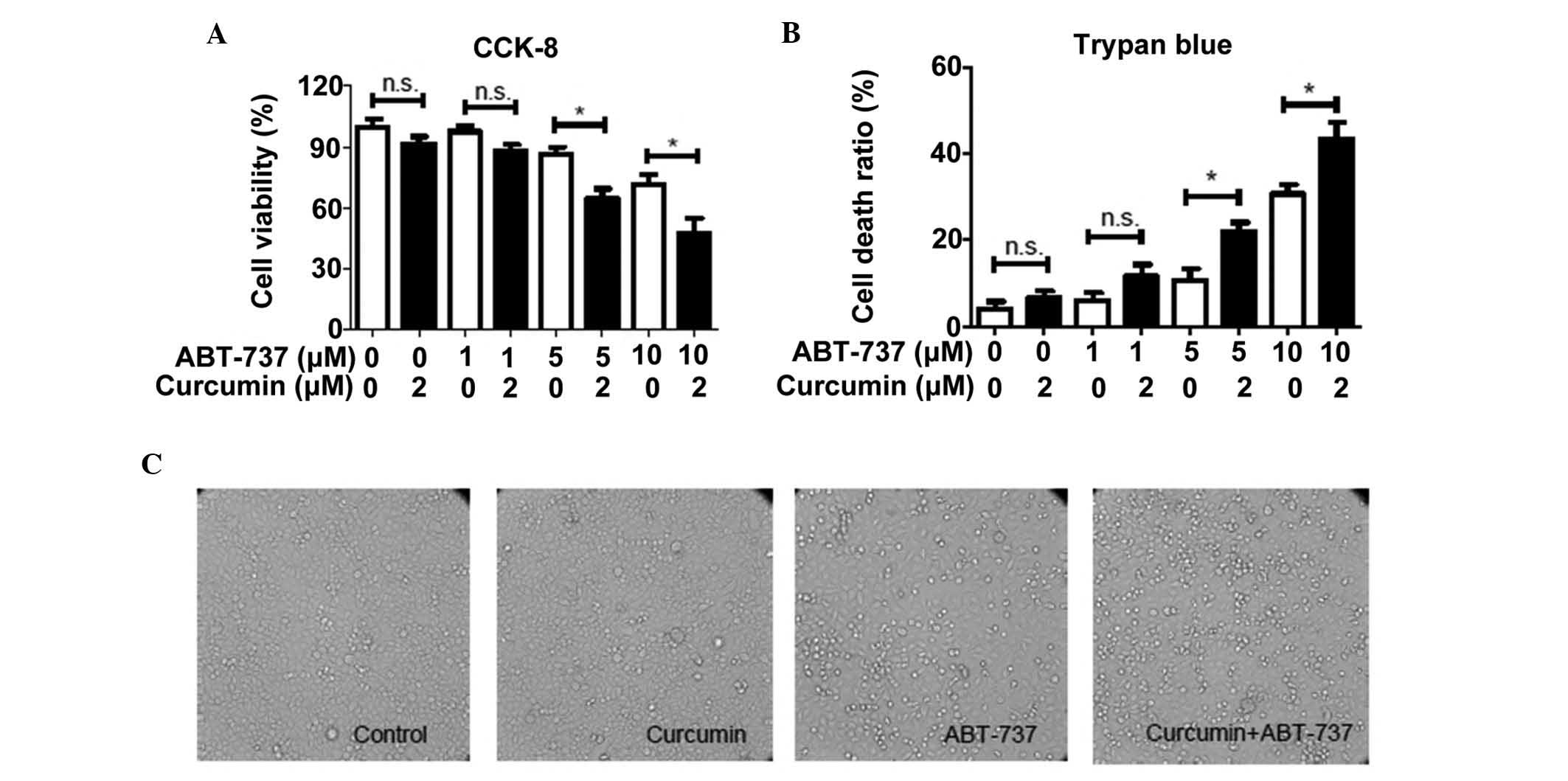
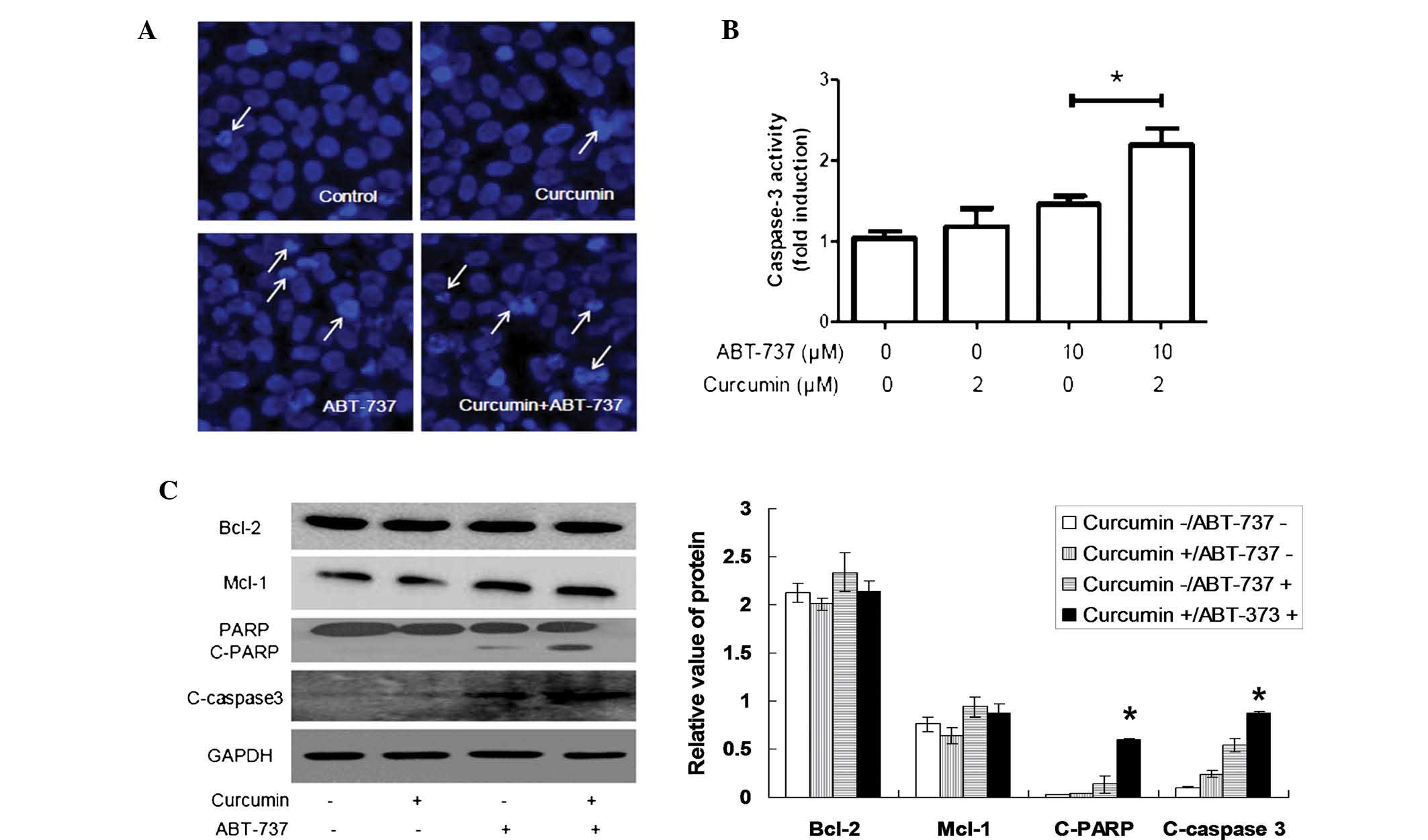
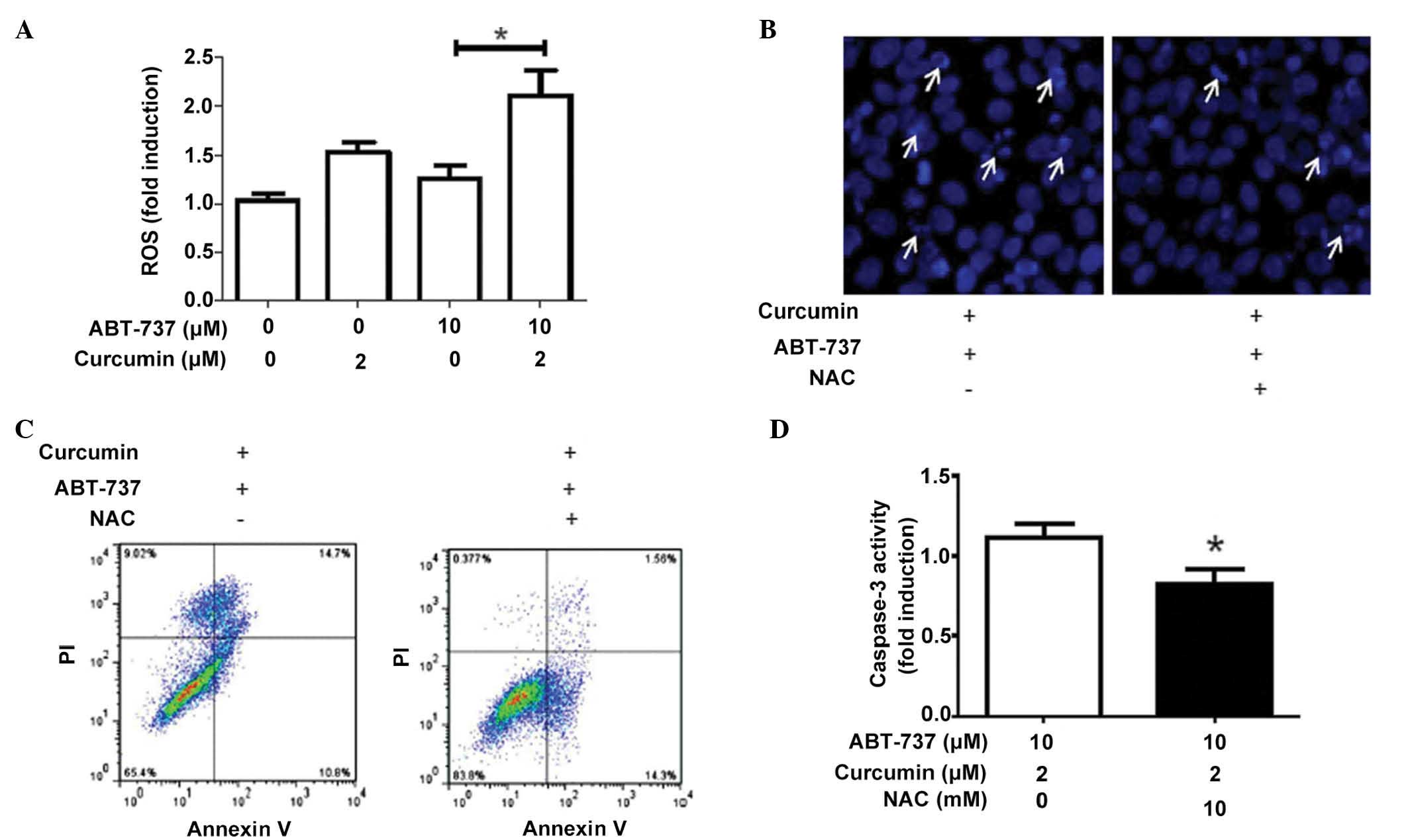
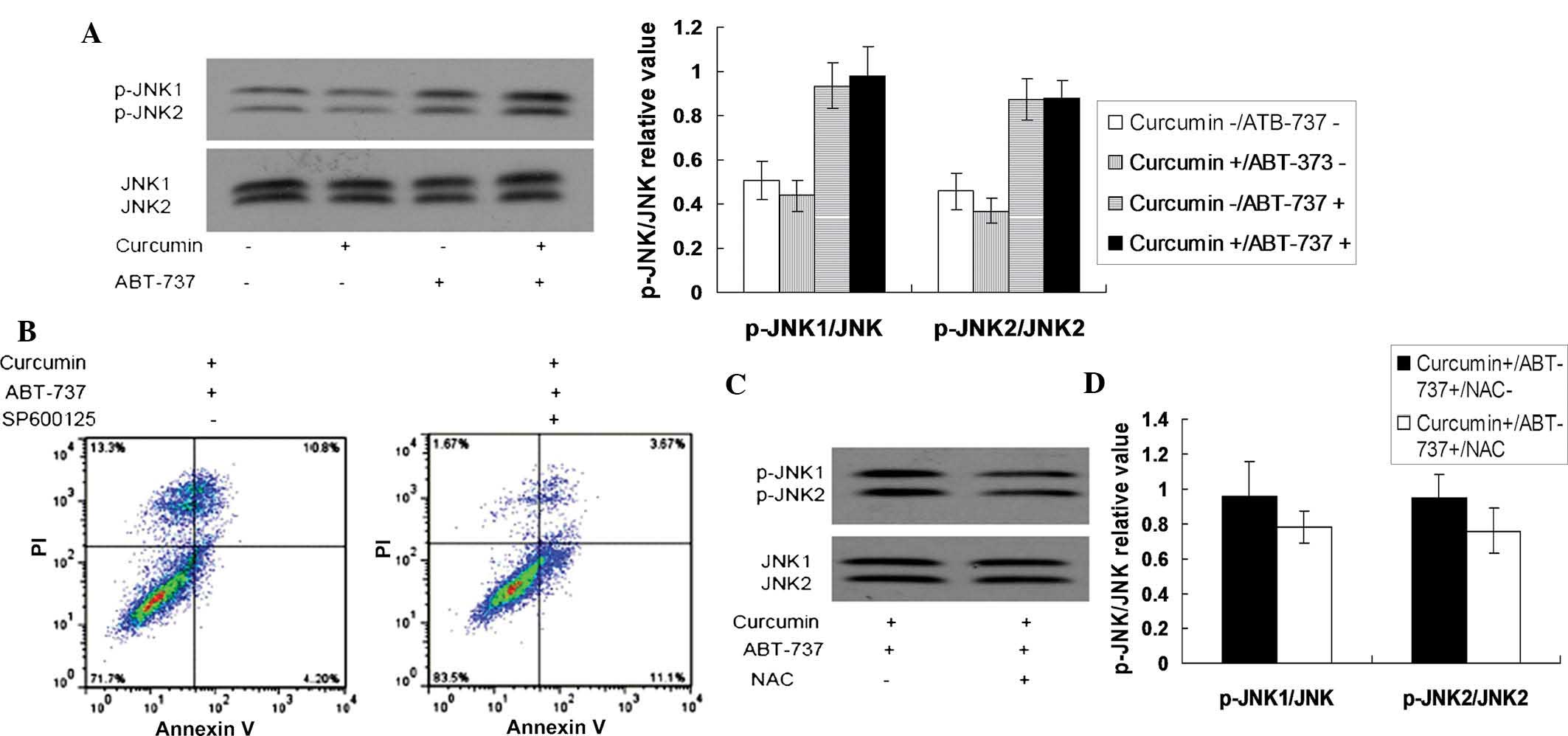
|
1
|
El-Serag HB and Rudolph KL: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: Epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 132:2557–2576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Llovet JM: Updated treatment approach to
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol. 40:225–235. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Peck-Radosavljevic M: Drug therapy for
advanced-stage liver cancer. Liver Cancer. 3:125–131. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Levine B, Sinha S and Kroemer G: Bcl-2
family members: Dual regulators of apoptosis and autophagy.
