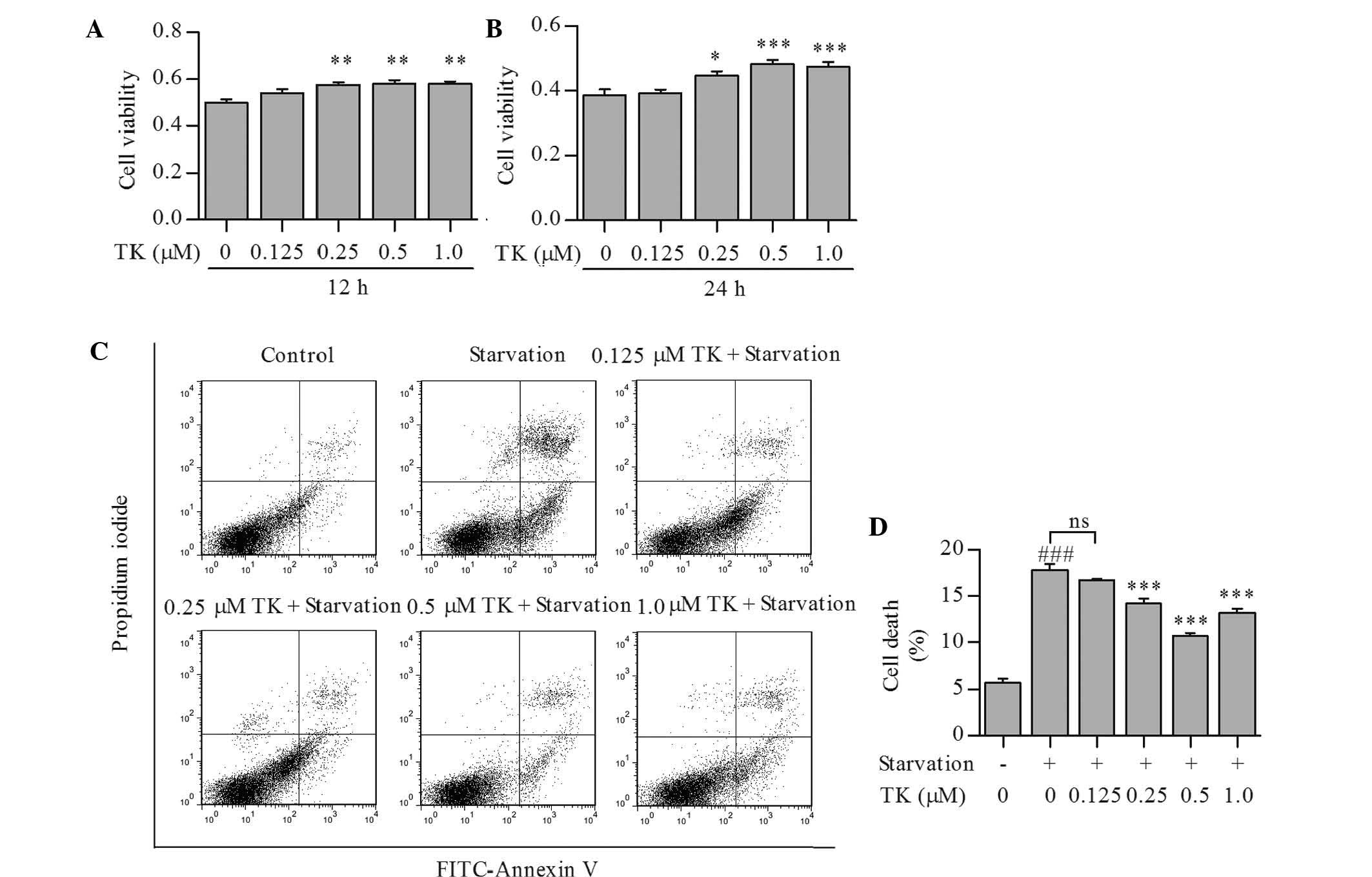
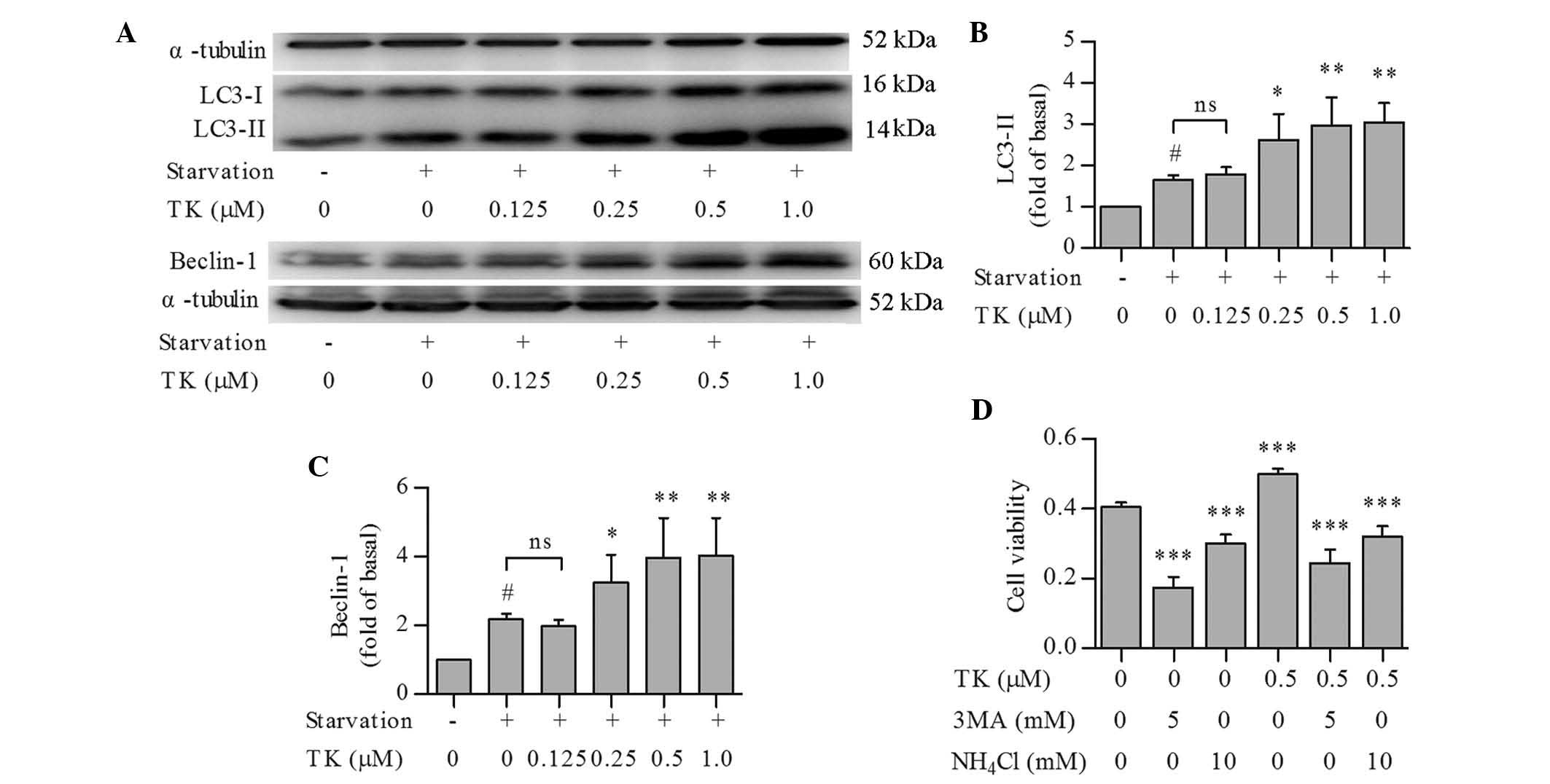
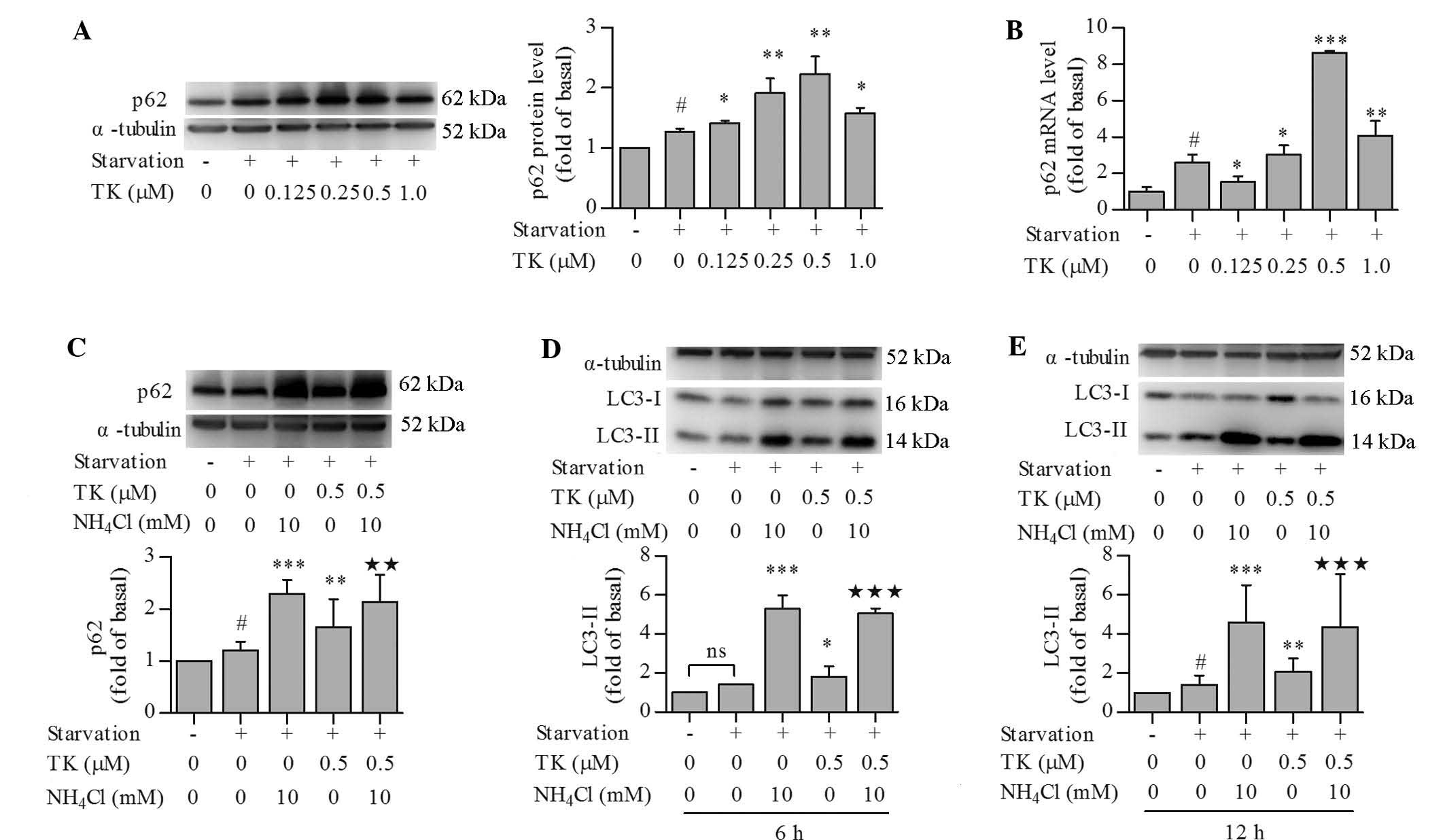
|
1
|
Tanida I: Autophagosome formation and
molecular mechanism of autophagy. Antioxid Redox Signal.
14:2201–2214. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bhoola KD, Figueroa CD and Worthy K:
Bioregulation of kinins: Kallikreins, kininogens and kininases.
