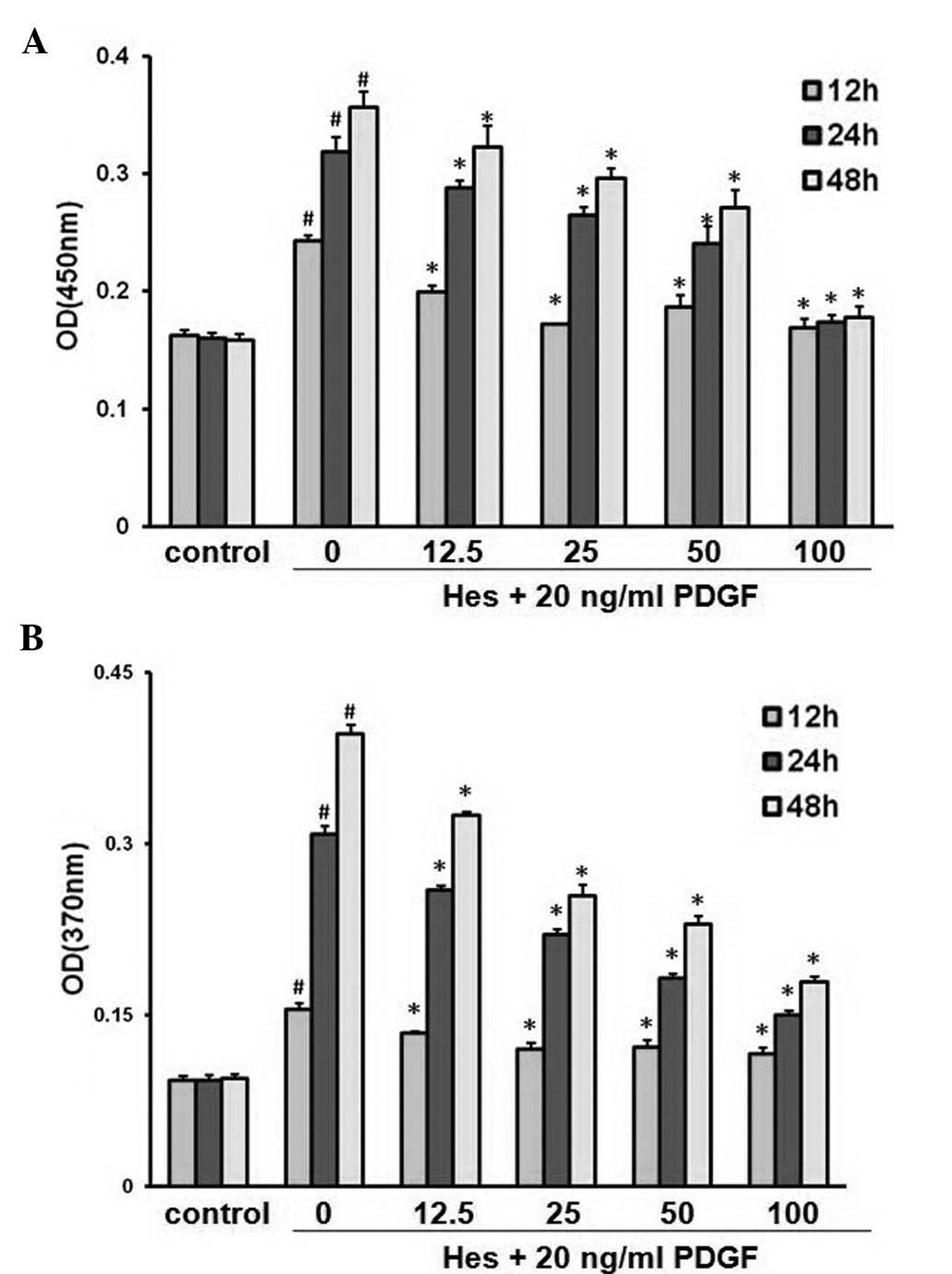
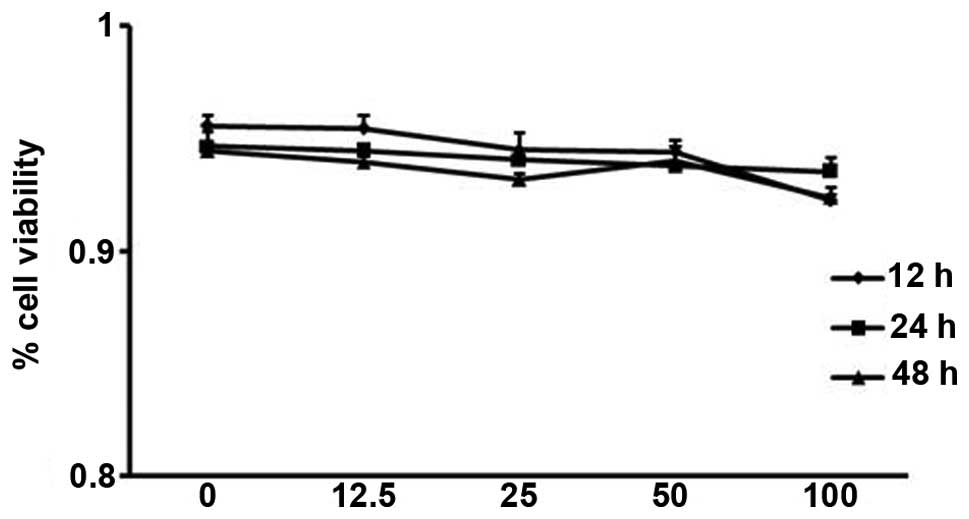
|
1
|
Archer SL, Weir EK and Wilkins MR: Basic
science of pulmonary arterial hypertension for clinicians: New
concepts and experimental therapies. Circulation. 121:2045–2066.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tuder RM, Abman SH, Braun T, Capron F,
Stevens T, Thistlethwaite PA and Haworth SG: Development and
pathology of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 54(Suppl
1): S3–S9. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pietra GG, Capron F, Stewart S, Leone O,
Humbert M, Robbins IM, Reid LM and Tuder RM: Pathologic assessment
of vasculopathies in pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol.
43(12 Suppl S): 25S–32S. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Crosswhite P and Sun Z: Molecular
mechanisms of pulmonary arterial remodeling. Mol Med. 20:191–201.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yildiz P: Molecular mechanisms of
pulmonary hypertension. Clin Chim Acta. 403:9–16. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Balasubramaniam V, Le Cras TD, Ivy DD,
Grover TR, Kinsella AP and Abman SH: Role of platelet-derived
growth factor in vascular remodeling during pulmonary hypertension
in the ovine fetus. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
284:L826–L833. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schermuly RT, Dony E, Ghofrani HA,
Pullamsetti S, Savai R, Roth M, Sydykov A, Lai YJ, Weissmann N,
Seeger W and Grimminger F: Reversal of experimental pulmonary
hypertension by PDGF inhibition. J Clin Invest. 115:2811–2821.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Perros F, Montani D, Dorfmüller P,
Durand-Gasselin I, Tcherakian C, Le Pavec J, Mazmanian M, Fadel E,
Mussot S, Mercier O, et al: Platelet-derived growth factor
expression and function in idiopathic pulmonary arterial
hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 178:81–88. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Humbert M, Monti G, Fartoukh M, Magnan A,
Brenot F, Rain B, Capron F, Galanaud P, Duroux P, Simmoneau G and
Emilie D: Platelet-derived growth factor expression in primary