Autophagy. 4:600–606. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Czabotar PE, Lessene G, Strasser A and
Adams JM: Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family:
Implications for physiology and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
15:49–63. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Su J, Zhou L, Xia MH, Xu Y, Xiang XY and
Sun LK: Bcl-2 family proteins are involved in the signal crosstalk
between endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial dysfunction
in tumor chemotherapy resistance. Biomed Res Int. 2014:2343702014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Guo XZ, Shao XD, Liu MP, Xu JH, Ren LN,
Zhao JJ, Li HY and Wang D: Effect of bax, bcl-2 and bcl-xL on
regulating apoptosis in tissues of normal liver and hepatocellular
carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 8:1059–1062. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chun E and Lee KY: Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL are
important for the induction of paclitaxel resistance in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
315:771–779. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schattenberg JM, Schuchmann M and Galle
PR: Cell death and hepatocarcinogenesis: Dysregulation of apoptosis
signaling pathways. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26(Suppl 1): 213–219.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Balakrishnan K and Gandhi V: Bcl-2
antagonists: A proof of concept for CLL therapy. Invest New Drugs.
31:1384–1394. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Billard C: BH3 mimetics: Status of the
field and new developments. Mol Cancer Ther. 12:1691–1700. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yu L and Liu S: Autophagy contributes to
modulating the cytotoxicities of Bcl-2 homology domain-3 mimetics.
Semin Cancer Biol. 23:553–560. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hikita H, Takehara T, Shimizu S, Kodama T,
Shigekawa M, Iwase K, Hosui A, Miyagi T, Tatsumi T and Ishida H:
The Bcl-xL inhibitor, ABT-737, efficiently induces apoptosis and
suppresses growth of hepatoma cells in combination with sorafenib.
Hepatology. 52:1310–1321. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang G, Zhan Y, Wang H and Li W: ABT-263
sensitizes TRAIL-resistant hepatocarcinoma cells by downregulating
the Bcl-2 family of anti-apoptotic protein. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 69:799–805. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang S, Li G, Ma X, Wang Y, Liu G, Feng
L, Zhao Y, Zhang G, Wu Y and Ye X: Norcantharidin enhances
ABT-737-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by
transcriptional repression of Mcl-1. Cell Signal. 24:1803–1809.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ni Z, Wang B, Dai X, Ding W, Yang T, Li X,
Lewin S, Xu L, Lian J and He F: HCC cells with high levels of Bcl-2
are resistant to ABT-737 via activation of the ROS-JNK-autophagy
pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 70:194–203. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang B, Ni Z, Dai X, Qin L, Li X, Xu L,
Lian J and He F: The Bcl-2/xL inhibitor ABT-263 increases the
stability of Mcl-1 mRNA and protein in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Mol Cancer. 13:982014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shehzad A, Lee J and Lee YS: Curcumin in
various cancers. Biofactors. 39:56–68. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Witkin JM and Li X: Curcumin, an active
constiuent of the ancient medicinal herb Curcuma longa L: Some uses
and the establishment and biological basis of medical efficacy. CNS
Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 12:487–497. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li Y and Zhang T: Targeting cancer stem
cells by curcumin and clinical applications. Cancer Lett.
346:197–205. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Prasad S, Gupta SC, Tyagi AK and Aggarwal
BB: Curcumin, a component of golden spice: From bedside to bench
and back. Biotechnol Adv. 32:1053–1064. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chuang SE, Kuo ML, Hsu CH, Chen CR, Lin
JK, Lai GM, Hsieh CY and Cheng AL: Curcumin-containing diet
inhibits diethylnitrosamine-induced murine hepatocarcinogenesis.
