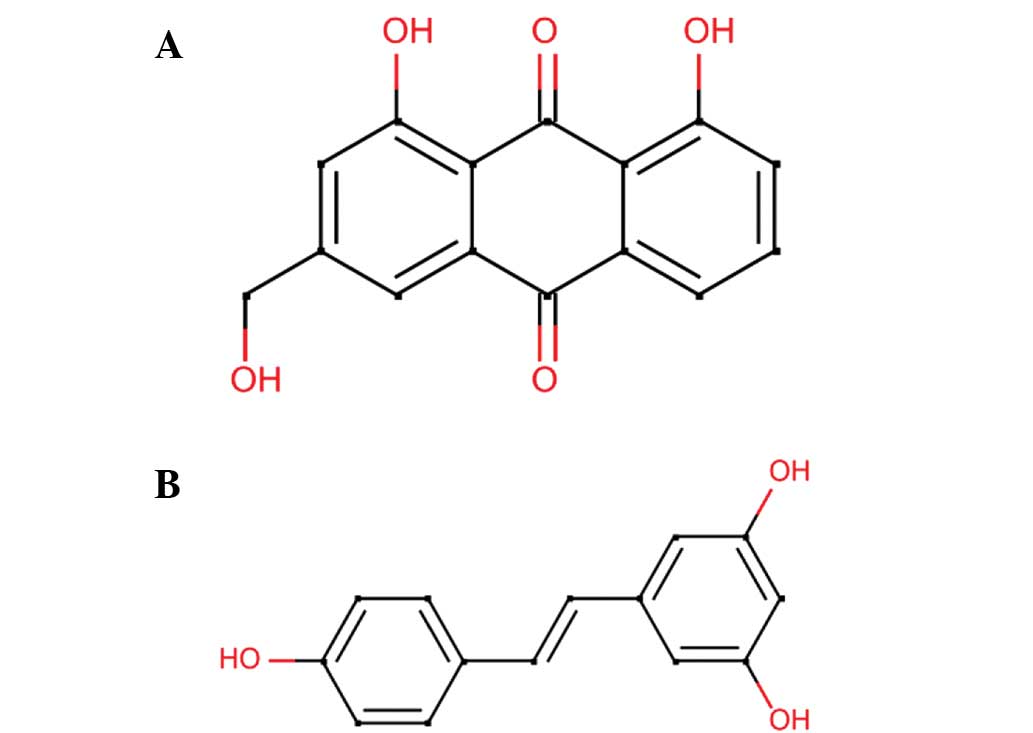
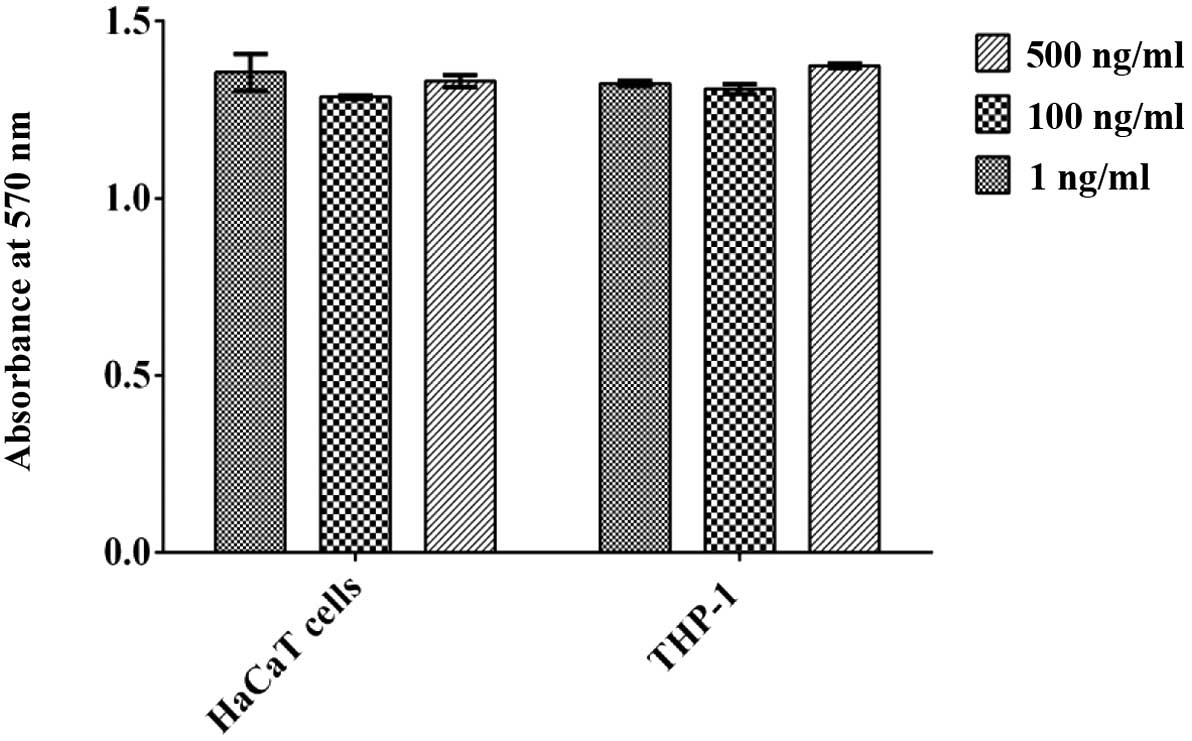
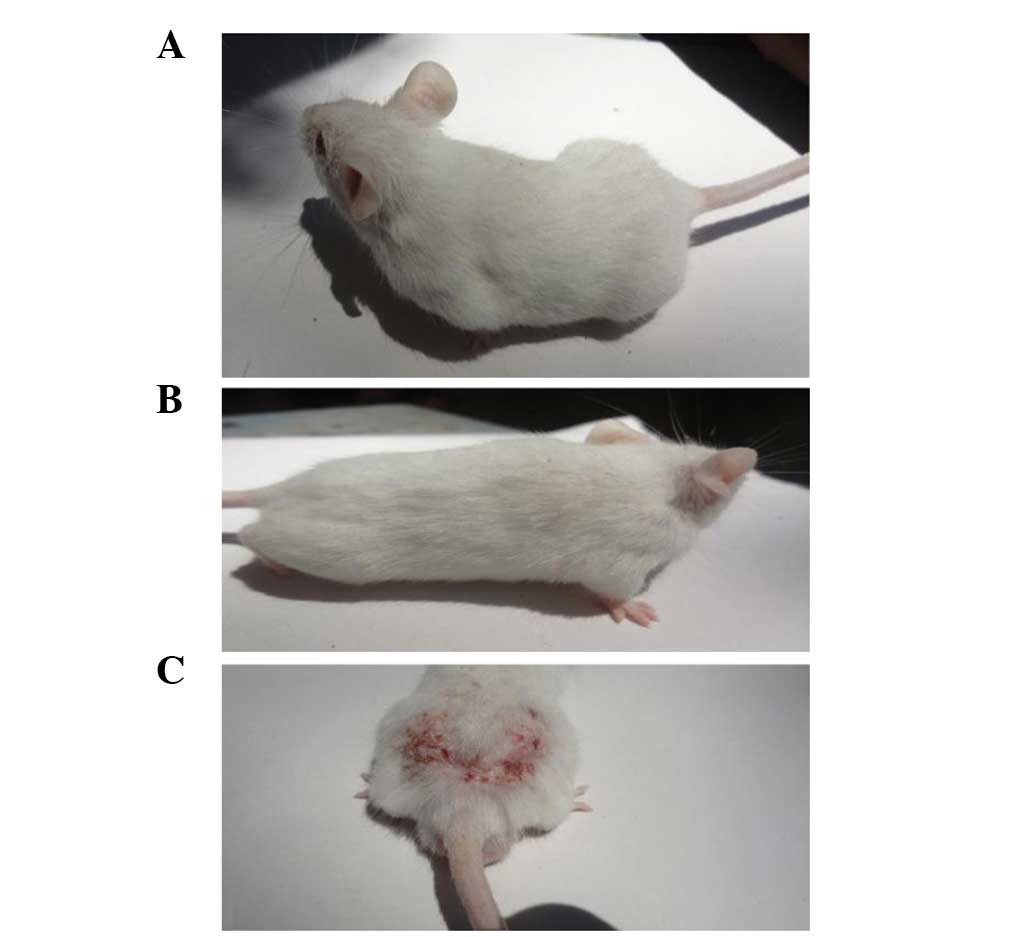
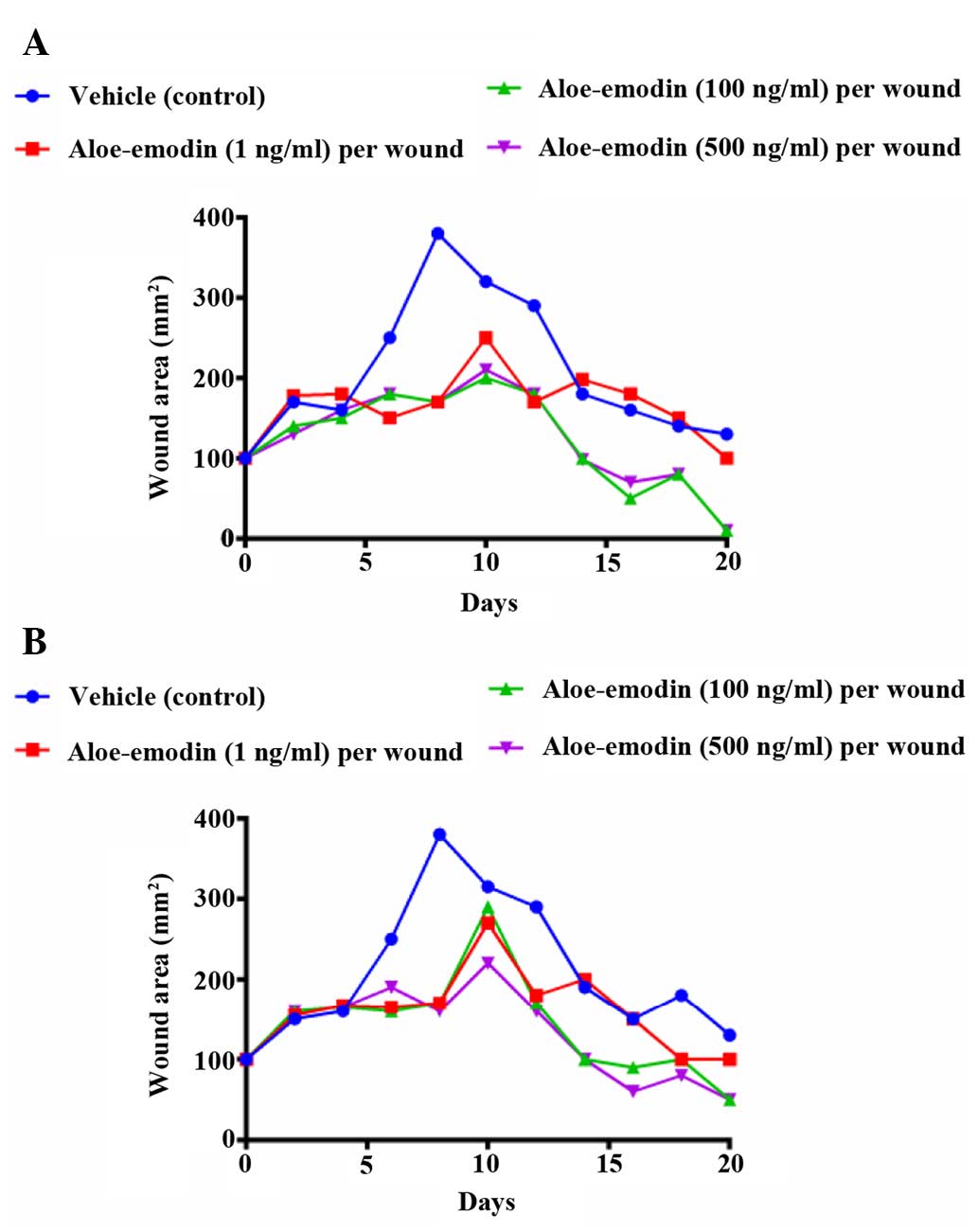
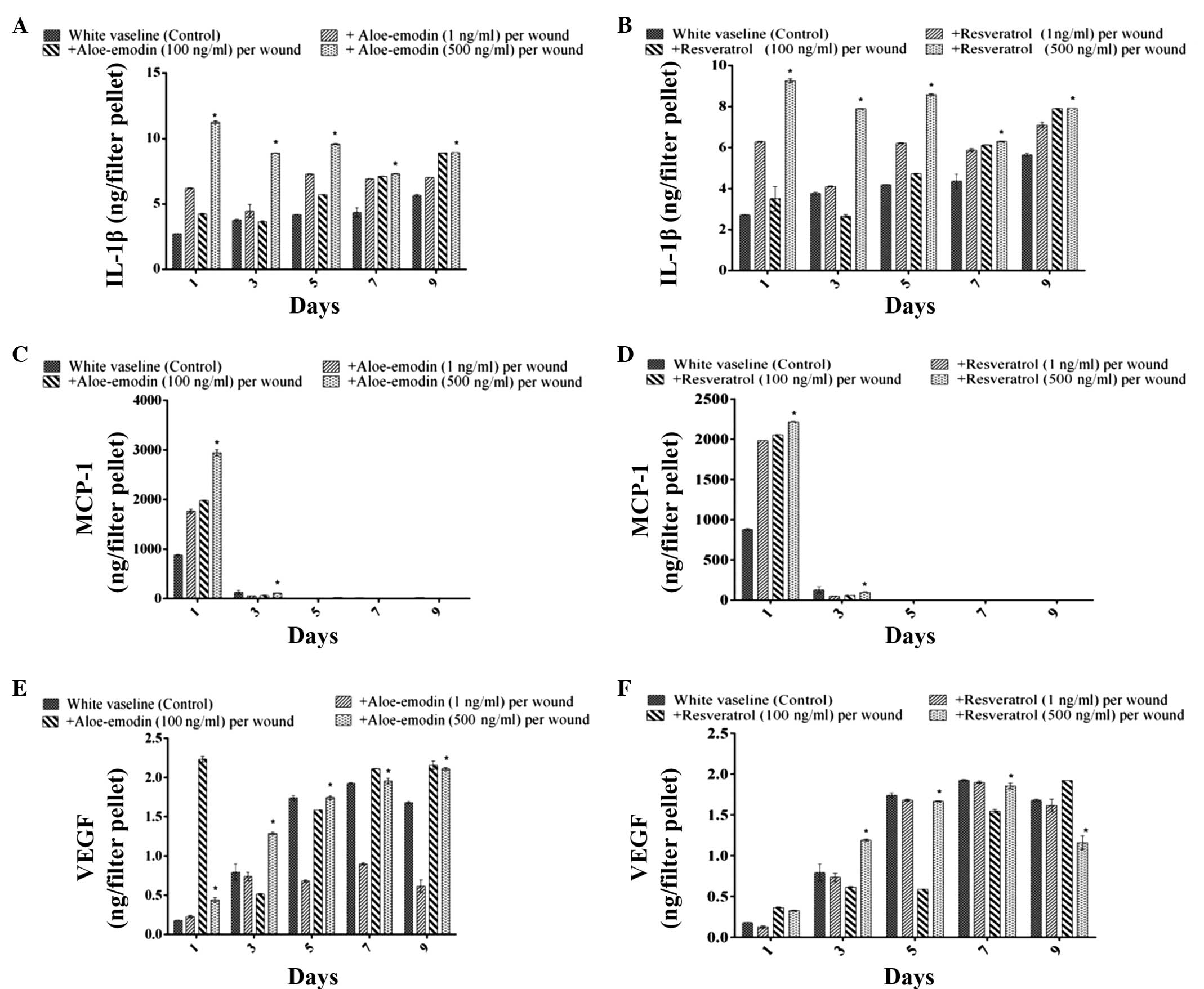
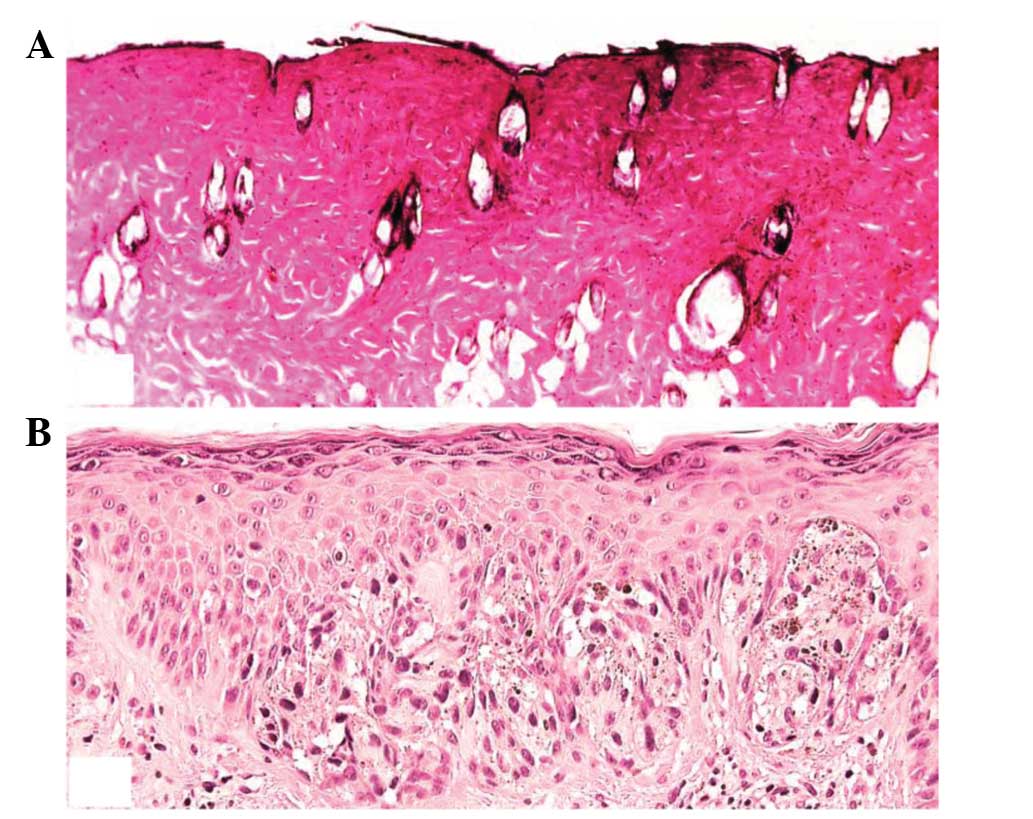
|
1
|
Reddy KK, Grossman L and Rogers GS: Common
complementary and alternative therapies with potential use in
dermatologic surgery: risks and benefits. J Am Acad Dermatol.
