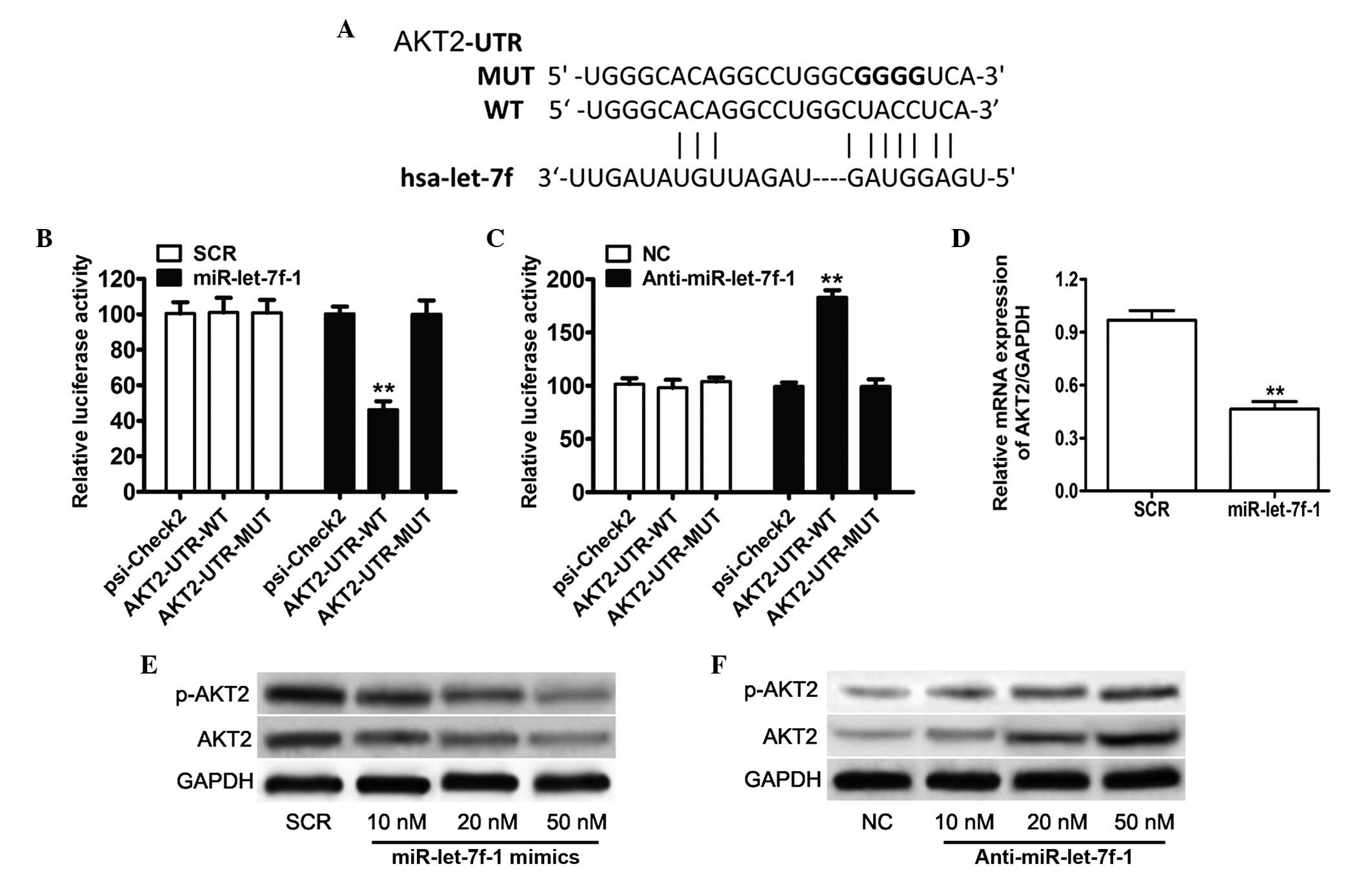
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zu K, Mucci L, Rosner BA, Clinton SK, Loda
M, Stampfer MJ and Giovannucci E: Dietary lycopene, angiogenesis
and prostate cancer: A prospective study in the prostate-specific
antigen era. J Natl Cancer Inst. 106:djt4302014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wei MY and Giovannucci EL: Lycopene,
tomato products and prostate cancer incidence: A review and
reassessment in the PSA screening era. J Oncol. 2012:2710632012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kristal AR, Till C, Platz EA, Song X, King
IB, Neuhouser ML, Ambrosone CB and Thompson IM: Serum lycopene
concentration and prostate cancer risk: Results from the prostate
cancer prevention trial. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
20:638–646. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Teodoro AJ, Oliveira FL, Martins NB, Maia
GA, Martucci RB and Borojevic R: Effect of lycopene on cell
viability and cell cycle progression in human cancer cell lines.
