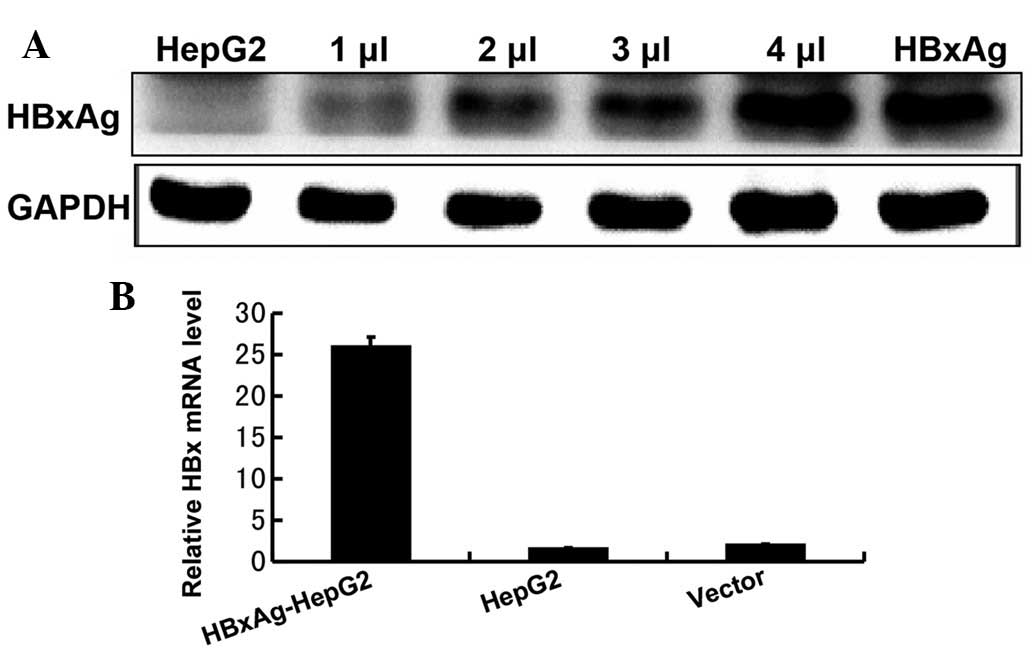
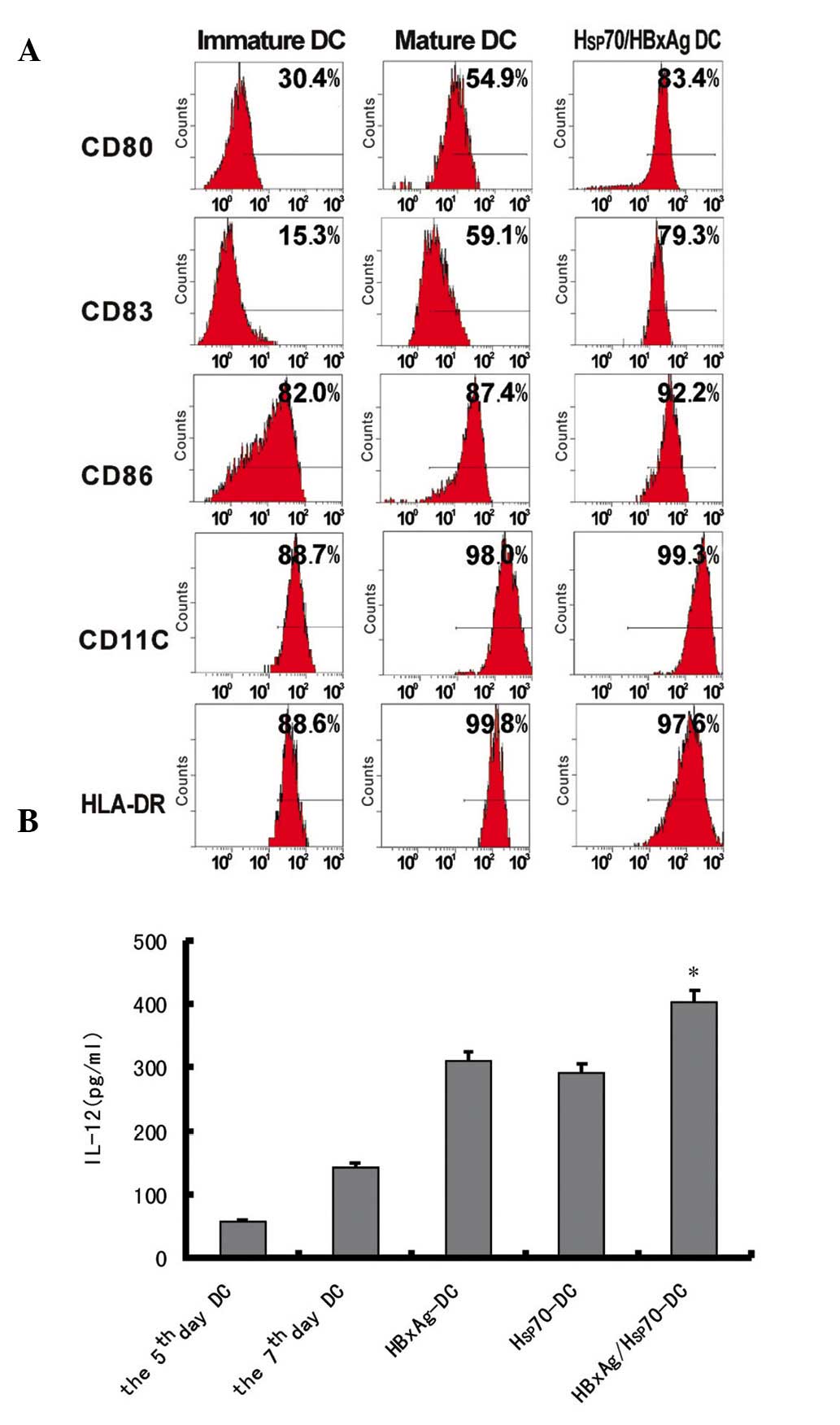
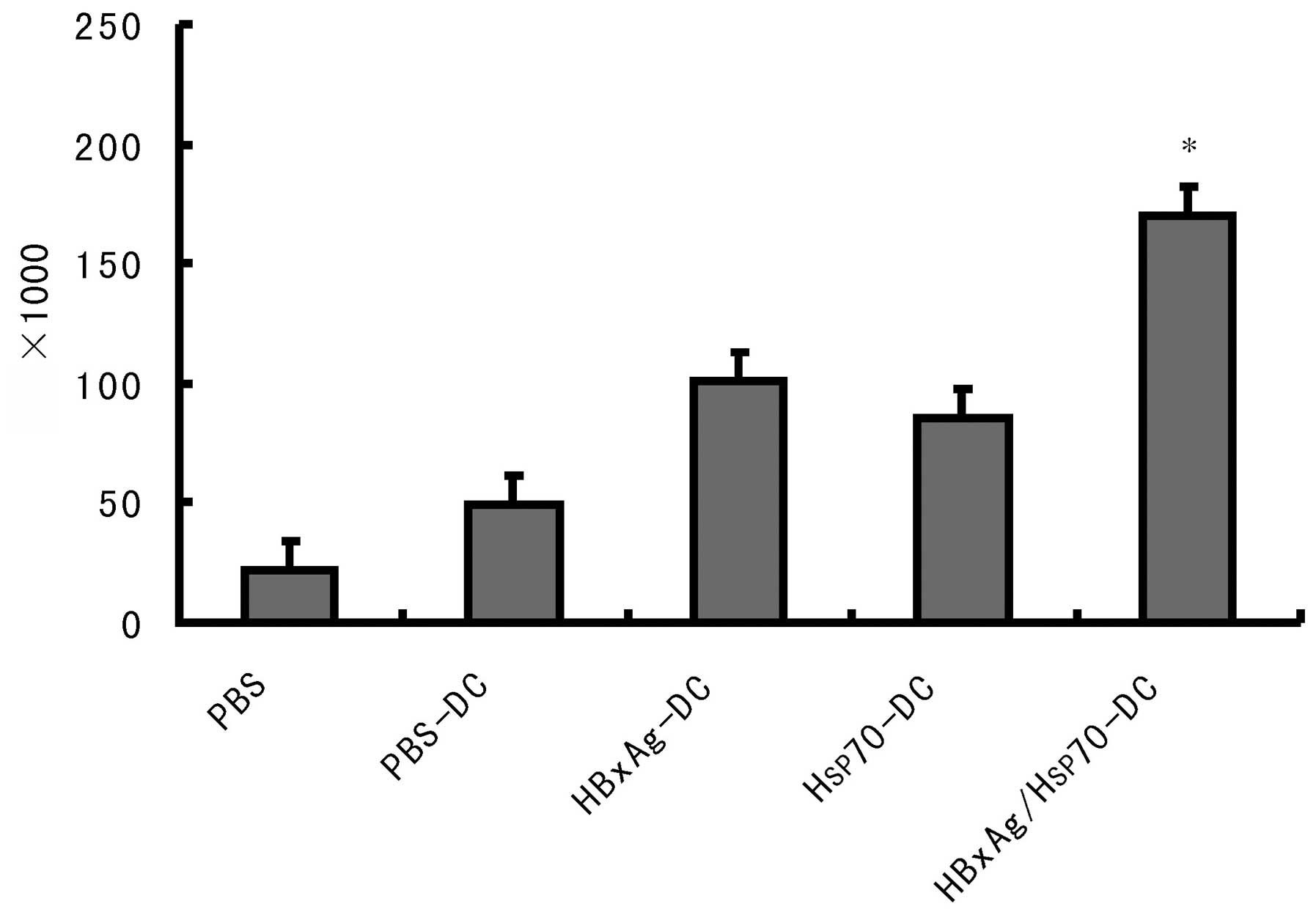
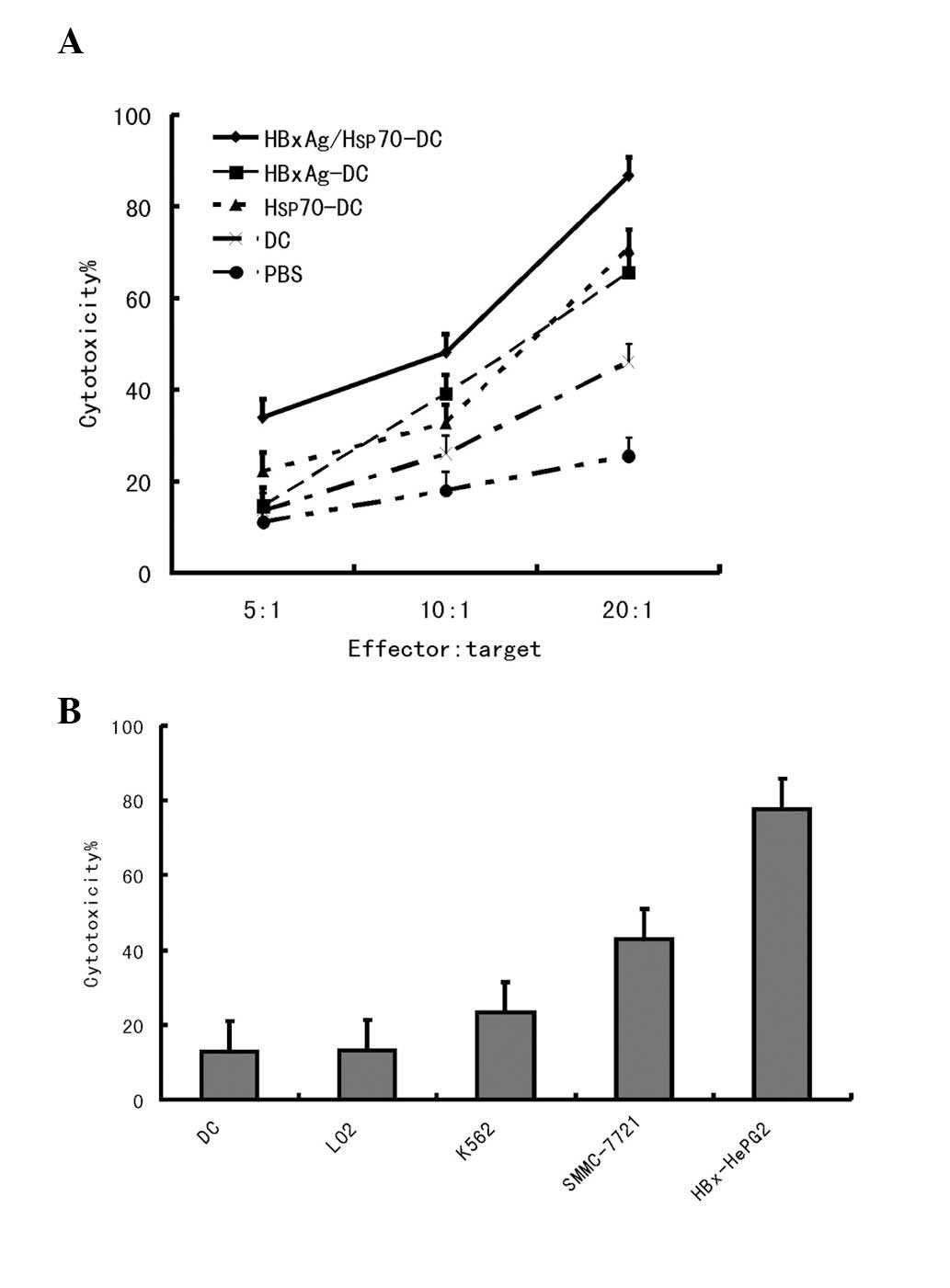
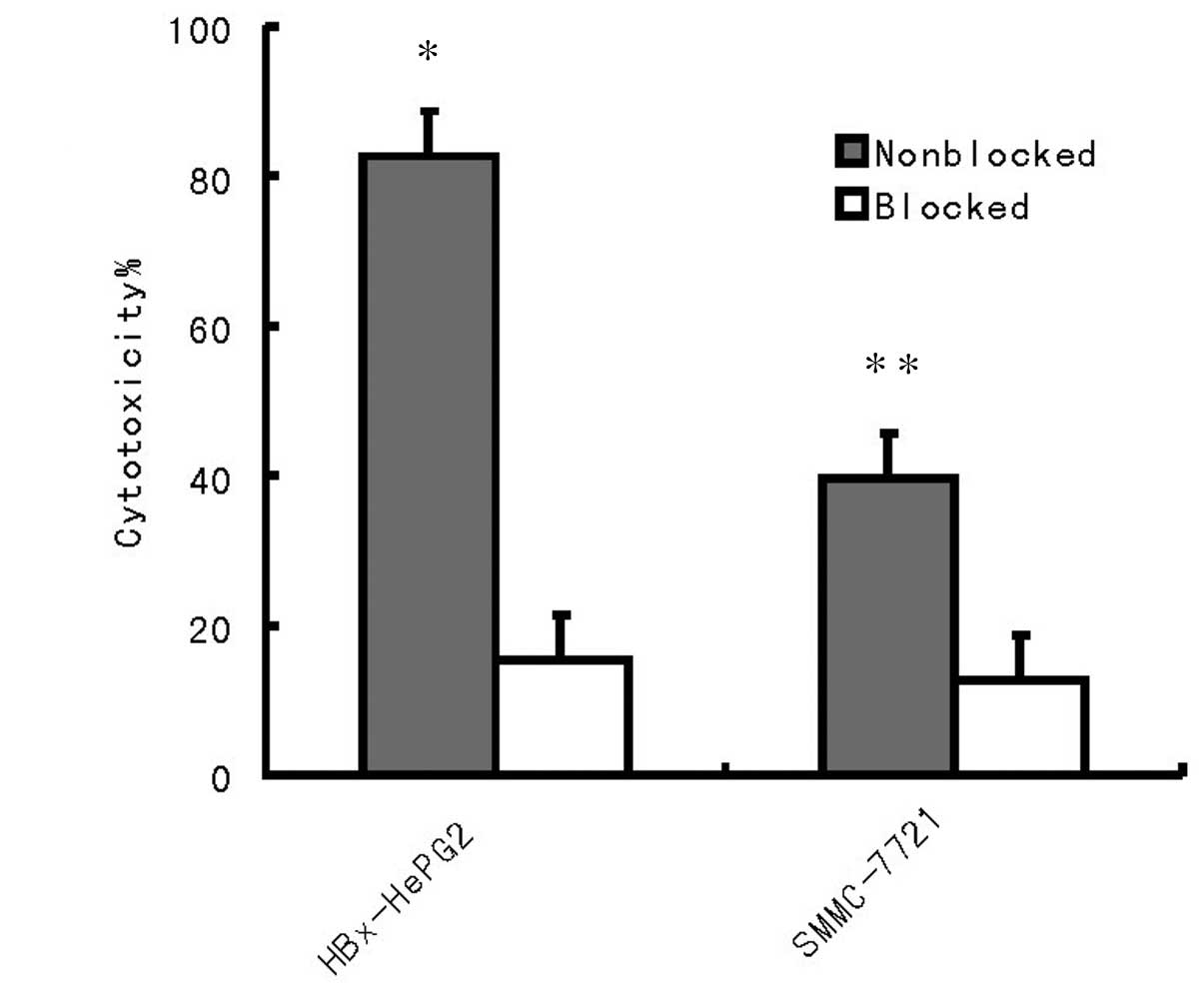
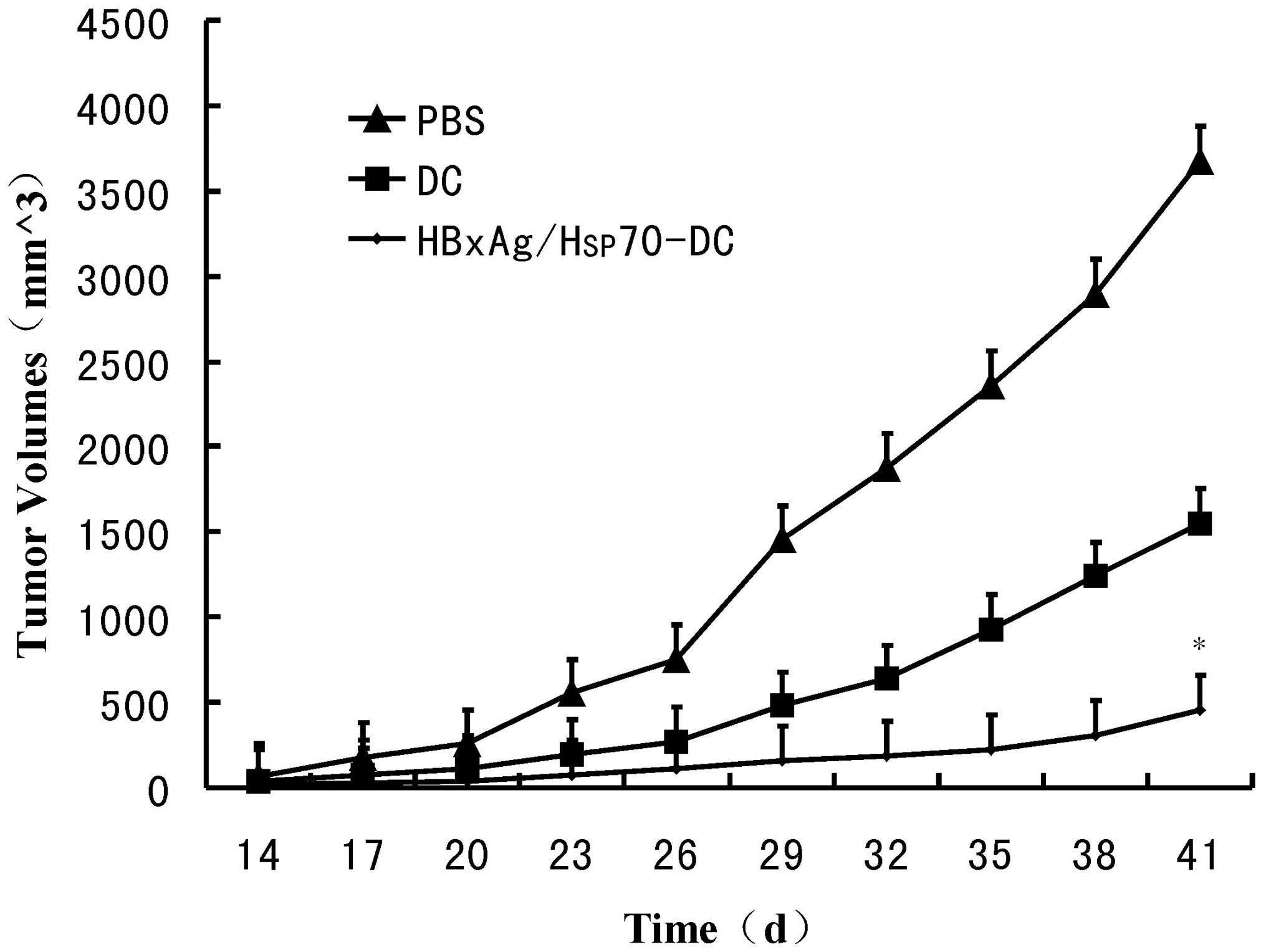
|
1
|
Arzumanyan A, Reis HM and Feitelson MA:
Pathogenic mechanisms in HBV- and HCV-associated hepatocellular
carcinoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:123–135. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu XH, Lin J, Zhang SH, Zhang SM,
Feitelson MA, Gao HJ and Zhu MH: COOH-terminal deletion of HBx gene
