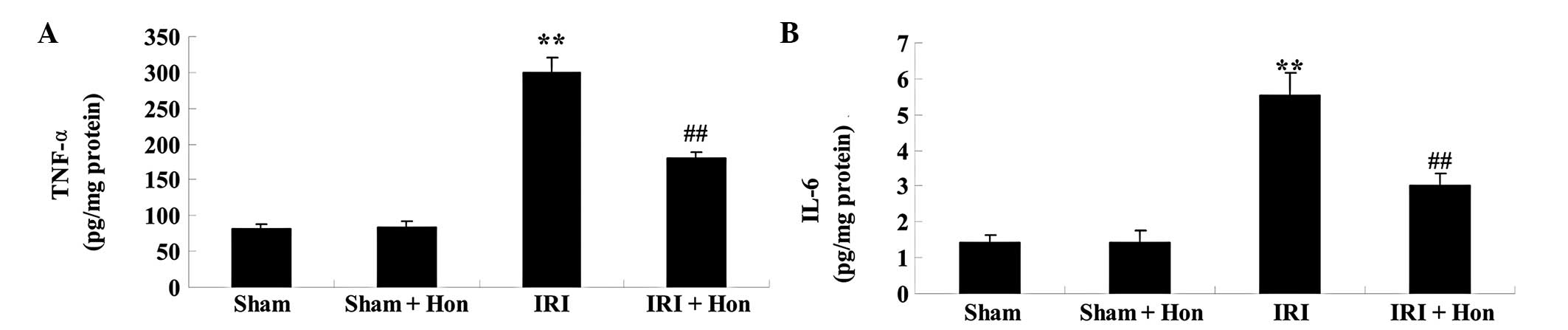
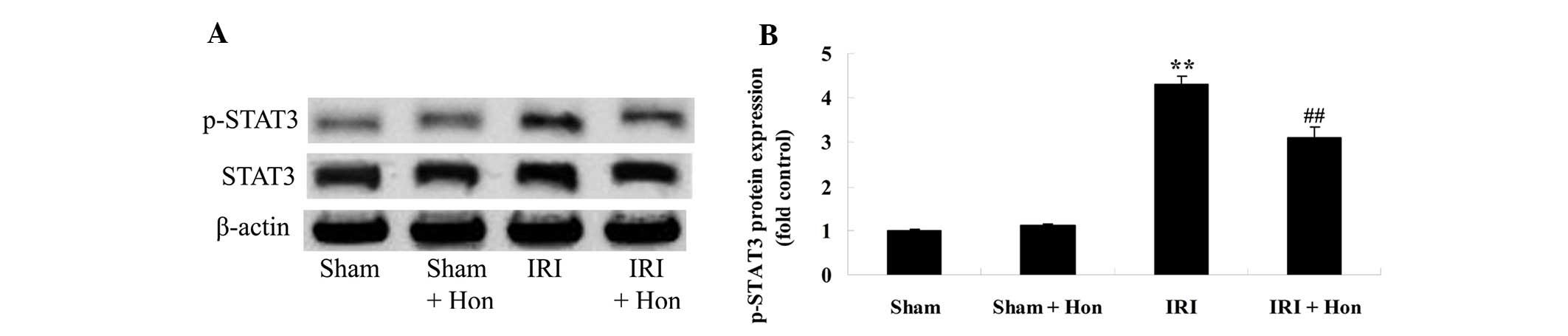
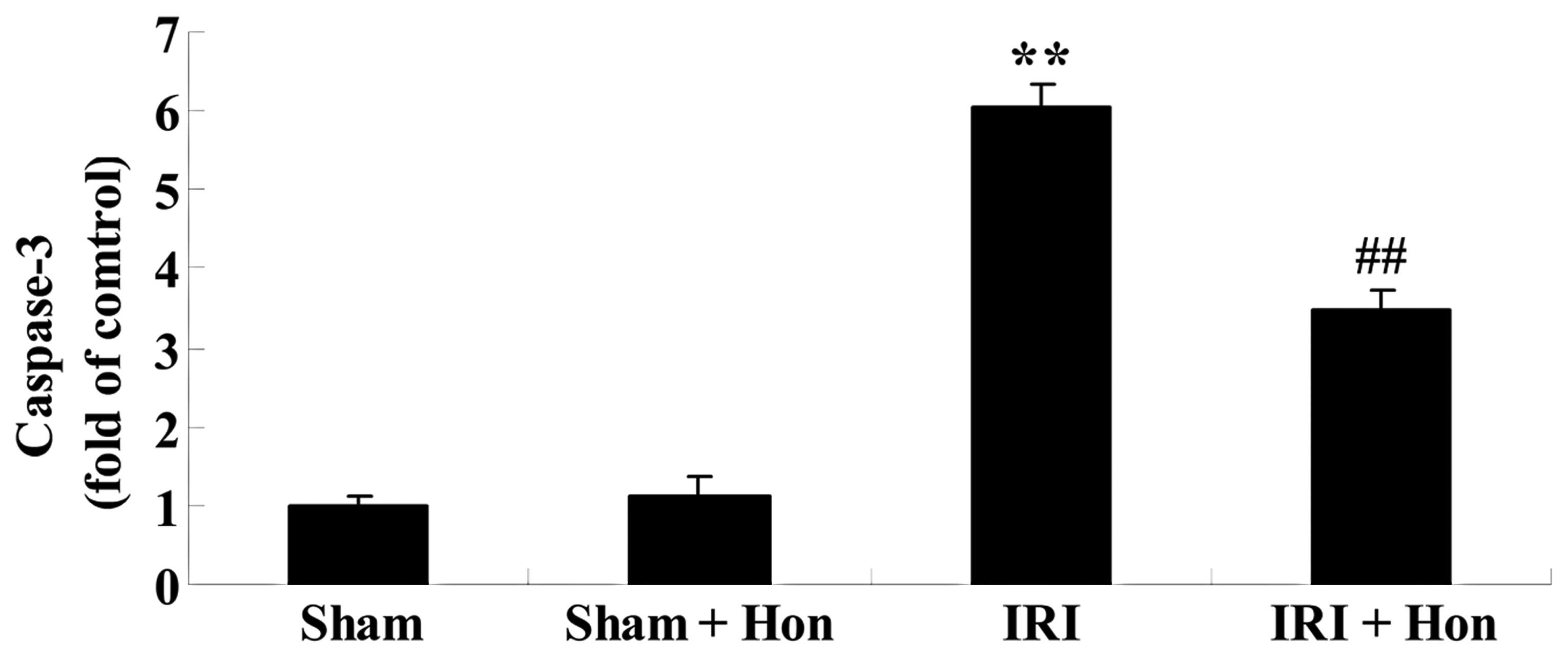
|
1
|
Senbel AM, AbdelMoneim L and Omar AG:
Celecoxib modulates nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species in
kidney ischemia/reperfusion injury and rat aorta model of
hypoxia/reoxygenation. Vascul Pharmacol. 62:24–31. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cai Y, Xu H, Yan J, Zhang L and Lu Y:
Molecular targets and mechanism of action of dexmedetomidine in
treatment of ischemia/reperfusion injury. Mol Med Rep. 9:1542–1550.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cetin N, Suleyman H, Sener E, Demirci E,
Gundogdu C and Akcay F: The prevention of ischemia/reperfusion
