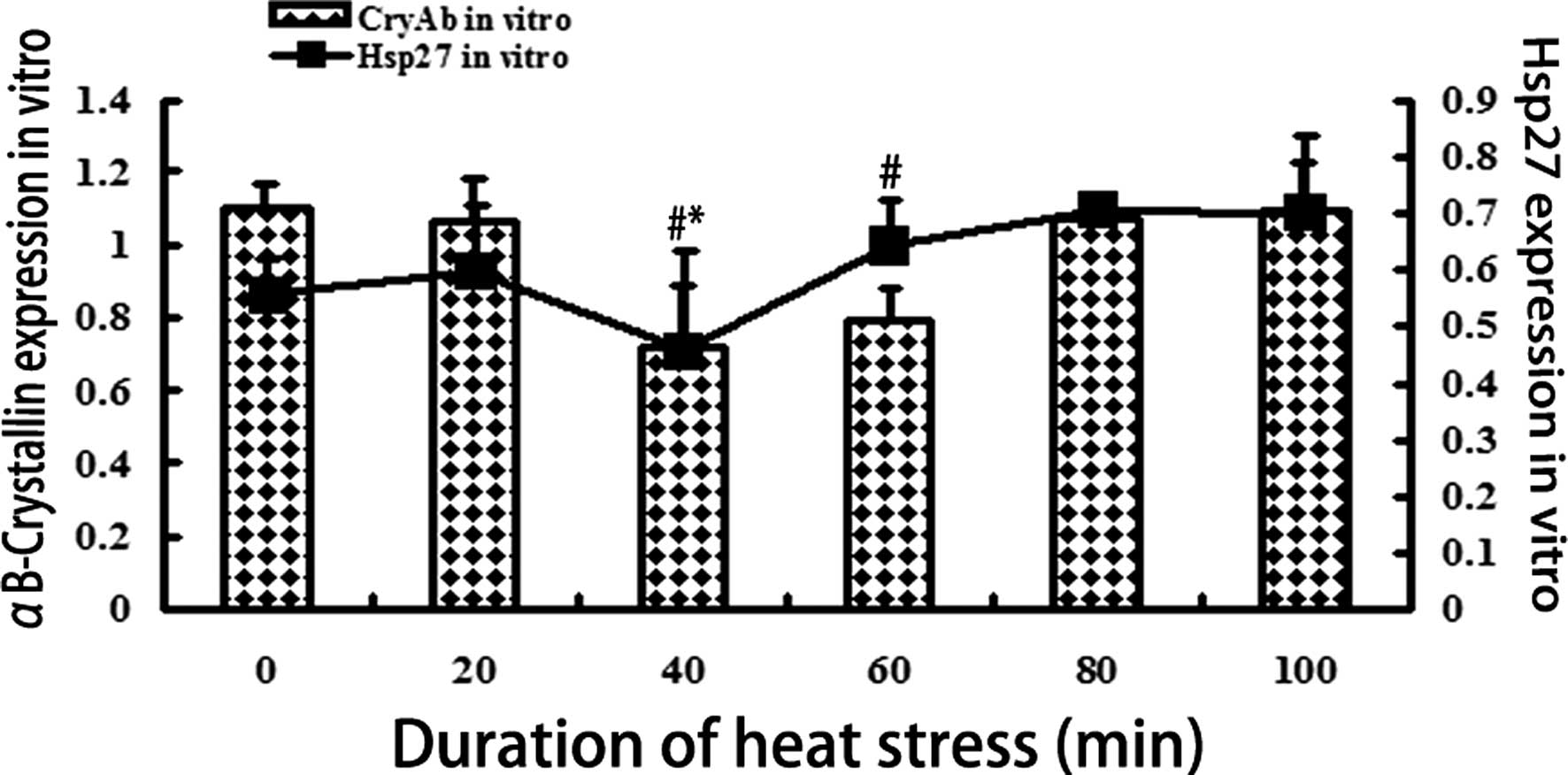
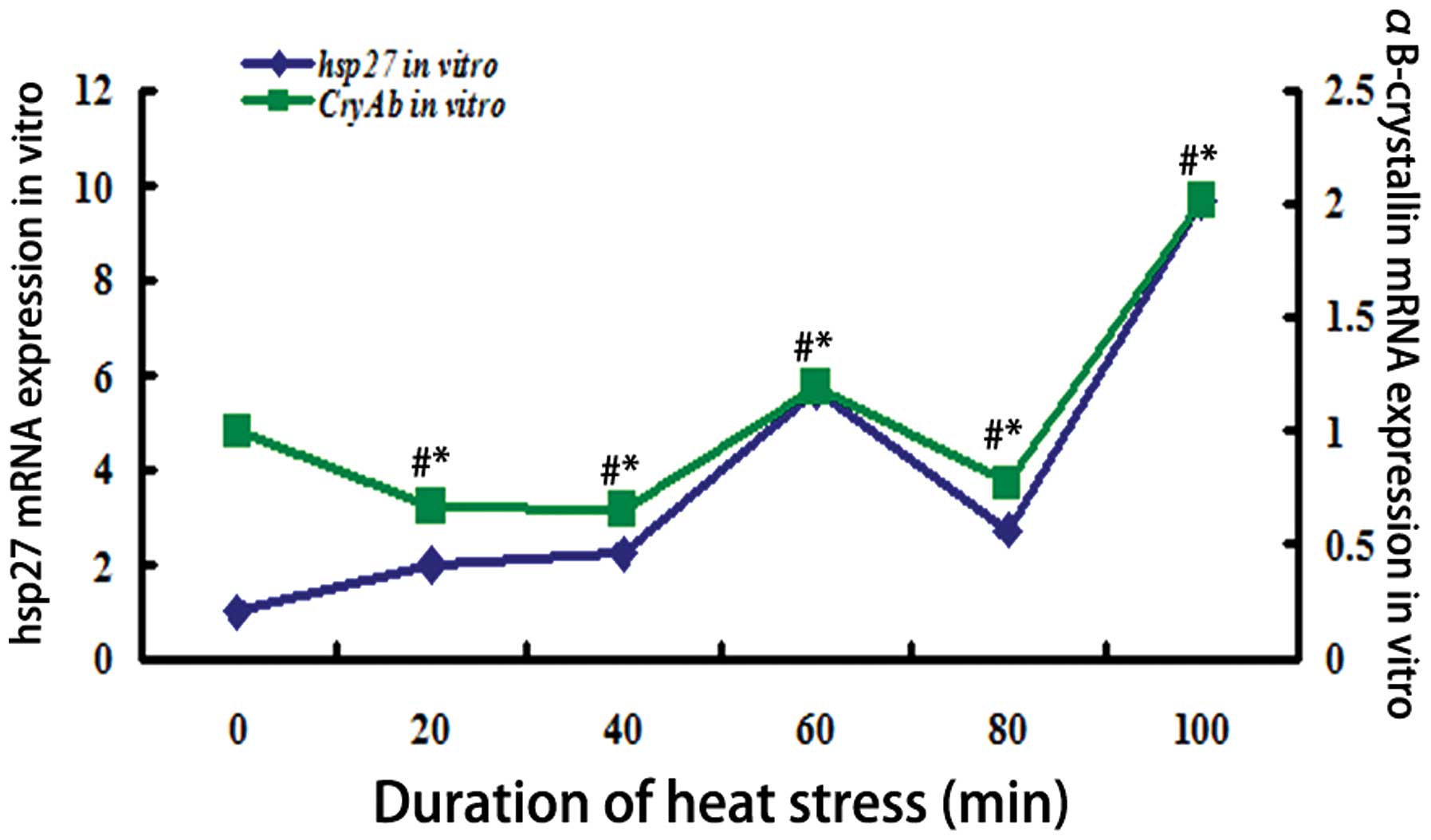
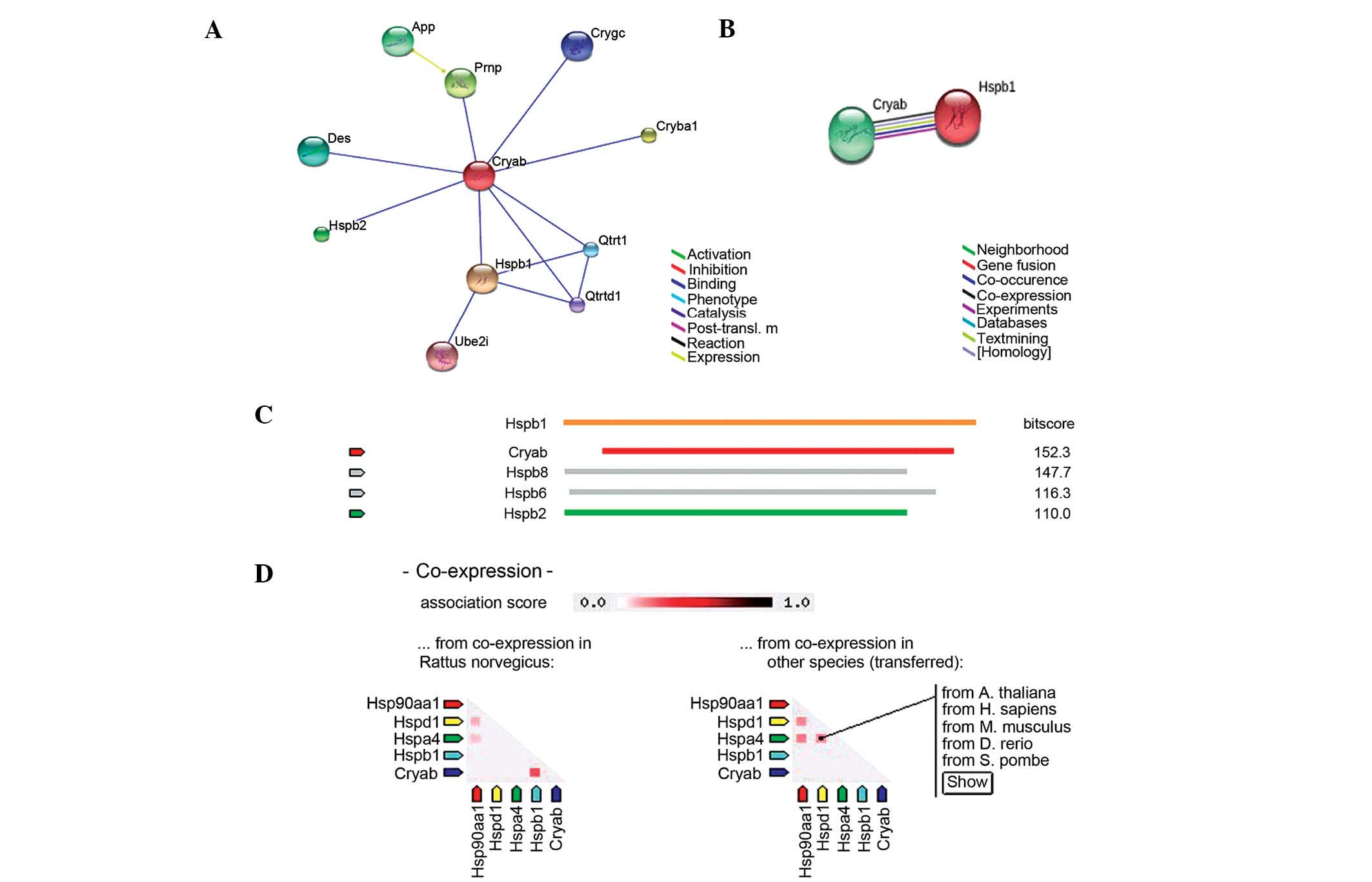
|
1
|
Rohde MC, Corydon TJ, Hansen J, Pedersen
CB, Schmidt SP, Gregersen N and Banner J: Heat stress and sudden
infant death syndrome - stress gene expression after exposure to
moderate heat stress. Forensic Sci Int. 232:16–24. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Feder ME and Hofmann GE: Heat-shock
proteins, molecular chaperones, and the stress response:
Evolutionary and ecological physiology. Annu Rev Physiol.
61:243–282. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Herbst J, Gilbert JD and Byard RW: Urinary
incontinence, hyperthermia, and sudden death. J Forensic Sci.
56:1062–1063. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhu Y, Lu X, Wu D, Cai S, Li S and Teng X:
The effect of manganese-induced cytotoxicity on mRNA expressions of
HSP27, HSP40, HSP60, HSP70 and HSP90 in chicken spleen lymphocytes
in vitro. Biol Trace Elem Res. 156:144–152. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Martin J, Horwich AL and Hartl FU:
Prevention of protein denaturation under heat stress by the
chaperonin Hsp60. Science. 258:995–998. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bagatell R, Paine-Murrieta GD, Taylor CW,
Pulcini EJ, Akinaga S, Benjamin IJ and Whitesell L: Induction of a
heat shock factor 1-dependent stress response alters the cytotoxic
activity of hsp90-binding agents. Clin Cancer Res. 6:3312–3318.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Garrido C, Paul C, Seigneuric R and
Kampinga HH: The small heat shock proteins family: The long
forgotten chaperones. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 44:1588–1592. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Singh IS and Hasday JD: Fever,
hyperthermia and the heat shock response. Int J Hyperthermia.
