|
1
|
Xu ZY, Liang JG, Jiang NY, et al:
Preliminary analysis of bone mineral mass variation in
perimenopausal and postmenopausal women. Chinese Journal of
Osteoporosis. 12:378–396. 2006.In Chinese.
|
|
2
|
Semerano L, Guillot X, Rossini M, Avice E,
Bégué T, Wargon M, Boissier MC and Saidenberg-Kermanac'h N: What
predicts initiation of osteoporosis treatment after fractures:
Education organisation or patients' characteristics? Clin Exp
Rheumatol. 29:89–92. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ma J and Zheng HG: Cellular and molecular
biological mechanisms for osteoporosis prevention and treatment
using traditional Chinese medicine for kidney function improvement.
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 20:161–162. 2002.In
Chinese.
|
|
4
|
Li J, Chen XG, Wu QF, et al: Experimental
study on the role of Jiugulin Pill in retinoic acid-induced
osteoporosis. Journal of First Military Medical University.
19:2421999.In Chinese.
|
|
5
|
Armamento-Villareal R, Napoli N, Panwar V
and Novack D: Suppressed bone turnover during alendronate therapy
for high-turnover osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 355:2048–2050. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kawai M, Mödder UI, Khosla S and Rosen CJ:
Emerging therapeutic opportunities for skeletal restoration. Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 10:141–156. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu MG, Wu BH, Liu XX, et al: experimental
and clinical studies on the effects of Moxibustion on
postmenopausal osteoporosis. Chinese acupuncture. 22:335–336.
2002.In Chinese.
|
|
8
|
Lu JP, Cui YL and Shi RH: Chinese
acupuncture and moxibustion. A Practical English-Chinese Library of
Traditional Chinese Medicine. Zhang EQ: 8. 1st edition. Publishing
House of Shanghai College of Traditional Chinese Medicine;
Shanghai: pp. 103–108. 1990
|
|
9
|
Zhang F, Feng Y, Zhou R, Zhang YQ and Chen
BY: Observation on the central afferent pathway of "Guanyuan" (CV
4) under normal and pathological states and the influence of
electroacupuncture. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 33:147–153. 2008.In Chinese.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li P, Ji F, Lin Y, et al: Effects of
acupuncture on 'Cuihui' point on the quality of life of patients
with postmenopausal osteoporosis. Journal of Gansu College of
Traditional Chinese Medicine. 27:45–47. 2010.In Chinese.
|
|
11
|
Li P, Ji F and Chen GZ: Clinical
observation of the effects of combined acupuncture and drug
treatment on bone metabolism-related hormones in postmenopausal
patients. Journal of Fujian College of Traditional Chinese
Medicine. 15:21–22. 2005.In Chinese.
|
|
12
|
Li P, Lin Y and Xu JB: Clinical studies on
the effects of combined acupuncture and drug treatment on bone
metabolism in postmenopausal women - analysis of 20 cases. Fujian
Journal of Medicine. 31:131–133. 2009.In Chinese.
|
|
13
|
Zhang ML, Ji F, Lin Y, et al: Effects of
electroacupunture on Guanyuan point on IGF-1 and bone biomechanics
in ovariectomized-induced rat osteoporosis model. Acupuncture
Study. 39:207–210. 2014.In Chinese.
|
|
14
|
Huang GR, Li P, Fan HL, et al: Effect of
electroacupunture on Mingmeng Point on bone formation protein-2 in
postmenopausal rat osteoporosis model. Acupuncture Study.
39:130–4135. 2014.In Chinese.
|
|
15
|
Liu F, Xiong J, Huang GY and Wang W: Study
on the underlying mechanism of acupuncture in regulating
neuroendocrine activity in dysmenorrhea rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu.
34:3–8. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zheng X, Wu G, Nie Y and Lin YL:
Electroacupuncture at the governor vessel and bladder meridian
acupoints improves postmenopausal osteoporosis through
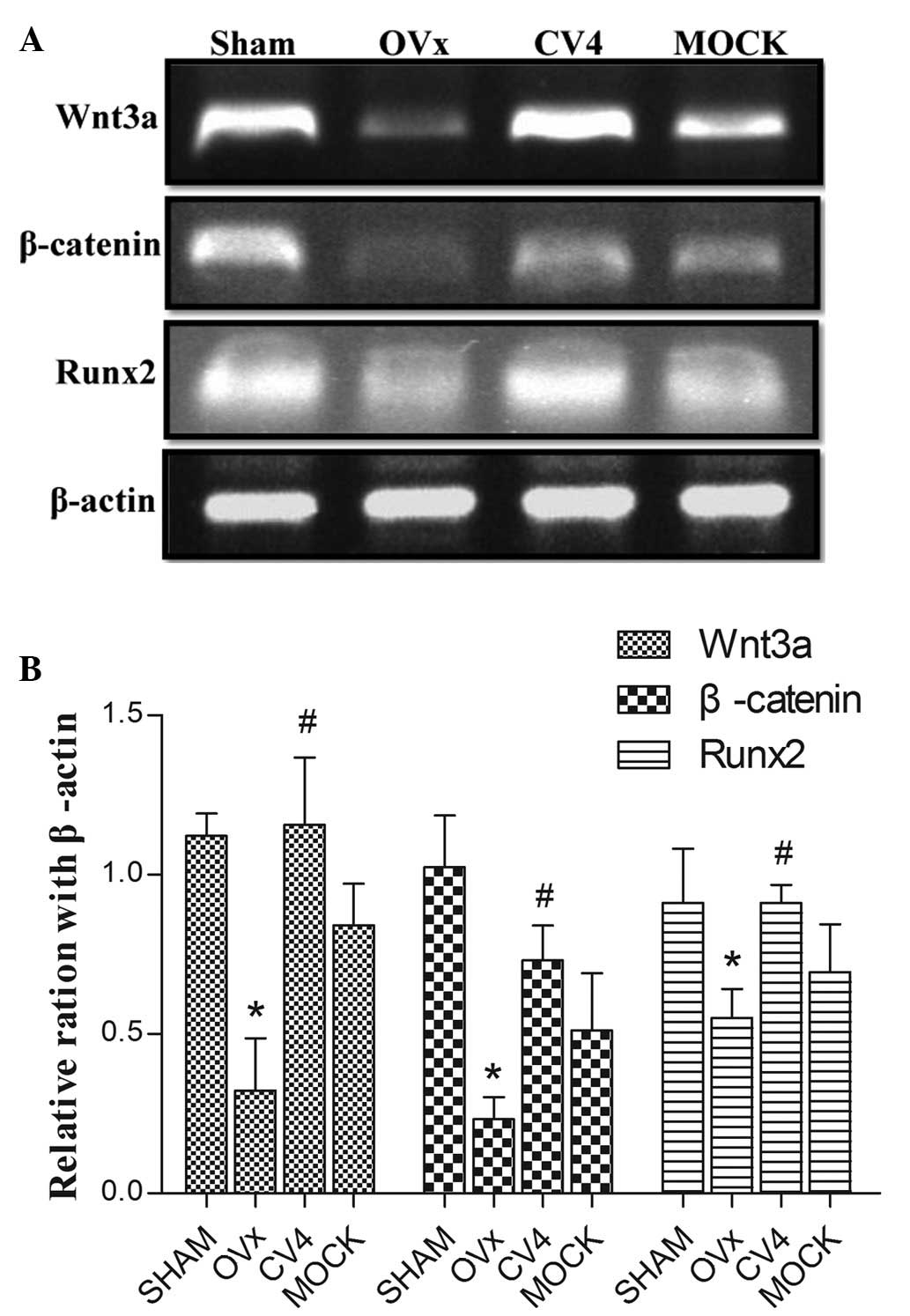