Cancer Cell Int. 12:362012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hwang ES and Bowen PE: Cell cycle arrest
and induction of apoptosis by lycopene in LNCaP human prostate
cancer cells. J Med Food. 7:284–289. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Venkateswaran V and Klotz LH: Diet and
prostate cancer: Mechanisms of action and implications for
chemoprevention. Nat Rev Urol. 7:442–453. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Syed DN, Suh Y, Afaq F and Mukhtar H:
Dietary agents for chemoprevention of prostate cancer. Cancer Lett.
265:167–176. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ventura A and Jacks T: MicroRNAs and
cancer: Short RNAs go a long way. Cell. 136:586–591. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M,
Kumamoto K, Yi M, Stephens RM, Okamoto A, Yokota J, Tanaka T, et
al: Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and
prognosis. Cancer Cell. 9:189–198. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A,
Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, Magri E, Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M,
et al: MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 65:7065–7070. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu XC, Dong QZ, Zhang XF, Deng B, Jia HL,
Ye QH, Qin LX and Wu XZ: microRNA-29a suppresses cell proliferation
by targeting SPARC in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Med.
30:1321–1326. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang B, Luo W, Sun L, Zhang Q, Jiang L,
Chang J, Qiu X and Wang E: MiRNA-125a-3p is a negative regulator of
the RhoA-actomyosin pathway in A549 cells. Int J Oncol.
42:1734–1742. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Coppola V, De Maria R and Bonci D:
MicroRNAs and prostate cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 17:F1–F17.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Rajendiran S, Parwani AV, Hare RJ,
Dasgupta S, Roby RK and Vishwanatha JK: MicroRNA-940 suppresses
prostate cancer migration and invasion by regulating MIEN1. Mol
Cancer. 13:2502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Goto Y, Kurozumi A, Enokida H, Ichikawa T
and Seki N: Functional significance of aberrantly expressed
microRNAs in prostate cancer. Int J Urol. 22:242–252. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jackson BL, Grabowska A and Ratan HL:
MicroRNA in prostate cancer: Functional importance and potential as
circulating biomarkers. BMC Cancer. 14:9302014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dong Q, Meng P, Wang T, Qin W, Qin W, Wang
F, Yuan J, Chen Z, Yang A and Wang H: MicroRNA let-7a inhibits
proliferation of human prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo
by targeting E2F2 and CCND2. PLoS One. 5:e101472010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pannuru P, Dontula R, Khan AA, Herbert E,
Ozer H, Chetty C and Lakka SS: miR-let-7f-1 regulates SPARC
mediated cisplatin resistance in medulloblastoma cells. Cell
Signal. 26:2193–2201. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yan LX, Huang XF, Shao Q, Huang MY, Deng
L, Wu QL, Zeng YX and Shao JY: MicroRNA miR-21 overexpression in
human breast cancer is associated with advanced clinical stage,
lymph node metastasis and patient poor prognosis. RNA.
