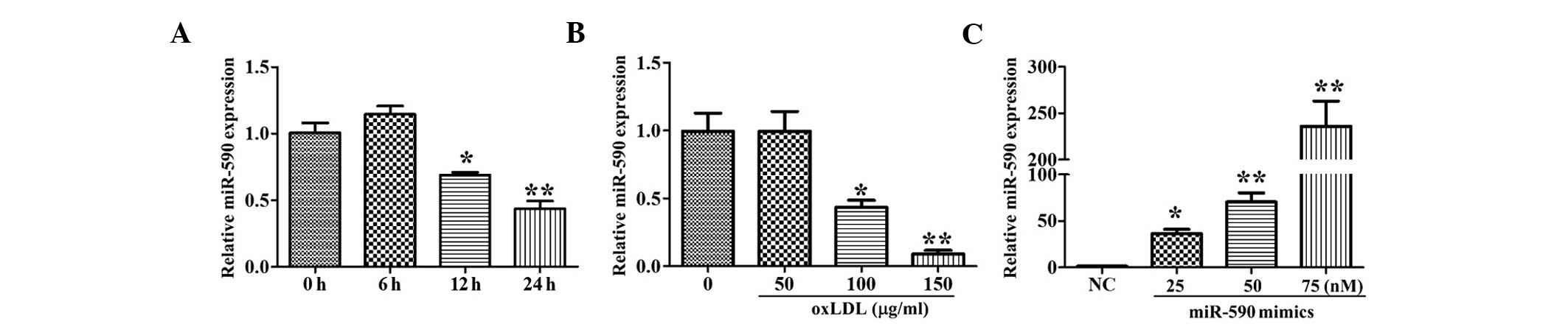
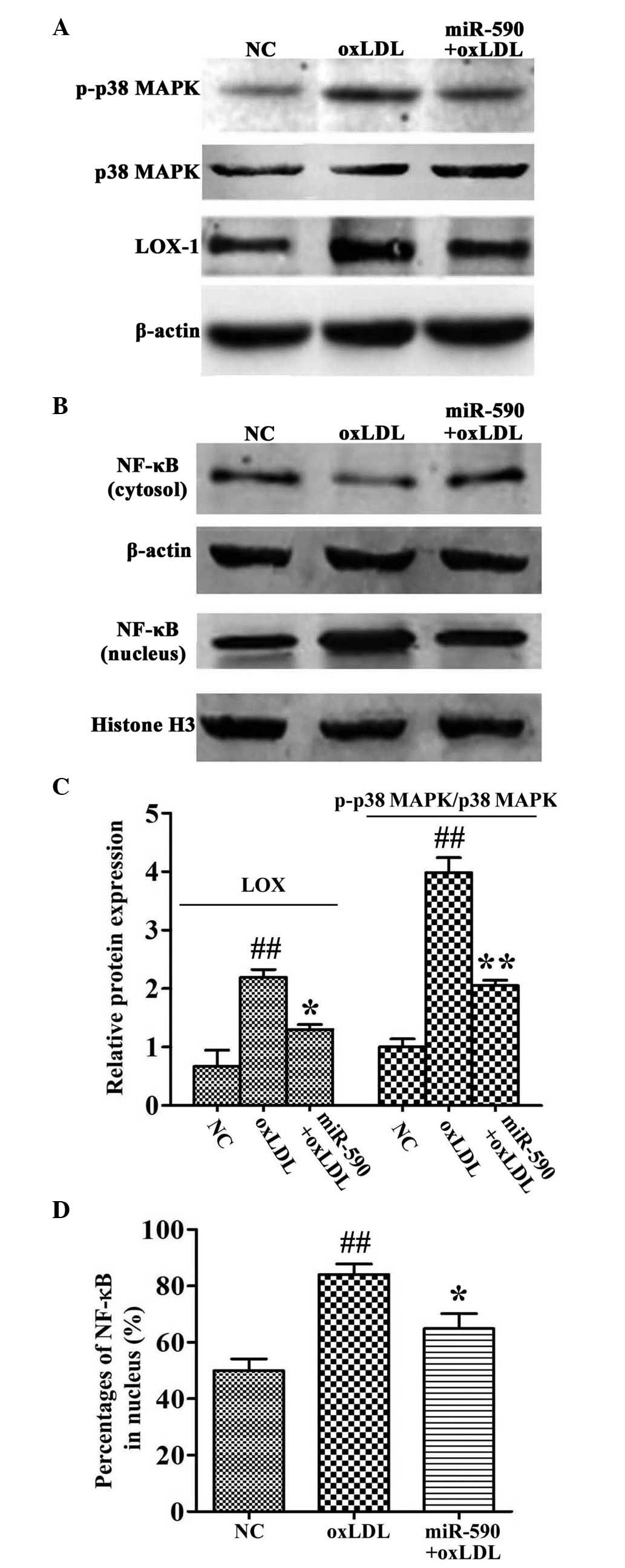
|
1
|
Pohl U, Holtz J, Busse R and Bassenge E:
Crucial role of endothelium in the vasodilator response to
increased flow in vivo. Hypertension. 8:37–44. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jiang F, Gibson AP and Dusting GJ:
Endothelial dysfunction induced by oxidized low-density
lipoproteins in isolated mouse aorta: A comparison with
apolipoprotein-E deficient mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 424:141–149.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li R, Mittelstein D, Fang K, Beebe T,
Quigley K, Berliner J and Hsiai TK: Angiopoeitin-2 modulates
survivin expression in OxLDL-induced endothelial cell apoptosis.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 417:619–622. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen WJ, Zhang M, Zhao GJ, Fu Y, Zhang DW,
Zhu HB and Tang CK: MicroRNA-33 in atherosclerosis etiology and
pathophysiology. Atherosclerosis. 227:201–208. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Gao S, Wassler M, Zhang L, Li Y, Wang J,
Zhang Y, Shelat H, Williams J and Geng YJ: MicroRNA-133a regulates
insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor expression and vascular
smooth muscle cell proliferation in murine atherosclerosis.
Atherosclerosis. 232:171–179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bao MH, Zhang YW, Lou XY, Cheng Y and Zhou
HH: Protective Effects of let-7a and let-7b on oxidized low-density
lipoprotein induced endothelial cell injuries. PLoS One.
9:e1065402014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhu XM, Han T, Sargent IL, Yin GW and Yao
YQ: Differential expression profile of microRNAs in human placentas
from preeclamptic pregnancies vs normal pregnancies. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 200:661.e1–7. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Qin B, Xiao B, Jiang T and Yang H: Effects
of miR-590-5p on ox-LDL-induced endothelial cells apoptosis and
LOX-1 expression. Journal of Central South University. Medical
sciences. 37:675–681. 2012.In Chinese.
|
|
10
|
Sawamura T, Kume N, Aoyama T, Moriwaki H,
Hoshikawa H, Aiba Y, Tanaka T, Miwa S, Katsura Y, Kita T and Masaki
T: An endothelial receptor for oxidized low-density lipoprotein.