Pharmacol Rev. 44:1–80. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Su J, Tang Y, Zhou H, Liu L and Dong Q:
Tissue kallikrein protects neurons from
hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cell injury through Homer1b/c. Cell
Signal. 24:2205–2215. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang Z, Han X, Cui M, Fang K, Lu Z and
Dong Q: Tissue kallikrein protects rat hippocampal CA1 neurons
against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury through the
B2R-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 pathway. J Neurosci Res. 92:651–657. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tang Y, Shao Y, Su J, Zhou H, Liu L, Ren H
and Dong Q: The protein therapy of kallikrein in cerebral ischemic
reperfusion injury. Curr Med Chem. 16:4502–4510. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Papadakis M, Hadley G, Xilouri M, Hoyte
LC, Nagel S, McMenamin MM, Tsaknakis G, Watt SM, Drakesmith CW,
Chen R, et al: Tsc1 (hamartin) confers neuroprotection against
ischemia by inducing autophagy. Nat Med. 19:351–357. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yuan G, Deng J, Wang T, Zhao C, Xu X, Wang
P, Voltz JW, Edin ML, Xiao X, Chao L, et al: Tissue kallikrein
reverses insulin resistance and attenuates nephropathy in diabetic
rats by activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinaseB
and adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase signaling
pathways. Endocrinology. 148:2016–2026. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim JH, Hong SK, Wu PK, Richards AL,
Jackson WT and Park JI: Raf/MEK/ERK can regulate cellular levels of
LC3B and SQSTM1/p62 at expression levels. Exp Cell Res.
327:340–352. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang J, Whiteman MW, Lian H, Wang G, Singh
A, Huang D and Denmark T: A non-canonical MEK/ERK signaling pathway
regulates autophagy via regulating Beclin 1. J Biol Chem.
284:21412–21424. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Moon RT: Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Sci
STKE. 2005:2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Petherick KJ, Williams AC, Lane JD,
Ordóñez-Morán P, Huelsken J, Collard TJ, Smartt HJ, Batson J, Malik
K, Paraskeva C and Greenhough A: Autolysosomal β-catenin
degradation regulates Wnt-autophagy-p62 crosstalk. EMBO J.
32:1903–1916. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdalla FC, Abeliovich H,
Abraham RT, Acevedo-Arozena A, Adeli K, Agholme L, Agnello M,
Agostinis P, Aguirre-Ghiso JA, et al: Guidelines for the use and
interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy. Autophagy.
8:445–544. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Waeckel L, Potier L, Richer C, Roussel R,
Bouby N and Alhenc-Gelas F: Pathophysiology of genetic deficiency
in tissue kallikrein activity in mouse and man. Thromb Haemost.
110:476–483. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chao J, Shen B, Gao L, Xia CF, Bledsoe G
and Chao L: Tissue kallikrein in cardiovascular, cerebrovascular
and renal diseases and skin wound healing. Biol Chem. 391:345–355.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yao YY, Yin H, Shen B, Smith RS Jr, Liu Y,
Gao L, Chao L and Chao J: Tissue kallikrein promotes
neovascularization and improves cardiac function by the
Akt-glycogen synthase kinase-3beta pathway. Cardiovasc Res.
80:354–364. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lu Z, Yang Q, Cui M, Liu Y, Wang T, Zhao H
and Dong Q: Tissue kallikrein induces SH-SY5Y cell proliferation
via epidermal growth factor receptor and extracellular
signal-regulated kinase1/2 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
446:25–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chong ZZ and Maiese K: Targeting WNT,
protein kinase B and mitochondrial membrane integrity to foster
cellular survival in the nervous system. Histol Histopathol.
19:495–504. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Heras-Sandoval D, Pérez-Rojas JM,
Hernández-Damián J and Pedraza-Chaverri J: The role of
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in the modulation of autophagy and the
clearance of protein aggregates in neurodegeneration. Cell Signal.
26:2694–2701. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Georgopoulos NT, Kirkwood LA and Southgate
J: A novel bidirectional positive-feedback loop between
Wnt-β-catenin and EGFR-ERK plays a role in context-specific
modulation of epithelial tissue regeneration. J Cell Sci.
127:2967–2982. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wei Y, Zou Z, Becker N, Anderson M,
Sumpter R, Xiao G, Kinch L, Koduru P, Christudass CS, Veltri RW, et
al: EGFR-mediated Beclin 1 phosphorylation in autophagy
suppression, tumor progression, and tumor chemoresistance. Cell.
154:1269–1284. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bjørkøy G, Lamark T, Brech A, Outzen H,
Perander M, Overvatn A, Stenmark H and Johansen T: P62/SQSTM1 forms
protein aggregates degraded by autophagy and has a protective
effect on huntingtin-induced cell death. J Cell Biol. 171:603–614.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|