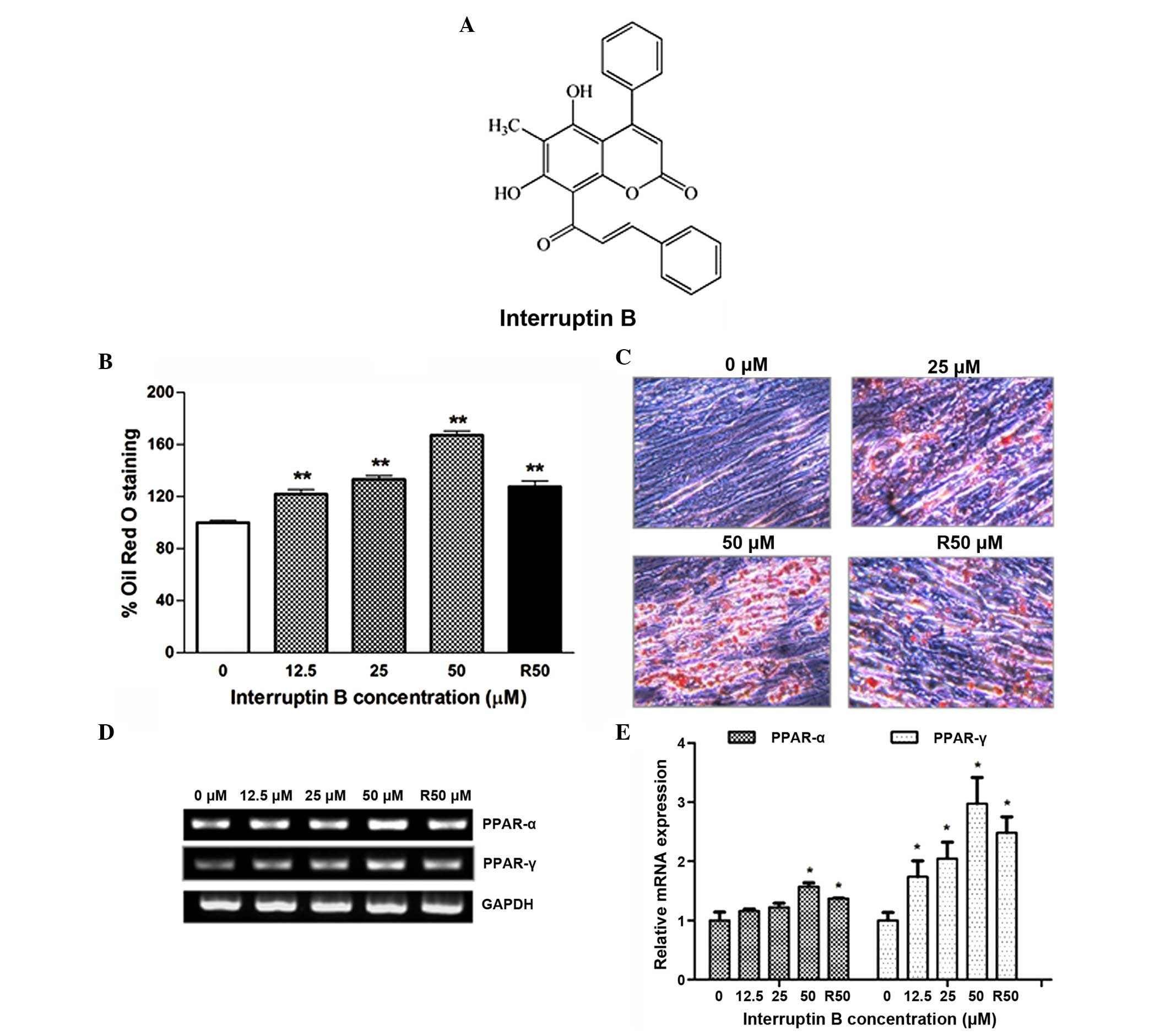
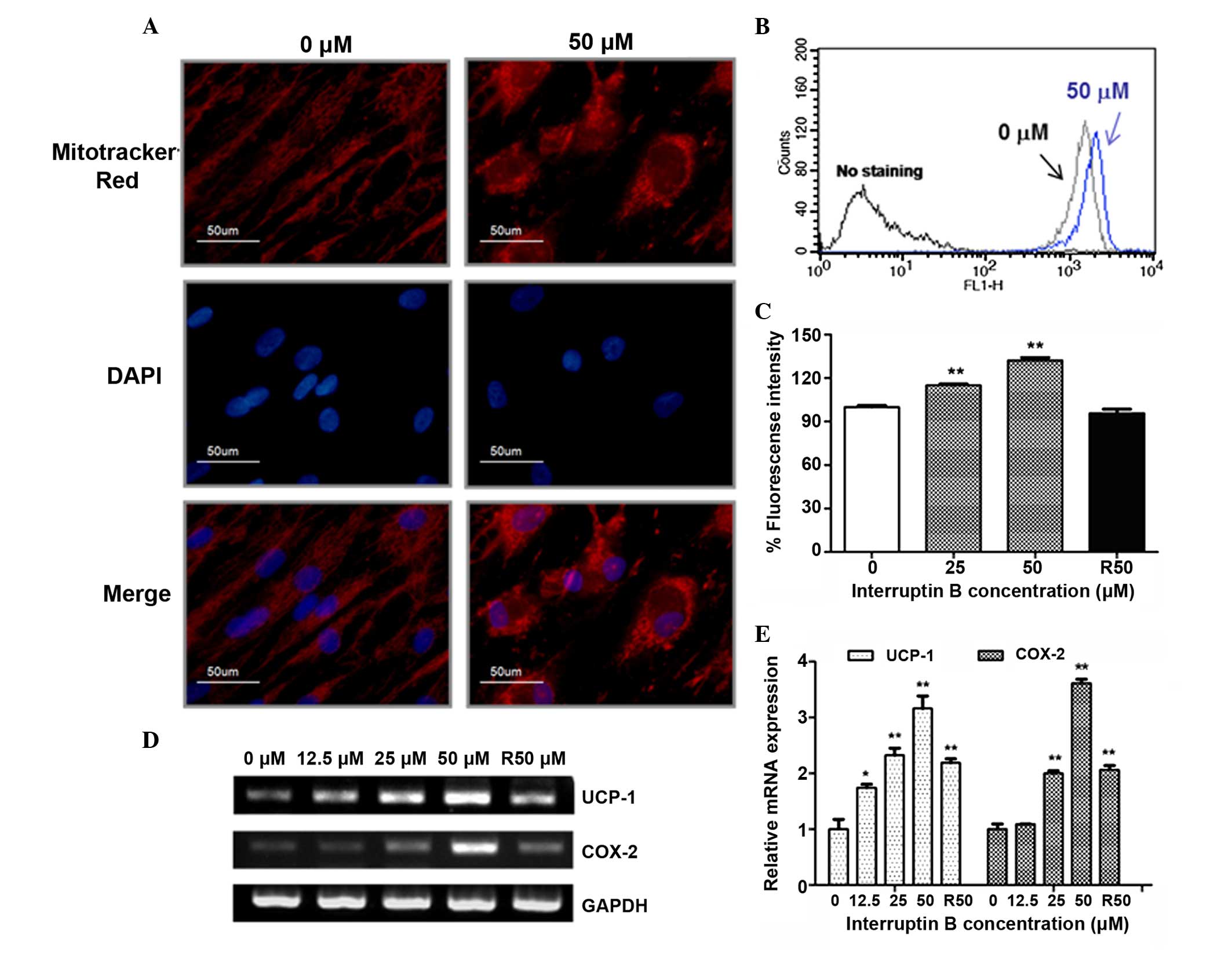
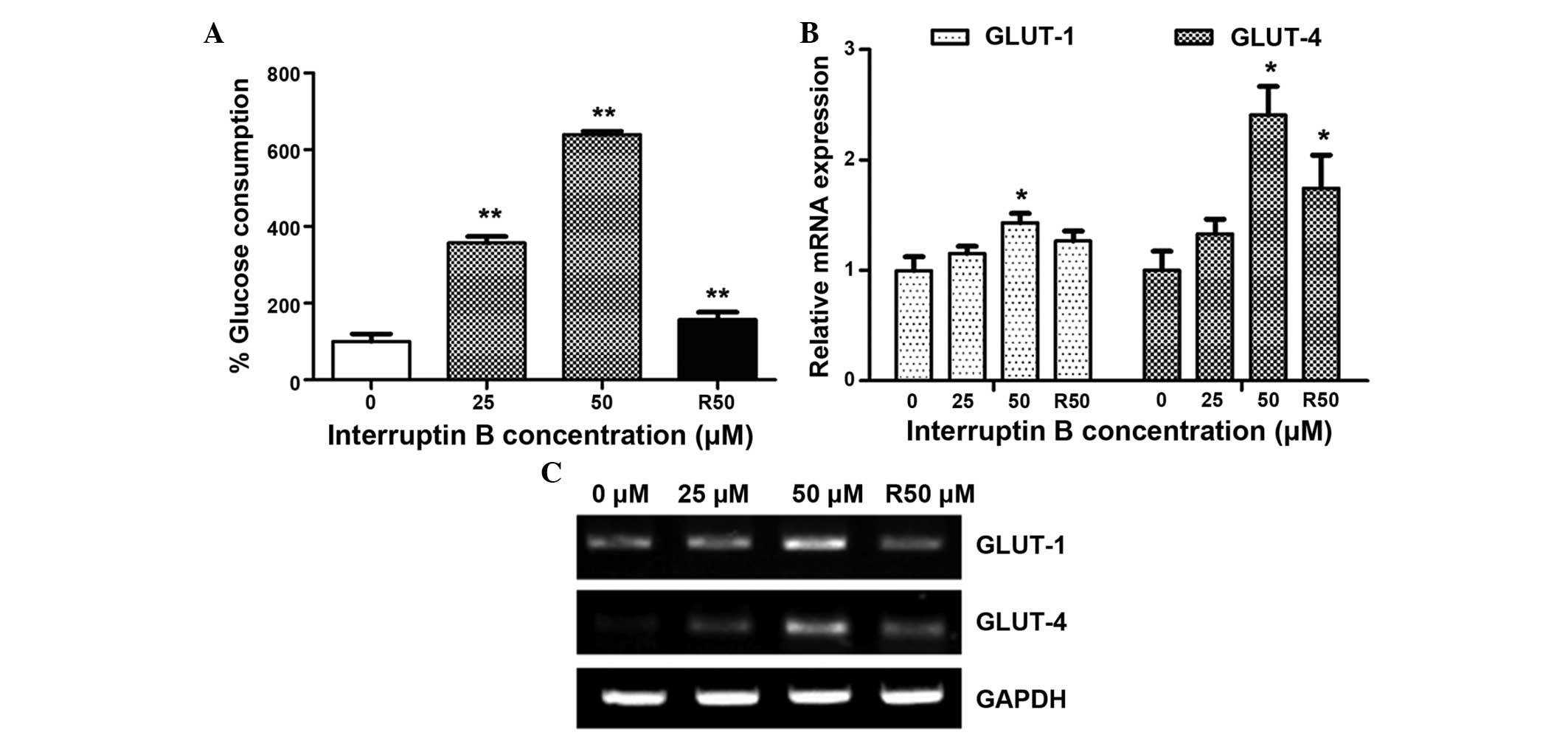
|
1
|
Hauptman J, Lucas C, Boldrin MN, Collins H
and Segal KR: Orlistat in the long-term treatment of obesity in
primary care settings. Arch Fam Med. 9:160–167. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Haslam DW and James WP: Obesity. Lancet.
366:1197–1209. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Halford JC: Pharmacotherapy for obesity.
Appetite. 46:6–10. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Filippatos TD, Derdemezis CS, Gazi IF,
Nakou ES, Mikhailidis DP and Elisaf MS: Orlistat-associated adverse
effects and drug interactions: A critical review. Drug Saf.
31:53–65. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yao X, Shan S, Zhang Y and Ying H: Recent
progress in the study of brown adipose tissue. Cell Biosci.
1(35)2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Amos AF, McCarty DJ and Zimmet P: The
rising global burden of diabetes and its complications: Estimates
and projections to the year 2010. Diabet Med. 14(Suppl 5): S1–S85.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Takada I and Makishima M: PPARγ ligands
and their therapeutic applications: a patent review (2008 – 2014).