Nature. 386:73–77. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li D and Mehta JL: Antisense to LOX-1
inhibits oxidized LDL-mediated upregulation of monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1 and monocyte adhesion to human coronary
artery endothelial cells. Circulation. 101:2889–2895. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bao MH, Zhang YW and Zhou HH: Paeonol
suppresses oxidized low-density lipoprotein induced endothelial
cell apoptosis via activation of LOX-1/p38MAPK/NF-κB pathway. J
Ethnopharmacol. 146:543–551. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bao MH, Zhang YW, Lou XY, Xiao Y, Cheng Y
and Zhou HH: Puerarin protects endothelial cells from oxidized low
density lipoprotein induced injuries via the suppression of LOX-1
and induction of eNOS. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 92:299–306. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen M, Masaki T and Sawamura T: LOX-1,
the receptor for oxidized low-density lipoprotein identified from
endothelial cells: Implications in endothelial dysfunction and
atherosclerosis. Pharmacol Ther. 95:89–100. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yamaguchi H, Chen J, Bhalla K and Wang HG:
Regulation of bax activation and apoptotic response to
microtubule-damaging agents by p53 transcription-dependent and
-independent pathways. J Biol Chem. 279:39431–39437. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu Y, Mehew JW, Heckman CA, Arcinas M and
Boxer LM: Negative regulation of bcl-2 expression by p53 in
hematopoietic cells. Oncogene. 20:240–251. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Borghetti G, Yamaguchi AA, Aikawa J,
Yamazaki RK, de Brito GA and Fernandes LC: Fish oil administration
mediates apoptosis of Walker 256 tumor cells by modulation of p53,
Bcl-2, caspase-7 and caspase-3 protein expression. Lipids Health
Dis. 14:942015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–8. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Beckman JA, Creager MA and Libby P:
Diabetes and atherosclerosis: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and
management. JAMA. 287:2570–2581. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Choy JC, Granville DJ, Hunt DW and Mcmanus
BM: Endothelial cell apoptosis: Biochemical characteristics and
potential implications for atherosclerosis. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
33:1673–1690. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang T, Tian F, Wang J, Jing J, Zhou SS
and Chen YD: Endothelial cell autophagy in atherosclerosis is
regulated by miR-30-mediated translational control of ATG6. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 37:1369–1378. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bazan HA, Hatfield SA, O'Malley CB, Brooks
AJ, Lightell D Jr and Woods TC: Acute loss of miR-221 and miR-222
in the atherosclerotic plaque shoulder accompanies plaque rupture.
Stroke. 46:3285–3287. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Levne AJ: p53, the cellular gatekeeper for
growth and division. Cell. 88:323–331. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Bennett MR, Littlewood TD, Schwartz SM and
Weissberg PL: Increased sensitivity of human vascular smooth muscle
cells from atherosclerotic plaques to p53-mediated apoptosis. Circ
Res. 81:591–599. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bialik S, Geenen DL, Sasson IE, Cheng R,
Horner JW, Evans SM, Lord EM, Koch CJ and Kitsis RN: Myocyte
apoptosis during acute myocardial infarction in the mouse localizes
to hypoxic regions but occurs independently of p53. J Clin Invest.
100:1363–1372. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Alves da Costa C, Sunyach C,
Pardossi-piquard R, Sévalle J, Vincent B, Boyer N, Kawarai T,
Girardot N, St George-Hyslop P and Checler F: Presenilin-dependent
gamma-secretase-mediated control of p53-associated cell death in
alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci. 26:6377–6385. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mercer J and Bennett M: The role of p53 in
atherosclerosis. Cell Cycle. 5:1907–1909. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Khan MS, Halagowder D and Devaraj SN:
Methylated chrysin induces co-ordinated attenuation of the
canonical Wnt and NF-kB signaling pathway and upregulates apoptotic
gene expression in the early hepatocarcinogenesis rat model. Chem
Biol Interact. 193:12–21. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kiang JG, Agravante NG, Smith JT and
Bowman PD: 17-DMAG diminishes hemorrhage-induced small intestine
injury by elevating Bcl-2 protein and inhibiting iNOS pathway,
TNF-α increase and caspase-3 activation. Cell Biosci. 1:212011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Nakai M, Qin Z, Wang Y and Chase TN: NMDA
and non-NMDA receptor-stimulated IkappaB-alpha degradation:
Differential effects of the caspase-3 inhibitor DEVD.CHO, ethanol
and free radical scavenger OPC-14117. Brain Res. 859:207–216. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pal S, Bhattacharjee A, Ali A, Mandal NC,
Mandal SC and Pal M: Chronic inflammation and cancer: Potential
chemoprevention through nuclear factor kappa B and p53 mutual
antagonism. J Inflamm (Lond). 11:232014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Aoki M, Nata T, Morishita R, Matsushita H,
Nakagami H, Yamamoto K, Yamazaki K, Nakabayashi M, Ogihara T and
Kaneda Y: Endothelial apoptosis induced by oxidative stress through
activation of NF-kappaB: Antiapoptotic effect of antioxidant agents
on endothelial cells. Hypertension. 38:48–55. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang L, Zhou G, Song W, Tan X, Guo Y,
Zhou B, Jing H, Zhao S and Chen L: Pterostilbene protects vascular
endothelial cells against oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced
apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Apoptosis. 17:25–36. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|