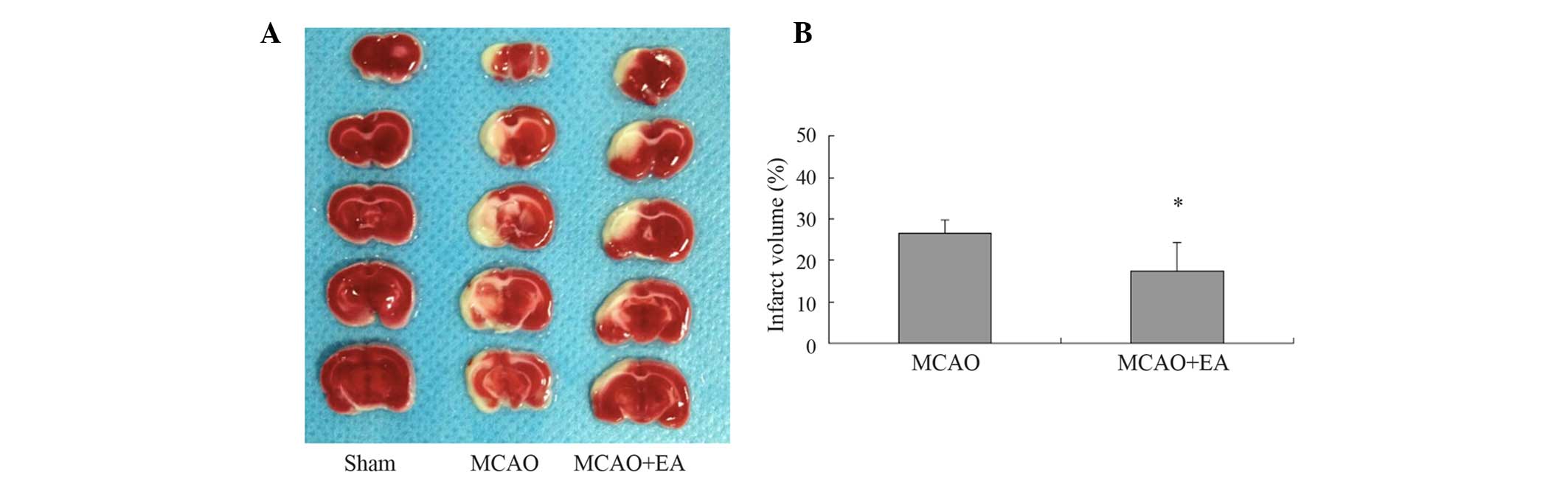
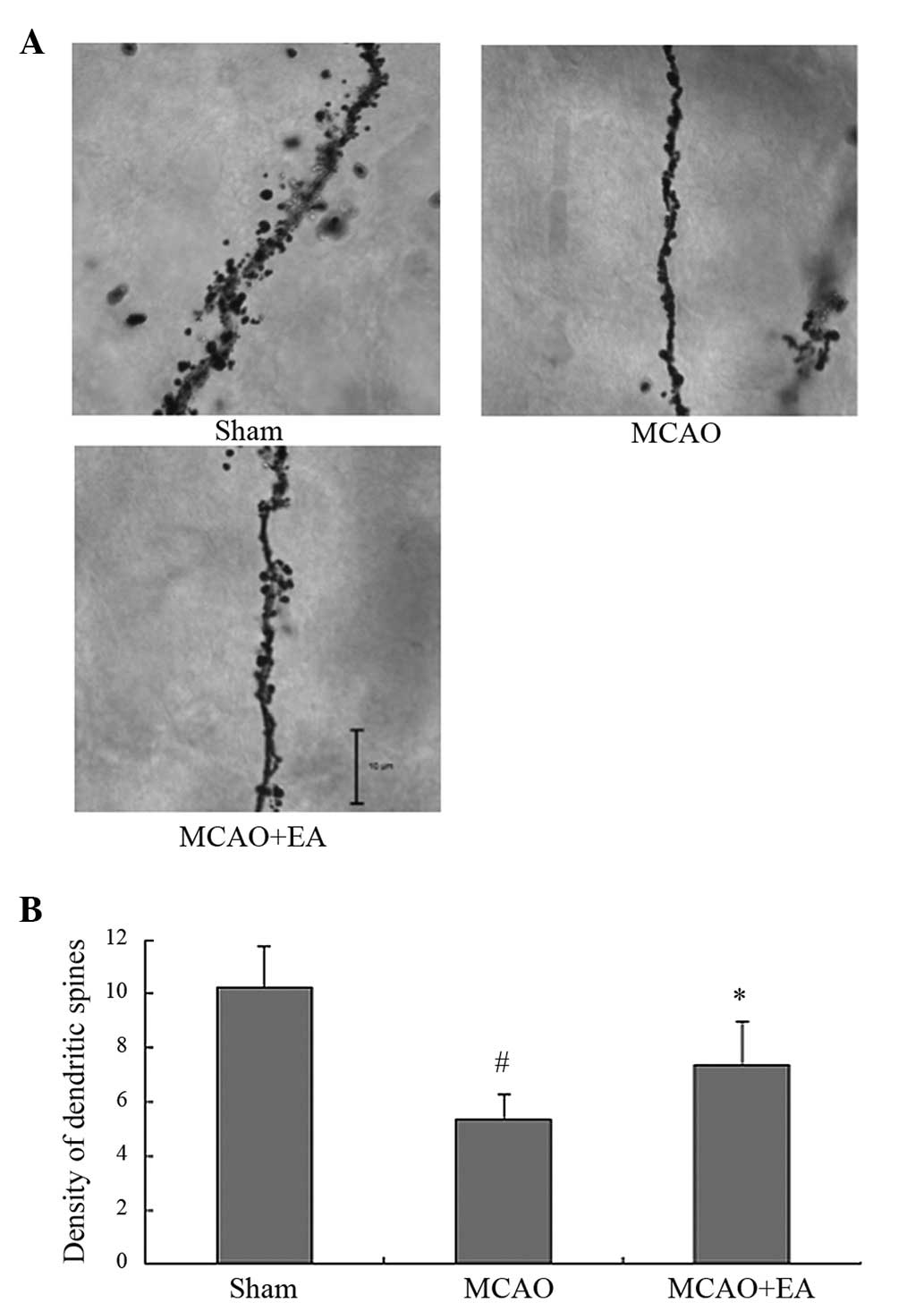
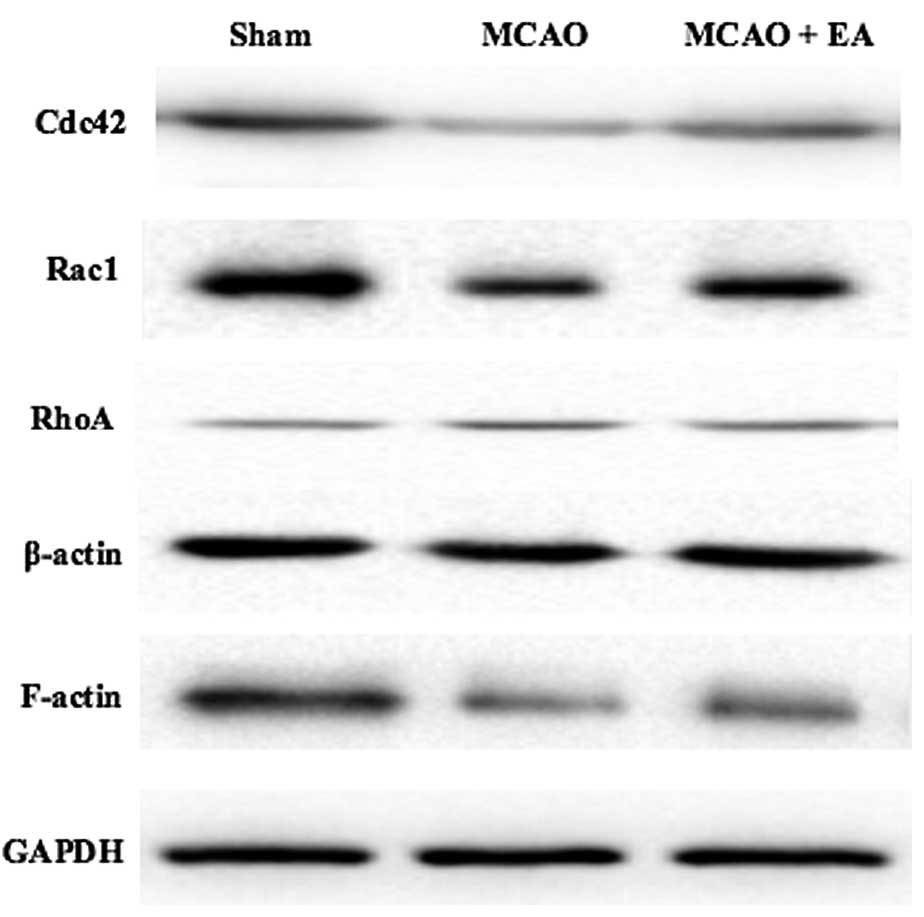
|
1
|
Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin
EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, Bravata DM, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, et al:
Heart disease and stroke statistics-2013 update: A report from the
American heart association. Circulation. 127:e6–e245. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Shim H: Vascular cognitive impairment and
post-stroke cognitive deficits. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep.
