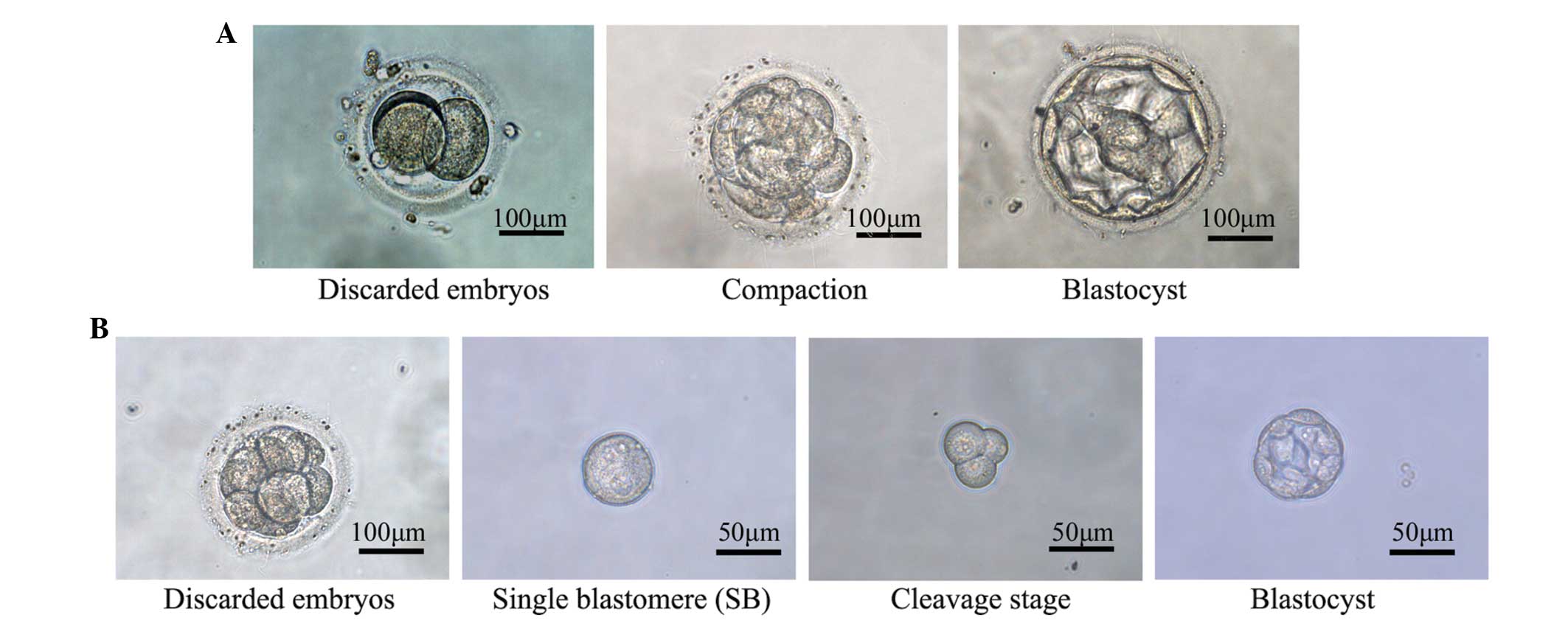
|
1
|
Sutcliffe AG and Ludwig M: Outcome of
assisted reproduction. Lancet. 370:351–359. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mantikou E, Youssef MA, van Wely M, van
der Veen F, Al-Inany HG, Repping S and Mastenbroek S: Embryo
culture media and IVF/ICSI success rates: a systematic review. Hum
Reprod Update. 19:210–220. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bontekoe S, Blake D, Heineman MJ, Williams
EC and Johnson N: Adherence compounds in embryo transfer media for
assisted reproductive technologies. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
7:CD0074212010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Carney SK, Das S, Blake D, Farquhar C,
Seif MM and Nelson L: Assisted hatching on assisted conception (in
vitro fertilization (IVF) and intracytoplasmic sperm injection
(ICSI). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 12:CD0018942012.
|
|
5
|
Bontekoe S, Mantikou E, van Wely M,
Seshadri S, Repping S and Mastenbroek S: Low oxygen concentrations
for embryo culture in assisted reproductive technologies. Cochrane
Database Syst Rev. 7:CD0089502012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Watson AJ and Barcroft LC: Regulation of
blastocyst formation. Front Biosci. 6:D708–D730. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dard N, Breuer M, Maro B and Louvet-Vallée
S: Morphogenesis of the mammalian blastocyst. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
282:70–77. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Gumus E, Bulut HE and Kaloglu C:
Cytoskeletal changes in oocytes and early embryos during in vitro
fertilization process in mice. Anat Histol Embryol. 39:51–58. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Rawe VY, Payne C and Schatten G: Profilin
and actin-related proteins regulate microfilament dynamics during
early mammalian embryogenesis. Hum Reprod. 21:1143–1153. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ishizaki T, Uehata M, Tamechika I, Keel J,
Nonomura K, Maekawa M and Narumiya S: Pharmacological properties of
Y-27632, a specific inhibitor of rho-associated kinases. Mol
Pharmacol. 57:976–983. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kawagishi R, Tahara M, Sawada K, Ikebuchi
Y, Morishige K, Sakata M, Tasaka K and Murata Y: Rho-kinase is
involved in mouse blastocyst cavity formation. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 319:643–648. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Duan X, Chen KL, Zhang Y, Cui XS, Kim NH
and Sun SC: ROCK inhibition prevents early mouse embryo
development. Histochem Cell Biol. 142:227–233. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hochi S, Abdalla H, Hara H, Shimoda M,
Morita H, Kuwayama M and Hirabayashi M: Stimulatory effect of
Rho-associated coiled-coil kinase (ROCK) inhibitor on revivability
of in vitro-produced bovine blastocysts after vitrification.
