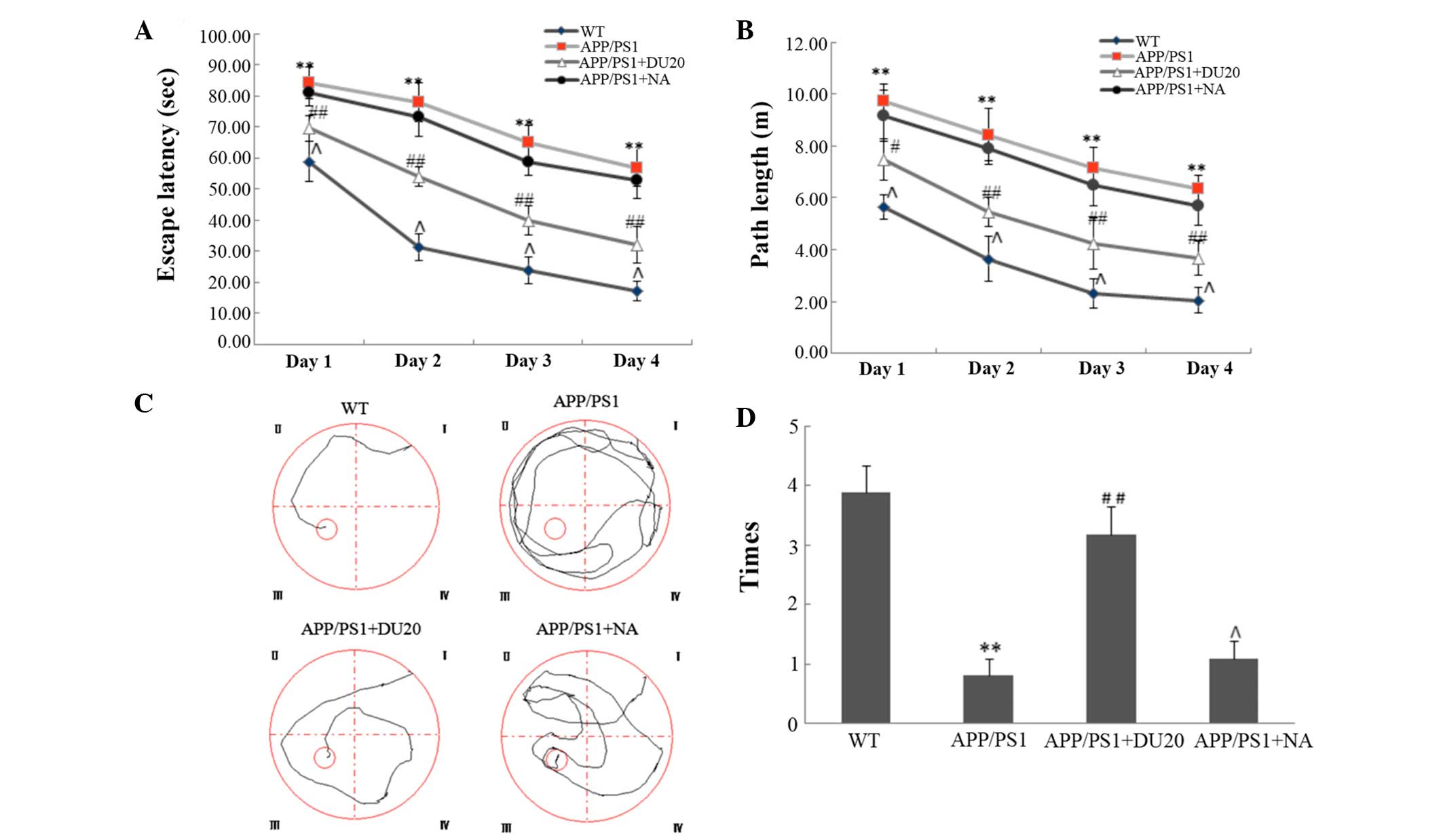
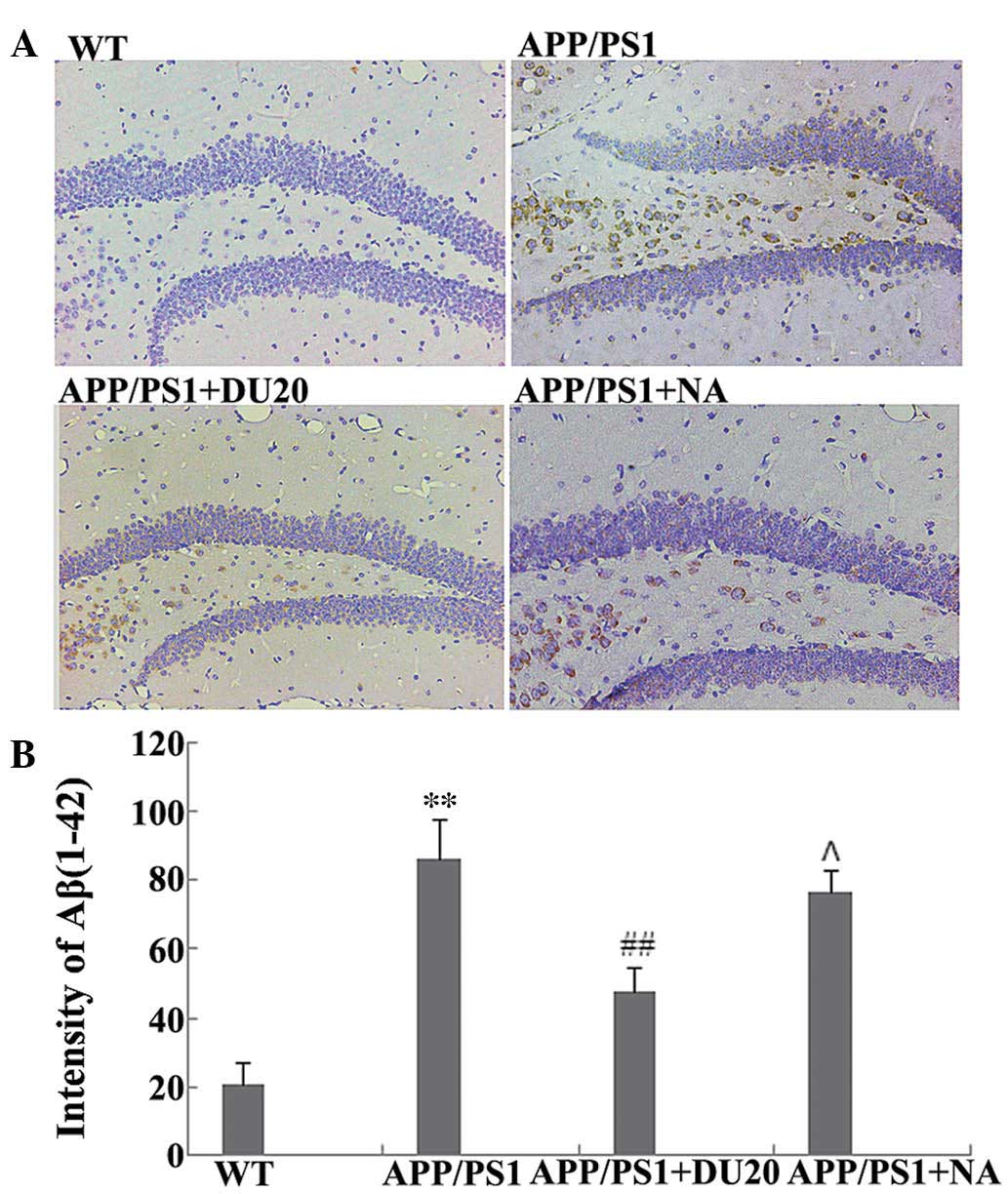
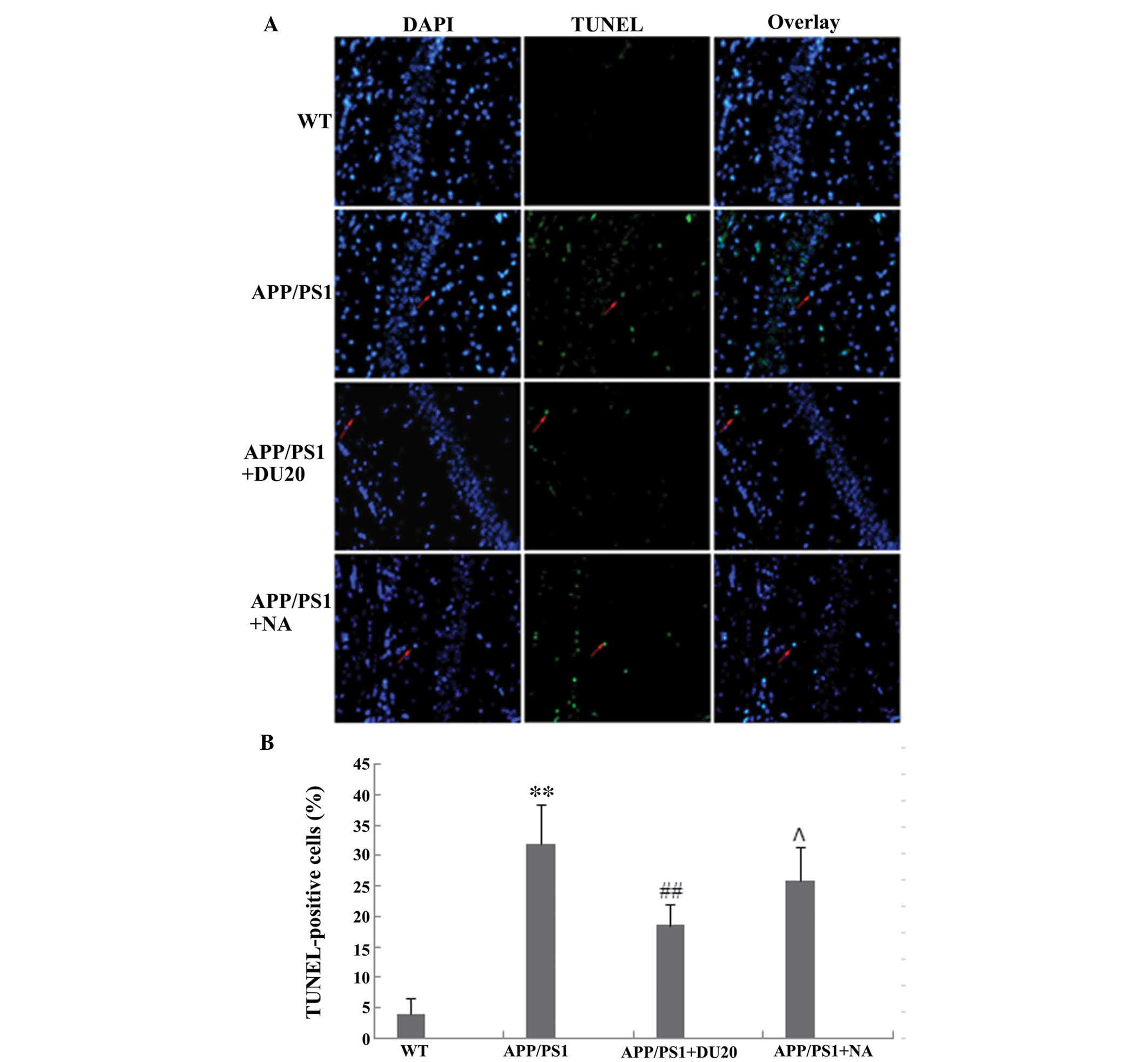
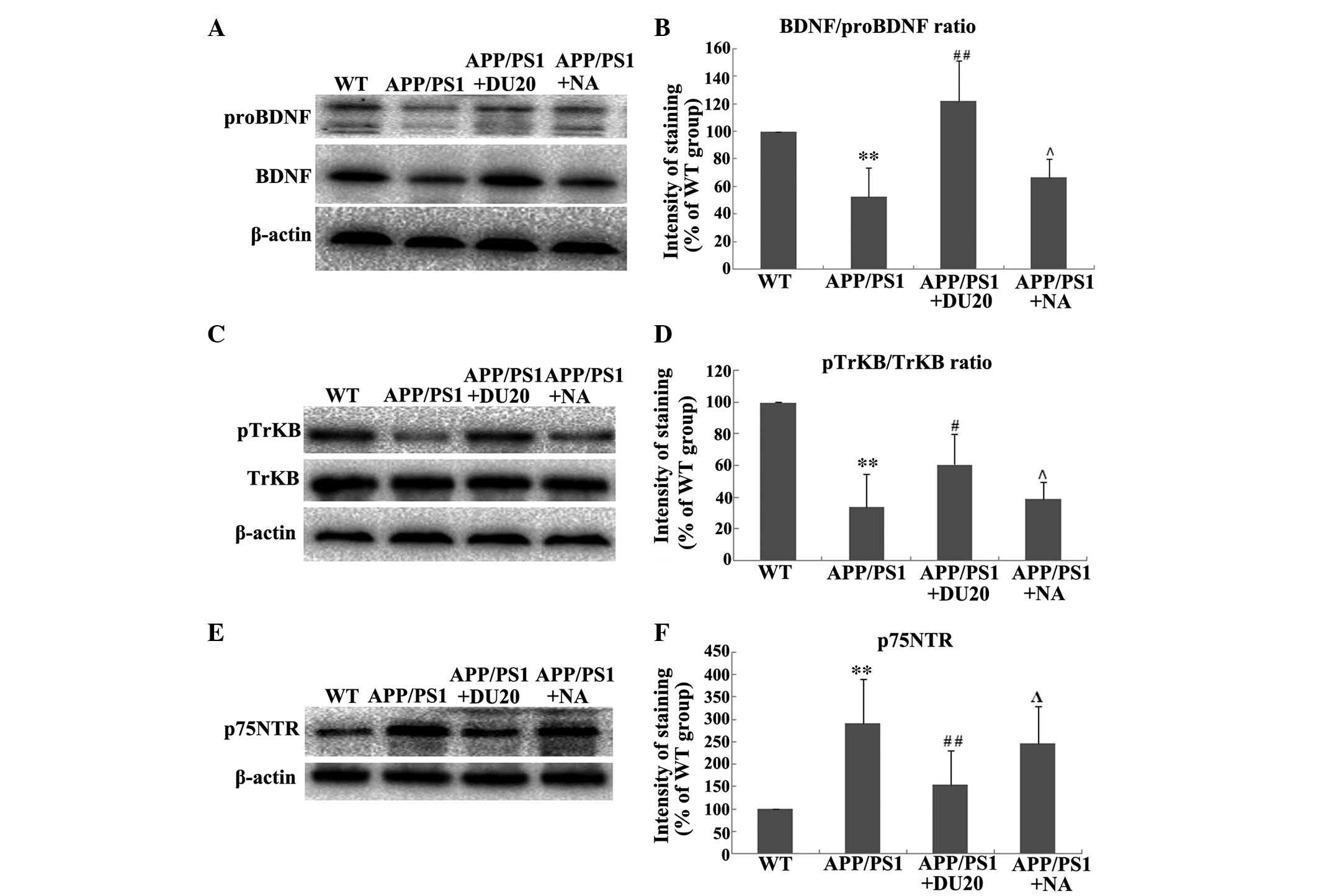
|
1
|
Mayeux R: Clinical practice. Early
Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 362:2194–2201. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Querfurth HW and LaFerla FM: Alzheimer's
disease. N Engl J Med. 362:329–344. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Serrano-Pozo A, Frosch MP, Masliah E and
Hyman BT: Neuropathological alterations in Alzheimer disease. