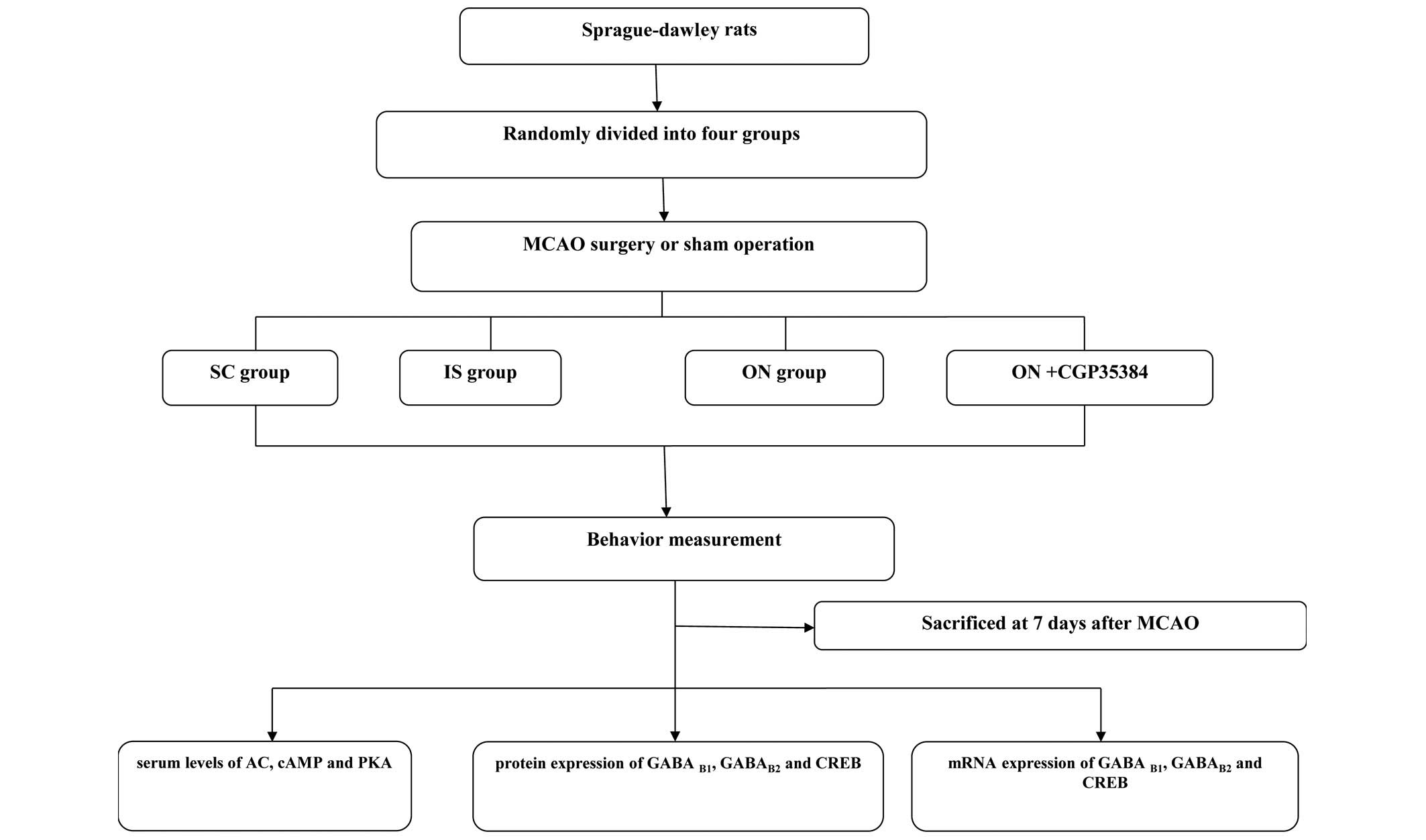
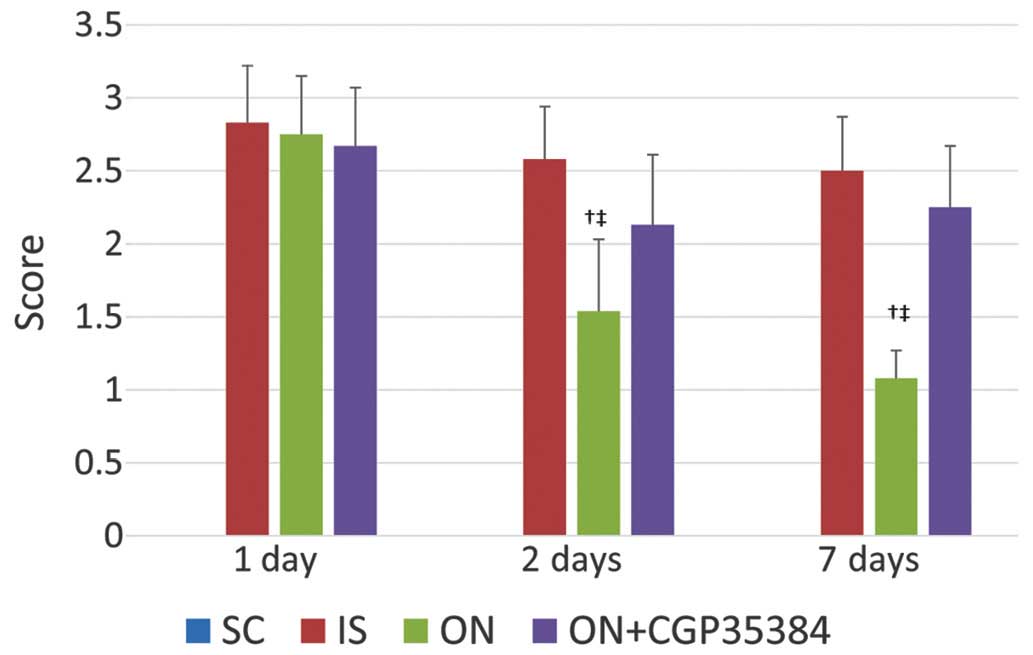
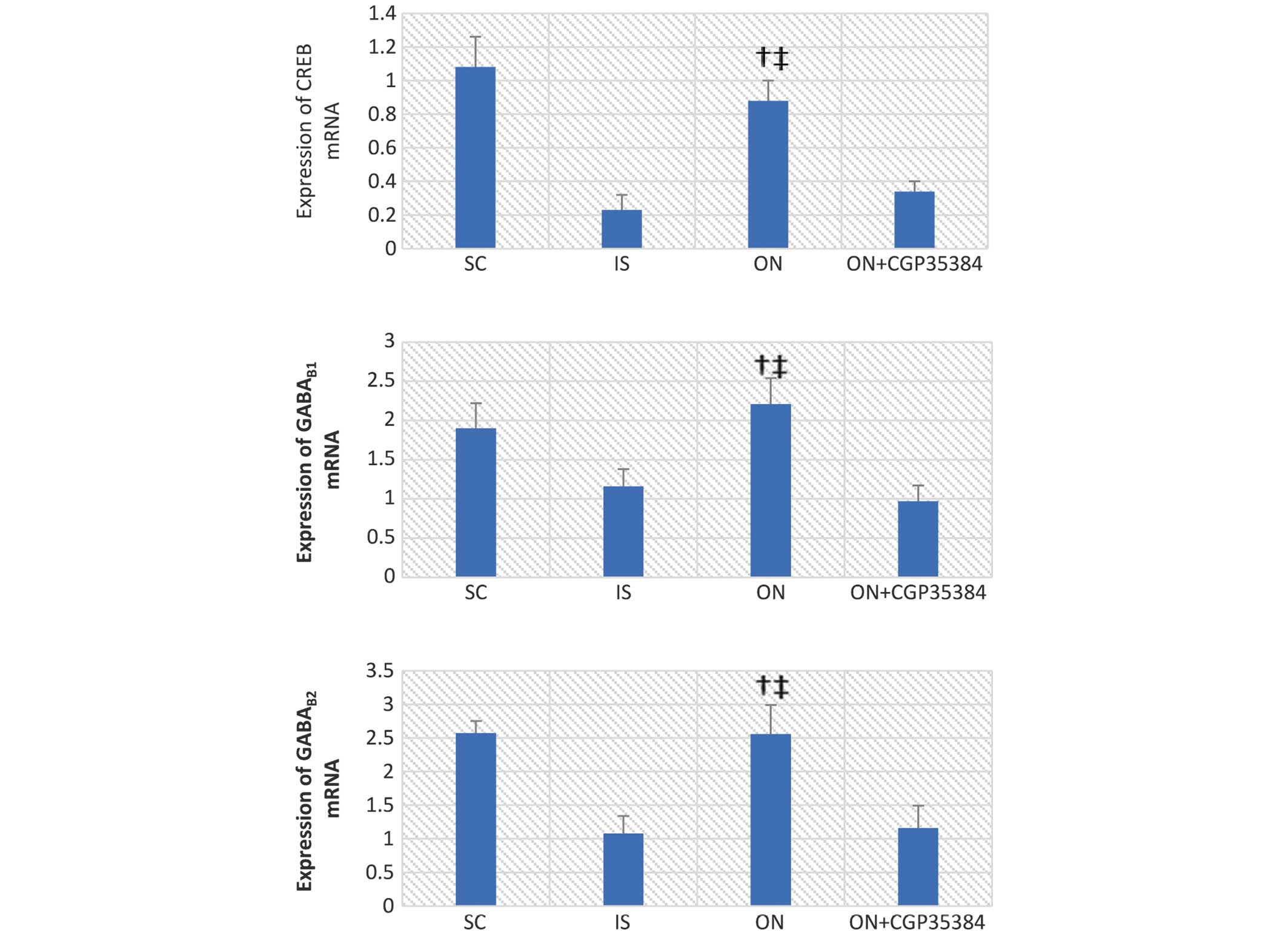
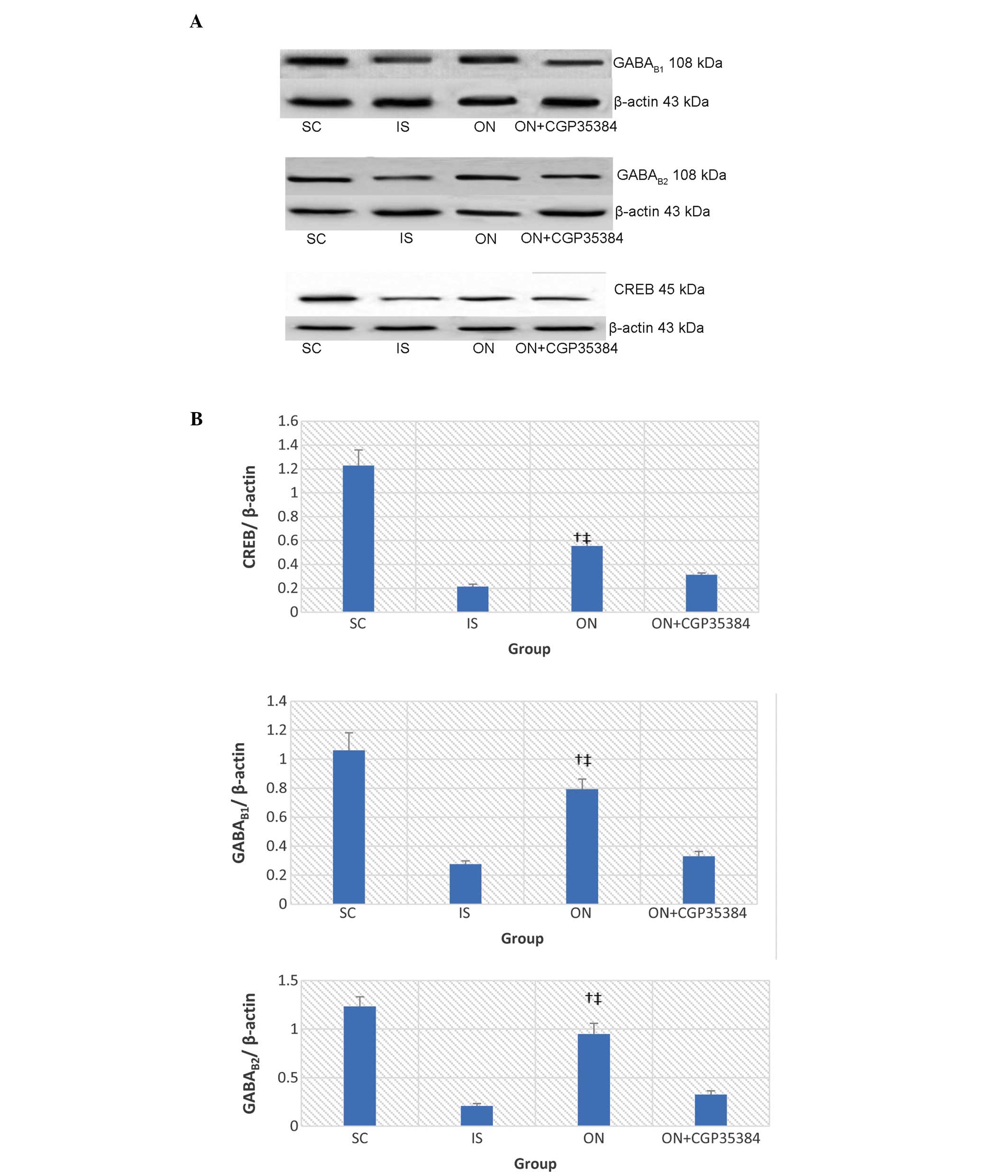
|
1
|
Minino AM, Xu J and Kochanek KD: Deaths:
preliminary data for 2008. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 59:1–52. 2008.
|
|
2
|
Xu J, Kochanek KD, Murphy SL and Arias E:
Mortality in the United States, 2012. NCHS Data Brief. 168:1–8.
2012.
|
|
3
|
Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin
EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, Bravata DM, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, et al:
