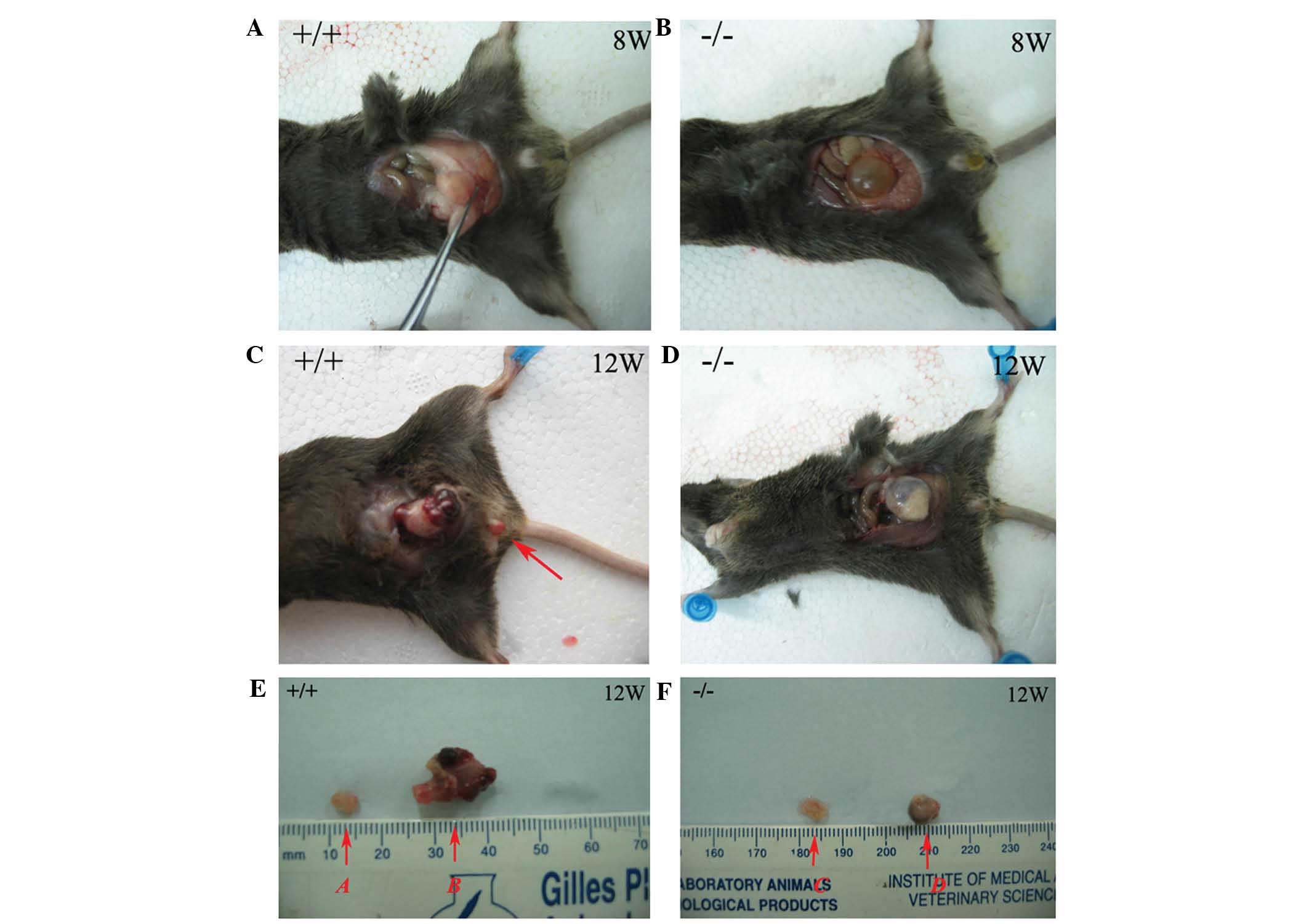
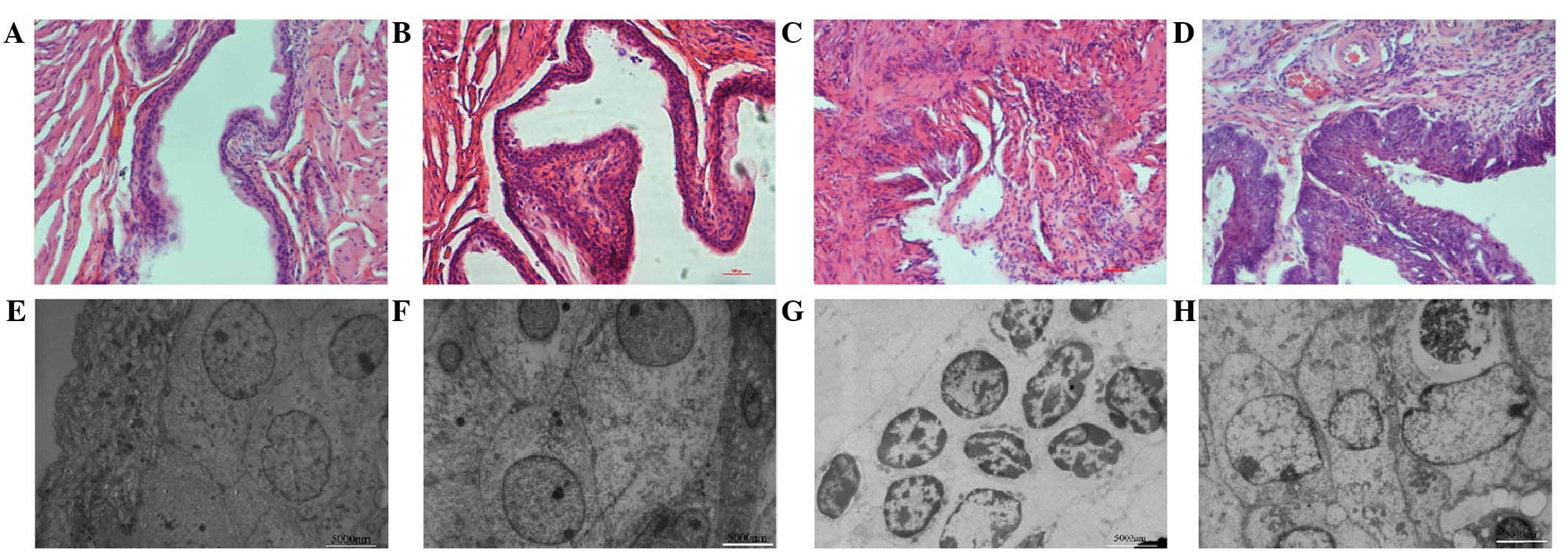
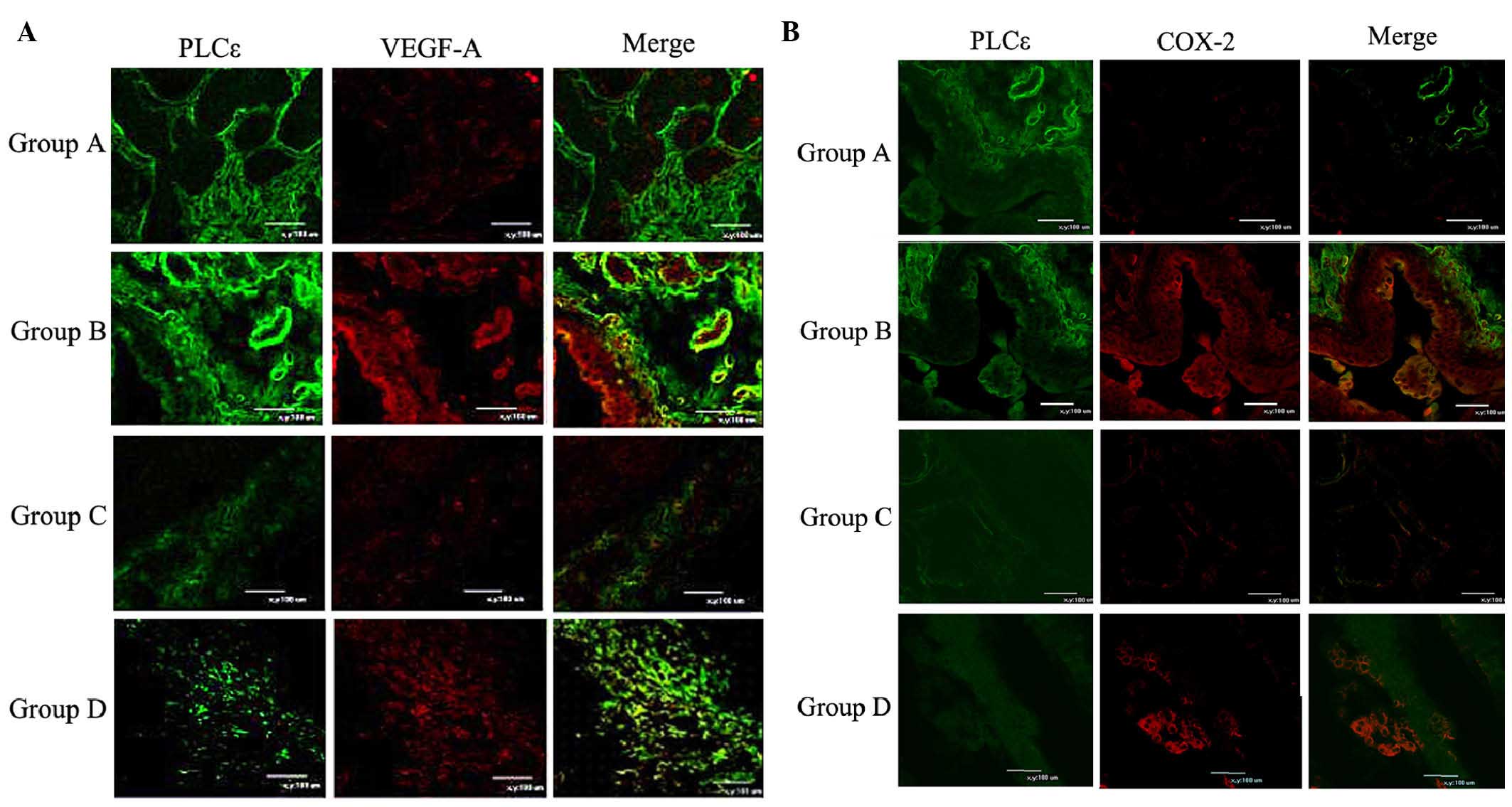
|
1
|
Beland FA, Beranek DT, Dooley KL, Heflich
RH and Kadlubar FF: Arylamine-DNA adducts in vitro and in vivo:
Their role in bacterial mutagenesis and urinary bladder
carcinogenesis. Environ Health Perspect. 49:125–134. 1983.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Akaza H, Murphy WM and Soloway MS: Bladder
cancer induced by noncarcinogenic substances. J Urol. 131:152–155.
1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cohen SM: Role of urinary physiology and
chemistry in bladder carcinogenesis. Food Chem Toxicol. 33:715–730.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Katan M: New insights into the families of