induced oxidative damage by venous blood in rabbit kidneys
monitored with biochemical, histopatological and
immunohistochemical analysis. J Physiol Pharmacol. 65:383–392.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
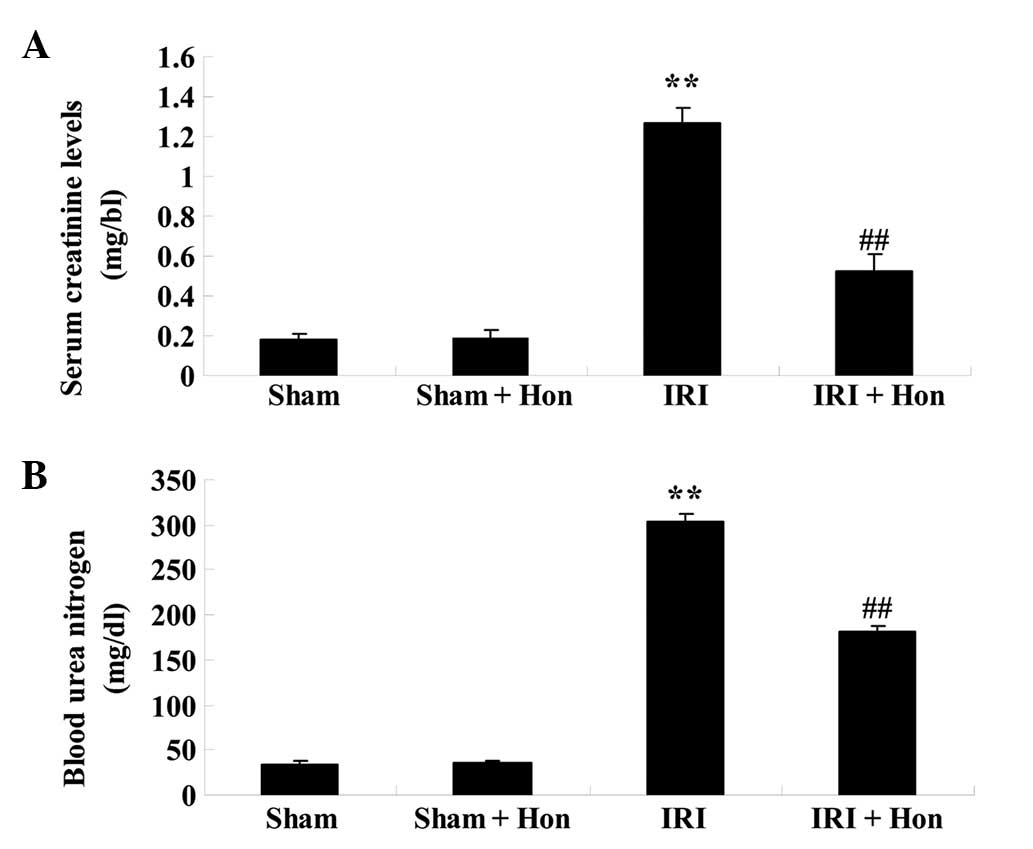
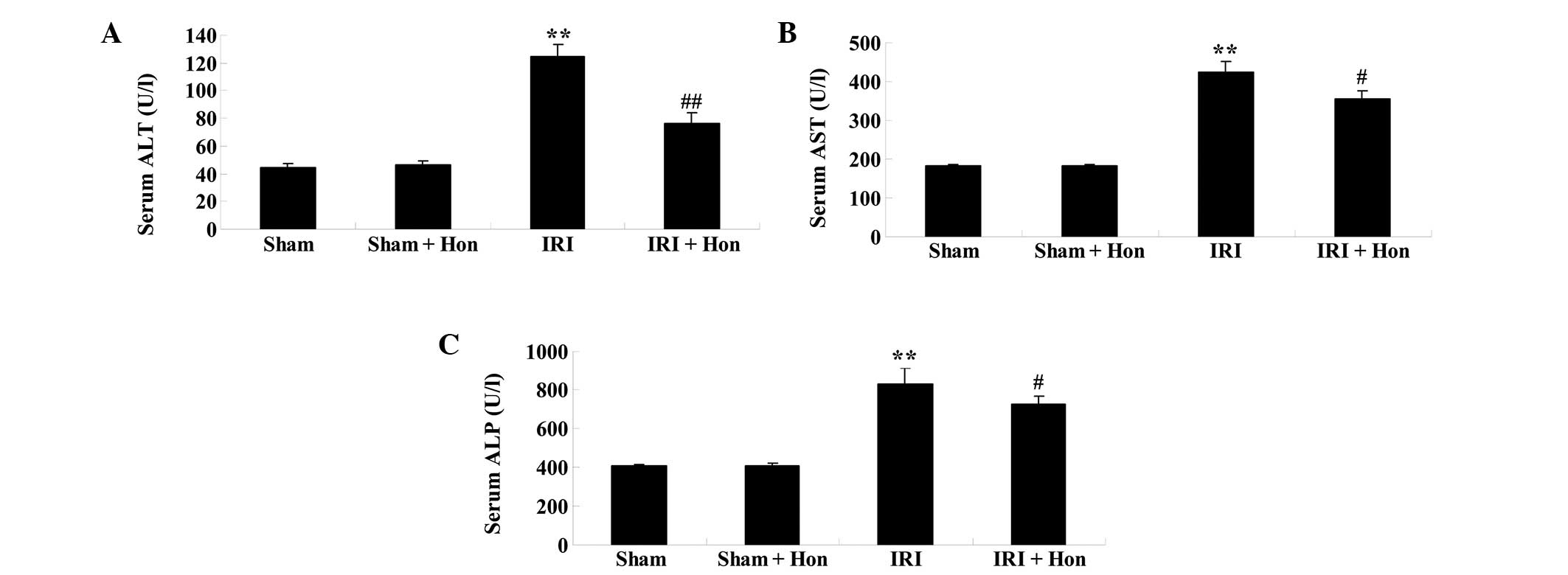
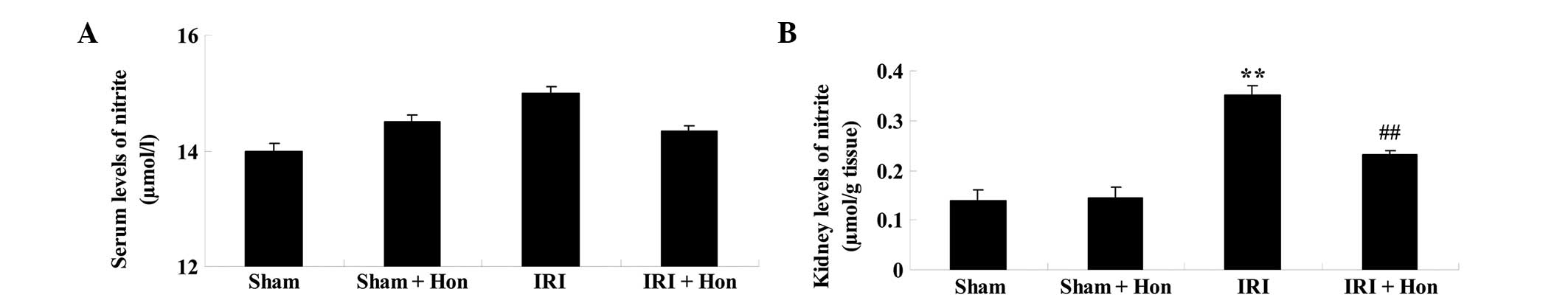
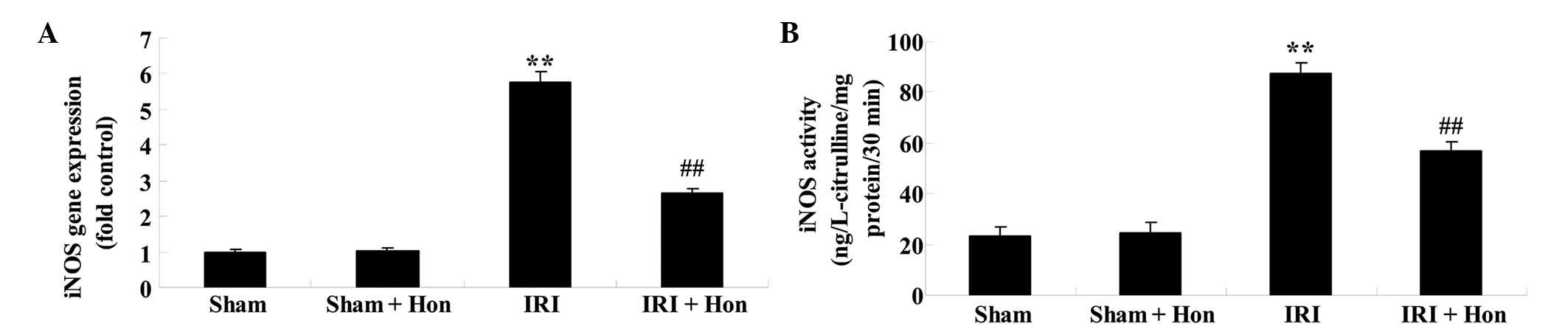
|
Cetin N, Suleyman H, Sener E, Demirci E,
Gundogdu C and Akcay F: The prevention of ischemia/reperfusion
induced oxidative damage by venous blood in rabbit kidneys
monitored with biochemical, histopatological and
immunohistochemical analysis. J Physiol Pharmacol. 65:383–392.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jiang G, Liu X, Wang M, Chen H, Chen Z and