Heart disease and stroke statistics - 2013 update: A report from
the American Heart Association. Circulation. 127:e6–e245. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Prevalence and most common causes of
disability among adults - United States, 2005. MMWR Morb Mortal
Wkly Rep. 58:421–426. 2009.
|
|
5
|
Ovbiagele B, Goldstein LB, Higashida RT,
Howard VJ, Johnston SC, Khavjou OA, Lackland DT, Lichtman JH, Mohl
S, Sacco RL, et al: Forecasting the future of stroke in the United
States: A policy statement from the American Heart Association and
American Stroke Association. Stroke. 44:2361–2375. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sun H and Zou X: A survey of the current
status in china. J Stroke. 15:109–114. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xu G, Zhang Z, Lv Q, Li Y, Ye R, Xiong Y,
Jiang Y and Liu X: NSFC health research funding and burden of
disease in China. PLoS One. 9:e1114582014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu L, Wang D, Wong KS and Wang Y: Stroke
and stroke care in China: Huge burden, significant workload, and a
national priority. Stroke. 42:3651–3654. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Towfighi A and Saver JL: Stroke declines
from third to fourth leading cause of death in the United States:
Historical perspective and challenges ahead. Stroke. 42:2351–2355.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sun Liuhe WY: Study on applied law of
opposing needling. Zhongguo Zhenjiu. 23:540–542. 2003.In
Chinese.
|
|
11
|
Gangting L: Effects of opposing needling
with large needle on rheoencephalogram, hemorheology and blood
lipids in the patient of cerebral infarction. Zhongguo Zhenjiu.
