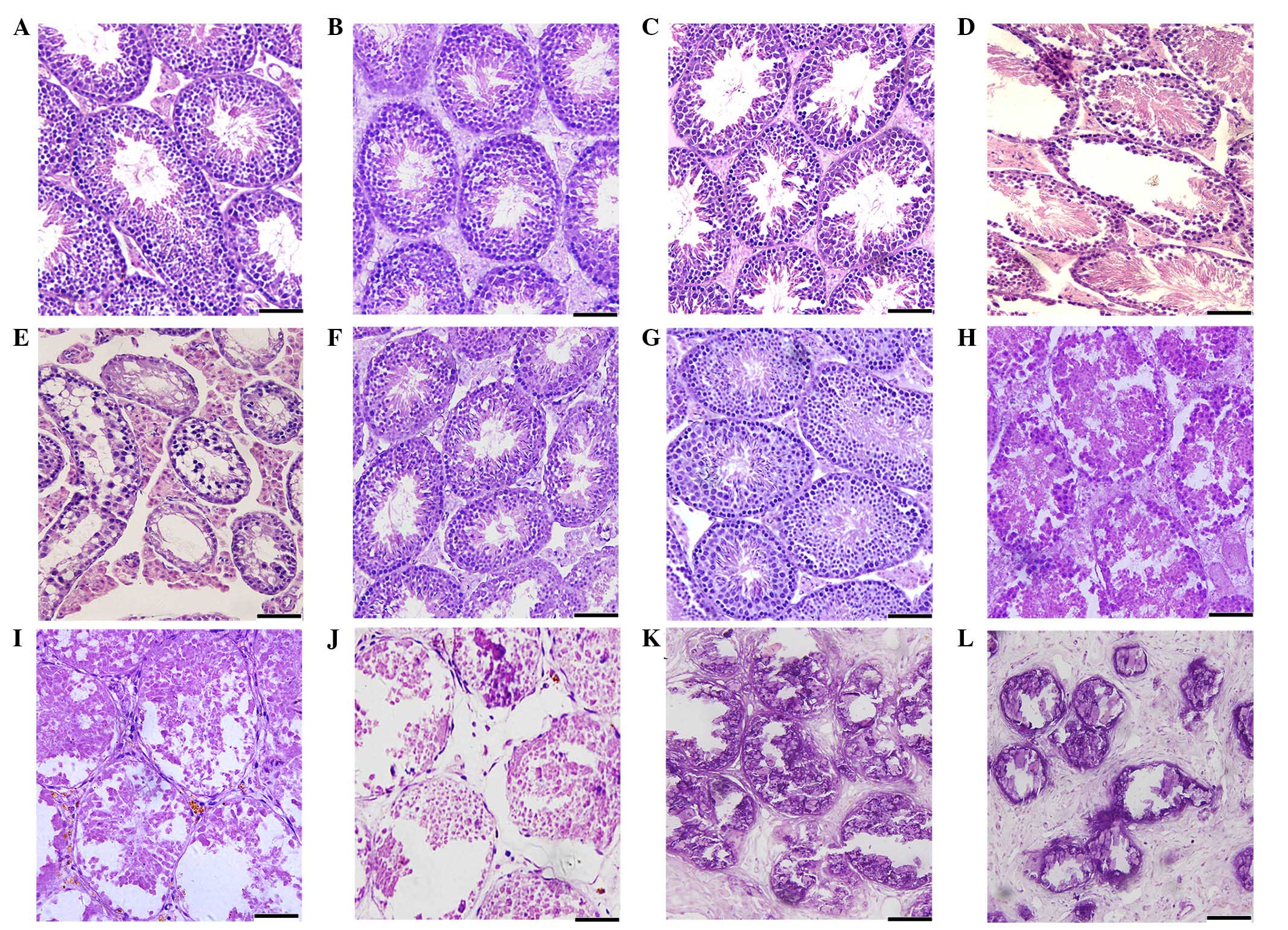
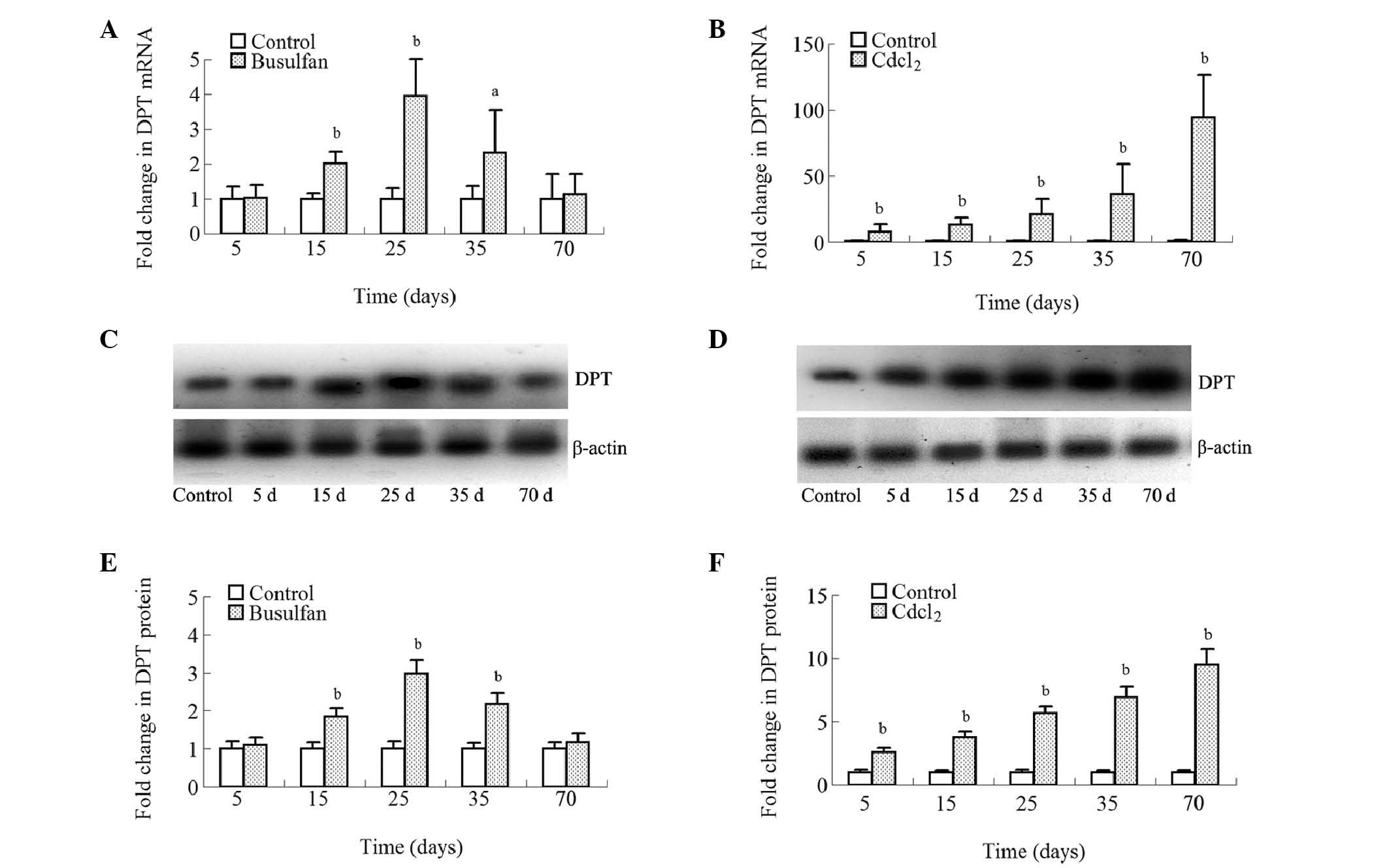
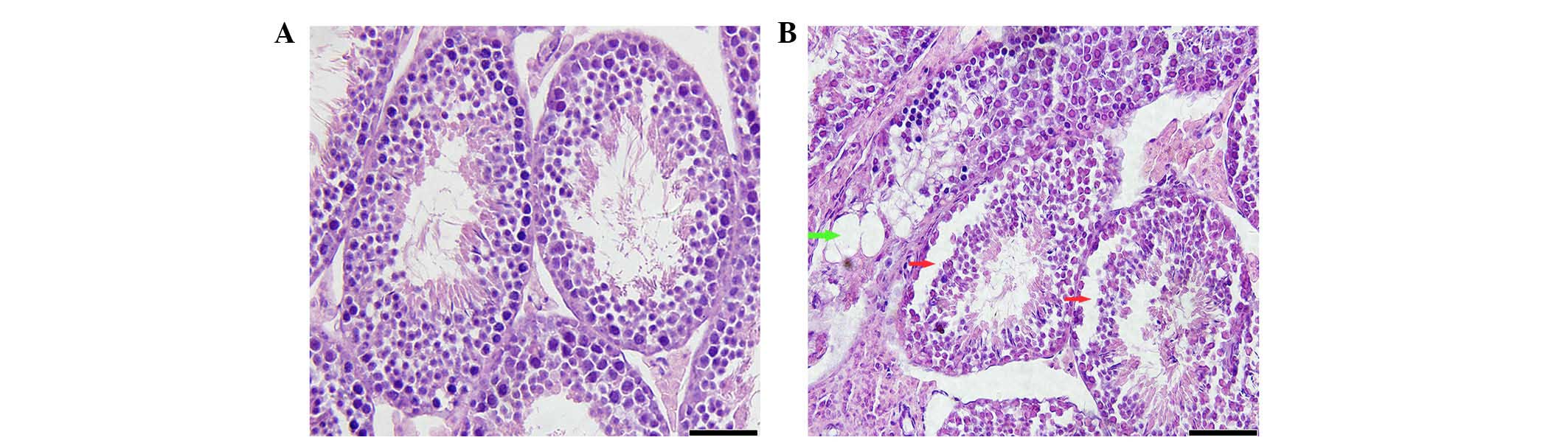
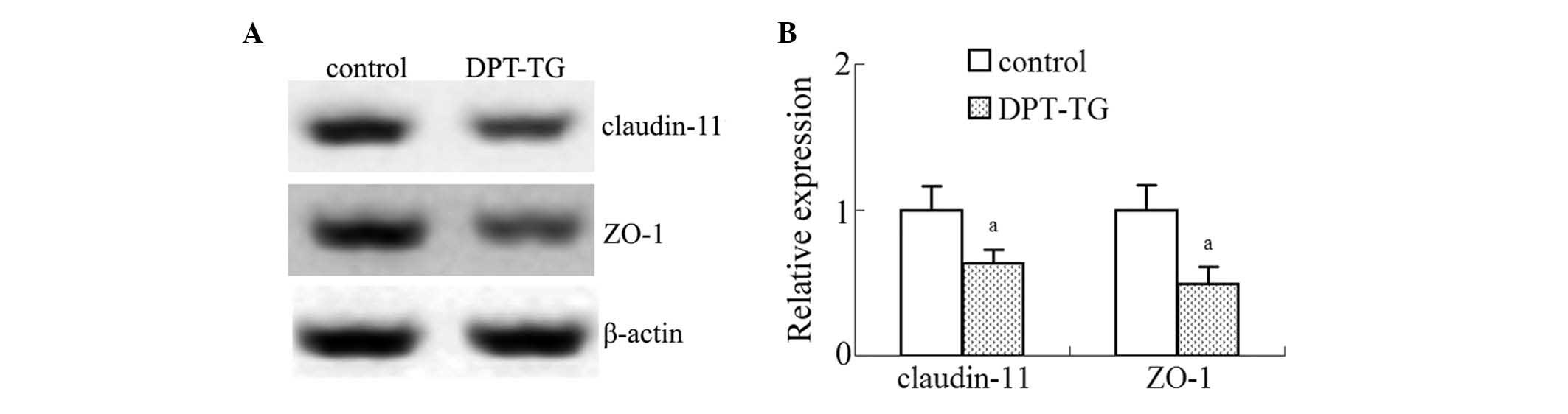
|
1
|
Irvine DS: Epidemiology and aetiology of
male infertility. Hum Reprod. 13(Suppl 1): 33–44. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gnoth C, Godehardt E, Frank-Herrmann P,
Friol K, Tigges J and Freundl G: Definition and prevalence of
subfertility and infertility. Hum Reprod. 20:1144–1147. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sepehrimanesh M, Kazemipour N, Saeb M and
Nazifi S: Analysis of rat testicular proteome following 30-day
exposure to 900 MHz electromagnetic field radiation.