is a frequent event in HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma.
World J Gastroenterol. 14:1346–1352. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lehman EM and Wilson ML: Epidemiology of
hepatitis viruses among hepatocellular carcinoma cases and healthy
people in Egypt: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J
Cancer. 124:690–697. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wang Z, Zhang G, Wu J and Jia M: Adjuvant
therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Current situation and
prospect. Drug Discov Ther. 7:137–143. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ibrahim SM, Lewandowski RJ, Sato KT, Gates
VL, Kulik L, Mulcahy MF, Ryu RK, Omary RA and Salem R:
Radioembolization for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular
carcinoma: A clinical review. World J Gastroenterol. 14:1664–1669.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Palucka K and Banchereau J: Cancer
immunotherapy via dendritic cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:265–277.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhan HL, Gao X, Pu XY, Li W, Li ZJ, Zhou
XF and Qiu JG: A randomized controlled trial of postoperative tumor
lysate-pulsed dendritic cells and cytokine-induced killer cells
immunotherapy in patients with localized and locally advanced renal
cell carcinoma. Chin Med J (Engl). 125:3771–3777. 2012.
|
|
8
|
Berntsen A, Trepiakas R, Wenandy L,
Geertsen PF, thor Straten P, Andersen MH, Pedersen AE, Claesson MH,
Lorentzen T, Johansen JS and Svane IM: Therapeutic dendritic cell
vaccination of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A
clinical phase 1/2 trial. J Immunother. 31:771–780. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Murphy ME: The HSP70 family and cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 34:1181–1188. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Multhoff G, Pockley AG, Streffer C and
Gaipl US: Dual role of heat shock proteins (HSPs) in anti-tumor
immunity. Curr Mol Med. 12:1174–1182. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ciocca DR, Cayado-Gutierrez N, Maccioni M
and Cuello-Carrion FD: Heat shock proteins (HSPs) based anti-cancer
vaccines. Curr Mol Med. 12:1183–1197. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang XH, Qin Y, Hu MH and Xie Y: Dendritic
cells pulsed with hsp70-peptide complexes derived from human
hepatocellular carcinoma induce specific anti-tumor immune
responses. World J Gastroenterol. 11:5614–5620. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li QL, Bu N, Yu YC, Hua W and Xin XY: Ex
vivo experiments of human ovarian cancer ascites-derived exosomes
presented by dendritic cells derived from umbilical cord blood for
immunotherapy treatment. Clin Med Oncol. 2:461–467. 2008.
