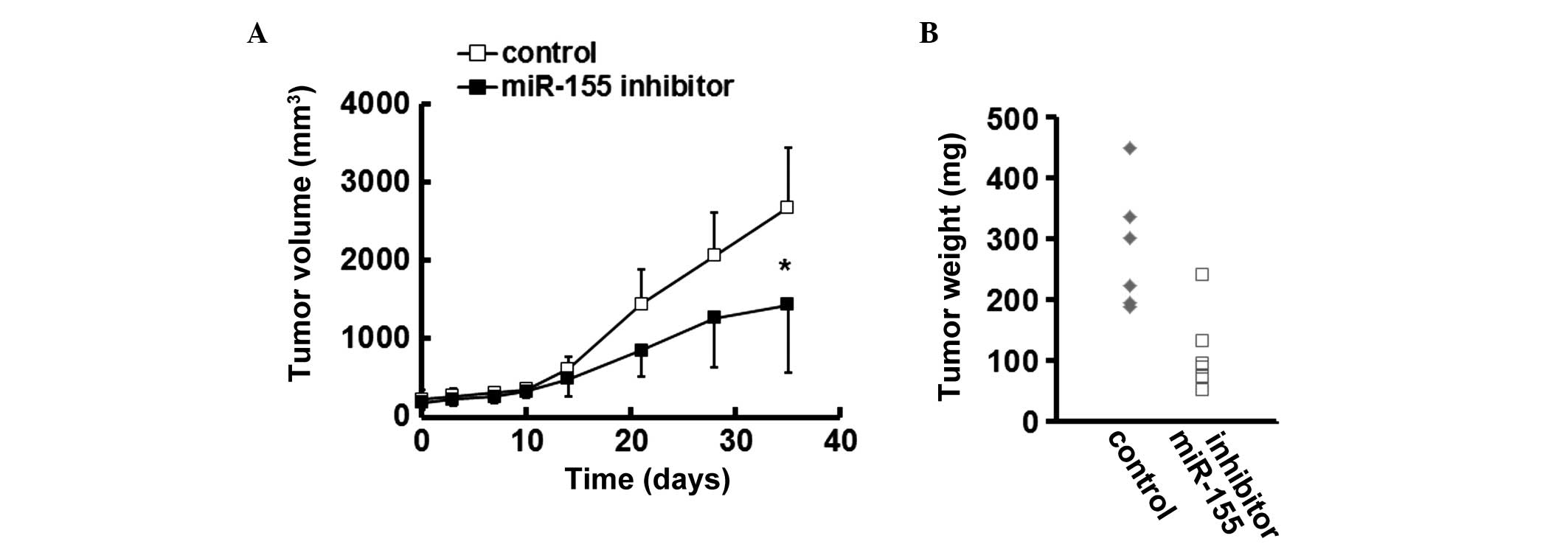
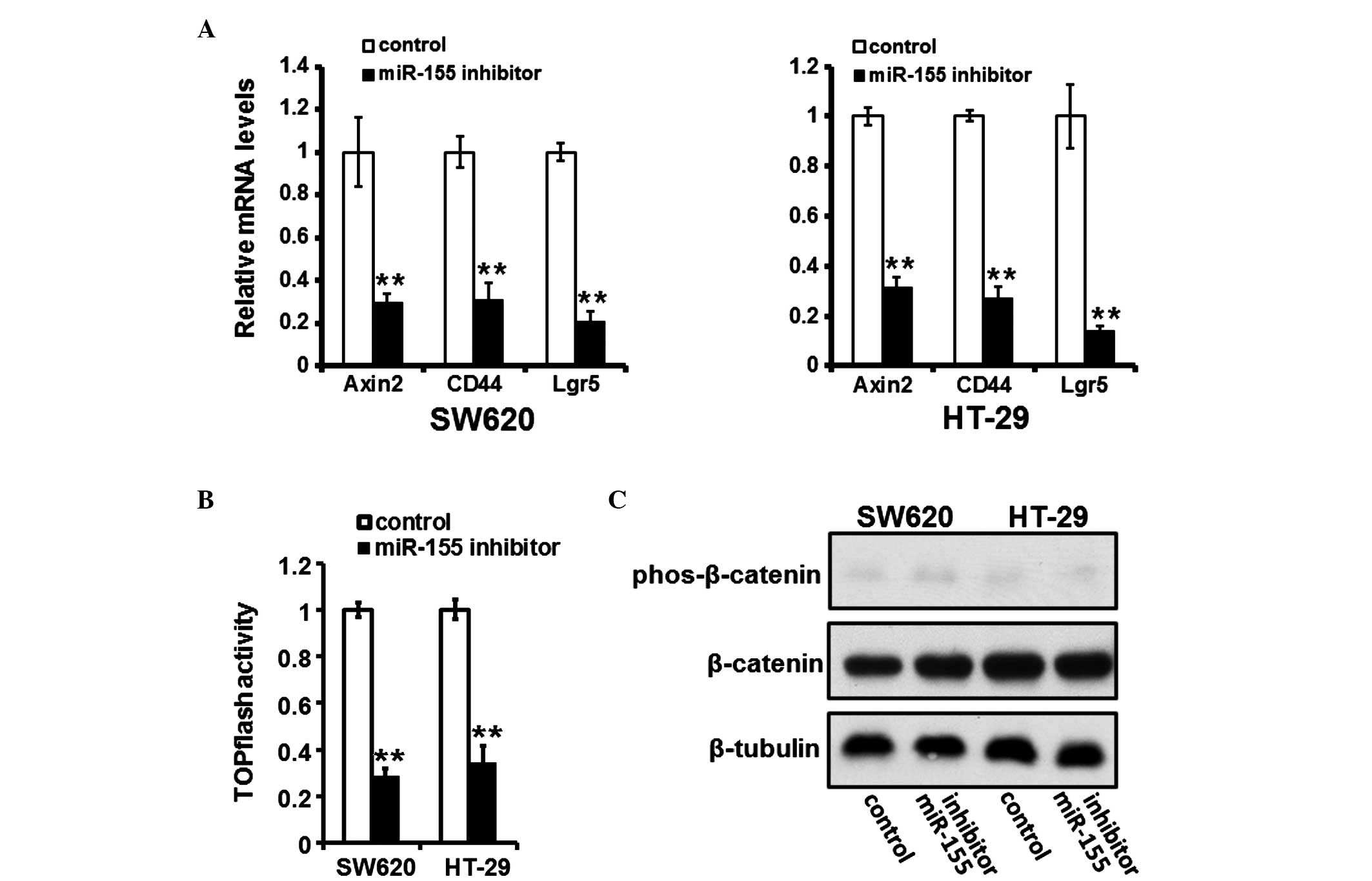
|
1
|
Papamichael D, Audisio RA, Glimelius B, de
Gramont A, Glynne-Jones R, Haller D, Köhne CH, Rostoft S, Lemmens
V, Mitry E, et al: Treatment of colorectal cancer in older
patients: International Society of Geriatric Oncology (SIOG)
consensus recommendations 2013. Ann Oncol. 26:463–476. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Dietvorst MH and Eskens FA: Current and
novel treatment options for metastatic colorectal cancer: Emphasis
on aflibercept. Biol Ther. 3:25–33. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Sontheimer EJ and Carthew RW: Silence from
within: Endogenous siRNAs and miRNAs. Cell. 122:9–12. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Croce CM and Calin GA: miRNAs, cancer, and
stem cell division. Cell. 122:6–7. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Faraoni I, Antonetti FR, Cardone J and
Bonmassar E: miR-155 gene: A typical multifunctional microRNA.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1792:497–505. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jurkovicova D, Magyerkova M, Kulcsar L,
Krivjanska M, Krivjansky V, Gibadulinova A, Oveckova I and Chovanec
M: miR-155 as a diagnostic and prognostic marker in hematological
and solid malignancies. Neoplasma. 61:241–251. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shibuya H, Iinuma H, Shimada R, Horiuchi A
and Watanabe T: Clinicopathological and prognostic value of
microRNA-21 and microRNA-155 in colorectal cancer. Oncology.