14:2348–2360. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Trejo-Solís C, Pedraza-Chaverrí J,
Torres-Ramos M, Jiménez-Farfán D, Cruz Salgado A, Serrano-García N,
Osorio-Rico L and Sotelo J: Multiple molecular and cellular
mechanisms of action of lycopene in cancer inhibition. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2013:7051212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tang Y, Parmakhtiar B, Simoneau AR, Xie J,
Fruehauf J, Lilly M and Zi X: Lycopene enhances docetaxel's effect
in castration-resistant prostate cancer associated with
insulin-like growth factor I receptor levels. Neoplasia.
13:108–119. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lo HM, Hung CF, Tseng YL, Chen BH, Jian JS
and Wu WB: Lycopene binds PDGF-BB and inhibits PDGFBB-induced
intracellular signaling transduction pathway in rat smooth muscle
cells. Biochemical Pharmacology. 74:54–63. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chen ML, Lin YH, Yang CM and Hu ML:
Lycopene inhibits angiogenesis both in vitro and in vivo by
inhibiting MMP-2/uPA system through VEGFR2-mediated PI3K-AKT and
ERK/p38 signaling pathways. Molecular Nutrition & Food
Research. 56:889–899. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Livak and Schmittgen: Analysis of relative
gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the
2-ΔΔCt method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Tang FY, Shih CJ, Cheng LH, Ho HJ and Chen
HJ: Lycopene inhibits growth of human colon cancer cells via
suppression of the Akt signaling pathway. Mol Nutr Food Res.
52:646–654. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Takeshima M, Ono M, Higuchi T, Chen C,
Hara T and Nakano S: Anti-proliferative and apoptosis-inducing
activity of lycopene against three subtypes of human breast cancer
cell lines. Cancer Sci. 105:252–257. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Palozza P, Colangelo M, Simone R, Catalano
A, Boninsegna A, Lanza P, Monego G and Ranelletti FO: Lycopene
induces cell growth inhibition by altering mevalonate pathway and
Ras signaling in cancer cell lines. Carcinogenesis. 31:1813–1821.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Carver BS, Chapinski C, Wongvipat J,
Hieronymus H, Chen Y, Chandarlapaty S, Arora VK, Le C, Koutcher J,
Scher H, et al: Reciprocal feedback regulation of PI3K and androgen
receptor signaling in PTEN-deficient prostate cancer. Cancer Cell.
19:575–586. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hsu AL, Ching TT, Wang DS, Song X,
Rangnekar VM and Chen CS: The cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib
induces apoptosis by blocking Akt activation in human prostate
cancer cells independently of Bcl-2. J Biol Chem. 275:11397–11403.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kim DJ, Takasuka N, Kim JM, Sekine K, Ota
T, Asamoto M, Murakoshi M, Nishino H, Nir Z and Tsuda H:
Chemoprevention by lycopene of mouse lung neoplasia after combined
initiation treatment with DEN, MNU and DMH. Cancer Lett. 120:15–22.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Narisawa T, Fukaura Y, Hasebe M, Nomura S,
Oshima S, Sakamoto H, Inakuma T, Ishiguro Y, Takayasu J and Nishino
H: Prevention of N-methylnitrosourea-induced colon carcinogenesis
in F344 rats by lycopene and tomato juice rich in lycopene. Jpn J
Cancer Res. 89:1003–1008. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Giovannucci E: A review of epidemiologic
studies of tomatoes, lycopene and prostate cancer. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 227:852–859. 2002.
|
|
35
|
Pohar KS, Gong MC, Bahnson R, Miller EC
and Clinton SK: Tomatoes, lycopene and prostate cancer: A
clinician's guide for counseling those at risk for prostate cancer.
World J Urol. 21:9–14. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhong H, Chiles K, Feldser D, Laughner E,
Hanrahan C and Georgescu MM: Modulation of hypoxia-inducible factor
1alpha expression by the epidermal growth
factor/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/PTEN/AKT/FRAP pathway in human
prostate cancer cells: Implications for tumor angiogenesis and
therapeutics. Cancer Res. 60:1541–1545. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|