24:701–703. 2004.In Chinese.
|
|
12
|
Xiaohui Y: Clinical observation on
post-stroke hemiplegic patients with the treatment of Ju-ci
method's massage. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med. 25:1741–1742. 2007.In
Chinese.
|
|
13
|
Rothman SM and Olney JW: Glutamate and the
pathophysiology of hypoxic - ischemic brain damage. Ann Neurol.
19:105–111. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gillani Q, Iqbal S, Arfa F, Khakwani S,
Akbar A, Ullah A, Ali M and Iqbal F: Effect of GABAB receptor
antagonist (CGP35348) on learning and memory in albino mice.
Scientific World Journal. 2014(983651)2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bettler B and Tiao JY: Molecular
diversity, trafficking and subcellular localization of GABAB
receptors. Pharmacol Ther. 110:533–543. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li CJ, Lu Y, Zhou M, Zong XG, Li C, Xu XL,
Guo LJ and Lu Q: Activation of GABAB receptors ameliorates
cognitive impairment via restoring the balance of HCN1/HCN2 surface
expression in the hippocampal CA1 area in rats with chronic
cerebral hypoperfusion. Mol Neurobiol. 50:704–720. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cryan JF and Slattery DA: GABAB receptors
and depression. Current status. Adv Pharmacol. 58:427–451. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cimarosti H, Kantamneni S and Henley JM:
Ischaemia differentially regulates GABA(B) receptor subunits in
organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. Neuropharmacology.
56:1088–1096. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cheng CY, Su SY, Tang NY, Ho TY, Lo WY and
Hsieh CL: Ferulic acid inhibits nitric oxide-induced apoptosis by
enhancing GABA(B1) receptor expression in transient focal cerebral
ischemia in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 31:889–899. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jiang Y, Yang S and Tao J: Exploration of
neuroprotective mechanism of opposing needling on the
ischemia-reperfusion injured rats. Chin J Rehab Med. 29:605–609.
2014.In Chinese.
|
|
21
|
Bardutzky J, Shen Q, Henninger N, Bouley
J, Duong TQ and Fisher M: Differences in ischemic lesion evolution
in different rat strains using diffusion and perfusion imaging.
Stroke. 36:2000–2005. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lipsanen A and Jolkkonen J: Experimental
approaches to study functional recovery following cerebral
ischemia. Cell Mol Life Sci. 68:3007–3017. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bozkurt A, Deumens R, Scheffel J, O'Dey
DM, Weis J, Joosten EA, Führmann T, Brook GA and Pallua N: CatWalk
gait analysis in assessment of functional recovery after sciatic
nerve injury. J Neurosci Methods. 173:91–98. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deumens R, Jaken RJ, Marcus MA and Joosten
EA: The CatWalk gait analysis in assessment of both dynamic and
static gait changes after adult rat sciatic nerve resection. J
Neurosci Methods. 164:120–130. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Encarnacion A, Horie N, Keren-Gill H,
O'Dey DM, Weis J, Joosten EA, Führmann T, Brook GA and Pallua N:
Long-term behavioral assessment of function in an experimental
model for ischemic stroke. J Neurosci Methods. 196:247–257. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Balkaya M, Kröber J, Gertz K, Peruzzaro S
and Endres M: Characterization of long-term functional outcome in a
murine model of mild brain ischemia. J Neurosci Methods.
213:179–187. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Parkkinen S, Ortega FJ, Kuptsova K,
Huttunen J, Tarkka I and Jolkkonen J: Gait impairment in a rat
model of focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke Res Treat.