Electrophoresis. 35:3331–3338. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fowler PA, Cassie S, Rhind SM, Brewer MJ,
Collinson JM, Lea RG, Baker PJ, Bhattacharya S and O'Shaughnessy
PJ: Maternal smoking during pregnancy specifically reduces human
fetal desert hedgehog gene expression during testis development. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 93:619–626. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Thonneau P, Bujan L, Multigner L and
Mieusset R: Occupational heat exposure and male fertility: A
review. Hum Reprod. 13:2122–2125. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Benavides-Garcia R, Joachim R, Pina NA,
Mutoji KN, Reilly MA and Hermann BP: Granulocyte colony-stimulating
factor prevents loss of spermatogenesis after sterilizing busulfan
chemotherapy. Fertil Steril. 103:270.e8–280.e8. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Spiazzi CC, Manfredini V, Barcellos da
Silva FE, Flores EM, Izaguirry AP, Vargas LM, Soares MB and Santos
FW: γ-Oryzanol protects against acute cadmium-induced oxidative
damage in mice testes. Food Chem Toxicol. 55:526–532. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Haouem S, Najjar MF, El Hani A and Sakly
R: Accumulation of cadmium and its effects on testis function in
rats given diet containing cadmium-polluted radish bulb. Exp
Toxicol Pathol. 59:307–311. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Mabrouk A and Cheikh HB: Thymoquinone
supplementation ameliorates lead-induced testis function impairment
in adult rats. Toxicol Ind Health. 2014.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sharma P, Huq AU and Singh R:
Cypermethrin-induced reproductive toxicity in the rat is prevented
by resveratrol. J Hum Reprod Sci. 7:99–106. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ismail MF and Mohamed HM:
Deltamethrin-induced genotoxicity and testicular injury in rats:
Comparison with biopesticide. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:3421–3425.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Walczak-Jedrzejowska R, Wolski JK and
Slowikowska-Hilczer J: The role of oxidative stress and
antioxidants in male fertility. Cent European J Urol. 66:60–67.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Desai SS, Roy BS and Mahale SD: Mutations
and polymorphisms in FSH receptor: Functional implications in human
reproduction. Reproduction. 146:R235–R248. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Smith LB and Walker WH: The regulation of
spermatogenesis by androgens. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 30:2–13. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xiao X, Mruk DD and Cheng CY:
Intercellular adhesion molecules (ICAMs) and spermatogenesis. Hum
Reprod Update. 19:167–186. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Eid N, Ito Y and Otsuki Y: Enhanced
mitophagy in Sertoli cells of ethanol-treated rats: Morphological
evidence and clinical relevance. J Mol Histol. 43:71–80. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Li MW, Mruk DD, Lee WM and Cheng CY:
Disruption of the blood-testis barrier integrity by bisphenol A in
vitro: Is this a suitable model for studying blood-testis barrier
dynamics? Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 41:2302–2314. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Alam MS, Ohsako S, Tay TW, Tsunekawa N,
Kanai Y and Kurohmaru M: Di (n-butyl) phthalate induces vimentin
filaments disruption in rat Sertoli cells: A possible relation with
spermatogenic cell apoptosis. Anat Histol Embryol. 39:186–193.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang X and Lui WY: Dysregulation of
nectin-2 in the testicular cells: An explanation of cadmium-induced
male infertility. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1839:873–884. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Neame PJ, Choi HU and Rosenberg LC: The
isolation and primary structure of a 22-kDa extracellular matrix
protein from bovine skin. J Biol Chem. 264:5474–5479.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Choi HU, Johnson TL, Pal S, Tang LH,
Rosenberg L and Neame PJ: Characterization of the dermatan sulfate
proteoglycans, DS-PGI and DS-PGII, from bovine articular cartilage
and skin isolated by octyl-sepharose chromatography. J Biol Chem.