pulmonary hypertension: Comparison of HIV seropositive and HIV
seronegative patients. Eur Respir J. 11:554–559. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sachinidis A, Locher R, Hoppe J and Vetter
W: The platelet-derived growth factor isomers, PDGF-AA, PDGF-AB and
PDGF-BB, induce contraction of vascular smooth muscle cells by
different intracellular mechanisms. FEBS Lett. 275:95–98. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sakao S, Tatsumi K and Voelkel NF:
Reversible or irreversible remodeling in pulmonary arterial
hypertension. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 43:629–634. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Jawien A, Bowen-Pope DF, Lindner V,
Schwartz SM and Clowes AW: Platelet-derived growth factor promotes
smooth muscle migration and intimal thickening in a rat model of
balloon angioplasty. J Clin Invest. 89:507–511. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang Y, Wolfram J, Boom K, Fang X, Shen H
and Ferrari M: Hesperetin impairs glucose uptake and inhibits
proliferation of breast cancer cells. Cell Biochem Funct.
31:374–379. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zarebczan B, Pinchot SN, Kunnimalaiyaan M
and Chen H: Hesperetin, a potential therapy for carcinoid cancer.
Am J Surg. 201:329–333. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Choi EJ: Hesperetin induced G1-phase cell
cycle arrest in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells: Involvement of
CDK4 and p21. Nutr Cancer. 59:115–119. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang J, Zhu H, Yang Z and Liu Z:
Antioxidative effects of hesperetin against lead acetate-induced
oxidative stress in rats. Indian J Pharmacol. 45:395–398. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Deng W, Jiang D, Fang Y, Zhou H, Cheng Z,
Lin Y, Zhang R, Zhang J, Pu P, Liu Y, Bian Z and Tang Q: Hesperetin
protects against cardiac remodelling induced by pressure overload
in mice. J Mol Histol. 44:575–585. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cho J: Antioxidant and neuroprotective
effects of hesperidin and its aglycone hesperetin. Arch Pharm Res.