Theriogenology. 73:1139–1145. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cortes JL, Sanchez L, Ligero G,
Gutierrez-Aranda I, Catalina P, Elosua C, Leone PE, Montes R, Bueno
C, Ramos-Mejía V, et al: Mesenchymal stem cells facilitate the
derivation of human embryonic stem cells from cryopreserved
poor-quality embryos. Hum Reprod. 24:1844–1851. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Clayton L, Hall A and Johnson MH: A role
for Rho-like GTPases in the polarisation of mouse eight-cell
blastomeres. Dev Biol. 205:322–331. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Koike S, Keino-Masu K and Masu M:
Deficiency of autotaxin/lysophospholipase D results in head cavity
formation in mouse embryos through the LPA receptor-Rho-ROCK
pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 400:66–71. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Laeno AM, Tamashiro DA and Alarcon VB:
Rho-associated kinase activity is required for proper morphogenesis
of the inner cell mass in the mouse blastocyst. Biol Reprod.
89:1222013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Geens M, Mateizel I, Sermon K, De Rycke M,
Spits C, Cauffman G, Devroey P, Tournaye H, Liebaers I and Van de
Velde H: Human embryonic stem cell lines derived from single
blastomeres of two 4-cell stage embryos. Hum Reprod. 24:2709–2717.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Van de Velde H, Cauffman G, Tournaye H,
Devroey P and Liebaers I: The four blastomeres of a 4-cell stage
human embryo are able to develop individually into blastocysts with
inner cell mass and trophectoderm. Hum Reprod. 23:1742–1747. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Watanabe K, Ueno M, Kamiya D, Nishiyama A,
Matsumura M, Wataya T, Takahashi JB, Nishikawa S, Nishikawa S,
Muguruma K and Sasai Y: A ROCK inhibitor permits survival of
dissociated human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 25:681–686.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pakzad M, Totonchi M, Taei A, Seifinejad
A, Hassani SN and Baharvand H: Presence of a ROCK inhibitor in
extracellular matrix supports more undifferentiated growth of
feeder-free human embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells upon
passaging. Stem Cell Rev. 6:96–107. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Rizzino A: Stimulating progress in
regenerative medicine: Improving the cloning and recovery of
cryopreserved human pluripotent stem cells with ROCK inhibitors.
Regen Med. 5:799–807. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang P, Wu X, Hu C, Wang P and Li X: Rho
kinase inhibitor Y-27632 and Accutase dramatically increase mouse
embryonic stem cell derivation. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim.
48:30–36. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Horiguchi A, Yazaki K, Aoyagi M, Ohnuki Y
and Kurosawa H: Effective Rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor
treatment to dissociate human iPS cells for suspension culture to
form embryoid body-like cell aggregates. J Biosci Bioeng.
118:588–592. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sivasubramaiyan K, Totey S, Bhat V, Totey
SM and Deb K: Y-27632 enhances differentiation of blastocyst like
cystic human embryoid bodies to endocrinologically active
trophoblast cells on a biomimetic platform. J Biomed Sci.
16:882009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang Y, Duan X, Xiong B, Cui XS, Kim NH,
Rui R and Sun SC: ROCK inhibitor Y-27632 prevents porcine oocyte
maturation. Theriogenology. 82:49–56. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Steer CV, Mills CL, Tan SL, Campbell S and
Edwards RG: The cumulative embryo score: A predictive embryo
scoring technique to select the optimal number of embryos to
transfer in an in-vitro fertilization and embryo transfer
programme. Hum Reprod. 7:117–119. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gardner DK, Lane M and Schoolcraft WB:
Culture and transfer of viable blastocysts: A feasible proposition
for human IVF. Hum Reprod. 15(Suppl 6): S9–S23. 2000.
|
|
29
|
Taei A, Hassani SN, Eftekhari-Yazdi P,
Rezazadeh Valojerdi M, Nokhbatolfoghahai M, Masoudi NS, Pakzad M,
Gourabi H and Baharvand H: Enhanced generation of human embryonic
stem cells from single blastomeres of fair and poor-quality
cleavage embryos via inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase β and
Rho-associated kinase signaling. Hum Reprod. 28:2661–2671. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|