osteoprotegerin/RANKL/RANK and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways.
Exp Ther Med. 10:541–548. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kondo A, Tokuda H, Mizutani J,
Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Kozawa O and Otsuka T: Wnt3a upregulates
prostaglandin F2α-stimulated vascular endothelial growth factor
synthesis in osteoblasts. Mol Med Rep. 6:421–425. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li X, Peng J, Wu M, Ye H, Zheng C, Wu G,
Xu H, Chen X and Liu X: BMP2 promotes chondrocyte proliferation via
the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 4:621–626.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang HX, Mei H and Luo XD: Preventive
effects of Xianlinggubao on ovariectomized-induce rats osteoporosis
model. Chinese Journal of Traditional Medical Traumatology.
19:672–675. 2011.In Chinese.
|
|
20
|
Liu F, Xiong J, Huang GY and Wang W: Study
on the underlying mechanism of acupuncture in regulating
neuroendocrine activity in dysmenorrhea rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu.
34:3–8. 2009.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rulifson EJ, Wu CH and Nusse R: Pathway
specificity by the bifunctional receptor frizzled is determined by
affinity for wingless. Mol Cell. 6:117–126. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kestler HA and Kühl M: From individual Wnt
pathways towards a Wnt signaling network. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B
Biol Sci. 363:1333–1347. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kieslinger M, Folberth S, Dobreva G, Dorn
T, Croci L, Erben R, Consalez GG and Grosschedl R: EBF2 regulates
osteoblast-dependent differentiation of osteoclasts. Dev Cell.
9:757–767. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shi YC, Worton L, Estehen L, Baldock P,
Fong C, Eisman JA and Gardiner EM: Effects of continuous activation
of vitamin D and Wnt response pathways on osteoblastic
proliferation and differentiation. Bone. 41:87–96. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Price MA: CKI, there's more than one:
Casein kinase I family members in Wnt and Hedgehog signaling. Genes
Dev. 20:399–410. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Taurin S, Sandbo N, Qin Y, Browning D and
Dulin NO: Phosphorylation of beta-catenin by cyclic AMP-dependent
protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 281:9971–9976. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Takemaru KI and Moon RT: The
transcriptional coactivator CBP interacts with beta-catenin to
activate gene expression. J Cell Biol. 149:249–254. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shtutman M, Zhurinsky I, Simcha I,
Albanese C, D'Amico M, Pestell R and Ben-Ze'ev A: The cyclin D1
gene is a target of the beta-catenin/LEF-1 pathway. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 96:5522–5527. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jaiswal AS, Marlow BP, Gupta N and Narayan
S: Beta-catenin-mediated transactivation and cell-cell adhesion
pathways are important in curcumin (difemylmethane)-induced growth
arrest and apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Oncogene. 21:8414–8427.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Licchesi JD, Van Neste L, Tiwari VK, Cope
L, Lin X, Baylin SB and Herman JG: Transcriptional regulation of
Wnt inhibitory factor-1 by Miz-1/c-Myc. Oncogene. 29:5923–5934.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gaur T, Lengner CJ, Hovhannisyan H, Bhat
RA, Bodine PV, Komm BS, Javed A, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Stein GS
and Lian JB: Canonical Wnt signaling promotes osteogenesis by
directly stimulating Runx2 gene expression. J Biol Chem.
280:33132–33140. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|