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Med. 1:a0061892011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Phillips HS, Hains JM, Armanini M, Laramee
GR, Johnson SA and Winslow JW: BDNF mRNA is decreased in the
hippocampus of individuals with Alzheimer's disease. Neuron.
7:695–702. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee J, Fukumoto H, Orne J, Klucken J, Raju
S, Vanderburg CR, Irizarry MC, Hyman BT and Ingelsson M: Decreased
levels of BDNF protein in Alzheimer temporal cortex are independent
of BDNF polymorphisms. Exp Neurol. 194:91–96. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Peng S, Wuu J, Mufson EJ and Fahnestock M:
Precursor form of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and mature
brain-derived neurotrophic factor are decreased in the pre-clinical
stages of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 93:1412–1421. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Weinstein G, Beiser AS, Choi SH, Preis SR,
Chen TC, Vorgas D, Au R, Pikula A, Wolf PA, DeStefano AL, et al:
Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor and the risk for dementia:
The Framingham Heart Study. JAMA Neurol. 71:55–61. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Barker PA: Whither proBDNF? Nat Neurosci.
12:105–106. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Greenberg ME, Xu B, Lu B and Hempstead BL:
New insights in the biology of BDNF synthesis and release:
Implications in CNS function. J Neurosci. 29:12764–12767. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang J, Harte-Hargrove LC, Siao CJ,
Marinic T, Clarke R, Ma Q, Jing D, Lafrancois JJ, Bath KG, Mark W,
et al: proBDNF negatively regulates neuronal remodeling, synaptic
transmission, and synaptic plasticity in hippocampus. Cell Reports.