68:e127–e135. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wild T, Rahbarnia A, Kellner M, Sobotka L
and Eberlein T: Basics in nutrition and wound healing. Nutrition.
26:862–866. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pereira RF, Carvalho A, Gil MH, Mendes A
and Bartolo PJ: Influence of Aloe vera on water absorption and
enzymatic in vitro degradation of alginate hydrogel films.
Carbohydr Polym. 98:311–320. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Eshun K and He Q: Aloe vera: a valuable
ingredient for the food, pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries - a
review. Crit Rev Food Science Nutri. 44:91–96. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Naqvi S, Ullah MF and Hadi SM: DNA
degradation by aqueous extract of Aloe vera in the presence of
copper ions. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 47:161–165. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Blumenhal M, Busse NR and Golddberg A: The
complete commission E. monographs therapeutic guide to herbal
medicine. Integrative Medicines Communications; Boston, MA: pp.
80–81. 1998
|
|
7
|
WHO Monographs on Selected Medicinal
Plants. 1. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 1999
|
|
8
|
Dat AD, Poon F, Pham KB and Doust J: Aloe
vera for treating acute and chronic wounds. Cochrane Database Syst
Rev. 2:CD0087622012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hamman JH: Composition and applications of
Aloe vera Leaf Gel. Molecules. 13:1599–1616. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Im SA, Lee YR, Lee YH, Lee MK, Park YI,
Lee S, Kim K and Lee CK: In vivo evidence of the immunomodulatory
activity of orally administered Aloe vera gel. Arch Pharm Res.