PLC enzymes: Looking back and going forward. Biochem J. 391:e7–e9.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kelley GG, Reks SE, Ondrako JM and Smrcka
AV: Phospholipase C(epsilon): A novel Ras effector. EMBO J.
20:743–754. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mitin N, Rossman KL and Der CJ: Signaling
interplay in Ras superfamily function. Curr Biol. 15:R563–R574.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lopez I, Mak EC, Ding J, Hamm HE and
Lomasney JW: A novel bifunctional phospholipase c that is regulated
by Galpha 12 and stimulates the Ras/mitogen-activated protein
kinase pathway. J Biol Chem. 276:2758–2765. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Song C, Hu CD, Masago M, Kariyai K,
Yamawaki-Kataoka Y, Shibatohge M, Wu D, Satoh T and Kataoka T:
Regulation of a novel human phospholipase C, PLCepsilon, through
membrane targeting by Ras. J Biol Chem. 276:2752–2757. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Bunney TD and Katan M: Phospholipase C
epsilon: Linking second messengers and small GTPases. Trends Cell
Biol. 16:640–648. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Smrcka AV, Brown JH and Holz GG: Role of
phospholipase Cε in physiological phosphoinositide signaling
networks. Cell Signal. 24:1333–1343. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Edamatsu H, Satoh T and Kataoka T: Ras and
Rap1 activation of PLCepsilon lipase activity. Methods Enzymol.