Expert Opin Ther Pat. 25:175–191. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Nathan DM: Diabetes: Advances in diagnosis
and treatment. JAMA. 314:1052–1062. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fujimura T, Kimura C, Oe T, Takata Y,
Sakuma H, Aramori I and Mutoh S: A selective peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma modulator with distinct fat
cell regulation properties. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 318:863–871.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Teboul L, Gaillard D, Staccini L, Inadera
H, Amri EZ and Grimaldi PA: Thiazolidinediones and fatty acids
convert myogenic cells into adipose-like cells. J Biol Chem.
270:28183–28187. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Patel C, Wyne KL and McGuire DK:
Thiazolidinediones, peripheral oedema and congestive cardiac
failure: What is the evidence? Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2:61–66. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Semple RK, Chatterjee VK and O'Rahilly S:
PPAR gamma and human metabolic disease. J Clin Invest. 116:581–586.
2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Diamond GA, Bax L and Kaul S: Uncertain
effects of rosiglitazone on the risk for myocardial infarction and
cardiovascular dealth. Ann Intern Med. 147:578–581. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Medina-Gómez G: Mitochondria and endocrine
function of adipose tissue. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab.
26:791–804. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kumboonruang N: Fern diversity at Silaphet
waterfall, Pua district, Nan province. (unpublished Master's
Project, M.Ed.). Graduate School, Srinakharinwirot University;
Bangkok, Thailand: 2009
|
|
16
|
Kaewsuwan S, Yuenyongsawad S, Plubr ukarn
A, Kaewchoothong A, Raksawong A, Puttarak P and Apirug C:
Biological activities of interruptins A and B from Cyclosorus
terminans. Songklanakarin J Sci Technol. In press.
|
|
17
|
Kim WS, Park BS, Park SH, Kim HK and Sung
JH: Antiwrinkle effect of adipose-derived stem cell: Activation of
dermal fibroblast by secretory factors. J Dermatol Sci. 53:96–102.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sherman W, Day T, Jacobson MP, Friesner RA
and Farid R: Novel procedure for modeling ligand/receptor induced
fit effects. J Med Chem. 49:534–553. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kumari V and Li C: Comparative docking
assessment of glucokinase interactions with its allosteric
activators. Curr Chem Genomics. 2:76–89. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner MF,
Belew RK, Goodsell DS and Olson AJ: AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4:
Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput
Chem. 30:2785–2791. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cannon B and Nedergaard J: Brown adipose
tissue: Function and physiological significance. Physiol Rev.
84:277–359. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rehman J: Empowering self-renewal and
differentiation: The role of mitochondria in stem cells. J Mol Med
(Berl). 88:981–986. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Gallicchio E, Lapelosa M and Levy RM: The
binding energy distribution analysis method (BEDAM) for the
estimation of protein-ligand binding affinities. J Chem Theory
Comput. 6:2961–2977. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cho KW, Lee OH, Banz WJ, Moustaid-Moussa
N, Shay NF and Kim YC: Daidzein and the daidzein metabolite, equol,
enhance adipocyte differentiation and PPARgamma transcriptional
activity. J Nutr Biochem. 21:841–847. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Choi SS, Cha BY, Lee YS, Yonezawa T,
Teruya T, Nagai K and Woo JT: Magnolol enhances adipocyte
differentiation and glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 cells. Life Sci.
84:908–914. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Choi SS, Cha BY, Iida K, Lee YS, Yonezawa
T, Teruya T, Nagai K and Woo JT: Artepillin C, as a PPARγ ligand,
enhances adipocyte differentiation and glucose uptake in 3T3-L1
cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 81:925–933. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nissen SE and Wolski K: Rosiglitazone
revisted: An updated meta-analysis of risk for myocardial
infarction and cardiovascular mortality. Arch Intern Med.
170:1191–1201. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Henry RR, Lincoff AM, Mudaliar S, Rabbia
M, Chognot C and Herz M: Effect of the dual peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-alpha/gamma agonist aleglitazar on
risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes
(SYNCHRONY): A phase II, randomised, dose-ranging study. Lancet.
374:126–135. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|