7:796–806. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Minichiello L: TrkB signalling pathways in
LTP and learning. Nat Rev Neurosci. 10:850–860. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Arancibia S, Silhol M, Moulière F, Meffre
J, Höllinger I, Maurice T and Tapia-Arancibia L: Protective effect
of BDNF against beta-amyloid induced neurotoxicity in vitro and in
vivo in rats. Neurobiol Dis. 31:316–326. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kemppainen S, Rantamäki T, Jerónimo-Santos
A, Lavasseur G, Autio H, Karpova N, Kärkkäinen E, Stavén S, Vicente
Miranda H, Outeiro TF, et al: Impaired TrkB receptor signaling
contributes to memory impairment in APP/PS1 mice. Neurobiol Aging.
33:2012.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu ZQ, Li J, Deng J, Jiang XJ and Zhou HD:
Effects of proBDNF on cell proliferation and differentiation in
hippocampal dentate gyrus in Alzheimer's disease rat model. Chin
Med J. 90:1353–1356. 2010.In Chinese.
|
|
15
|
Feng X, Yang S, Liu J, Huang J, Peng J,
Lin J, Tao J and Chen L: Electroacupuncture ameliorates cognitive
impairment through inhibition of NF-κB-mediated neuronal cell
apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injured rats. Mol Med
Rep. 7:1516–1522. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
International Ethical Guidelines for
Biomedical Research Involving Human Subjects. WHO/CIOMS; Geneva:
1993
|
|
17
|
Vorhees CV and Williams MT: Morris water
maze: Procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of
learning and memory. Nat Protoc. 1:848–858. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Selkoe DJ: Alzheimer's disease is a
synaptic failure. Science. 298:789–791. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Haas HL, Sergeeva OA and Selbach O:
Histamine in the nervous system. Physiol Rev. 88:1183–1241. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Brioni JD, Esbenshade TA, Garrison TR,
Bitner SR and Cowart MD: Discovery of histamine H3 antagonists for
the treatment of cognitive disorders and Alzheimer's disease. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 336:38–46. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ballard C, Gauthier S, Corbett A, Brayne
C, Aarsland D and Jones E: Alzheimer's disease. Lancet.
377:1019–1031. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Radde R, Bolmont T, Kaeser SA,
Coomaraswamy J, Lindau D, Stoltze L, Calhoun ME, Jäggi F, Wolburg
H, Gengler S, et al: Abeta42-driven cerebral amyloidosis in
transgenic mice reveals early and robust pathology. EMBO Rep.
7:940–946. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Borchelt DR, Ratovitski T, van Lare J, Lee
MK, Gonzales V, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Price DL and Sisodia SS:
Accelerated amyloid deposition in the brains of transgenic mice
coexpressing mutant presenilin 1 and amyloid precursor proteins.
Neuron. 19:939–945. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bilkei-Gorzo A: Genetic mouse models of
brain ageing and Alzheimer's disease. Pharmacol Ther. 142:244–257.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Binder DK and Scharfman HE: Brain-derived
neurotrophic factor. Growth Factors. 22:123–131. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cosker KE, Courchesne SL and Segal RA:
Action in the axon: generation and transport of signaling
endosomes. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 18:270–275. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schindowski K, Belarbi K and Buée L:
Neurotrophic factors in Alzheimer's disease: role of axonal
transport. Genes, Brain Behav. 7(suppl 1): 43–56. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Tapia-Arancibia L, Aliaga E, Silhol M and
Arancibia S: New insights into brain BDNF function in normal aging
and Alzheimer disease. Brain Res Rev. 59:201–220. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Castello NA, Nguyen MH, Tran JD, Cheng D,
Green KN and LaFerla FM: 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone, a small molecule
TrkB agonist, improves spatial memory and increases thin spine
density in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease-like neuronal loss.
PLoS One. 9:e914532014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lu B, Pang PT and Woo NH: The yin and yang
of neurotrophin action. Nat Rev Neurosci. 6:603–614. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Woo NH, Teng HK, Siao CJ, Chiaruttini C,
Pang PT, Milner TA, Hempstead BL and Lu B: Activation of p75NTR by
proBDNF facilitates hippocampal long-term depression. Nat Neurosci.
8:1069–1077. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Teng HK, Teng KK, Lee R, Wright S, Tevar
S, Almeida RD, Kermani P, Torkin R, Chen ZY, Lee FS, et al: ProBDNF
induces neuronal apoptosis via activation of a receptor complex of
p75NTR and sortilin. J Neurosci. 25:5455–5463. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|