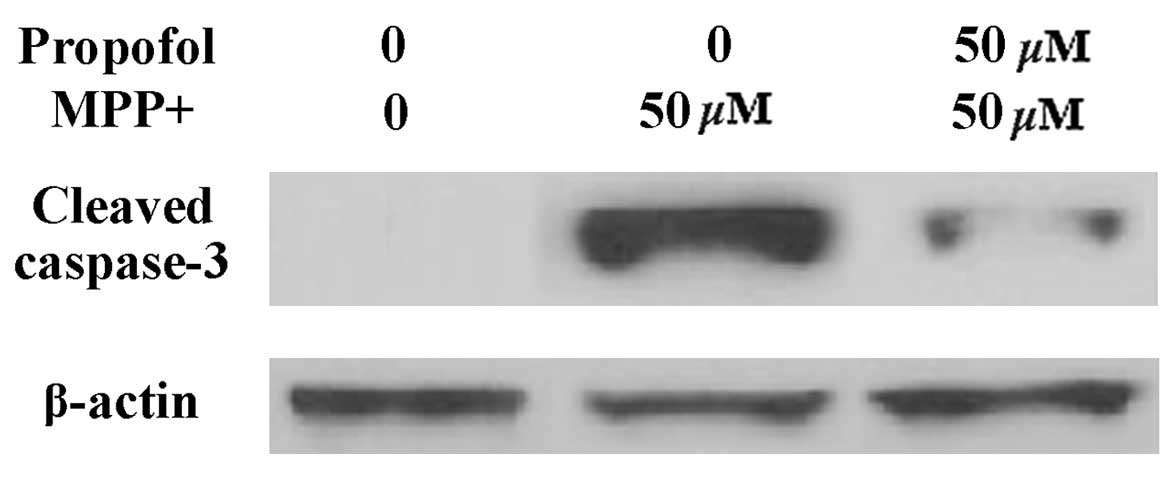
|
1
|
Dauer W and Przedborski S: Parkinson's
disease: Mechanisms and models. Neuron. 39:889–909. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chiba K, Trevor AJ and Castagnoli N Jr:
Active uptake of MPP+, a metabolite of MPTP, by brain
synaptosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 128:1228–1232. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kopin IJ and Markey SP: MPTP toxicity:
Implications for research in Parkinson's disease. Annu Rev
Neurosci. 11:81–96. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Obata T: Nitric oxide and MPP+-induced
hydroxyl radical generation. J Neural Transm. 113:1131–1144. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dawson TM and Dawson VL: Molecular
pathways of neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease. Science.
302:819–822. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Saraghi M, Badner VM, Golden LR and Hersh
EV: Propofol: An overview of its risks and benefits. Compend Contin
Educ Dent. 34:252–258. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yamaguchi S, Hamaguchi S, Mishio M, Okuda
Y and Kitajima T: Propofol prevents lipid peroxidation following
transient forebrain ischemia in gerbils. Can J Anaesth.
47:1025–1030. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Inada T, Kubo K and Shingu K: Possible
link between cyclooxygenase-inhibiting and antitumor properties of
propofol. J Anesth. 25:569–575. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Aarts L, van der Hee R, Dekker I, de Jong
J, Langemeijer H and Bast A: The widely used anesthetic agent
propofol can replace alpha-tocopherol as an antioxidant. FEBS Lett.
357:83–85. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li H, Tan J, Zou Z, Huang CG and Shi XY:
Propofol post-conditioning protects against cardiomyocyte apoptosis
in hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by suppressing nuclear factor-kappa
B translocation via extracellular signal-regulated kinase
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Eur J Anaesthesiol.
28:525–534. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Harman F, Hasturk AE, Yaman M, Arca T,
Kilinc K, Sargon MF and Kaptanoglu E: Neuroprotective effects of
propofol, thiopental, etomidate, and midazolam in fetal rat brain
in ischemia-reperfusion model. Childs Nerv Syst. 28:1055–1062.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sheng B, Gong K, Niu Y, Liu L, Yan Y, Lu
G, Zhang L, Hu M, Zhao N, Zhang X, et al: Inhibition of γ-secretase
activity reduces Abeta production, reduces oxidative stress,
increases mitochondrial activity and leads to reduced vulnerability
to apoptosis: implications for the treatment of Alzheimer's
disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 46:1362–1375. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sheng BY, Niu Y, Zhou H, Yan JX, Zhao NM,
Zhang XF and Gong YD: The mitochondrial function was impaired in
APP knockout mouse embryo fibroblast cells. Chin Sci Bull.
54:1725–1731. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Park JR and Hockenbery DM: BCL-2, a novel
regulator of apoptosis. J Cell Biochem. 60:12–17. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhou J, Sun Y, Zhao X, Deng Z and P u X:
3-O-demethylswertipunicoside inhibits MPP+-induced
oxidative stress and apoptosis in PC12 cells. Brain Res.
1508:53–62. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Crosiers D, Theuns J, Cras P and Van
Broeckhoven C: Parkinson disease: Insights in clinical, genetic and
pathological features of monogenic disease subtypes. J Chem
Neuroanat. 42:131–141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Moore DJ, West AB, Dawson VL and Dawson
TM: Molecular pathophysiology of Parkinson's disease. Annu Rev
Neurosci. 28:57–87. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Boada J, Cutillas B, Roig T, Bermúdez J
and Ambrosio S: MPP(+)-induced mitochondrial dysfunction is
potentiated by dopamine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 268:916–920.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sheehan JP, Palmer PE, Helm GA and Tuttle
JB: MPP+ induced apoptotic cell death in SH-SY5Y
neuroblastoma cells: An electron microscope study. J Neurosci Res.
48:226–237. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kanto JH: Propofol, the newest induction
agent of anesthesia. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 26:41–57.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
McNeir DA, Mainous EG and Trieger N:
Propofol as an intravenous agent in general anesthesia and
conscious sedation. Anesth Prog. 35:147–151. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Corcoran TB, O'Shea A, Engel A and Shorten
GD: The influence of propofol on P-selectin expression and nitric
oxide production in re-oxygenated human umbilical vein endothelial
cells. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 50:348–354. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang R, Xu J, Liu YY, Zuo PP, Yang N, Ji
C, Wang Y, Wang H, Wu AS and Yue Y: Propofol may protect PC12 cells
from β-amyloid25–35 induced apoptosis through the GSK-3β
signaling pathway. Chin Med J (Engl). 126:1884–1889. 2013.
|