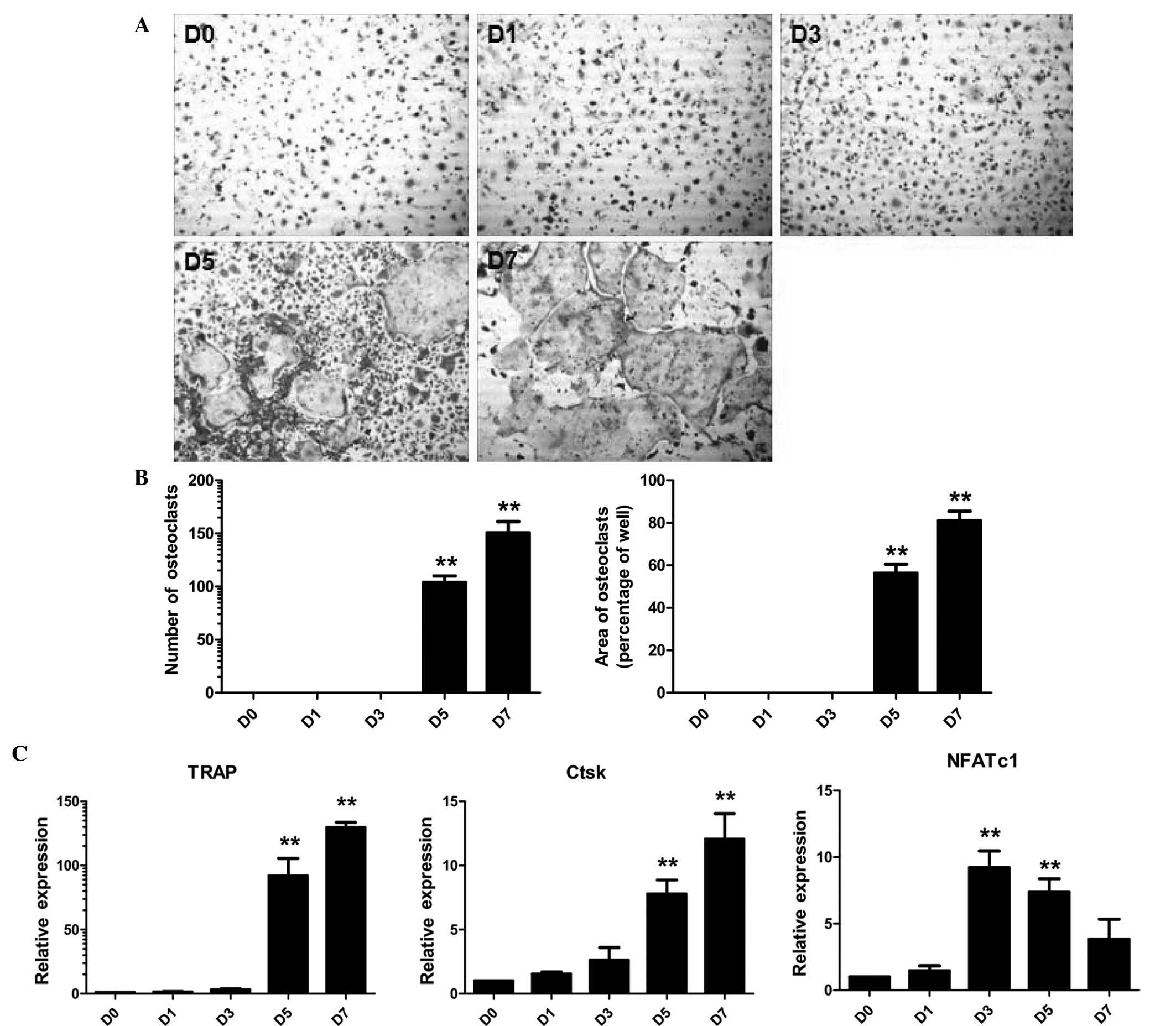
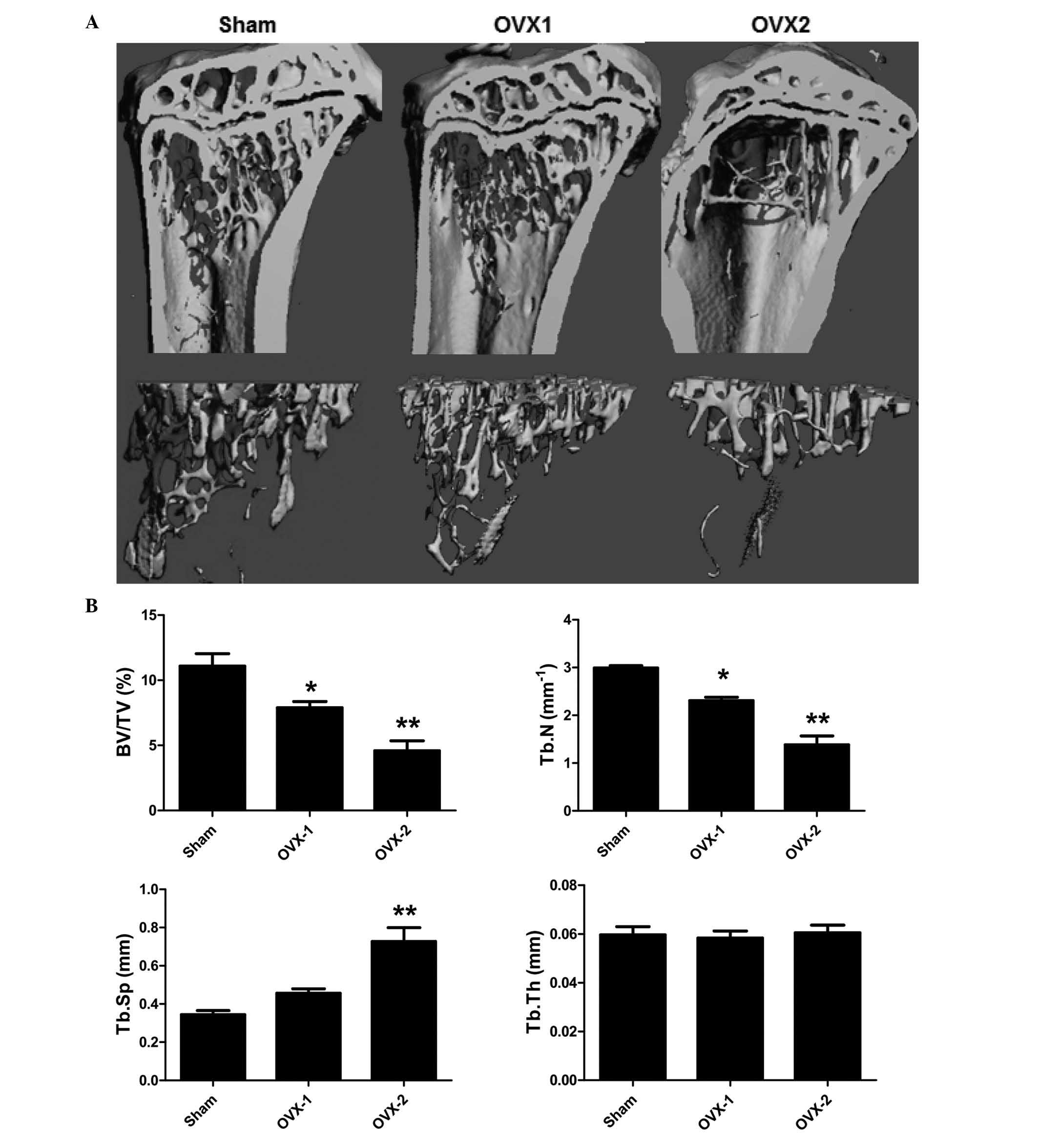
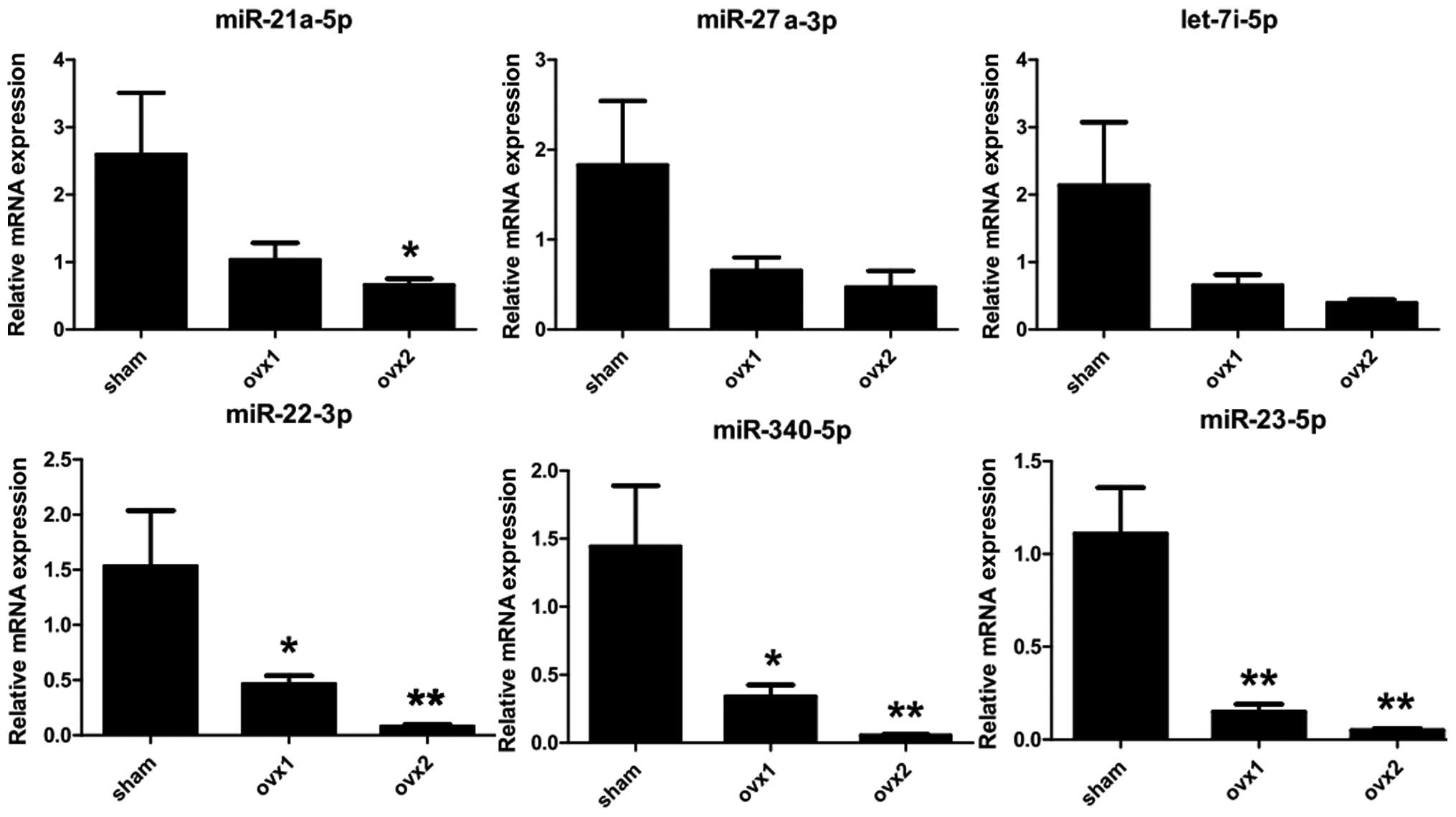
|
1
|
Rachner TD, Khosla S and Hofbauer LC:
Osteoporosis: Now and the future. Lancet. 377:1276–1287. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kim MS, Magno CL, Day CJ and Morrison NA:
Induction of chemokines and chemokine receptors CCR2b and CCR4 in
authentic human osteoclasts differentiated with RANKL and
osteoclast like cells differentiated by MCP-1 and RANTES. J Cell
Biochem. 97:512–518. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Matsuo K and Irie N: Osteoclastosteoblast
communication. Arch Biochem Biophys. 473:201–209. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dempster DW, Lambing CL, Kostenuik PJ and
Grauer A: Role of RANK ligand and denosumab, a targeted RANK ligand
inhibitor, in bone health and osteoporosis: A review of preclinical