Qiu T: Oxymatrine ameliorates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury
from oxidative stress through Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Acta Cir Bras.
30:422–429. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhuan-Yun LI, Xue-Ping Y, Bin L, Reheman
HN, Yang G, Zhan S and Qi MA: Auricularia auricular-judae
polysaccharide attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation. Biomed Rep.
3:478–482. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jin X, Zhang Y, Li X, Zhang J and Xu D:
C-type natriuretic peptide ameliorates ischemia/reperfusion-induced
acute kidney injury by inhibiting apoptosis and oxidative stress in
rats. Life Sci. 117:40–45. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tripatara P, Patel NS, Webb A, Rathod K,
Lecomte FM, Mazzon E, Cuzzocrea S, Yaqoob MM, Ahluwalia A and
Thiemermann C: Nitrite-derived nitric oxide protects the rat kidney
against ischemia/reperfusion injury in vivo: Role for xanthine
oxidoreductase. J Am Soc Nephrol. 18:570–580. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Reyes-Ocampo J, Ramirez-Ortega D, Vazquez
Cervantes GI, Pineda B, Montes de Oca Balderas P, González-Esquivel
D, Sánchez-Chapul L, Lugo-Huitrón R, Silva-Adaya D, Ríos C, et al:
Mitochondrial dysfunction related to cell damage induced by
3-hydroxykynurenine and 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid:
Non-dependent-effect of early reactive oxygen species production.
