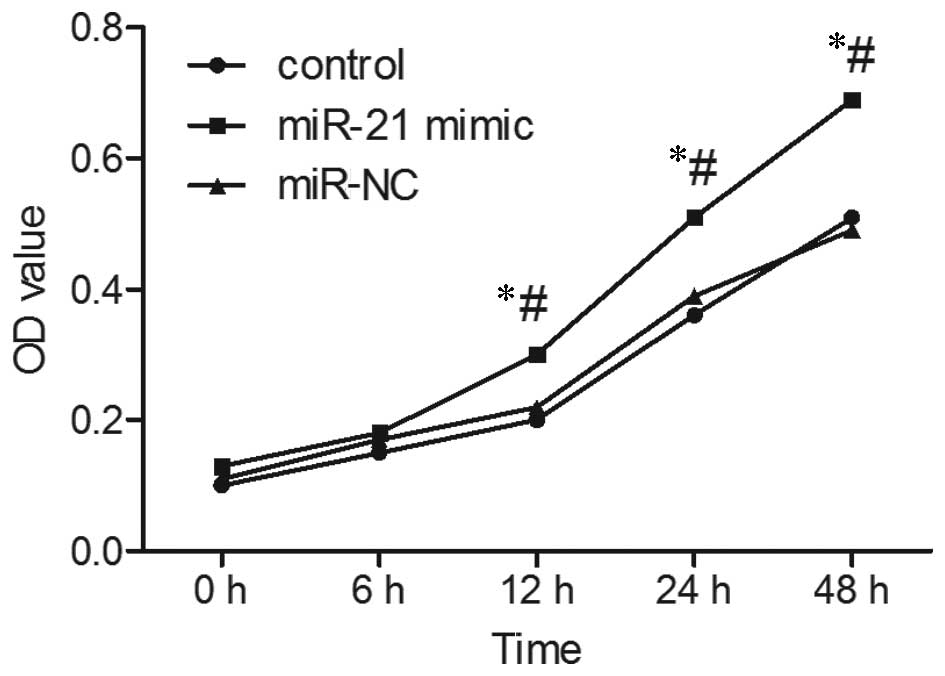
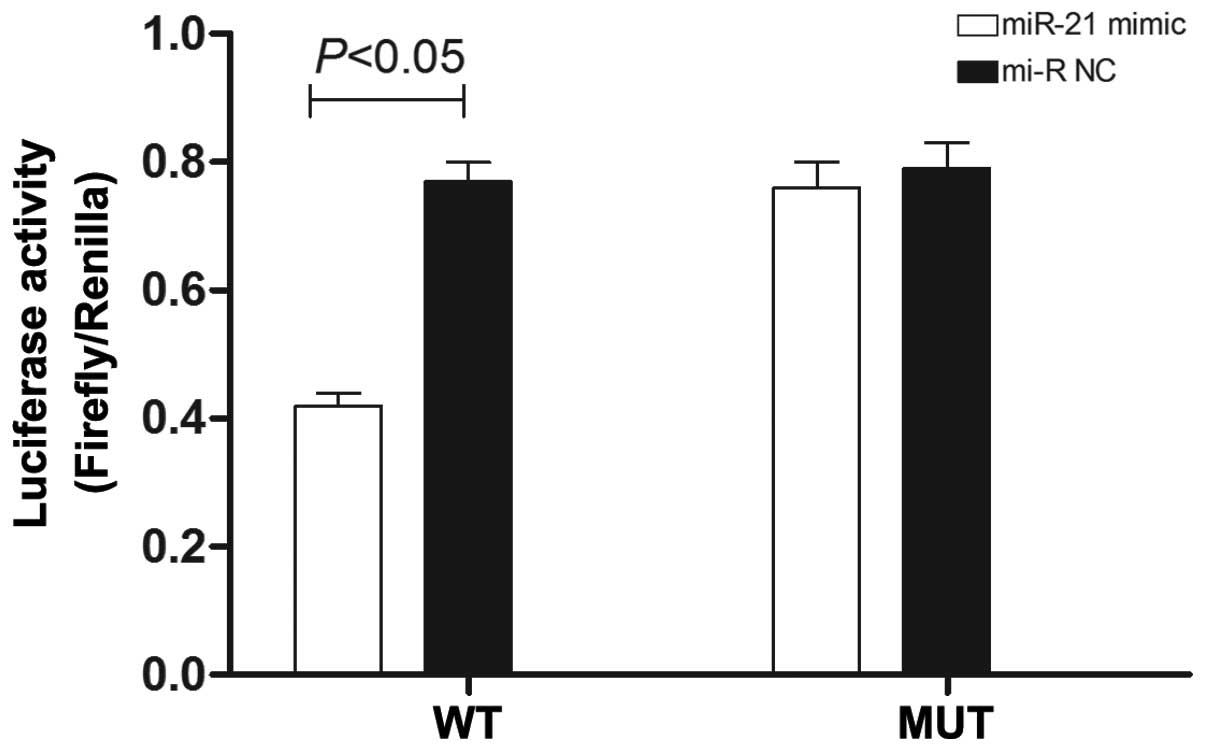
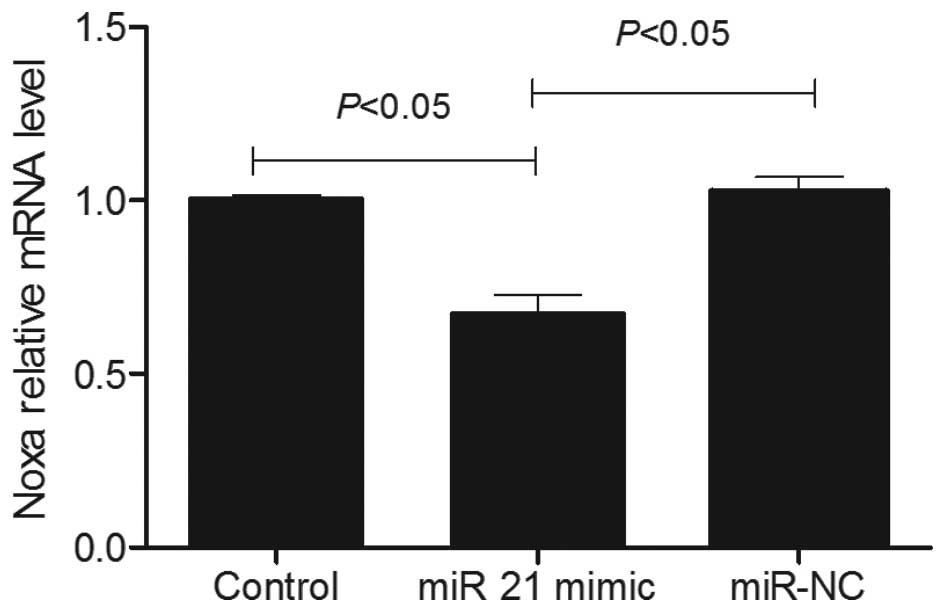
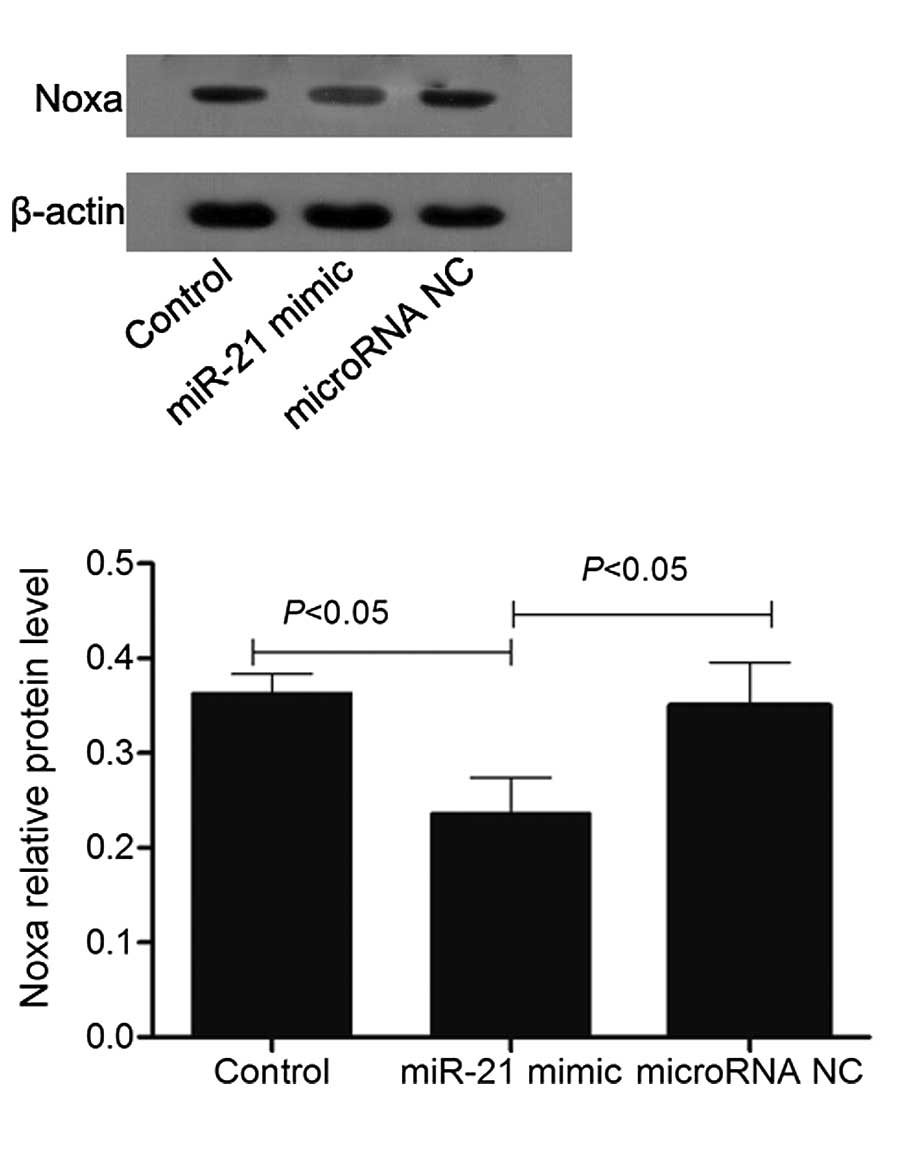
|
1
|
Ferro A, Peleteiro B, Malvezzi M, Bosetti
C, Bertuccio P, Levi F, Negri E, La Vecchia C and Lunet N:
Worldwide trends in gastric cancer mortality (1980–2011), with
predictions to 2015, and incidence by subtype. Eur J Cancer.
50:1330–1344. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ding YB, Xia TS, Wu JD, Chen GY, Wang S
and Xia JG: Surgical outcomes for gastric cancer of a single
institute in southeast China. Am J Surg. 203:217–221. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wang R and Chen XZ: High mortality from
hepatic, gastric and esophageal cancers in mainland China: 40 years
of experience and development. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol.
38:751–756. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bhattacharyya M, Nath J and Bandyopadhyay
S: MicroRNA signatures highlight new breast cancer subtypes. Gene.
556:192–198. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Rane JK, Scaravilli M, Ylipää A, Pellacani
D, Mann VM, Simms MS, Nykter M, Collins AT, Visakorpi T and
Maitland NJ: MicroRNA expression profile of primary prostate cancer
stem cells as a source of biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Eur
Urol. 67:7–10. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Xue Z, Wen J, Chu X and Xue X: A microRNA
gene signature for identification of lung cancer. Surg Oncol.
23:126–131. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yu J, Feng J, Zhi X, Tang J, Li Z, Xu Y,
Yang L, Hu Z and Xu Z: Let-7b inhibits cell proliferation,
migration, and invasion through targeting Cthrc1 in gastric cancer.