407:99–107. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kelley GG, Kaproth-Joslin KA, Reks SE,
Smrcka AV and Wojcikiewicz RJ: G-protein-coupled receptor agonists
activate endogenous phospholipase Cepsilon and phospholipase Cbeta3
in a temporally distinct manner. J Biol Chem. 281:2639–2648. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Satoh T, Edamatsu H and Kataoka T:
Phospholipase Cepsilon guanine nucleotide exchange factor activity
and activation of Rap1. Methods Enzymol. 407:281–290. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tadano M, Edamatsu H, Minamisawa S,
Yokoyama U, Ishikawa Y, Suzuki N, Saito H, Wu D, Masago-Toda M,
Yamawaki-Kataoka Y, et al: Congenital semilunar valvulogenesis
defect in mice deficient in phospholipase C epsilon. Mol Cell Biol.
25:2191–2199. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang H, Oestreich EA, Maekawa N, Bullard
TA, Vikstrom KL, Dirksen RT, Kelley GG, Blaxall BC and Smrcka AV:
Phospholipase C epsilon modulates beta-adrenergic
receptor-dependent cardiac contraction and inhibits cardiac
hypertrophy. Circ Res. 97:1305–1313. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kariya K, Bui YK, Gao X, Sternberg PW and
Kataoka T: Phospholipase Cepsilon regulates ovulation in
Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Biol. 274:201–210. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bai Y, Edamatsu H, Maeda S, Saito H,
Suzuki N, Satoh T and Kataoka T: Crucial role of phospholipase
Cepsilon in chemical carcinogen-induced skin tumor development.
Cancer Res. 64:8808–8810. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fujita J, Ohuchi N, Ito N, Reynolds SH,
Yoshida O, Nakayama H and Kitamura Y: Activation of H-ras oncogene
in rat bladder tumors induced by
N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl)nitro-samine. J Natl Cancer Inst.
80:37–43. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Vecchione A, Sevignani C, Giarnieri E,
Zanesi N, Ishii H, Cesari R, Fong LY, Gomella LG, Croce CM and
Baffa R: Inactivation of the FHIT gene favors bladder cancer
development. Clin Cancer Res. 10:7607–7612. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ikuta S, Edamatsu H, Li M, Hu L and
Kataoka T: Crucial role of phospholipase C epsilon in skin
inflammation induced by tumor-promoting phorbol ester. Cancer Res.
68:64–72. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A and
Balkwill F: Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 454:436–444. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Greten FR, Eckmann L, Greten TF, Park JM,
Li ZW, Egan LJ, Kagnoff MF and Karin M: IKKbeta links inflammation
and tumorigenesis in a mouse model of colitis-associated cancer.
Cell. 118:285–296. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Karin M and Greten FR: NF-kappaB: Linking
inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression.