Neurotoxicology. 50:81–91. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Koc M, Kumral ZN, Özkan N, Memi G, Kaçar
Ö, Bilsel S, Çetinel Ş and Yeğen BÇ: Obestatin improves
ischemia/reperfusion-induced renal injury in rats via its
antioxidant and anti-apoptotic effects: Role of the nitric oxide.
Peptides. 60:23–31. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yan R, Li Y, Zhang L, Xia N, Liu Q, Sun H
and Guo H: Augmenter of liver regeneration attenuates inflammation
of renal ischemia/reperfusion injury through the NF-kappa B pathway
in rats. Int Urol Nephrol. 47:861–868. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Garcia-Criado FJ, Rodriguez-Barca P,
Garcia-Cenador MB, Rivas-Elena JV, Grande MT, Lopez-Marcos JF,
Mourelle M and López-Novoa JM: Protective effect of new
nitrosothiols on the early inflammatory response to kidney
ischemia/reperfusion and transplantation in rats. J Interferon
Cytokine Res. 29:441–450. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen YY, Yeh CH, So EC, Sun DP, Wang LY
and Hsing CH: Anticancer drug 2-methoxyestradiol protects against
renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by reducing inflammatory
cytokines expression. Biomed Res Int. 2014:4315242014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hsu YH, Li HH, Sung JM, Chen WT, Hou YC
and Chang MS: Interleukin-19 mediates tissue damage in murine
ischemic acute kidney injury. PLoS One. 8:e560282013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Seo KH, Nam YH, Lee DY, Ahn EM, Kang TH
and Baek NI: Recovery effect of phenylpropanoid glycosides from
Magnolia obovata fruit on alloxan-induced pancreatic islet damage
in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Carbohydr Res. 416:70–74. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kumar A, Kumar Singh U and Chaudhary A:
Honokiol analogs: A novel class of anticancer agents targeting cell
signaling pathways and other bioactivities. Future Med Chem.
5:809–829. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kumar A, Kumar Singh U and Chaudhary A:
Honokiol analogs: A novel class of anticancer agents targeting cell
signaling pathways and other bioactivities. Future Med Chem.
5:809–829. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Raison-Peyron N, Cesaire A, Du-Thanh A and
Dereure O: Allergic contact dermatitis caused by Magnolia
officinalis bark extract in a facial anti-ageing cream. Contact
Dermatitis. 72:416–417. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ghys K, De Palma A, Vandevenne A,
Werbrouck J and Goossens A: Magnolia officinalis bark extract, a
recently identified contact allergen in 'anti-ageing' cosmetics.
Contact Dermatitis. 73:130–132. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Woodbury A, Yu SP, Wei L and Garcia P:
Neuro-modulating effects of honokiol: A review. Front Neurol.
4:1302013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fried LE and Arbiser JL: Honokiol, a
multifunctional anti-angiogenic and antitumor agent. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 11:1139–1148. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tian W, Xu D and Deng YC: Honokiol, a
multifunctional tumor cell death inducer. Pharmazie. 67:811–816.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shen JL, Man KM, Huang PH, Chen WC, Chen
DC, Cheng YW, Liu PL, Chou MC and Chen YH: Honokiol and magnolol as
multifunctional antioxidative molecules for dermatologic disorders.
Molecules. 15:6452–6465. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mozaffari-Khosravi H, Ahadi Z and Fallah
Tafti M: The effect of green tea versus sour tea on insulin
resistance, lipids profiles and oxidative stress in patients with
type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized clinical trial. Iran J Med
Sci. 39:424–432. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Monji A, Mitsui T, Bando YK, Aoyama M,
Shigeta T and Murohara T: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor
activation reverses cardiac remodeling via normalizing cardiac
steatosis and oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 305:H295–H304. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zheng Z, Ge Y, Zhang J, et al: PUFA diets
alter the microRNA expression profiles in an inflammation rat
model. Mol Med Rep. 11:4149–4157. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW and Dempfle L:
Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison
and statistical analysis of relative expression results in
real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 30:e362002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sagiroglu T, Torun N, Yagci M, Yalta T,
Sagiroglu G and Oguz S: Effects of apelin and leptin on renal
functions following renal ischemia/reperfusion: An experimental
study. Exp Ther Med. 3:908–914. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu ZG, Qi ZC, Liu WL and Wang WZ: Lutein
protects against ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat kidneys. Mol
Med Rep. 11:2179–2184. 2015.