and clinical data. Clin Ther. 34:521–536. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chong Y, Zhang J, Guo X, Li G, Zhang S, Li
C, Jiao Z and Shao M: MicroRNA-503 acts as a tumor suppressor in
osteosarcoma by targeting L1CAM. PLoS One. 9:e1145852014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kloos W, Vogel B and Blessing E: MiRNAs in
peripheral artery disease-something gripping this way comes. Vasa.
43:163–170. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schneider MR: MicroRNAs as novel players
in skin development, homeostasis and disease. Br J Dermatol.
166:22–28. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Jayaswal V, Lutherborrow M, Ma DD and Yang
YH: Identification of microRNA-mRNA modules using microarray data.
BMC Genomics. 12:1382011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sugatani T and Hruska KA: MicroRNA-223 is
a key factor in osteoclast differentiation. J Cell Biochem.
101:996–999. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bluml S, Bonelli M, Niederreiter B,
Puchner A, Mayr G, Hayer S, Koenders MI, van den Berg WB, Smolen J
and Redlich K: Essential role of microRNA-155 in the pathogenesis
of autoimmune arthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 63:1281–1288.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rossi M, Pitari MR, Amodio N, Di Martino
MT, Conforti F, Leone E, Botta C, Paolino FM, Del Giudice T,
Iuliano E, et al: miR-29b negatively regulates human osteoclastic
cell differentiation and function: Implications for the treatment
of multiple myeloma-related bone disease. J Cell Physiol.
228:1506–1515. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Sugatani T, Vacher J and Hruska KA: A
microRNA expression signature of osteoclastogenesis. Blood.