Carcinogenesis. 21:331–335. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu H, Liang Y, Wang L, Tian L, Song R,
Han T, Pan S and Liu L: In vivo and in vitro suppression of
hepatocellular carcinoma by EF24, a curcumin analog. PLoS One.
7:e480752012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xu MX, Zhao L, Deng C, Yang L, Wang Y, Guo
T, Li L, Lin J and Zhang L: Curcumin suppresses proliferation and
induces apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the
wnt signaling pathway. Int J Oncol. 43:1951–1959. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang K, Rui X and Yan X: Curcumin
inhibits the proliferation and invasiveness of MHCC97-H cells via
p38 signaling pathway. Drug Dev Res. 75:463–468. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yin H, Guo R, Xu Y, Zheng Y, Hou Z, Dai X,
Zhang Z, Zheng D and Xu H: Synergistic antitumor efficiency of
docetaxel and curcumin against lung cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys
Sin (Shanghai). 44:147–153. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Boztas AO, Karakuzu O, Galante G, Ugur Z,
Kocabas F, Altuntas CZ and Yazaydin AO: Synergistic interaction of
paclitaxel and curcumin with cyclodextrin polymer complexation in
human cancer cells. Mol Pharm. 10:2676–2683. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Debata PR, Begum S, Mata A, Genzer O,
Kleiner MJ, Banerjee P and Castellanos MR: Curcumin potentiates the
ability of sunitinib to eliminate the VHL-lacking renal cancer
cells 786-O: Rapid inhibition of Rb phosphorylation as a preamble
to cyclin D1 inhibition. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 13:1508–1513.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Guo J, Li W, Shi H, Xie X, Li L, Tang H,
Wu M, Kong Y, Yang L and Gao J: Synergistic effects of curcumin
with emodin against the proliferation and invasion of breast cancer
cells through upregulation of miR-34a. Mol Cell Biochem.
382:103–111. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Meiyanto E, Putri DD, Susidarti RA,
Murwanti R, Sardjiman, Fitriasari A, Husnaa U, Purnomo H and
Kawaichi M: Curcumin and its analogues (PGV-0 and PGV-1) enhance
sensitivity of resistant MCF-7 cells to doxorubicin through
inhibition of HER2 and NF-kB activation. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:179–184. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ranjan K, Sharma A, Surolia A and Pathak
C: Regulation of HA14-1 mediated oxidative stress, toxic response
and autophagy by curcumin to enhance apoptotic activity in human
embryonic kidney cells. Biofactors. 40:157–169. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhou QM, Chen QL, Du J, Wang XF, Lu YY,
Zhang H and Su SB: Synergistic effect of combinatorial treatment
with curcumin and mitomycin C on the induction of apoptosis of
breast cancer cells: A cDNA microarray analysis. Int J Mol Sci.
15:16284–16301. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Konopleva M, Contractor R, Tsao T, Samudio
I, Ruvolo PP, Kitada S, Deng X, Zhai D, Shi YX, Sneed T, et al:
Mechanisms of apoptosis sensitivity and resistance to the BH3
mimetic ABT-737 in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell. 10:375–388.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kline MP, Rajkumar SV, Timm MM, Kimlinger
TK, Haug JL, Lust JA, Greipp PR and Kumar S: ABT-737, an inhibitor
of Bcl-2 family proteins, is a potent inducer of apoptosis in
multiple myeloma cells. Leukemia. 21:1549–1560. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Biswas N, Mahato SK, Chowdhury AA,
Chaudhuri J, Manna A, Vinayagam J, Chatterjee S, Jaisankar P,
Chaudhuri U and Bandyopadhyay S: ICB3E induces iNOS expression by
ROS-dependent JNK and ERK activation for apoptosis of leukemic
cells. Apoptosis. 17:612–626. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shi Y, Nikulenkov F, Zawacka-Pankau J, Li
H, Gabdoulline R, Xu J, Eriksson S, Hedström E, Issaeva N, Kel A,
et al: ROS-dependent activation of JNK converts p53 into an
efficient inhibitor of oncogenes leading to robust apoptosis. Cell
Death Differ. 21:612–623. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kalinski T and Roessner A: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: Pathology and liver biopsy. Dig Dis. 27:102–108. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Effendi K and Sakamoto M: Molecular
pathology in early hepatocarcinogenesis. Oncology. 78:157–160.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ibrahim N, Yu Y, Walsh WR and Yang JL:
Molecular targeted therapies for cancer: Sorafenib mono-therapy and
its combination with other therapies (review). Oncol Rep.