264:2876–2884. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Superti-Furga A, Rocchi M, Schäfer BW and
Gitzelmann R: Complementary DNA sequence and chromosomal mapping of
a human proteoglycan-binding cell-adhesion protein (dermatopontin).
Genomics. 17:463–467. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Okamoto O, Suzuki Y, Kimura S and Shinkai
H: Extracellular matrix 22-kDa protein interacts with decorin core
protein and is expressed in cutaneous fibrosis. J Biochem.
119:106–114. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Okamoto O, Fujiwara S, Abe M and Sato Y:
Dermatopontin interacts with transforming growth factor beta and
enhances its biological activity. Biochem J. 337:537–541. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cooper LJ, Bentley AJ, Nieduszynski IA,
Talabani S, Thomson A, Utani A, Shinkai H, Fullwood NJ and Brown
GM: The role of dermatopontin in the stromal organization of the
cornea. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 47:3303–3310. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Takeuchi T, Suzuki M, Kumagai J, Kamijo T,
Sakai M and Kitamura T: Extracellular matrix dermatopontin
modulates prostate cell growth in vivo. J Endocrinol. 190:351–361.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang Q, Hao J, Chen M and Li G:
Dermatopontin is a novel regulator of the CdCl2-induced decrease in
claudin-11 expression. Toxicol In Vitro. 28:1158–1164. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Giuili G, Shen WH and Ingraham HA: The
nuclear receptor SF-1 mediates sexually dimorphic expression of
mullerian inhibiting substance, in vivo. Development.
124:1799–1807. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jeffs B, Ito M, Yu RN, Martinson FA, Wang
ZJ, Doglio LT and Jameson JL: Sertoli cell-specific rescue of
fertility, but not testicular pathology, in Dax1 (Ahch)-deficient
male mice. Endocrinology. 142:2481–2488. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Narula A, Kilen S, Ma E, Kroeger J,
Goldberg E and Woodruff TK: Smad4 overexpression causes germ cell
ablation and leydig cell hyperplasia in transgenic mice. Am J
Pathol. 161:1723–1734. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zohni K, Zhang X, Tan SL, Chan P and
Nagano MC: The efficiency of male fertility restoration is
dependent on the recovery kinetics of spermatogonial stem cells
after cytotoxic treatment with busulfan in mice. Hum Reprod.
27:44–53. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kanatsu-Shinohara M, Toyokuni S, Morimoto
T, Matsui S, Honjo T and Shinohara T: Functional assessment of
self-renewal activity of male germline stem cells following
cytotoxic damage and serial transplantation. Biol Reprod.
68:1801–1807. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Siu ER, Mruk DD, Porto CS and Cheng CY:
Cadmium-induced testicular injury. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
238:240–249. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Koksal IT, Ishak Y, Usta M, Danisman A,
Guntekin E, Bassorgun IC and Ciftcioglu A: Varicocele-induced
testicular dysfunction may be associated with disruption of
blood-testis barrier. Arch Androl. 53:43–48. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Erkanlı Şentürk G, Ersoy Canillioglu Y,
Umay C, Demiralp-Eksioglu E and Ercan F: Distribution of Zonula
Occludens-1 and Occludin and alterations of testicular morphology
after in utero radiation and postnatal hyperthermia in rats. Int J
Exp Pathol. 93:438–449. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Xia W, Wong EW, Mruk DD and Cheng CY:
TGF-beta3 and TNFalpha perturb blood-testis barrier (BTB) dynamics
by accelerating the clathrin-mediated endocytosis of integral
membrane proteins: A new concept of BTB regulation during
spermatogenesis. Dev Biol. 327:48–61. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|