|
|
14
|
Yang JY, Cao DY, Xue Y, Yu ZC and Liu WC:
Improvement of dendritic-based vaccine efficacy against hepatitis B
virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma by two tumor-associated
antigen gene-infected dendritic cells. Hum Immunol. 71:255–262.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang Z, Du X, Zhao C, Cao B, Zhao Y and
Mao X: The antidepressant amitriptyline shows potent therapeutic
activity against multiple myeloma. Anticancer Drugs. 24:792–798.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Steinman RM: Dendritic cells and the
control of immunity: Enhancing the efficiency of antigen
presentation. Mt Sinai J Med. 68:160–166. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Banchereau J and Steinman RM: Dendritic
cells and the control of immunity. Nature. 392:245–252. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ovali E, Dikmen T, Sonmez M, Yilmaz M,
Unal A, Dalbasti T, Kuzeyli K, Erturk M and Omay SB: Active
immunotherapy for cancer patients using tumor lysate pulsed
dendritic cell vaccine: A safety study. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
26:209–214. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dannull J, Haley NR, Archer G, Nair S,
Boczkowski D, Harper M, De Rosa N, Pickett N, Mosca PJ, Burchette
J, et al: Melanoma immunotherapy using mature DCs expressing the
constitutive proteasome. J Clin Invest. 123:3135–3145. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Abdul Hafid SR, Chakravarthi S, Nesaretnam
K and Radhakrishnan AK: Tocotrienol-adjuvanted dendritic cells
inhibit tumor growth and metastasis: A murine model of breast
cancer. PLoS One. 8:e747532013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kandalaft LE, Powell DJ Jr, Chiang CL,
Tanyi J, Kim S, Bosch M, Montone K, Mick R, Levine BL, Torigian DA,
et al: Autologous lysate-pulsed dendritic cell vaccination followed
by adoptive transfer of vaccine-primed ex vivo co-stimulated T
cells in recurrent ovarian cancer. Oncoimmunology. 2:e226642013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gautam PK, Kumar S, Deepak P and Acharya
A: Morphological effects of autologous hsp70 on peritoneal
macrophages in a murine T cell lymphoma. Tumour Biol. 34:3407–3415.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vrieling M, Santema W, Vordermeier M,
Rutten V and Koets A: Hsp70 vaccination-induced primary immune
responses in efferent lymph of the draining lymph node. Vaccine.
31:4720–4727. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Khanna R: Tumour surveillance: Missing
peptides and MHC molecules. Immunol Cell Biol. 76:20–26. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lu JW, Yang WY, Tsai SM, Lin YM, Chang PH,
Chen JR, Wang HD, Wu JL, Jin SL, Yuh CH, et al: Liver-specific
expressions of HBx and src in the p53 mutant trigger
hepatocarcinogenesis in zebrafish. PLoS One. 8:e769512013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Buchmann P, Dembek C, Kuklick L, Jäger C,
Tedjokusumo R, von Freyend MJ, Drebber U, Janowicz Z, Melber K,
Protzer U, et al: A novel therapeutic hepatitis B vaccine induces
cellular and humoral immune responses and breaks tolerance in
hepatitis B virus (HBV) transgenic mice. Vaccine. 31:1197–1203.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shi M, Qian S, Chen WW, Zhang H, Zhang B,
Tang ZR, Zhang Z and Wang FS: Hepatitis B virus (HBV)
antigen-pulsed monocyte-derived dendritic cells from HBV-associated
hepatocellular carcinoma patients significantly enhance specific T
cell responses in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol. 147:277–286. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cassel JA, Ilyin S, McDonnell ME and Reitz
AB: Novel inhibitors of heat shock protein Hsp70-mediated
luciferase refolding that bind to DnaJ. Bioorg Med Chem.
20:3609–3614. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bajana S, Herrera-González N, Narváez J,
Torres-Aguilar H, Rivas-Carvalho A, Aguilar SR and Sánchez-Torres
C: Differential CD4(+) T-cell memory responses induced by two
subsets of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Immunology.
122:381–393. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Harty JT, Tvinnereim AR and White DW: CD8+
T cell effector mechanisms in resistance to infection. Annu Rev
Immunol. 18:275–308. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hanson HL, Donermeyer DL, Ikeda H, White
JM, Shankaran V, Old LJ, Shiku H, Schreiber RD and Allen PM:
Eradication of established tumors by CD8+ T cell
adoptive immunotherapy. Immunity. 13:265–276. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|