Tumour Biol. 36:3221–3229. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Volinia S, Nuovo G, Drusco A, Costinean S,
Abujarour R, Desponts C, Garofalo M, Baffa R, Aeqilan R, Maharry K,
et al: Pluripotent stem cell miRNAs and metastasis in invasive
breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 106:1062014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Rudner J, Elsaesser SJ, Müller AC, Belka C
and Jendrossek V: Differential effects of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2
family members Mcl-1, Bcl-2, and Bcl-xL on celecoxib-induced
apoptosis. Biochem Pharmac. 79:10–20. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Aikawa T, Shinzawa K, Tanaka N and
Tsujimoto Y: Noxa is necessary for hydrogen peroxide-induced
caspase-dependent cell death. FEBS Lett. 584:681–688. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cheng EHYA, Wei MC, Weiler S, Flavell RA,
Mak TW and Lindsten T: BCL-2, BCL-X(L) sequester BH3 domain-only
molecules preventing BAX- and BAK-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis.
Mol Cell. 8:705–711. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
C: TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors. 7th Edition.
Wiley-Blackwell; Oxford: 2010
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hong L, Han Y, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Zhao Q,
Wu K and Fan D: MicroRNA-21: A therapeutic target for reversing
drug resistance in cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 17:1073–1080.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Z, Han J, Cui Y, Fan K and Zhou X:
Circulating microRNA-21 as noninvasive predictive biomarker for
response in cancer immunotherapy. Med Hypotheses. 81:41–43. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Halimi M, Parsian H, Asghari SM, Sariri R,
Moslemi D, Yeganeh F and Zabihi E: Clinical translation of human
microRNA 21 as a potential biomarker for exposure to ionizing
radiation. Transl Res. 163:578–584. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mace TA, Collins AL, Wojcik SE, Croce CM,
Lesinski GB and Bloomston M: Hypoxia induces the overexpression of
microRNA-21 in pancreatic cancer cells. J Surg Res. 184:855–860.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tomimaru Y, Eguchi H, Nagano H, Wada H,
Kobayashi S, Marubashi S, Tanemura M, Tomokuni A, Takemasa I,
Umeshita K, et al: Circulating microRNA-21 as a novel biomarker for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of Hepatology. 56:167–175. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wang ZX, Lu BB, Wang H, Cheng ZX and Yin
YM: MicroRNA-21 modulates chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells
to doxorubicin by targeting PTEN. Arch Med Res. 42:281–290. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hsu CC, Wu YC, Farh L, Du YC, Tseng WK, Wu
CC and Chang FR: Physalin B from Physalis angulata triggers the
NOXA-related apoptosis pathway of human melanoma A375 cells. Food
Chem Toxicol. 50:619–624. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nakajima W and Tanaka N: Noxa induces
apoptosis in oncogene-expressing cells through catch-and-release
mechanism operating between Puma and Mcl-1. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 413:643–648. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huskey NE, Guo T, Evason KJ, Momcilovic O,
Pardo D, Creasman KJ, Judson RL, Blelloch R, Oakes SA, Hebrok M and
Goga L: CDK1 Inhibition targets the p53-NOXA-MCL1 axis, selectively
kills embryonic stem cells, and prevents teratoma formation. Stem
Cell Reports. 4:374–389. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Leal AS, Wang R, Salvador JA and Jing Y:
Synthesis of novel ursolic acid heterocyclic derivatives with
improved abilities of antiproliferation and induction of p53,
p21waf1 and NOXA in pancreatic cancer cells. Bioorg Med Chem.
20:5774–5786. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Park SY, Jeong MS and Jang SB: In vitro
binding properties of tumor suppressor p53 with PUMA and NOXA.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 420:350–356. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Belmar J and Fesik SW: Small molecule
Mcl-1 inhibitors for the treatment of cancer. Pharmacol Ther.
145:76–84. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Kuwahara Y, Wei D, Durand J and Weissman
BE: SNF5 reex-pression in malignant rhabdoid tumors regulates
transcription of target genes by recruitment of SWI/SNF complexes
and RNAPII to the transcription start site of their promoters. Mol
Cancer Res. 11:251–260. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ehrhardt H, Höfig I, Wachter F, Obexer P,
Fulda S, Terziyska N and Jeremias I: NOXA as critical mediator for
drug combinations in polychemotherapy. Cell Death Dis. 3:e3272012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|