79:313–320. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhang GJ, Xiao HX, Tian HP, Liu ZL, Xia SS
and Zhou T: Upregulation of microRNA-155 promotes the migration and
invasion of colorectal cancer cells through the regulation of
claudin-1 expression. Int J Mol Med. 31:1375–1380. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Svrcek M, El-Murr N, Wanherdrick K, Dumont
S, Beaugerie L, Cosnes J, Colombel JF, Tiret E, Fléjou JF,
Lesuffleur T and Duval A: Overexpression of microRNAs-155 and 21
targeting mismatch repair proteins in inflammatory bowel diseases.
Carcinogenesis. 34:828–834. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bai J, Li Y, Shao T, Zhao Z, Wang Y, Wu A,
Chen H, Li S, Jiang C, Xu J and Li X: Integrating analysis reveals
microRNA-mediated pathway crosstalk among Crohn's disease,
ulcerative colitis and colorectal cancer. Mol Biosyst.
10:2317–2328. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Slaby O, Sachlova M, Brezkova V, Hezova R,
Kovarikova A, Bischofová S, Sevcikova S, Bienertova-Vasku J, Vasku
A, Svoboda M and Vyzula R: Identification of microRNAs regulated by
isothiocyanates and association of polymorphisms inside their
target sites with risk of sporadic colorectal cancer. Nutr Cancer.
65:247–254. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ma L, Liu J, Shen J, Liu L, Wu J, Li W,
Luo J, Chen Q and Qian C: Expression of miR-122 mediated by
adenoviral vector induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of cancer
cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 9:554–561. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu J, Ma L, Li C, Zhang Z, Yang G and
Zhang W: Tumor-targeting TRAIL expression mediated by miRNA
response elements suppressed growth of uveal melanoma cells. Mol
Oncol. 7:1043–1055. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ma L, Liu J, Liu L, Duan G, Wang Q, Xu Y,
Xia F, Shan J, Shen J, Yang Z, et al: Overexpression of the
transcription factor MEF2D in hepatocellular cancer sustains
malignant character by suppressing G2-M transition genes. Cancer
Res. 74:1452–1462. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang B, Liu J, Ma LN, Xiao HL, Wang YZ, Li
Y, Wang Z, Fan L, Lan C, Yang M, et al: Chimeric 5/35
adenovirus-mediated Dickkopf-1 overexpression suppressed
tumorigenicity of CD44+ gastric cancer cells via
attenuating Wnt signaling. J Gastroenterol. 48:798–808. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhang X, Li M, Zuo K, Li D, Ye M, Ding L,
Cai H, Fu D, Fan Y and Lv Z: Upregulated miR-155 in papillary
thyroid carcinoma promotes tumor growth by targeting APC and
activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
98:E1305–E1313. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang Y, Wei W, Cheng N, Wang K, Li B,
Jiang X and Sun S: Hepatitis C virus-induced up-regulation of
microRNA-155 promotes hepatocarcinogenesis by activating Wnt
signaling. Hepatology. 56:1631–1640. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee MF, Chan CY, Hung HC, Chou IT, Yee AS
and Huang CY: N-acetylcysteine (NAC) inhibits cell growth by
mediating the EGFR/Akt/HMG box-containing protein 1 (HBP1)
signaling pathway in invasive oral cancer. Oral Oncol. 49:129–135.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Tseng RC, Huang WR, Lin SF, Wu PC, Hsu HS
and Wang YC: HBP1 promoter methylation augments the oncogenic
β-catenin to correlate with prognosis in NSCLC. J Cell Mol Med.
18:1752–1761. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li H, Bian C, Liao L, Li J and Zhao RC:
miR-17-5p promotes human breast cancer cell migration and invasion
through suppression of HBP1. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 126:565–575.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yan Z, Wang J, Wang C, Jiao Y, Qi W and
Che S: miR-96/HBP1/Wnt/β-catenin regulatory circuitry promotes
glioma growth. FEBS Lett. 588:3038–3046. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|