29:699–706. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang HL, Chen SC, Senthil Kumar KJ, Yu KN,
Lee Chao PD, Tsai SY, Hou YC and Hseu YC: Antioxidant and
anti-inflammatory potential of hesperetin metabolites obtained from
hesperetin-administered rat serum: An ex vivo approach. J Agric
Food Chem. 60:522–532. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kim SY, Lee JY, Park YD, Kang KL, Lee JC
and Heo JS: Hesperetin alleviates the inhibitory effects of high
glucose on the osteoblastic differentiation of periodontal ligament
stem cells. PLoS One. 8:e675042013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen C, Tang Y, Deng W, Huang C and Wu T:
Salidroside blocks the proliferation of pulmonary artery smooth
muscle cells induced by platelet-derived growth factor-BB. Mol Med
Rep. 10:917–922. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Deng W, Jiang D, Fang Y, Zhou H, Cheng Z,
Lin Y, Zhang R, Pu P, Liu Y, et al: Hesperetin protects against
cardiac remodelling induced by pressure overload in mice. J Mol
Histol. 44:575–585. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Abukhdeir AM and Park BH: P21 and p27:
Roles in carcinogenesis and drug resistance. Expert Rev Mol Med.
10:e192008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cogolludo A, Moreno L and Villamor E:
Mechanisms controlling vascular tone in pulmonary arterial
hypertension: Implications for vasodilator therapy. Pharmacology.
79:65–75. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Paulin R, Meloche J and Bonnet S: STAT3
signaling in pulmonary arterial hypertension. JAKSTAT. 1:223–233.
2012.
|
|
26
|
Besson A, Dowdy SF and Roberts JM: CDK
inhibitors: Cell cycle regulators and beyond. Dev Cell. 14:159–169.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jirawatnotai S, Aziyu A, Osmundson EC,
Moons DS, Zou X, Kineman RD and Kiyokawa H: Cdk4 is indispensable
for postnatal proliferation of the anterior pituitary. J Biol Chem.
279:51100–51106. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Martín A, Odajima J, Hunt SL, Dubus P,
Ortega S, Malumbres M and Barbacid M: Cdk2 is dispensable for cell
cycle inhibition and tumor suppression mediated by p27(Kip1) and
p21(Cip1). Cancer Cell. 7:591–598. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chu I, Sun J, Arnaout A, Kahn H, Narod S,
Sun P, Tan CK, Hengst L and Slingerland J: p27 phosphorylation by
Src regulates inhibition of cyclin E-Cdk2. Cell. 128:281–294. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
James MK, Ray A, Leznova D and Blain SW:
Differential modification of p27Kip1 controls its cyclin D-cdk4
inhibitory activity. Mol Cell Biol. 28:498–510. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Guan H, Chen C, Zhu L, Cui C, Guo Y, Fu M,
Wang L and Tang Q: Indole-3-carbinol blocks platelet-derived growth
factor-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cell function and reduces
neointima formation in vivo. J Nutr Biochem. 24:62–69. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Hwang SL and Yen GC: Modulation of Akt,
JNK, and p38 activation is involved in citrus flavonoid-mediated
cytoprotection of PC12 cells challenged by hydrogen peroxide. J
Agric Food Chem. 57:2576–2582. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jin YR, Han XH, Zhang YH, Lee JJ, Lim Y,
Kim TJ, Yoo HS and Yun YP: Hesperetin, a bioflavonoid, inhibits rat
aortic vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation by arresting cell
cycle. J Cell Biochem. 104:1–14. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Diehl JA, Cheng M, Roussel MF and Sherr
CJ: Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta regulates cyclin D1 proteolysis
and subcellular localization. Genes Dev. 12:3499–3511. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pontano LL and Diehl JA: DNA
damage-dependent cyclin D1 proteolysis: GSK3beta holds the smoking
gun. Cell Cycle. 8:824–827. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Malumbres M and Barbacid M: To cycle or
not to cycle: A critical decision in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
1:222–231. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Yin M, Tian S, Huang X, Huang Y and Jiang
M: Role and mechanism of tissue plasminogen activator in venous
wall fibrosis remodeling after deep venous thrombosis via the
glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta signaling pathway. J Surg Res.
184:1182–1195. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tseng AS, Engel FB and Keating MT: The
GSK-3 inhibitor BIO promotes proliferation in mammalian
cardiomyocytes. Chem Biol. 13:957–963. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|