14:4182014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Béjot Y and Giroud M: Mean age at stroke
onset: An instructive tool from epidemiological studies. Eur J
Neurol. 16:e32009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Douiri A, Rudd AG and Wolfe CD: Prevalence
of poststroke cognitive impairment: South London stroke register
1995–2010. Stroke. 44:138–145. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Feng X, Yang S, Liu J, Huang J, Peng J,
Lin J, Tao J and Chen L: Electroacupuncture ameliorates cognitive
impairment through inhibition of NF-κ-mediated neuronal cell
apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injured rats. Mol Med
Rep. 7:1516–1522. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang H, Zhao L, Yang S, Chen Z, Li Y,
Peng X, Yang Y and Zhu M: Clinical observation on effect of scalp
electroacupuncture for mild cognitive impairment. J Tradit Chin
Med. 33:46–50. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhao L, Zhang H, Zheng Z and Huang J:
Electroacupuncture on the head points for improving gnosia in
patients with vascular dementia. J Tradit Chin Med. 29:29–34. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen Y, Zhou J, Li J, Yang SB, Mo LQ, Hu
JH and Yuan WL: Electroacupuncture pretreatment prevents cognitive
impairment induced by limb ischemia-reperfusion via inhibition of
microglial activation and attenuation of oxidative stress in rats.
Brain Res. 1432:36–45. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Govek EE, Hatten ME and Van Aelst L: The
role of Rho GTPase proteins in CNS neuronal migration. Dev
Neurobiol. 71:528–553. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Matus A: Actin-based plasticity in
dendritic spines. Science. 290:754–758. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Newey SE, Velamoor V, Govek EE and Van
Aelst L: Rho GTPases, dendritic structure and mental retardation. J
Neurobiol. 64:58–74. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bosch M and Hayashi Y: Structural
plasticity of dendritic spines. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 22:383–388.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Vadodaria KC, Brakebusch C, Suter U and
Jessberger S: Stage-specific functions of the small Rho GTPases
Cdc42 and Rac1 for adult hippocampal neurogenesis. J Neurosci.
33:1179–1189. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Georges PC, Hadzimichalis NM, Sweet ES and
Firestein BL: The yin-yang of dendrite morphology: Unity of actin
and microtubules. Mol Neurobiol. 38:270–284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kasai H, Fukuda M, Watanabe S,
Hayashi-Takagi A and Noguchi J: Structural dynamics of dendritic
spines in memory and cognition. Trends Neurosci. 33:121–129. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rodriguez GA, Burns MP, Weeber EJ and
Rebeck GW: Young APOE4 targeted replacement mice exhibit poor
spatial learning and memory, with reduced dendritic spine density
in the medial entorhinal cortex. Learn Mem. 20:256–266. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Koyama Y and Tohyama M: A modified and
highly sensitive Golgi-Cox method to enable complete and stable
impregnation of embryonic neurons. J Neurosci Methods. 209:58–61.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jacquin A, Binquet C, Rouaud O,
Graule-Petot A, Daubail B, Osseby GV, Bonithon-Kopp C, Giroud M and
Béjot Y: Post-stroke cognitive impairment: High prevalence and
determining factors in a cohort of mild stroke. J Alzheimers Dis.