117:3648–3657. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Krzeszinski JY, Wei W, Huynh H, Jin Z,
Wang X, Chang TC, Xie XJ, He L, Mangala LS, Lopez-Berestein G, et
al: miR-34a blocks osteoporosis and bone metastasis by inhibiting
osteoclastogenesis and Tgif2. Nature. 512:431–435. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Seeliger C, Karpinski K, Haug AT, Vester
H, Schmitt A, Bauer JS and van Griensven M: Five freely circulating
miRNAs and bone tissue miRNAs are associated with osteoporotic
fractures. J Bone Miner Res. 29:1718–1728. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li H, Zhai Z, Liu G, Tang T, Lin Z, Zheng
M, Qin A and Dai K: Sanguinarine inhibits osteoclast formation and
bone resorption via suppressing RANKL-induced activation of NF-kB
and ERK signaling pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
430:951–956. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Bouxsein ML, Boyd SK, Christiansen BA,
Guldberg RE, Jepsen KJ and Müller R: Guidelines for assessment of
bone microstructure in rodents using micro-computed tomography. J
Bone Miner Res. 25:1468–1486. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Imai T, et al: Evaluation of reference
genes for accurate normalization of gene expression for real
time-quantitative PCR in Pyrus pyrifolia using different tissue
samples and seasonal conditions. PLoS One. 9:e864922014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shibuya H, Nakasa T, Adachi N, Nagata Y,
Ishikawa M, Deie M, Suzuki O and Ochi M: Overexpression of
microRNA-223 in rheumatoid arthritis synovium controls osteoclast
differentiation. Mod Rheumatol. 23:674–685. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang J, Zhao H, Chen J, Xia B, Jin Y, Wei
W, Shen J and Huang Y: Interferon-β-induced miR-155 inhibits
osteoclast differentiation by targeting SOCS1 and MITF. FEBS Lett.
586:3255–3262. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nakasa T, Shibuya H, Nagata Y, Niimoto T
and Ochi M: The inhibitory effect of microRNA-146a expression on
bone destruction in collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum.
63:1582–1590. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ell B, Mercatali L, Ibrahim T, Campbell N,
Schwarzenbach H, Pantel K, Amadori D and Kang Y: Tumor-induced
osteoclast miRNA changes as regulators and biomarkers of osteolytic
bone metastasis. Cancer Cell. 24:542–556. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cheng P, Chen C, He HB, Hu R, Zhou HD, Xie
H, Zhu W, Dai RC, Wu XP, Liao EY and Luo XH: miR-148a regulates
osteoclastogenesis by targeting V-maf musculoaponeurotic
fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog B. J Bone Miner Res. 28:1180–1190.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lee Y, Kim HJ, Park CK, Kim YG, Lee HJ,
Kim JY and Kim HH: MicroRNA-124 regulates osteoclast
differentiation. Bone. 56:383–389. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mizoguchi F, Murakami Y, Saito T, Miyasaka
N and Kohsaka H: miR-31 controls osteoclast formation and bone
resorption by targeting RhoA. Arthritis Res Ther. 15:R1022013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen C, Cheng P, Xie H, Zhou HD, Wu XP,
Liao EY and Luo XH: MiR-503 regulates osteoclastogenesis via
targeting RANK. J Bone Miner Res. 29:338–347. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Guo LJ, Liao L, Yang L, Li Y and Jiang TJ:
MiR-125a TNF receptor-associated factor 6 to inhibit
osteoclastogenesis. Exp Cell Res. 321:142–152. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wu S, Huang S, Ding J, Zhao Y, Liang L,
Liu T, Zhan R and He X: Multiple microRNAs modulate p21Cip1/Waf1
expression by directly targeting its 3′untranslated region.
Oncogene. 29:2302–2308. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Park MG, Kim JS, Park SY, Lee SA, Kim HJ,
Kim CS, Kim JS, Chun HS, Park JC and Kim do K: MicroRNA-27 promotes
the differentiation of odontoblastic cell by targeting APC and
activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Gene. 538:266–272. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang T and Xu Z: miR-27 promotes
osteoblast differentiation by modulating Wnt signaling. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 402:186–189. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lin J, Huo R, Xiao L, Zhu X, Xie J, Sun S,
He Y, Zhang J, Sun Y, Zhou Z, et al: A novel p53/microRNA-22/Cyr61
axis in synovial cells regulates inflammation in rheumatoid
arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 66:49–59. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Takata A, Otsuka M, Kojima K, Yoshikawa T,
Kishikawa T, Yoshida H and Koike K: MicroRNA-22 and microRNA-140
suppress NF-kB activity by regulating the expression of NF-kB
coactivators. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 411:826–831. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Poenitzsch Strong AM, Setaluri V and
Spiegelman VS: microRNA-340 as a modulator of RAS-RAF-MAPK
signaling in melanoma. Arch Biochem Biophys. 563:118–124. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|