2013(410972)2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rasoulpanah M, Kharazmi F and Hatam M:
Evaluation of GABA Receptors of Ventral Tegmental Area in
Cardiovascular Responses in Rat. Iran J Med Sci. 39:374–381.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li XL, Fan NX, Meng HZ, Shi MX, Luo D and
Zhang NY: Specific neuroprotective effects of manual stimulation of
real acupoints versus non-acupoints in rats after middle cerebral
artery occlusion. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 10:186–195.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
O'Donnell ME, Chen YJ, Lam TI, Taylor KC,
Walton JH and Anderson SE: Intravenous HOE-642 reduces brain edema
and Na uptake in the rat permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion
model of stroke: Evidence for participation of the blood-brain
barrier Na/H exchanger. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 33:225–234. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Luo D, Fan X, Ma C, Fan T, Wang X, Chang
N, Li L, Zhang Y, Meng Z, Wang S and Shi X: A Study on the Effect
of Neurogenesis and Regulation of GSK3beta/PP2A Expression in
Acupuncture Treatment of Neural Functional Damage Caused by Focal
Ischemia in MCAO Rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2014:9623432014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Chen A: The mechanism of
electroacupuncture for cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury by
means of PI3K/AKT signal transduction pathway Master's thesis.
Fujian TCM University; 2013
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Du Y, Yan L, Wang J, Zhan W, Song K, Han
X, Li X, Cao J and Liu H: β1-Adrenoceptor autoantibodies from DCM
patients enhance the proliferation of T lymphocytes through the
β1-AR-cAMP/PKA and p38 MAPK pathways. PLoS One. 7:e529112012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Choi DW: Glutamate neurotoxicity in
cortical cell culture is calcium dependent. Neurosci Lett.
58:293–297. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Smith WS: Pathophysiology of focal
cerebral ischemia: a therapeutic perspective. J Vasc Interv Radiol.
15:S3–S12. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ouyang C, Guo L, Lu Q and Qu L: Effects of
γ-aminobutyric acid on amino acids and calcium levels in rat brain
of acute incomplete global cerebral ischemia. Chin J Pharmacol
Toxicol. 18:248–252. 2004.
|
|
39
|
Nelson RM, Hainsworth AH, Lambert DG,
Jones JA, Murray TK, Richards DA, Gabrielsson J, Cross AJ and Green
AR: Neuroprotective efficacy of AR-A008055, a clomethiazole
analogue, in a global model of acute ischaemic stroke and its
effect on ischaemia-induced glutamate and GABA efflux in vitro.
Neuropharmacology. 41:159–166. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dave KR, Lange-Asschenfeldt C, Raval AP,
Prado R, Busto R, Saul I and Pérez-Pinzón MA: Ischemic
preconditioning ameliorates excitotoxicity by shifting
glutamate/gamma-aminobutyric acid release and biosynthesis. J
Neurosci Res. 82:665–673. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Takeo S, Niimura M, Miyake-Takagi K,
Nagakura A, Fukatsu T, Ando T, Takagi N, Tanonaka K and Hara J: A
possible mechanism for improvement by a cognition-enhancer
nefiracetam of spatial memory function and cAMP-mediated signal
transduction system in sustained cerebral ischaemia in rats. Br J
Pharmacol. 138:642–654. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wu W, Yu X, Luo XP, Yang SH and Zheng D:
Tetramethylpyrazine protects against scopolamine-induced memory
impairments in rats by reversing the cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway. Behav
Brain Res. 253:212–216. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nu LC, Zhang YH, Li CQ, Liu B, Jiang Y and
Li LL: Effects of rehabilitation training on motor function
recovery and cAMP-PKA signal transduction pathway after ischemic
stroke in rats. Acta Laboratorium Animalis Scientia Sinica. 21:
View Article : Google Scholar : 2014.
|
|
44
|
Bowery NG, Bettler B, Froestl W, Gallagher
JP, Marshall F, Raiteri M, Bonner TI and Enna SJ: International
Union of Pharmacology. XXXIII. Mammalian gamma-aminobutyric acid(B)
receptors: Structure and Function. Pharmacol Rev. 54:247–264. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dawson TM and Ginty DD: CREB family
transcription factors inhibit neuronal suicide. Nat Med. 8:450–451.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ao H, Ko SW and Zhuo M: CREB activity
maintains the survival of cingulate cortical pyramidal neurons in
the adult mouse brain. Mol Pain. 2(15)2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|