40:1029–1038. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Thrift AG, Dewey HM, Macdonell RA, McNeil
JJ and Donnan GA: Incidence of the major stroke subtypes: Initial
findings from the north east Melbourne stroke incidence study
(NEMESIS). Stroke. 32:1732–1738. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen L, Fang J, Ma R, Froym R, Gu X, Li J,
Chen L, Xu S and Ji C: Acupuncture for acute stroke: Study protocol
for a multi-center, randomized, controlled trial. Trials.
15:2142014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Liu F, Li ZM, Jiang YJ and Chen LD: A
meta-analysis of acupuncture use in the treatment of cognitive
impairment after stroke. J Alternat Complement Med. 20:535–544.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Deng W, Aimone JB and Gage FH: New neurons
and new memories: How does adult hippocampal neurogenesis affect
learning and memory? Nat Rev Neurosci. 11:339–350. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Manns JR and Eichenbaum H: A cognitive map
for object memory in the hippocampus. Learn Mem. 16:616–624. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Eyre MD, Richter-Levin G, Avital A and
Stewart MG: Morphological changes in hippocampal dentate gyrus
synapses following spatial learning in rats are transient. Eur J
Neurosci. 17:1973–1980. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Halpain S, Spencer K and Graber S:
Dynamics and pathology of dendritic spines. Prog Brain Res.
147:29–37. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Govek EE, Newey SE and Van Aelst L: The
role of the Rho GTPases in neuronal development. Genes Dev.
19:1–49. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Babayan AH and Kramár EA: Rapid effects of
oestrogen on synaptic plasticity: Interactions with actin and its
signaling proteins. J Neuroendocrinol. 25:1163–1172. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Santos Da Silva J, Schubert V and Dotti
CG: RhoA, Rac1 and cdc42 intracellular distribution shift during
hippocampal neuron development. Mol Cell Neurosci. 27:1–7. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Murakoshi H, Wang H and Yasuda R: Local,
persistent activation of Rho GTPases during plasticity of single
dendritic spines. Nature. 472:100–104. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Auer M, Hausott B and Klimaschewski L: Rho
GTPases as regulators of morphological neuroplasticity. Ann Anat.
193:259–266. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Iden S and Collard JG: Crosstalk between
small GTPases and polarity proteins in cell polarization. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 9:846–859. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Edwards DC, Sanders LC, Bokoch GM and Gill
GN: Activation of LIM-kinase by Pak1 couples Rac/Cdc42 GTPase
signalling to actin cytoskeletal dynamics. Nat Cell Biol.
1:253–259. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Meng Y, Zhang Y, Tregoubov V, Janus C,
Cruz L, Jackson M, Lu WY, MacDonald JF, Wang JY, Falls DL and Jia
Z: Abnormal spine morphology and enhanced LTP in LIMK-1 knockout
mice. Neuron. 35:121–133. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sun ico CR, González-Forero D, Dom ínguez
G, García-Verdugo JM and Moreno-López B: Nitric oxide induces
pathological synapse loss by a protein kinase G-, Rho
kinase-dependent mechanism preceded by myosin light chain
phosphorylation. J Neurosci. 30:973–984. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Aburima A, Wraith KS, Raslan Z, Law R,
Magwenzi S and Naseem KM: cAMP signaling regulates platelet myosin
light chain (MLC) phosphorylation and shape change through
targeting the RhoA-Rho kinase-MLC phosphatase signaling pathway.
Blood. 122:3533–3545. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pilpel Y and Segal M: Activation of PKC
induces rapid morphological plasticity in dendrites of hippocampal
neurons via Rac and Rho-dependent mechanisms. Eur J Neurosci.
19:3151–3164. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lin X, Ogiya M, Takahara M, Yamaguchi W,
Furuyama T, Tanaka H, Tohyama M and Inagaki S: Sema4D-plexin-B1
implicated in regulation of dendritic spine density through
RhoA/ROCK pathway. Neurosci Lett. 428:1–6. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tashiro A, Minden A and Yuste R:
Regulation of dendritic spine morphology by the rho family of small
GTPases: Antagonistic roles of Rac and Rho. Cereb Cortex.
10:927–938. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|