33:451–456. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Talmadge J, Chavez J, Jacobs L, Munger C,
Chinnah T, Chow JT, Williamson D and Yates K: Fractionation of Aloe
vera L. inner gel, purification and molecular profiling of
activity. Int Immunopharmacol. 4:1757–1773. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Oryan A, Naeini AT, Nikahval B and Gorjian
E: Effect of aqueous extract of Aloe vera on experimental cutaneous
wound healing in rat. Veterinarski Arhiv. 80:509–522. 2010.
|
|
13
|
Nayak BS, Ramdath DD, Marshall JR, Isitor
GN, Eversley M, Xue S and Shi J: Wound-healing activity of the skin
of the common grape (Vitis Vinifera) variant, Cabernet Sauvignon.
Phytother Res. 24:1151–1157. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hemmati AA, Aghel N, Rashidi I and
Gholampur-Aghdami A: Topical grape (Vitis vinifera) seed extract
promotes repair of full thickness wound in rabbit. Int Wound J.
8:514–520. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chan MMY: Antimicrobial effect of
resveratrol on dermatophytes and bacterial pathogens of the skin.
Biochem Pharmacol. 63:99–104. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schneider Y, Vincent F, Duranton B, Badolo
L, Gossé F, Bergmann C, Seiler N and Raul F: Anti-proliferative
effect of resveratrol, a natural component of grapes and wine, on
human colonic cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 158:85–91. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Romero-Pérez AI, Ibern-Gómez M,
Lamuela-Raventós RM and de La Torre-Boronat MC: Piceid, the major
resveratrol derivative in grape juices. J Agric Food Chem.
47:1533–1536. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dinarello CA: Immunological and
inflammatory functions of the interleukin-1 family. Annu Rev
Immunol. 27:519–550. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Park J and Boo YC: Isolation of
resveratrol from vitis viniferae caulis and its potent inhibition
of human tyrosinase. Evidence-Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013:6452572013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lee E and Surh YJ: Induction of apoptosis
in HL-60 cells by pungent vanilloids, (6)-gingerol and (6)-paradol.
Cancer Lett. 134:163–168. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Mosmann T: Rapid colorimetric assay for
cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and
cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 65:55–63. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Maenthaisong R, Chaiyakunapruk N,
Niruntraporn S and Kongkaew C: The efficacy of Aloe vera used for
burn wound healing: A systematic review. Burns. 33:713–718. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Singer AJ and Clark RA: Cutaneous wound
healing. N Engl J Med. 341:738–746. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jettanacheawchankit S, Sasithanasate S,
Sangvanich P, Banlunara W and Thunyakitpisal P: Acemannan
stimulates gingival fibroblast proliferation; Expressions of
keratinocyte growth factor-1, vascular endothelial growth factor
and type I collagen; and wound healing. J Pharmacol Sci.
109:525–531. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
İnan A, Meral Ş, Cemile K, Metin E and
Cenap D: Effects of Aloe vera on colonic anastomoses of rats. Surg
Prac. 11:60–65. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Moon EJ, Lee YM, Lee OH, Lee MJ, Lee SK,
Chung MH, Park YI, Sung CK, Choi JS and Kim KW: A novel angiogenic
factor derived from Aloe vera gel: Beta-sitosterol, a plant sterol.
Angiogenesis. 3:117–123. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Szabo S, Kusstatscher S, Sakoulas G,
Sandor Z, Vincze A and Jadus M: Growth factors: New 'endogenous
drugs' for ulcer healing. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 210:15–18.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tischer E, Gospodarowicz D, Mitchell R,
Silva M, Schilling J, Lau K, Crisp T, Fiddes JC and Abraham JA:
Vascular endothelial growth factor: A new member of the
platelet-derived growth factor gene family. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 165:1198–1206. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kitano A, Saika S, Yamanaka O, Ikeda K,
Okada Y, Shirai K and Reinach PS: Emodin suppression of ocular
surface inflammatory reaction. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
48:5013–5022. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Simpson JE, Newcombe J, Cuzner ML and
Woodroofe MN: Expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and
other β-chemokines by resident glia and inflammatory cells in
multiple sclerosis lesions. J Neuroimmunol. 84:238–249. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|