29:423–435. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Adhikari AS, Sridhar Rao K, Rangaraj N,
Parnaik VK and Mohan Rao Ch: Heat stress-induced localization of
small heat shock proteins in mouse myoblasts: Intranuclear lamin
A/C speckles as target for alphaB-crystallin and Hsp25. Exp Cell
Res. 299:393–403. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ananthan J, Goldberg AL and Voellmy R:
Abnormal proteins serve as eukaryotic stress signals and trigger
the activation of heat shock genes. Science. 232:522–524. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Beere HM: “The stress of dying”: The role
of heat shock proteins in the regulation of apoptosis. J Cell Sci.
117:2641–2651. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Arya R, Mallik M and Lakhotia SC: Heat
shock genes - integrating cell survival and death. J Biosci.
32:595–610. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Knowlton AA, Brecher P and Apstein CS:
Rapid expression of heat shock protein in the rabbit after brief
cardiac ischemia. J Clin Invest. 87:139–147. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Acunzo J, Katsogiannou M and Rocchi P:
Small heat shock proteins HSP27 (HspB1), αB-crystallin (HspB5) and
HSP22 (HspB8) as regulators of cell death. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
44:1622–1631. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Concannon CG, Gorman AM and Samali A: On
the role of Hsp27 in regulating apoptosis. Apoptosis. 8:61–70.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kappé G, Franck E, Verschuure P, Boelens
WC, Leunissen JA and de Jong WW: The human genome encodes 10
alpha-crystallin-related small heat shock proteins: HspB1-10. Cell
Stress Chaperones. 8:53–61. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lanneau D, Wettstein G, Bonniaud P and
Garrido C: Heat shock proteins: Cell protection through protein
triage. ScientificWorldJournal. 10:1543–1552. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wettstein G, Bellaye PS, Micheau O and
Bonniaud P: Small heat shock proteins and the cytoskeleton: An
essential interplay for cell integrity? Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
44:1680–1686. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zoubeidi A and Gleave M: Small heat shock
proteins in cancer therapy and prognosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
44:1646–1656. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Moseley PL: Heat shock proteins and heat
adaptation of the whole organism. J Appl Physiol (1985).
83:1413–1417. 1997.
|
|
21
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering C
and Jensen LJ: STRING v9.1: Protein-protein interaction networks,
with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:D808–D815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Clements RT, Feng J, Cordeiro B, Bianchi C
and Sellke FW: p38-MAPK-dependent small HSP27 and αB-crystallin
phosphorylation in regulation of myocardial function following
cardioplegic arrest. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
300:H1669–H1677. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Baler R, Dahl G and Voellmy R: Activation
of human heat shock genes is accompanied by oligomerization,
modification, and rapid translocation of heat shock transcription
factor HSF1. Mol Cell Biol. 13:2486–2496. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Parcellier A, Schmitt E, Brunet M, Hammann
A, Solary E and Garrido C: Small heat shock proteins HSP27 and
alphaB-crystallin: Cytoprotective and oncogenic functions. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 7:404–413. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sugiyama Y, Suzuki A, Kishikawa M, Akutsu
R, Hirose T, Waye MM, Tsui SK, Yoshida S and Ohno S: Muscle
develops a specific form of small heat shock protein complex
composed of MKBP/HSPB2 and HSPB3 during myogenic differentiation. J
Biol Chem. 275:1095–1104. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fostinis Y, Theodoropoulos PA, Gravanis A
and Stournaras C: Heat shock protein HSP90 and its association with
the cytoskeleton: A morphological study. Biochem Cell Biol.
70:779–786. 1992. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Knowlton AA and Sun L: Heat-shock
factor-1, steroid hormones, and regulation of heat-shock protein
expression in the heart. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
280:H455–H464. 2001.
|
|
28
|
Tang S, Buriro R, Liu Z, Zhang M, Ali I,
Adam A, Hartung J and Bao E: Localization and expression of Hsp27
and αB-crystallin in rat primary myocardial cells during heat
stress in vitro. PloS One. 8:e690662013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ito H, Kamei K, Iwamoto I, Inaguma Y,
Tsuzuki M, Kishikawa M, Shimada A, Hosokawa M and Kato K: Hsp27
suppresses the formation of inclusion bodies induced by expression
of R120G α B-crystallin, a cause of desmin-related myopathy. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 60:1217–1223. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chávez Zobel AT, Loranger A, Marceau N,
Thériault JR, Lambert H and Landry J: Distinct chaperone mechanisms
can delay the formation of aggresomes by the myopathy-causing R120G
alphaB-crystallin mutant. Hum Mol Genet. 12:1609–1620. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|