27:1303–1311. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lachenmayer A, Toffanin S, Cabellos L,
Alsinet C, Hoshida Y, Villanueva A, Minguez B, Tsai HW, Ward SC,
Thung S, et al: Combination therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma:
Additive preclinical efficacy of the HDAC inhibitor panobinostat
with sorafenib. J Hepatol. 56:1343–1350. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
He S, Wei YZ, Wang GL, Xu YY, Zhou JM,
Zhang YX and Chen L: Study of RNA interference targeting NET-1
combination with sorafenib for hepatocellular carcinoma therapy in
vitro and in vivo. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2013:6851502013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Geng J, Li X, Lang X, Qiao C, Hu M, Yang
J, Feng J and Lv M: Combination of cetuximab and rapamycin enhances
the therapeutic efficacy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Technol
Cancer Res Treat. 13:377–385. 2014.
|
|
43
|
Nasr M, Selima E, Hamed O and Kazem A:
Targeting different angiogenic pathways with combination of
curcumin, leflunomide and perindopril inhibits
diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. Eur J
Pharmacol. 723:267–275. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Wang F, Dai W, Wang Y, Shen M, Chen K,
Cheng P, Zhang Y, Wang C, Li J, Zheng Y, et al: The synergistic in
vitro and in vivo antitumor effect of combination therapy with
salinomycin and 5-fluorouracil against hepatocellular carcinoma.
PLoS One. 9:e974142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Darvesh AS, Aggarwal BB and Bishayee A:
Curcumin and liver cancer: A review. Curr Pharm Biotechnol.
13:218–228. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Wang WH, Chiang IT, Ding K, Chung JG, Lin
WJ, Lin SS and Hwang JJ: Curcumin-induced apoptosis in human
hepatocellular carcinoma j5 cells: Critical role of
Ca(+2)-dependent pathway Evid Based Complement. Alternat Med.
2012:5129072012.
|
|
47
|
Navarro-Yepes J, Burns M, Anandhan A,
Khalimonchuk O, del Razo LM, Quintanilla-Vega B, Pappa A,
Panayiotidis MI and Franco R: Oxidative stress, redox signaling and
autophagy: Cell death versus survival. Antioxid Redox Signal.
21:66–85. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sehgal V and Ram PT: Network motifs in JNK
signaling. Genes Cancer. 4:409–413. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Deng YT, Huang HC and Lin JK: Rotenone
induces apoptosis in MCF-7 human breast cancer cell-mediated ROS
through JNK and p38 signaling. Mol Carcinog. 49:141–151. 2010.
|
|
50
|
Bubici C and Papa S: JNK signalling in
cancer: In need of new, smarter therapeutic targets. Br J
Pharmacol. 171:24–37. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
51
|
Seki E, Brenner DA and Karin M: A liver
full of JNK: Signaling in regulation of cell function and disease
pathogenesis and clinical approaches. Gastroenterology.
143:307–320. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yan F, Wang XM, Liu ZC, Pan C, Yuan SB and
Ma QM: JNK1, JNK2 and JNK3 are involved in P-glycoprotein-mediated
multidrug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 9:287–295. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hayakawa R, Hayakawa T, Takeda K and
Ichijo H: Therapeutic targets in the ASK1-dependent stress
signaling pathways. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 88:434–453.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|