|
|
30
|
Hsu CC, Chen LF, Lin MT and Tian YF:
Honokiol protected against heatstroke-induced oxidative stress and
inflammation in diabetic rats. Int J Endocrinol. 2014:1345752014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kinaci MK, Erkasap N, Kucuk A, Koken T and
Tosun M: Effects of quercetin on apoptosis, NF-κB and NOS gene
expression in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Exp Ther Med.
3:249–254. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang J, Li JH, Wang L, Han M, Xiao F, Lan
XQ, Li YQ, Xu G and Yao Y: Glucocorticoid receptor agonist
dexamethasone attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by
up-regulating eNOS/iNOS. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci.
34:516–520. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen YJ, Tsai KS, Chan DC, Lan KC, Chen
CF, Yang RS and Liu SH: Honokiol, a low molecular weight natural
product, prevents inflammatory response and cartilage matrix
degradation in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. J Orthop Res.
32:573–580. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li N, Xie H, Li L, Wang J, Fang M, Yang N
and Lin H: Effects of honokiol on sepsis-induced acute kidney
injury in an experimental model of sepsis in rats. Inflammation.
37:1191–1199. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang B, Rong R, Li H, Peng X, Xiong L,
Wang Y, Yu X and Mao H: Heat shock protein 72 suppresses apoptosis
by increasing the stability of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis
protein in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Mol Med Rep.
11:1793–1799. 2015.
|
|
36
|
Asaga T, Ueki M, Chujo K and Taie S:
JTE-607, an inflammatory cytokine synthesis inhibitor, attenuates
ischemia/reperfusion-induced renal injury by reducing neutrophil
activation in rats. J Biosci Bioeng. 106:22–26. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chiang J, Shen YC, Wang YH, Hou YC, Chen
CC, Liao JF, Yu MC, Juan CW and Liou KT: Honokiol protects rats
against eccentric exercise-induced skeletal muscle damage by
inhibiting NF-kappaB induced oxidative stress and inflammation. Eur
J Pharmacol. 610:119–127. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Munroe ME, Businga TR, Kline JN and Bishop
GA: Anti-inflammatory effects of the neurotransmitter agonist
Honokiol in a mouse model of allergic asthma. J Immunol.
185:5586–5597. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ishikawa C, Arbiser JL and Mori N:
Honokiol induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis via inhibition of
survival signals in adult T-cell leukemia. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1820:879–887. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Di Domenico F, Casalena G, Jia J, Sultana
R, Barone E, Cai J, Pierce WM, Cini C, Mancuso C, Perluigi M, et
al: Sex differences in brain proteomes of neuron-specific
STAT3-null mice after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. J Neurochem.
121:680–692. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yang Y, Duan W, Jin Z, Yi W, Yan J, Zhang
S, Wang N, Liang Z, Li Y, Chen W, et al: JAK2/STAT3 activation by
melatonin attenuates the mitochondrial oxidative damage induced by
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Pineal Res. 55:275–286.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yu C, Zhang Q, Zhang HY, Zhang X, Huo X,
Cheng E, Wang DH, Arbiser JL, Spechler SJ and Souza RF: Targeting
the intrinsic inflammatory pathway: Honokiol exerts proapoptotic
effects through STAT3 inhibition in transformed Barrett's cells. Am
J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 303:G561–569. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Luan HF, Zhao ZB, Zhao QH, Zhu P, Xiu MY
and Ji Y: Hydrogen sulfide postconditioning protects isolated rat
hearts against ischemia and reperfusion injury mediated by the
JAK2/STAT3 survival pathway. Braz J Med Biol Res. 45:898–905.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Weng TI, Wu HY, Chen BL and Liu SH:
Honokiol attenuates the severity of acute pancreatitis and
associated lung injury via acceleration of acinar cell apoptosis.
Shock. 37:478–484. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Xia J, Wu Z, Yu C, He W, Zheng H, He Y,
Jian W, Chen L, Zhang L and Li W: miR-124 inhibits cell
proliferation in gastric cancer through down-regulation of SPHK1. J
Pathol. 227:470–480. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|