Nat Rev Immunol. 5:749–759. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bartoletti R, Cai T, Nesi G, Sardi I and
Rizzo M: Qualitative and quantitative analysis of angiogenetic
factors in transitional cell bladder carcinoma: Relationship with
clinical course at 10 years follow-up. Oncol Rep. 14:251–255.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cui L, Shi Y, Dai G, Pan H, Chen J, Song
L, Wang S, Chang HC, Sheng H and Wang X: Modification of
N-Methyl-N-Nitrosourea initiated bladder carcinogenesis in Wistar
rats by terephthalic acid. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 210:24–31. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ariel I, Ayesh S, Gofrit O, Ayesh B,
Abdul-Ghani R, Pizov G, Smith Y, Sidi AA, Birman T, Schneider T, et
al: Gene expression in the bladder carcinoma rat model. Mol
Carcinog. 41:69–76. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ding J, Xu D, Pan C, Ye M, Kang J, Bai Q
and Qi J: Current animal models of bladder cancer: Awareness of
translatability (Review). Exp Ther Med. 8:691–699. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gofrit ON, Birman T, Dinaburg A, Ayesh S,
Ohana P and Hochberg A: Chemically induced bladder cancer-a
sonographic and morphologic description. Urology. 68:231–235. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang RY, Du WQ, Zhang YC, Zheng JN and
Pei DS: PLCε signaling in cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. June
25–2015.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Gofrit ON, Birman T, Dinaburg A, Ayesh S,
Ohana P and Hochberg A: Chemically induced bladder cancer-a
sonographic and morphologic description. Urology. 68:231–235. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chu H, Wang M and Zhang Z: Bladder cancer
epidemiology and genetic susceptibility. J Biomed Res. 27:170–178.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Murta-Nascimento C, Schmitz-Drager BJ,
Zeegers MP, Steineck G, Kogevinas M, Real FX and Malats N:
Epidemiology of urinary bladder cancer: from tumor development to
patient's death. World J Uro. 25:285–295. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Malats N and Real FX: Epidemiology of
bladder cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 29:177–189. vii2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Burchill SA, Neal DE and Lunec J:
Frequency of H-ras mutations in human bladder cancer detected by
direct sequencing. Br J Urol. 73:516–521. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Traczyk M, Borkowska E, Rozniecki M,
Purpurowicz R, Jędrzejczyk A, Marks P, Pietrusiński M, Jabłonowski
Z, Sosnowski M and Kałużewski B: Polymorphic variants of H-RAS
protooncogene and their possible role in bladder cancer etiology.
Cent European J Urol. 65:84–87. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ahmad I, Patel R, Liu Y, Singh LB, Taketo
MM, Wu XR, Leung HY and Sansom OJ: Ras mutation cooperates with
β-catenin activation to drive bladder tumourigenesis. Cell Death
Dis. 2:e1242011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Shibatohge M, Kariya K, Liao Y, Hu CD,
Watari Y, Goshima M, Shima F and Kataoka T: Identification of
PLC210, a Caenorhabditis elegans phospholipase C, as a putative
effector of Ras. J Biol Chem. 273:6218–6222. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bourguignon LY, Gilad E, Brightman A,
Diedrich F and Singleton P: Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction with
leukemia-associated RhoGEF and epidermal growth factor receptor
promotes Rho/Ras co-activation, phospholipase C
epsilon-Ca2+ signaling and cytoskeleton modification in
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem.
281:14026–14040. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cheng H, Luo C, Wu X, Zhang Y, He Y, Wu Q,
Xia Y and Zhang J: shRNA targeting PLCε inhibits bladder cancer
cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Urology. 78:474.e477–411. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ling Y, Chunli L, Xiaohou W and Qiaoling
Z: Involvement of the PLCε/PKCα pathway in human BIU-87 bladder
cancer cell proliferation. Cell Biol Int. 35:1031–1036. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Du HF, Ou LP, Yang X, Song XD, Fan YR, Tan
B, Luo CL and Wu X: A new PKCα/β/TBX3/E-cadherin pathway is
involved in PLCε-regulated invasion and migration in human bladder
cancer cells. Cell Signal. 26:580–593. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Nagano T, Edamatsu H, Kobayashi K,
Takenaka N, Yamamoto M, Sasaki N, Nishimura Y and Kataoka T:
Phospholipase cε, an effector of ras and rap small GTPases, is
required for airway inflammatory response in a mouse model of
bronchial asthma. PLoS One. 9:e1083732014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Li M, Edamatsu H, Kitazawa R, Kitazawa S
and Kataoka T: Phospholipase Cepsilon promotes intestinal
tumorigenesis of Apc (Min/+) mice through augmentation of
inflammation and angiogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 30:1424–1432. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|